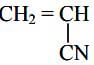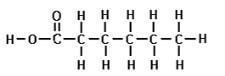Instruction to the candidates
- Write your Name and Index number, Admission Number and Class in the spaces provided at the top of this page.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces in the spaces provided in this paper using English.
- KNEC Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary
For Examiner’s use only
|
Questions |
Maximum score |
Candidate’s Score |
|
1 |
10 |
|
|
2 |
14 |
|
|
3 |
14 |
|
|
4 |
10 |
|
|
5 |
11 |
|
|
6 |
11 |
|
|
7 |
10 |
|
|
|
80 |
QUESTIONS
-
- Define nuclear fission. (1 mark)
- State two similarities between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion? (2 marks)
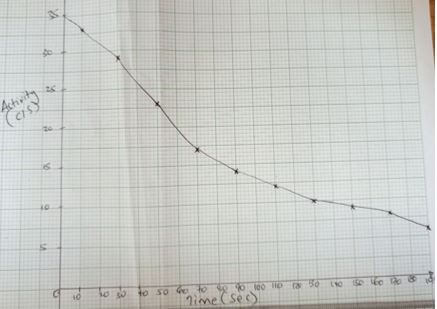
- The following table shows the activity of a sample of protactinium (23491Pa), a radioactive element, measured at regular intervals.
Time (sec)
10
30
50
70
90
110
130
150
170
190
Activity(c/s)
33
29
23
17
14
12
10
9
8
6
- Plot a graph of activity against time. (3 marks)
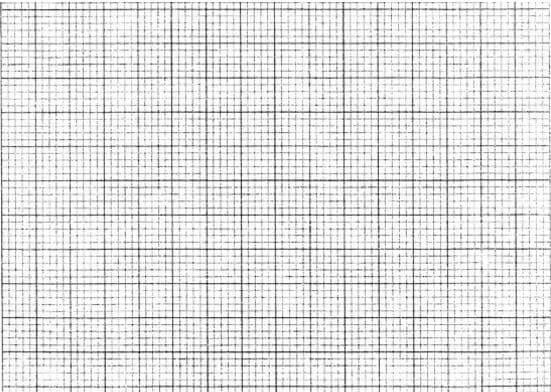
- From the graph:
- The initial activity of the element. (1 mark)
- Determine the half-life of the nuclide. (1 mark)
- Plot a graph of activity against time. (3 marks)
- State two dangers associated with radioactivity. (2 marks)
-
- Acrylan and orlon are names of fibers which are made of the polymer.
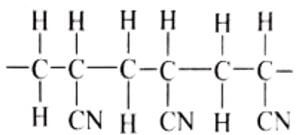
- How many repeat units are shown in this structure? (1 mark)
- Draw a structural formula of the monomer unit from which the polymer is made. (1 mark)
- State two disadvantages of using the above synthetic fiber. (2 marks)
- Detergents contain additives that enhance their cleaning performance. Name two such additives. (2 marks)
- Calculate the mass of ethanol that can be made from 56g of ethene. (2 marks)
- An organic compound P is found on analysis to have the empirical formula C6H14O. Compound P is slightly soluble in water. On oxidation compound P is converted into a compound Q of empirical formula C3H6O and relative molecular mass 116. Both compound P and Q react with sodium metal liberating hydrogen gas.
- To what class of compounds does compound P belong? (1 mark)
- Draw the displayed structural formula of P. (1 mark)
- Deduce the molecular formula of Q and draw its displayed structural formula. (2 marks)
- What other test would you carry out on Q to confirm the presence of the functional group you have indicated? (2 marks)
- Acrylan and orlon are names of fibers which are made of the polymer.
-
- During the electrolysis magnesium sulphate a current of 2 amperes was passed through the solution for 4 hours. Calculate the volume of the gas produced at the anode. (1 faraday 96,500 coulombs and volume of a gas at room temperature is 24,000cm3). (2 marks)
- Table gives standard reduction potentials for some half cells.
Half-cell
Half-cell equation
Eθ /V
I
Cr3+ (aq) + e- → Cr2+ (aq)
-0.41
II
Cd2+ (aq) + 2e- → Cd (s)
-0.40
III
Na+ (aq) + e-→ Na (s)
-2.71
IV
Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- → Cu (s)
+0.34
V
Pb2+ (aq) + 2e- → Pb (s)
-0.13
VI
Br2 (aq) + 2e- → 2Br- (aq)
+1.07
VII
2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g)
0.00
VIII
Fe2+(aq) + 2e- → Fe(s)
-0.44V
IX
O2(g) + 2H2O (l) + 4e- → 4OH-(aq)
+0.40V
X
H2O2(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2e- → 2H2O(l)
+1.23V
- Identify: (1 mark)
- The strongest oxidizing agent.
- The strongest reducing agent.
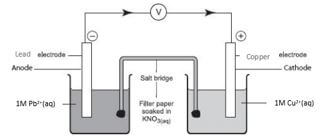
- Construct an electrochemical cell from half-cells V and VI. (3 marks)
- Write the equation and calculate the electrode potential for the electrochemical cell constructed from half-cells V and VI. (2 marks)
- Explain why it is not advisable to use aqueous sodium sulphate as the salt bridge in the electrochemical cell formed between half-cells V and VI. (1 mark)
- Write the cell diagram for an electrochemical cell made using half-cells V and VI. (1 mark)
- Write an equation to show how rusting occurs.(2 marks)
- Give two reasons why electroplating is necessary. (2 marks)
- Identify: (1 mark)
- Below is a periodic table grid study it and answer the questions. (The letters does not represent the actual symbols of the elements)
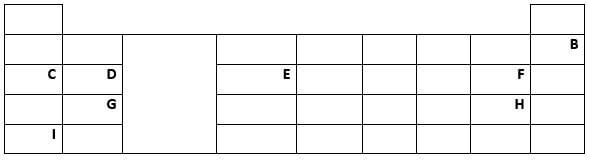
- Which element will require the least amount of energy to remove one of the outermost electrons. (1 mark)
- Select the most reactive metal. (1 mark)
- What name is given to the family of elements to which elements D and G belong? (1 mark)
- An element A has atomic number 9. Indicate the position of A on the grid. (1 mark)
- Explain why the atomic radius of D is smaller than that of C. (1 mark)
- Explain why the atomic radius of A is smaller than its ionic radius. (2 marks)
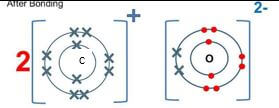
- Element C combines with oxygen to from an oxide. Using dots (•) and crosses(x) to represent the outermost electrons, show how the two elements combine. (1 mark)
- Explain why chloride of E has higher melting point than chloride of D. (2 marks)
-
- Describe how you can determine change in mass when magnesium is heated. (3 marks)
- The table below shows the tests that were carried out on five portions of a compound and the results obtained. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Test
Observation
1
Addition of few drops of sodium hydroxide to the first portion until in excess.
White precipitate soluble in excess.
2
Addition of few drops of aqueous potassium iodide to the second portion
No yellow precipitate is formed.
3
Addition of few drops of acidified barium nitrate to the third portion.
White precipitate formed.
4
Addition of few drops of Lead (II) nitrate to the fourth portion.
White precipitate formed.
5
Addition of few drops of dilute nitric (V) acid to the fifth portion.
Effervescence of a colorless gas.
- Identify the ions likely present in; (2 marks)
- Step 2
- Step 5
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction in the fifth portion. (1 mark)
- Dilute nitric (V) acid was added to a solid which is an alloy of copper. The resultant mixture was then filtered. To the filtrate, few drops of sodium hydroxide solution was added till in excess.
- Sate any two observations made when dilute nitric (V) acid is added to the alloy. (2 marks)
- Name the other metal present in the alloy. (1 mark)
- Write an ion equation for the reaction that took place when few and excess sodium hydroxide solution is added. (2 marks)
- Identify the ions likely present in; (2 marks)
-
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
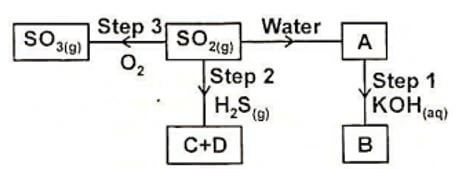
- Name a suitable method of gas collection that can used to collect Sulphur (VI) oxide gas in the laboratory. (1mark)
- Name substances A, B, C and D. (2 marks)
- State the property of Sulphur (IV) oxide exhibited in step 2. (1mark)
-
- Explain the observations made when burning magnesium is lowered into a gas jar containing carbon (IV) oxide. (3 marks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follows.
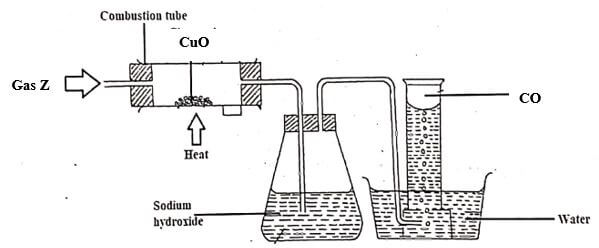
- Name gas Z. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the combustion tube. (1mark)
- State and explain the observations made in the combustion tube. (1 mark)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- The flow chart in the figure below represents some stages in the extraction of lead metal. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
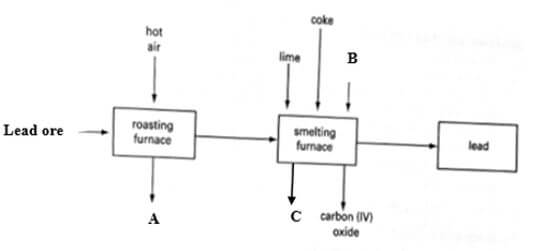
- Identify:
- The lead ore. (1 mark)
- Substance A, B and C. (3 marks)
- Write an equation for the reaction that forms substance C. (1 mark)
- Name an impurity resent in the ore. (1 mark)
- State the process by which the ore is concentrated. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction which occurs in the roasting chamber.(1 mark)
- State any one use of lead.(1 mark)
- Give one reason why the extraction of lead causes pollution to the environment.(1 mark)
- Identify:
MARKING SCHEME
|
Question |
Answer |
Marks |
|
|
1. |
(a) |
Nuclear fission is the splitting process a heavy nuclide undergoes when bombarded by a fast moving neutron. |
1 mark |
|
(b) |
In both cases a large quantity of energy is released. |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(c) (i) |
Scale:
|
1 mark 1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(ii)I |
35 |
|
|
|
II |
24.5 |
|
|
|
(d) |
Testing of nuclear weapons in the oceans also causes environmental pollution since plants and other living organisms may take in the radioactive materials released in the water. |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
Total |
10 marks |
||
|
2. |
(a) (i) |
3 units |
|
|
(ii) |
|
1 mark
|
|
|
(iii) |
They do not decompose easily, i.e., are non-biodegradable. This results in environmental pollution. |
2 marks |
|
|
(b) |
Tetraoxophosphate |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(c) |
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH |
1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark |
|
|
(d) (i) |
Alkanols |
1 mark |
|
|
(ii) |
|
1 mark |
|
|
(iii) |
(C3H6O)n = 116 |
1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(iv) |
Put 2 cm3 of Q in a test tube. |
1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark |
|
|
Total |
14 marks |
||
|
3. |
(a) |
Electricity charge 2 x 4 x 60 x 60=28,800C |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
(b) (i)(I) |
+1.23V/half-cellXI |
1/2 mark |
|
|
(II) |
-2.71V/ half-cell IV |
1/2 mark |
|
|
(ii) |
|
3 marks |
|
|
(iii) |
Pb(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Pb2+(aq) + Cu(s) |
2 marks |
|
|
(iv) |
Formation of insoluble PbSO4. This reduces the concentration of ions in the electrolyte/reduces the effectiveness of the cell. |
1 mark |
|
|
(v) |
Pb(s)|Pb2+(aq) || Cu2+(aq)|Cu(s) Eθ = +0.47V |
1 mark |
|
|
(vi) |
2Fe(s) → 2Fe2+(aq) + 4e- +0.44V |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(vii) |
Improve appearance. |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
Total |
14 marks |
||
|
4. |
(a) |
B |
1 mark |
|
(b) |
I |
1 mark |
|
|
(c) |
Alkaline Earth Metals |
1 mark |
|
|
(d) |
√ indicated on the diagram. |
1 mark |
|
|
(e) |
D has more protons which increases the effective nuclear charge attracting the valence electrons firmly to the nucleus. |
1 mark |
|
|
(f) |
The incoming electrons experiences repulsion from the existing electrons. |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(g) |
|
|
|
|
(h) |
Chloride of E has ionic bonds throughout its giant ionic structure while chloride of E is a molecule with weak van der waals forces of attraction throughout its simple molecular structure. |
1 mark |
|
|
Total |
10 marks |
||
|
5. |
(a) |
Weigh about 1g clean magnesium ribbon in a crucible. |
1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark |
|
(b) (i) |
Step 2 Zn2+ and Al3+ Step 5 CO32- and SO32- |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(ii) |
2H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) →H2O(l) + CO2(g)/ 2H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) →H2O(l) + SO2(g) |
1 mark |
|
|
(iii) I |
Formations of a colorless solution |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
II |
Zinc |
1 mark |
|
|
III |
Zn2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) |
1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
Total |
11 marks |
||
|
6. |
(a) (i) |
Solidification |
1 mark |
|
(ii) |
A Sulphorous acid/sulphuric (IV) acid |
1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark 1/2 mark |
|
|
(iii) |
Oxidizing |
1 mark |
|
|
(b) (i) |
Burning magnesium produces a lot of heat. |
1 mark 1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(ii) I |
Carbon (II) oxide |
1 mark |
|
|
II |
CO(g) + CuO(s) → Cu(s) + CO(g) |
1 mark |
|
|
III |
Black solid changes to brown. |
1 mark |
|
|
Total |
11 marks |
||
|
7. |
(a) (i) |
Galena/lead (II) sulphide/Cerussite |
1 mark |
|
(ii) |
A Sulphur (IV) oxide gas |
1 mark 1 mark 1 mark |
|
|
(b) |
SiO2(s) + CaO(s) →CaSiO3(l) |
1 mark |
|
|
(c) |
Zinc blende/Silica |
1 mark |
|
|
(d) |
Froth flotation |
1 mark |
|
|
(e) |
2PbS(s) + 3O2(g) →2PbO(s) + 2SO2(g) / PbCO3(s) →PbO(s) + CO2(g) |
1 mark |
|
|
(f) |
Used in lead acid accumulators as lead plates |
1 mark |
|
|
(g) |
Emission of Sulphur (IV) oxide forms acid rain which corrodes stone buildings and metallic structures. |
1 mark |
|
|
Total |
10 marks |
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
80 marks |
|||
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - KCSE 2022 Mock Exams Set 1.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students