SUKELLEMO JOINT MOCK
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education
BIOLOGY PAPER 2
(Theory)
2 HOURS
Instructions to Candidates
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- This paper consists of two sections. Section A and section B.
- Answer ALL questions in section A in the spaces provided. In section B answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
SECTION A. 40 MARKS
Answer all the Questions in this section.
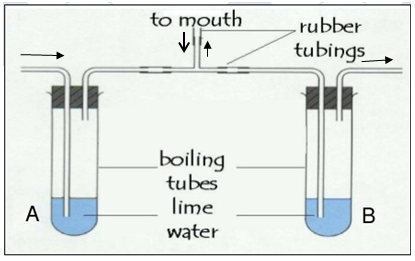
- The diagram below illustrates an experimental set up to compare relative amounts of a gas in inhaled air and exhaled air.
- On the diagram, show with arrows the direction of movement of inhaled and exhaled air into and out of the mouth. (2mks).
- What is the name of the gas being investigated in the experiment (1mk)
- What will happen to the lime water in. (2mks)
Boiling tube A?
Boiling tube B? - Explain the observations made in (c) above. (3mks).
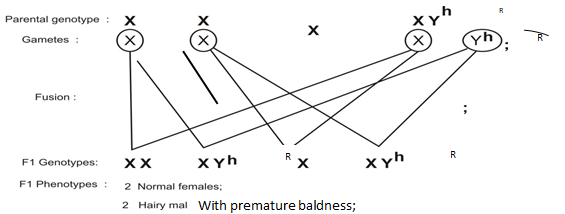
- A human gene which is Y-linked controls premature baldness. One allele leads to normal hair pattern while the other produces premature baldness
- What are alleles? (1mark)
- If a man with premature baldness marries, work-out the phenotypes of his children. (Use letter R to represent gene for premature baldness). (4 marks)
- Explain why this trait is not observed in females (2marks)
- Give one other trait in man that is Y—linked (1mark)
-
- What is active transport? (1mk)
- State three factors that increase the rate of active transport. (3mks)
- Give two roles of osmosis in animals. (2mk)
- What would happen if a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution (2mks)
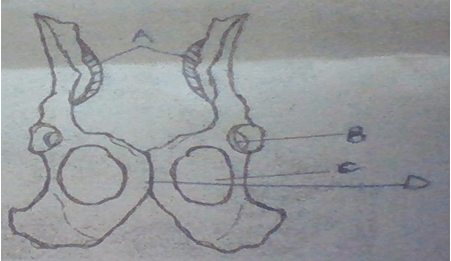
- The diagram below shows two fused bones of a mammal.
- Identify the fused bones. (1mk)
- Name:
- The bone that articulates at the point labelled A. (1mk)
- The structure labelled B. (1mk)
- State the type of joint formed at structure B. (1mk)
-
- Name: the structure labelled C (1mk)
- State two functions of the structure named in d(i) above (2 mks)
-
- Name the structure labelled D (1mk)
- State what happens to the structure during childbirth. (1mk)
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions that follow;
- Name the class the plant belongs to. ( 1mk)
- Give three OBSERVABLE characteristics that place the plant to the class named in (a)above ( 3mks)
- If a cross section was done on the young stem, draw and label the section observed. (3mks)
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either 7 or 8
- In an ecological study, a grasshopper population and that of crows was estimated in a certain grassland area over a period of one year. the results are as shown in the table below.
Months J F M A M J J A S O N D Number of adult
Grasshoppers x 10290 20 11 25 2500 1652 120 15 10 35 192 456 NUmber of crows 4 2 0 1 8 22 7 2 1 1 5 15 Amount of rainfall 20 0 55 350 520 350 12 10 25 190 256 350 -
- What is the relationship between the rainfall and grasshopper population?(1 mark)
- Account for the relationship stated in a (i) above. (3 marks)
- Explain the relationship between the grasshopper population and that of the crows. (3 marks)
- If the data was used in the construction of pyramid of numbers, what would be the trophic of;(3 marks)
- Grasshoppers
- Crows
- The grass in the study area
- If the area studied was one square kilometer, state:
- one method that could have been used to estimate the crow population. (1 mark)
- One method that could have been used to estimate the grasshopper population.(1mark)
- Suggest what would happen f a predator for grasshoppers entered the study area. (2 marks)
- What is meant by the term carrying capacity? (1 mark)
- Why would the carrying capacity of wild animals in a woodland grassland be higher than that of cattle? (2 marks)
- What is an ecosystem? (3 marks)
-
- Describe how water from the soil reaches the leaves of a tall tree and eventually to the atmosphere.(20mks)
- Explain how the human alimentary canal is adapted to perform its functions. (20mks).
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A. 40 MARKS
Answer all the Questions in this section.
- The diagram below illustrates an experimental set up to compare relative amounts of a gas in inhaled air and exhaled air.
- On the diagram, show with arrows the direction of movement of inhaled and exhaled air into and out of the mouth. (2mks).
- What is the name of the gas being investigated in the experiment (1mk)
- carbon (IV)oxide;
- carbon (IV)oxide;
- What will happen to the lime water in. (2mks)
Boiling tube A? - Boiling tube A Lime water remains clear
Boiling tube B? - Boiling tube B A white precipitate is formed. - Explain the observations made in (c) above. (3mks).
- In tube A the level of Carbon (IV) Oxide in inhaled air is low; compared to high amount of Carbon (IV) Oxide exhaled from the body; due to high rate of respiring cells;
- In tube A the level of Carbon (IV) Oxide in inhaled air is low; compared to high amount of Carbon (IV) Oxide exhaled from the body; due to high rate of respiring cells;
- On the diagram, show with arrows the direction of movement of inhaled and exhaled air into and out of the mouth. (2mks).
- A human gene which is Y-linked controls premature baldness. One allele leads to normal hair pattern while the other produces premature baldness
- What are alleles? (1mark)
- A pair of genes occurring on chromosomes, controlling a particular trait./ Alternative form of a gene controlling a particular trait
- A pair of genes occurring on chromosomes, controlling a particular trait./ Alternative form of a gene controlling a particular trait
- If a man with premature baldness marries, work-out the phenotypes of his children. (Use letter R to represent gene for premature baldness). (4 marks)
- A pair of genes occurring on chromosomes, controlling a particular trait./ Alternative form of a gene controlling a particular trait.
- The gene is located only on the y chromosome; /have no alleles on the chromosome; females do not inherit y-chromosome/females have xx only;
- The gene is located only on the y chromosome; /have no alleles on the chromosome; females do not inherit y-chromosome/females have xx only;
- Explain why this trait is not observed in females (2marks)
- Hairs on the pinna/ nose;
- Hairs on the pinna/ nose;
- Give one other trait in man that is Y—linked (1mark)
- What are alleles? (1mark)
-
- What is active transport? (1mk)
- Process that moves substances/ions/amino acids/sugar across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient by use of energy; OWTTE.
- Process that moves substances/ions/amino acids/sugar across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient by use of energy; OWTTE.
- State three factors that increase the rate of active transport. (3mks)
- Increase in oxygen concentration;
- Increase in glucose concentration;
- Increase in temperature towards optimum for best working of respiratory enzymes/optimum temperature for respiratory enzymes;
- Optimum pH for best working of respiratory enzymes;
- Give two roles of osmosis in animals. (2mk)
- Re-absorption of water from the kidney (tubules);
- Absorption of water in the large intestines;
- movement of water into the cells from tissue fluids;
MARK THE FIRST TWO
- What would happen if a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution (2mks)
- It gains water by osmosis; and become turgid ;
- It gains water by osmosis; and become turgid ;
- What is active transport? (1mk)
- The diagram below shows two fused bones of a mammal.
- Identify the fused bones. (1mk)
- Pelvic girdle/Pubic bones/ innominate bones;
- Pelvic girdle/Pubic bones/ innominate bones;
- Name:
- The bone that articulates at the point labelled A. (1mk)
- Sacral vertebra/Sacrum;
- Sacral vertebra/Sacrum;
- The structure labelled B. (1mk)
- Acetabulum;
- Acetabulum;
- The bone that articulates at the point labelled A. (1mk)
- State the type of joint formed at structure B. (1mk)
- Ball and socket joint;
-
- Name: the structure labelled C (1mk)
- Obturator foramen
- Obturator foramen
- State two functions of the structure named in d(i) above (2 mks)
- Its an aperture through which blood vessels nerves and muscles pass;
- Reduce the weight of the pelvic girdle;
- Name: the structure labelled C (1mk)
-
- Name the structure labelled D (1mk)
- Pubis symphysis;
- Pubis symphysis;
- State what happens to the structure during childbirth. (1mk)
- It relaxes thus expanding the size of pelvic cavity;
- It relaxes thus expanding the size of pelvic cavity;
- Name the structure labelled D (1mk)
- Identify the fused bones. (1mk)
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions that follow;
- Name the class the plant belongs to. ( 1mk)
- Dicotyledonae;
- Dicotyledonae;
- Give three OBSERVABLE characteristics that place the plant to the class named in (a)above ( 3mks)
- They have broad leaves;
- They have network veins;
- Their floral parts are arranged in fours or fives or their multiples;
- If a cross section was done on the young stem, draw and label the section observed. (3mks)
- Name the class the plant belongs to. ( 1mk)
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either 7 or 8
- In an ecological study, a grasshopper population and that of crows was estimated in a certain grassland area over a period of one year. the results are as shown in the table below.
Months J F M A M J J A S O N D Number of adult
Grasshoppers x 10290 20 11 25 2500 1652 120 15 10 35 192 456 NUmber of crows 4 2 0 1 8 22 7 2 1 1 5 15 Amount of rainfall 20 0 55 350 520 350 12 10 25 190 256 350 -
- What is the relationship between the rainfall and grasshopper population?(1 mark)
- High rainfall is followed a month later by high grasshopper population/low rainfall is followed a month later by low population of grasshoppers;
- High rainfall is followed a month later by high grasshopper population/low rainfall is followed a month later by low population of grasshoppers;
- Account for the relationship stated in a (i) above. (3 marks)
- vegetation/grass sprouts; vegetation/grass provide food for grasshoppers hence multiply rapidly; vegetation also offer shelter/camouflage for grasshoppers hence predators do not spot them easily;
- vegetation/grass sprouts; vegetation/grass provide food for grasshoppers hence multiply rapidly; vegetation also offer shelter/camouflage for grasshoppers hence predators do not spot them easily;
- What is the relationship between the rainfall and grasshopper population?(1 mark)
- Explain the relationship between the grasshopper population and that of the crows. (3 marks)
- Presence of large number of grasshopper is associated with large number of crows in the same month; Acc — the reverse. The crows feeding on grasshopper/predating on the grasshopper; if grasshopper population is low the crow population decrease due to migration to other areas in search of alternative food (sources);
- Presence of large number of grasshopper is associated with large number of crows in the same month; Acc — the reverse. The crows feeding on grasshopper/predating on the grasshopper; if grasshopper population is low the crow population decrease due to migration to other areas in search of alternative food (sources);
- If the data was used in the construction of pyramid of numbers, what would be the trophic of;(3 marks)
- Grasshoppers - 2nd (trophic) level/ primary consumers;
- Crows - 3rd (trophic) level/secondary consumers;
- The grass in the study area - 1st (trophic) level/producers;
- If the area studied was one square kilometer, state:
- one method that could have been used to estimate the crow population. (1 mark)
- Total count;
- Total count;
- One method that could have been used to estimate the grasshopper population.(1mark)
- Capture re-capture;
- Capture re-capture;
- one method that could have been used to estimate the crow population. (1 mark)
- Suggest what would happen if a predator for grasshoppers entered the study area. (2 marks)
- Vegetation/grass would sprout/increase due to decrease of grasshoppers; The predator would compete for food/grasshoppers with the crows (causing some grasshoppers to migrate) rapidly declining grasshopper population;
- Vegetation/grass would sprout/increase due to decrease of grasshoppers; The predator would compete for food/grasshoppers with the crows (causing some grasshoppers to migrate) rapidly declining grasshopper population;
- What is meant by the term carrying capacity? (1 mark)
- Maximum number of organism an area/habitat can comfortably support without depletion of the available resources; OWTTE.
- Maximum number of organism an area/habitat can comfortably support without depletion of the available resources; OWTTE.
- Why would the carrying capacity of wild animals in a woodland grassland be higher than that of cattle? (2 marks)
- Cattle feed on the same type of food/grass (hence high competition food); while wild animals feed on a variety of foods/some are browsers while some are carnivores/; or cattle occupy same ecological nitch; while wild animals occupy different ecological nitches;
- Cattle feed on the same type of food/grass (hence high competition food); while wild animals feed on a variety of foods/some are browsers while some are carnivores/; or cattle occupy same ecological nitch; while wild animals occupy different ecological nitches;
- What is an ecosystem? (3 marks)
- A natural unit composed of abiotic and biotic factors; whose interactions; lead to self- sustain ing system;
- A natural unit composed of abiotic and biotic factors; whose interactions; lead to self- sustain ing system;
-
- Describe how water from the soil reaches the leaves of a tall tree and eventually to the atmosphere.(20mks)
- Root hairs absorb water: by osmosis: from the spaces between the soil particles : passes into the root hair vacuole: through the cellulose cell wall and plasma/cell membrane: then through cell to cell in the cortex: or through intercellular spaces: then through the endodermis directing water into the xylem: water moves up in the xylem: in the vascular tissue. Once in the root xylem vessels water movement is aided by forces of capillarity: cohesion:adhesion:root pressure: and transpiration pull: into the stem xylem: water then enters into the xylem of the leaf veins/ leaf xyle: once in the leaves water moves into the mesophyll cells by osmosis: each time diluting the concentration of cell sap in the cells: this continues until water reaches the air spaces of the mesophyll cells: eventually escapes through stomata: as water vapor.
- Explain how the human alimentary canal is adapted to perform its functions. (20mks).
- The mouth has different types of teeth; that chew food increasing surface area for enzyme action;.
- The mouth has salivary glands; that secrete saliva which lubricates and softens food; Salivary amylase breaks down starch into maltose;
- The tongue rolls food into boluses; and pushes them to the back of the mouth for swallowing.
- The esophagus is hollow for easy swallowing of food; it has muscles that contract and relax; to move food boluses through peristalsis
- The alimentary canal is long; to provide a large surface area for digestion and absorption of food;
- Small intestine is highly coiled; offering a large surface area for digestion and absorption of food;
- the inner lining of the ileum has villi and micro-villi which increase surface area for absorption
- Doudenum has openings of duct; through which pancreatic juice and bile get into the lumen;
- The alimentary canal has goblet cells that secrets mucus; for lubrication of food; and protection of the wall from digestive enzymes;
- The Brunner’s glands also secretes an alkaline fluid ;which provide an optimum pH for action of intestinal enzymes;Small intestines has intestinal glands; that secrete digestive enzymes;
- the ileum has a rich network of blood capillaries that supply oxygen and remove metabolic waste from the intestinal tissues; and transports digested food and other nutrients
- The walls have circular and longitudinal muscles; whose peristaltic contractions causes movement of food in the gut; and mixing of food with digestive enzymes;
- The ileum has a thin epithelium; that allows soluble food materials to pass through rapidly into the bloodstream
- The villi has lacteal; to transport absorbed lipids
- The colon has a wide lumen; to increase surface area for absorption of water and mineral salts
- The anus has anal sphincter muscles; that relax and contract to eliminate the indigestible and undigestible materials; max 20mks
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sukellemo Joint Mock 2020/2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students