INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, index number and school in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the Date of Examination in the spaces provided above.
- This paper consists of two sections A and B and 12 printed pages
- Answer all questions in section A and B in the spaces provided
- All working must be clearly shown
- Mathematical tables and non-programmable electronic calculators may be used
- Where needed take g = 10ms-2
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
| SECTION | QUESTION | MAX. SCORE | CANDIDATES' SCORE |
| A | 1-10 | 25 | |
| B | 11 | ||
| 12 | |||
| 13 | |||
| 14 | |||
| 15 | |||
| 16 | |||
| Total | 80 |

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Attempt ALL the questions below in the spaces provided
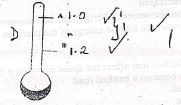
- The figure below shows a micrometer screw gauge used by a student to measure the loves thickness of a wire. If it has a zero error of -0.06mm, determine the actual thickness of the wire. (2mks)
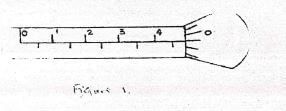
-
- State one disadvantage of frictional force. (1mk)
- Distinguish between cohesive and adhesive forces. (1 mk)
- Explain why a bus should not carry standing passengers. (2mks)
- A mass of 100g is hung at the 20cm marks and a 50g mass at the 70cm marks of a uniform metre rule balanced at the 40cm marks. Determine the weight of the rule. (3mks)
- Figure 2 shows a liquid being siphoned from one beaker to another.
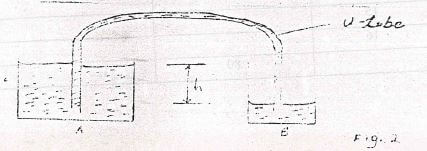
- State and explain what would happen to the flow if the system in figure was put in vacuum. (2mks)
- State one condition under which a syphon works. (1mk)
-
- Alcohol is sometimes very advantageous as thermometric liquid over mercury. Give possible reason. (1mk)
- State the function of a constriction in a clinical thermometer. (1mk)
- The water from a gardener hose pipe fills a bucket in 3.0s. The volume of the bucket is 8.00 x 10-3. Find the speed of the water that leaves the hose pipe at a cross section area of 2.85 x 10-4m2. (3mks)
- Figure 3 shows a simple bimetallic thermostat used for detecting fire.
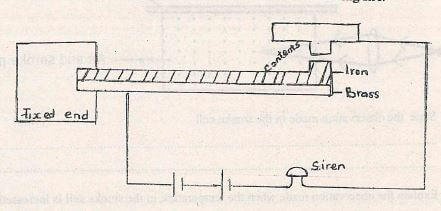
Describe how it works. (3mks) - Figure 4 shows two identical springs of springs constant 3N/cm supporting a load of 30N.
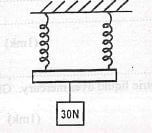
Determine the extension of each spring. (3mks) - The figure 4 shows the apparatus used to observe Brownian motion using a smoke cell.
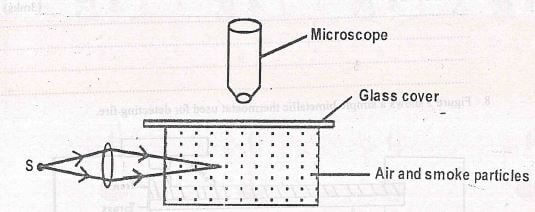
- State the observation made in the smoke cell (1mk)
- Explain the observation made when the temperature in the smoke cell is increased (2mks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
11.
- State two factors that affect the speed at which a driver can negotiate a bend on a banked road. (2mks)
- The figure 5 below shows a stone of mass 100g whirled in a vertical circle using a thread of length 56cm. (Take 9 = 10Nkg-1)
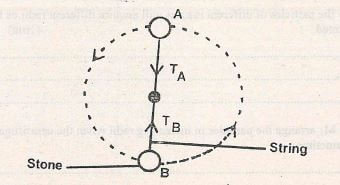
If the stone is whirled at a speed of 8 m/s. Calculate:- The centripetal force experienced by the stone. (3mks)
- The tension force on the string at TA (2mks)
- Calculate the angular velocity of the slope. (1mk)
- Figure 6 shows a centrifuge that is used to separate particles suspended in a liquid
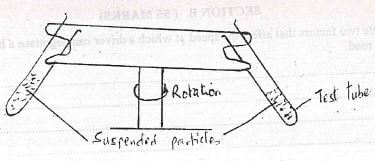
Particles of different mass M, M2 and M, are suspended in a liquid which they do not dissolve. The system is then rotated in the direction shown.- Explain why the particles of different masses will acquire different radii as the system is rotated. (1 mk)
- If M3>M2>M1 arrange the particles in increasing radii when the centrifuge is rotated for sometime
12.
-
- State Archimede's principle (1mk)
- An object weights 1.04N in air, 0.64N when fully immersed in water and 0.72N when fully immersed in a liquic. If the density of water is 1000kg/m3, find the density of the liquid. (3mks)
-
- Give a reason why a steel rod sinks in water while a ship made of steel floats on water.
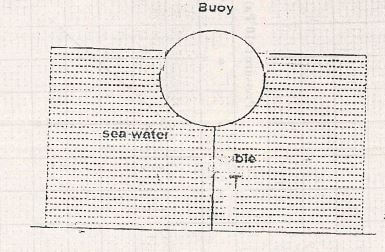
(Imk) - The figure 7 below shows a buoy of volume 42 litres and mass 10kg. It is held in position in sea-water of density 1.14g/cm3 by a light cable fixed to the bottom so that 3/4 of the volume of the buoy is below the surface of the sea water. Determine the tension T in the cable. (3mks)
- Give a reason why a steel rod sinks in water while a ship made of steel floats on water.
- The figure 8 below shows a diagram of a hydrometer which is suitable for measuring the densities of liquids varying between 1.0g/cm3 and 1.2g/cm3
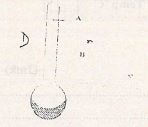
On the diagram indicate the label corresponding to 1.0 g/cm3 and 1.2 g/cm3 (1 mk)
13.
- State one condition necessary for pressure law to hold. (1mk)
- A bubble at the bottom of a pond expands as it rises to the top of the liquid. Explain (1mk)
- The graph below represents a graph of pressure against temperature °C
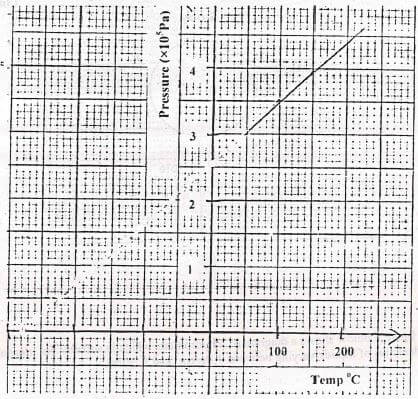
From the graph determine- the absolute temperature (1mk)
- the pressure at 373k (1mk)
- explain why temperature in (i) above cannot be achieved (1mk)
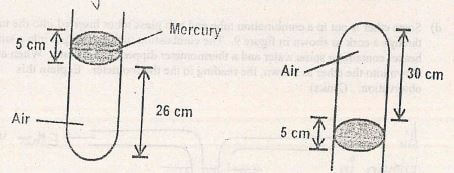
- A column of air 26cm long in trapped by mercury thread 5cm long. When the tube is inverted, the air column becomes 30cm long. Calculate the value of atmospheric pressure. (3mks)
- Explain using kinetic theory of gases why pressure of gases increases as temperature of the gas is increased. (2mks)
14.
- State two ways through which the rate of evaporation of a liquid may be increased (2mks)
- A metal of mass 10kg is heated to 120°C and then dropped into 2kg of water. The final temperature of the mixture is found to be 50°C. Calculate the initial temperature of the water. (Specific heat capacity of metal and water is 450Jkg-1k-1 and 42000kg-1k respectively.) (3mks)
- Give the property of water which makes it suitable for use as a coolant in machines. (1 mk)
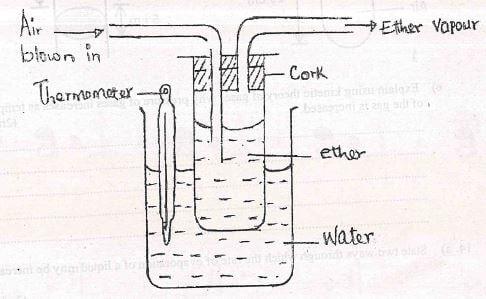
- Some ether is put in a combination tube and two glass tubes inserted into the tube through a cork as shown in figure 9. The combustion tube is then put into a small beaker containing some water and a thermometer dipped in the water. When air is blown into the ether as shown, the reading in the thermometer. Explain this observation. (2mks)
15.
- Define the term efficiency as used in machines. (1mk)
- Figure 10 shows the cross-section of a wheel and axle of radius 6.5cm and 1.5 cm respectively used to lift a load. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
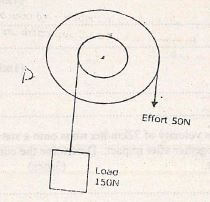
Determine the- mechanical advantages (MA) of the system (2mks)
- velocity ratio (V.R) of the system (2mks)
- efficiency of the machine (2mks)
- give one reason why the above machine is not 100% efficient (2mks)
16.
- Define impulse in terms of momentum. (1 mk)
- Give the reasons why a safety seat belt used in a vehicle should;
- have a wide surface area (1mk)
- be slightly extensible (1mk)
- A trailer of mass 30 tonnes travelling at a velocity of 72km/her rams onto a stationery bus of mass 10 tonnes. The two move together after impact. Determine the common velocity at which they move after impact. (3mks)
- A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 30m/s
- determine the maximum height reached. (2mks)
- time taken to come back to the point of projection. (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
Attempt all the questions below in the spaces provided
- The figure below shows a micrometer screw gauge used by a student to measure the thickness of a wire. If it has a zero error of 0.06mm, determine the actual thickness of the wire.
MSR = 4.50
TSR = 0.49
4.99
- 0.06
Actual = 5.05 mm -
- State one disadvantage of frictional force. Causes wear and tear (1 mk)
- Distinguish between cohesive and adhesive forces 1mk
Cohesive force is a force of attraction between molecule of the same kind whereas adhesive is force of attraction between molecules of different kinds.
- Explain why a bus should not carry standing passengers 2m Becomes unstable, the position of c.o.g is raised
- A mass of 100g is hung at the 20cm marks and a 50g mass at the 70cm marks of a uniform metre rule balanced at the 40cm marks. Determine the weight of the rule (3mks)
Sum of ACM - sum of CM
1 x 0.20 = (N x 0.10) + 0.5 x 0.30
0.20=0.10w+0.15
0.10w = 0.02 -0.15
0.10w = 0.05
0.10 0.10
W-0.5N -
- State and explain what would happen to the flow if the system in figure was put in vacuum (2mks)
The flow of liquid in siphon continues at slow rate this is due to decreased pressure in the vacuum. - State one condition under which a siphon works (1mk)
The tube must first be filled with water or liquid
- State and explain what would happen to the flow if the system in figure was put in vacuum (2mks)
-
- Alcohol is sometimes very advantageous as thermometric liquid over mercury. Give a possible reason. (1mk)
It has a slower freezing point - State the function of a constriction in clinical thermometer
Prevent backflow of mercury (1mk)
- Alcohol is sometimes very advantageous as thermometric liquid over mercury. Give a possible reason. (1mk)
- Find the speed of the water that leaves the hose pipe at a cross section area of 2,83 x 10-4m2
R= AV
8 x 10-3
30
= 2.85 x 10-4 x V
V=2.667 x 10-4
2.85 x 10-4
-0.9358m/s - Describe how it works
In case of fire, the bimetallic strip expands, curing upwards.
The contact is made completing the circuit and thus the thermometer works. - Determine the extension of each spring
è= F = 30
2k 2x3
= 5cm -
- State the observation made in the smoke cell
Bright specks are seen moving in constant random motion - Explain observation made when temperature in the smoke cell is increased
The random movement of bright specks increases; This is due to increased kinetic energy of the particles.
- State the observation made in the smoke cell
SECTION B
11.
- State two factors that affect the speed at which a driver can negotiate a bend on a banked road
- Radius of bend
- Banking angle
-
- The centripetal force experienced by the stone 3mks)
Fe = Mv2 = 0.1 x 82
0.56
= 6.4
0.56
= 11.43N - The tension force on the string at TA (2mks)
TA = Mv2 - MG
r
= 11.43-1
= 10.43N - Calculate the angular velocity of the slope.(1mk)
N= v = 8
r 0.56
= 14.29 rads
- The centripetal force experienced by the stone 3mks)
-
- Explain why the particles of different masses will acquire different radii as the system is rotated
- Due to their difference in masses
- If M1>M2>M3 arrange the particles in increasing radii when the centrifuge is rotated for sometime
M3→M2→M1
Largest radius
- Explain why the particles of different masses will acquire different radii as the system is rotated
12.
-
- State Archimede's principles
- A body partially or fully immersed in a fluid it experiences an upthrust equal to the weight of fluid displaced
- Find the density of the liquid
- Uwater = 1.04-0.64 = 0.36N
ULiquid = 1.04 -0.12 = 0.32N
R.D= U liq
U water
0.32
0.36
= 0.8889g/cm3
P liquid=wx0.8889
= 888.9kg/cm3
- Uwater = 1.04-0.64 = 0.36N
- State Archimede's principles
-
- Give a reason why a steel rod sinks in water in water while a ship made of steel floats on water
- It is hollow and displaces large volume of water.
- Determine the tension T in the cable
- W +T =U
T = U-W
U = vsg
= 42 x 1140 x 10 x 3/4
1000
= 359.IN
W= mg = 100N
T = 359.1 - 100
= 259.1N
- W +T =U
- Give a reason why a steel rod sinks in water in water while a ship made of steel floats on water
- On the diagram indicate the label corresponding to 1.0g/cm3 and 1.2g/cm3.
13.
- State one condition necessary for pressure law to hold
- Temperature should be kept constant.
- A bubble at the bottom of a pond expands as it rises to the top of the liquid. Explain
- As it rises, pressure decrease with height, hence volume increases.
- From the graph determine
- The absolute temperature
- 280°C ± 10°C
- the pressure at 373k
- Y-intercept = 2.5 x 105 ± 0.1 Pa
- Explain why temperature in (1) above cannot be achieved
- Real gases liquefy before OK is reached.
- The absolute temperature
- Calculate the value of atmospheric pressure
PIVI = P2V2
(x + 5)26 = (x - 5) 30
26x + 130 = 30x - 150
280 = 4x
x = 70cmHg - Explain using kinetic theory of gases why pressure of gases increases as temperature of the gas is increased
- Temperature increases K.E of gas particles and thus rate of collision per unit area also increases.
14.
- State two ways through which the rate of evaporation of a liquid may be increased.
- Increase the surface area
- Increase the temperature
- Calculate the initial temperature of the water.
Heat lost by metal = Heat gained by water
10 x 450 x (120 - 50) = 2 x 4200 (50-x)
315000 = 420000 - 8400x
8400 x = 105000
x = 12.5°C - Give the property of water which makes it suitable for use as a coolant in machines
- Has a higher heat capacity
- Explain this observation
- The warm air causes ether to evaporate taking away latent heat of evaporation of water and thus lowering the temperature.
15.
- Define the term efficiency as used in machines
- The ratio of words output to works input expressed as a percentage.
- determine the
- Mechanical advantages (MA) of the system
M.A= L = 150 -3
E 50 - Velocity ratio (V.R) of the system
V.R = R = 6.5 = 4.333 (4 sf)
8 1.5 - Efficiency of the machine
? = MA x 100
VR
= 3
4.333
= 69.24 - Give one reason why the above machine is not 100% efficient
- Some works is wasted in overcoming friction force between movable parts
- Mechanical advantages (MA) of the system
16.
- define impulse in terms of momentum
- It changes in momentum
- Give reasons why a safety seat belt used in a vehicle should
- have a wide surface area
- To reduce the pressure exerted by the seat belt
- be slightly extensible
- To decelerate gradually reducing impact force
- have a wide surface area
- Determine the common velocity at which they move after impact
M1U1 +M2U2 = (M1 + M2)V
(30000 x 20)+ 0 = 40000V
V = 600000
40000
= 15m/s -
- Determine the maximum height reached
hmax =U2
2g
= 30 = 90 = 45m
2 20 - time taken to come back to the point of projection
t = 2U = 2 x 30 = 6s
g 10
- Determine the maximum height reached
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Sukellemo Joint Mock Examinations July 2020.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students