INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- You are NOT allowed to start working with the apparatus for the first 15 minutes of the 13/4 Hours allowed for this paper. This time is to enable you to read the question paper and make sure you have all the chemicals and apparatus that you may need.
- All workings MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used.
For Examiners use only.
|
Section |
Question |
Maximum Score |
Candidates Score |
|
1 |
14 |
||
|
2 |
12 |
||
|
3 |
14 |
||
|
Total score |
40 |

QUESTIONS
- You are provided with liquids L1, L2, L3, L4
-
- Put 3 drops of L2 on a white tile.
Add one drop of iodine solution.
Observation …………………………………………………………………….. [1mk]
Conclusion ……………………………………………………………………… [1mk] - Put 2cm3 of L2 into the test tube and add equal volume of Benedict’s solution and heat.
Observation …………………………………………………………………… [1mk]
Conclusion …………………………………………………………………… [1mk]
- Put 3 drops of L2 on a white tile.
- Label two test tubes A and B. Into each of the test tubes put 2cm3 of the remaining L2 liquid.
To test tube A, add 10 drops of liquid L1 and 10 drops of liquid L3.
To test tube B, add 10 drops of liquid L1 and 4 drops of liquid L4
Put the two test tubes, A and B in a waterbath maintained at between 38-39ºC for 30 minutes.
Repeat iodine and Benedict’s tests in each of the test tubes and record your results in the table below. [4mks]Test tube
Observations
Iodine test
Benedict’s test
A
B
- Account for the results in:
- Test tube A
Iodine test ……………………………………………. [1mk]
Benedict’s test ………………………………............ [1mk] - Test tube B
Iodine test …………………………………………… [1mk]
Benedict’s test ……………………………………… [1mk]
- Test tube A
- Suggest the identity of liquid L1 [1mk]
- Why was the water bath maintained at 38oC [1mk]
-
- You are provided with specimens labelled A, B, C and D.
- Precisely, classify the specimens [2mks]
B ______________________________
D ______________________________ -
- Cut specimen A longitudinally and make a well labelled diagram. [4mks]
- Calculate magnification of the drawing in b (i) above. Show your working [2mks]
-
- Name the agent of dispersal of the cut specimen [1mk]
- Give two reasons for your answer [2mks]
-
- Open specimen C longitudinally, observe and name the type of placentation shown. [1mk]
- With reason, identify the agent of dispersal and give a reason for your answer. [2mks]
- Precisely, classify the specimens [2mks]
- Study the photographs below and answer the questions that follow.
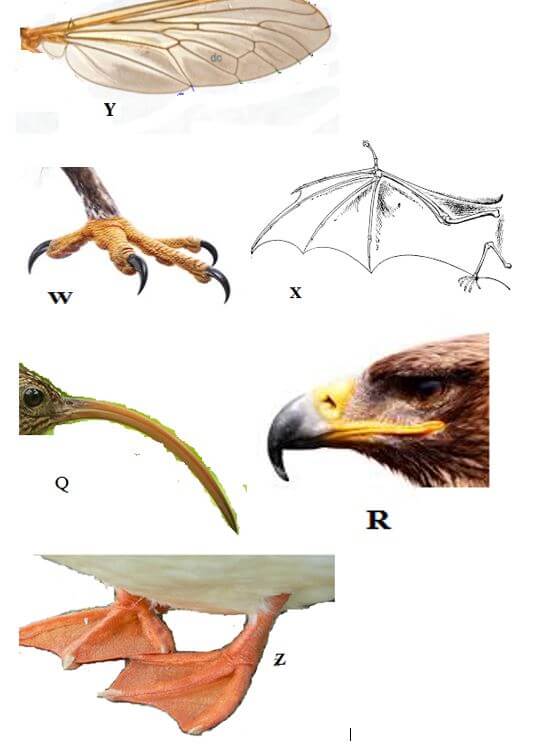
- Name the type of structures shown by: [2mks]
- X & Y ……………………………………………………..
- W & Z ……………………………………………………..
- State the structural difference between structures X and Y [1mk]
- Name the type of evolution shown by structures Q and R [1mk]
- State the adaptations of structures W and Z
W …………………………………………………..
Z …………………………………………………… - Name the types of skeletons shown by structures X and Y [2mks]
X ……………………………………………………
Y …………………………………………………… - By comparing structures Q and R, predict the type of food being fed on by the animals and give a reason in each case. [4mks]
Q ……………………………………………
R …………………………………………... - A part from structures X and Y, name two other examples of similar structures in animals. [2mks]
- Name the type of structures shown by: [2mks]

MARKING SCHEME
- You are provided with liquids L1, L2, L3, L4
-
- Put 3 drops of L2 on a white tile.
Add one drop of iodine solution.
Observation colour of iodine solution turns to blue- black [1mk]
Conclusion starch present [1mk] - Put 2cm3 of L2 into the test tube and add equal volume of Benedict’s solution and heat.
Observation colour of Benedict’s solution retained/persists [1mk]
Conclusion reducing sugars absent [1mk]
- Put 3 drops of L2 on a white tile.
- Label two test tubes A and B. Into each of the test tubes put 2cm3 of the remaining L2 liquid.
To test tube A, add 10 drops of liquid L1 and 10 drops of liquid L3.
To test tube B, add 10 drops of liquid L1 and 4 drops of liquid L4
Put the two test tubes, A and B in a waterbath maintained at between 38-39ºC for 30 minutes.
Repeat iodine and Benedict’s tests in each of the test tubes and record your results in the table below. [4mks]Test tube
Observations
Iodine test
Benedict’s test
A
Blue black colour
Blue colour persists
B
Colour of Iodine persists
Colour of Benedict’s soln turns yellow
- Account for the results in:
- Test tube A
Iodine test Starch present because HCl denatured enzyme diastase/amylase [1mk]
Benedict’s test Reducing sugars absent because HCl dentured diastase hence did not breakdown starch to maltose. [1mk] - Test tube B
Iodine test Amylase/diastase/invertase digested all starch; (to maltose) [1mk]
Benedict’s test NaOH provided suitable pH for action of diastase enzyme of diastase enzyme starch to maltose; [1mk]
- Test tube A
- Suggest the identity of liquid L1 [1mk]
Diastase/amylase/invertase/starch digesting enzyme - Why was the water bath maintained at 38ºC [1mk]
Optimum temperature; (for action of diastase)
-
- You are provided with specimens labelled A, B, C and D.
- Precisely, classify the specimens [2mks]
B cypsela Rej. Wrong spelling
D caryopsis rej. Wrong spelling -
- Cut specimen A longitudinally and make a well labelled diagram. [4mks]
First three clockwise
No mark for transverse section i.e wrong diagram (wd) - Calculate magnification of the drawing in b (i) above. Show your working [2mks]
Magnification = drawing length
actual length
- Cut specimen A longitudinally and make a well labelled diagram. [4mks]
-
- Name the agent of dispersal of the cut specimen [1mk]
Animal dispersal - Give two reasons for your answer [2mks]
Succulent/juicy
Brightly coloured
Conspicuous
Scented
Hard seed coat
- Name the agent of dispersal of the cut specimen [1mk]
-
- Open specimen C longitudinally, observe and name the type of placentation shown. [1mk]
Marginal placentation - With reason, identify the agent of dispersal and give a reason for your answer. [2mks]
- Self explosive mechanism
- Presence of sutures /lines of weakness
- Open specimen C longitudinally, observe and name the type of placentation shown. [1mk]
- Precisely, classify the specimens [2mks]
- Study the photographs below and answer the questions that follow.

- Name the type of structures shown by: [2mks]
- X & Y Analogous
- W & Z Homologous
- State the structural difference between structures X and Y [1mk]
X Y
Pentadactyl limb structure Toughened veins with cuticles - Name the type of evolution shown by structures Q and R [1mk]
Divergent evolution - State the adaptations of structures W and Z
W sharp and curved claws/tattoos to grasp and hold prey
Z webbed feet to wade/swim in water - Name the types of skeletons shown by structures X and Y [2mks]
X Endoskeleton
Y Exoskeleton - By comparing structures Q and R, predict the type of food being fed on by the animals and give a reason in each case. [4mks]
Q Nector – long and slender break to reach nectaries/nector
R Flesh/meat – strong curved for tearing flesh - A part from structures X and Y, name two other examples of similar structures in animals. [2mks]
Eyes of man and octopus
Flipperss in whales and fins in fish
- Name the type of structures shown by: [2mks]
Stuck on a topical question?
Visit the easyelimu.com website and get access to biology form 4 notes
link -> https://www.easyelimu.com/high-school-notes/biology/form-4-notes
For further revision get access to Biology Form 4 Topical Revision Questions and Answers.
Link -> https://www.easyelimu.com/high-school-notes/biology/itemlist/category/235-biology-form-4-topical
and KCSE-MOCKS Biology essays Questions and Answers
Link -> https://www.easyelimu.com/high-school-notes/biology/biology-essays
Download Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Eagle II Joint 2021 Mock Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

