Questions
INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATE
- This paper consists of three sections A, B, and C
- Answer all the questions in section A and B
- Answer any two questions in section C
SECTION A (30 MRKS)
Answer all question in this section in the space provided
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture as used in crop production. (1mrk)
- List the physical weathering agents in soil formation process (1 ½ mrks)
- Give four method of farming (2mrks)
- Give two examples for each of the following types of cost incurred in broiler production.
- Variable cost (2 marks)
- Fixed cost (2 marks)
- Give four advantages of crop rotation. (2mrk)
- State four factors that that should be considered when classifying crop pest (2mrks)
- Give three reasons why a water logged soil is unsuitable for most crops (1 ½ mrk)
- How do the following factors affect seed rate? (2mks)
- Seed purity?
- Spacing?
- Outline four observable indictors of economic development of a nation (2mrks)
- .Outline four indicators of well decomposed manure (1 ½ mrk)
- Outline four aspects of rainfall affecting agriculture (2mks)
- Give four management practice that promote high herbage yields in pasture production (2mrks)
- Give three reasons why primary cultivation should be done early before the onset of the rains (1½mrk)
- Give two examples of farm records that are kept by a bean farmer (1mrk)
- Give four role of nitrogen in plants (2mrks)
- Give four benefits of possessing a land title deed (2mrks)
SECTION B (20 MRKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
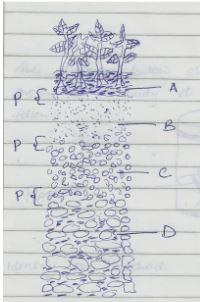
- The diagram below illustrates a feature observed after digging the soil several metres deep Study the diagram carefully and answer the question that follow
- Identify the feature that the diagram above represents in the study of soil (1mrk)
- What is the name given to the part labeled P (1mrk)
- State two ways in which the knowledge of the above feature would be of benefit to farmer (2mrks)
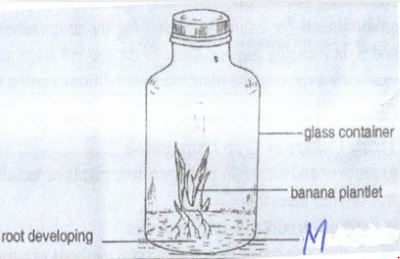
- The diagram below shows a method of crop propagation .Study it and answer the questions that follow
- Identify the method (1mrk)
- Name solution labeled M (1mk)
- State two advantages of using this method in crop propagation. (2mks)
- Mr. Mwangi wishes to know whether replacing 3 hectares of maize with Irish potatoes the following seasons would be worthwhile. The fertilizer cost would be increased from Ksh. 4,000 per hectare to Ksh. 6,000 per hectare. He also incurs cost of maize seeds at Ksh 1,200 per hectare. The cost of Irish potatoes seeds is Ksh. 3,000 per hectare. The income from maize was Ksh. 90,000 and for Irish potatoes will be Ksh. 120,000.
- Draw up a partial budget for Mr. Mwangi’s farm. (6mks)
- With a reason, what advice can you give to Mr. Mwangi? (1mk)
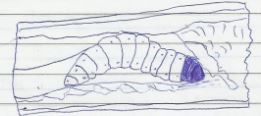
- The diagram below shows a maize stalk infected by a certain pest .Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the pest ( 1mrk)
- Apart from maize, two other crop attacked by the pest named above ( 2marks)
- Give three cultural measures that can be applied to control the pest (3mrks)
SECTION C (40MARKS)
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided
-
- Describe five advantages of rotational grazing (5mrks)
- Explain eight ways in which soil fertility can be maintained (8mrks)
- Describe the harmful effects of weeds (7mrks)
-
- Describe five importance of agro -forestry in soil and water conservation (5mrks)
- Explain six reasons for pruning coffee. (6mrks)
- Describe 6 ways in which labour productivity can be improved on a farm (6mrks)
- Outline three effects of over application of nitrogenous fertilizer (3mrks)
-
- Describe the procedure of silage making (8mrks)
- Discuss Cabbage production under the following subheading
- Varieties and example in each (2mks)
- Nursery establishment (4mks)
- Field management practices (3mks)
- Outline importances of a nursery in crop production (3mks)
Marking Scheme
- Differentiate between olericulture and pomoculture as used in crop production. (1mrk)
- Olericulture is growing of vegetables such as cabbages, tomatoes, onions and French beans while Pomoculture is the growing of fruits such as Avocados, piers and citrus.
- List the physical weathering agents in soil formation process (1 ½ mrks)
- Wind
- Water
- Moving ice
- Temperature
- Give four method of farming (2mrks)
- Mixed farming.
- Nomadic pastoralism.
- Shifting cultivation.
- Organic farming.
- Agroforestry.
- Give two examples for each of the following types of cost incurred in broiler production.
- Variable cost (2 marks)
- Cost of ; Fuel
- Fertilizers
- Seeds
- Wages of casual workers
- Fixed cost (2 marks)
- Land cost
- Depreciation of machinery
- Salaries of permanent workers
- Variable cost (2 marks)
- Give four advantages of crop rotation. (2mrk)
- Maximum utilisation of nutrients.
- Control of soil borne pest and diseases build up.
- Control of weeds.
- Improvement of soil fertility.
- Improvement of soil structure.
- State four factors that that should be considered when classifying crop pest (2mrks)
- Their mode of feeding.
- Crops attacked.
- Stage of development of the pest.
- Stage of growth of the cropattacked.
- Scientificclassification.
- The level ofdamage.
- The place where they arefound/habitat.
- Give three reasons why a water logged soil is unsuitable for most crops (1 ½ mrk)
- Not well aerated
- Less soil volume
- Low soil temperature
- Low microbial activities
- Easily eroded
- High level of toxic substances
- How do the following factors affect seed rate? (2mks)
- Seed purity?
- Pure seeds have a high germination % thus lower seed rate as opposed to impure/mixed seeds.
- Spacing?
- At closer spacing, more seeds are used than at wider spacing.
- Seed purity?
- Outline four observable indicators of economic development of a nation (2mrks)
- Gross domestic product
- Gross national product
- Per capita income
- Health
- Transport and communication
- Outline four indicators of well decomposed manure (1 ½ mrk)
- Absence of bad odour and instead the smell of forest soil
- Light weight
- Brown colour
- Moist but not wet
- Original nature of material not noticeable
- Outline four aspects of rainfall affecting agriculture (2mrks)
- Rainfall imtensity
- Rainfall distribution
- Rainfall reliability
- Amount of rainfall
- Give four management practice that promote high herbage yields in pasture production (2mrks)
- Top dressing.
- Weeding.
- Topping
- Reseeding/Gapping
- Give three reasons why primary cultivation should be done early before the onset of the rains (1½mrk)
- To remove weeds.
- To bury organic matter for easy decomposition.
- To facilitate water infiltration and aeration.
- To destroy soil-borne pests by exposing them to predators and sun.
- To make planting easy.
- Give two examples of farm records that are kept by a bean farmer (1mrk)
- Production records
- Labour records
- Marketing records
- Field operation record records
- Inventory record
- Give four role of nitrogen in plants (2mrks)
- Plays an important role in protein formation .
- it is a constituent element of proteins and protoplasm.
- Forms parts of chlorophyll molecule and makes the plant succulent with a deep green colour.
- Encourages vegetative growth especially in horticultural crops where leaves are harvested.
- Regulate availability of phosphorus and potassium in plants.
- In cereals, nitrogen increases size of grains and their protein content.
- Give four benefits of possessing a land title deed (2mrks)
- It can be used to secure credit facilities necessary for land development, hence encouraging commercial farming.
- Since the registration confers security of tenure, any land disputes are minimised.
- Tenure security encourages farmers to invest in long term and permanent projects and care for the soil.
- Enables the occupant to lease all the land nor part of it thus get extra income.
- .The diagram below illustrates a feature observed after digging the soil several metres deep Study the diagram carefully and answer the question that follow
- Identify the feature that the diagram above represents in the study of soil (1mrk)
- Soil profile
- What is the name given to the part labeled P (1mrk)
- Transitional zone
- State two ways in which the knowledge of the above feature would be of benefit to farmer (2mrks)
- It influences the availability of nutrients
- It determines the crop to be grown
- It influences the method and type of implement used
- It influences the amount of moisture held by the soil
- Identify the feature that the diagram above represents in the study of soil (1mrk)
- The diagram below shows a method of crop propagation .Study it and answer the questions that follow
- Identify the method (1mrk)
- Tissue culture
- Name solution labeled M (1mk)
- Rooting medium
- State two advantages of using this method in crop propagation. (2mks)
- Used to recover and establish pathogen free plants especially in control of viral diseases.
- Used in mass propagation of propagules.
- Fast and requires less space than cultural methods.
- Identify the method (1mrk)
- Mr. Mwangi wishes to know whether replacing 3 hectares of maize with Irish potatoes the following seasons would be worthwhile. The fertilizer cost would be increased from Ksh. 4,000 per hectare to Ksh. 6,000 per hectare. He also incurs cost of maize seeds at Ksh 1,200 per hectare. The cost of Irish potatoes seeds is Ksh. 3,000 per hectare. The income from maize was Ksh. 90,000 and for Irish potatoes will be Ksh. 120,000.
- Draw up a partial budget for Mr. Mwangi’s farm. (6mks)
-
DEBIT (-) kSH CREDIT (+) KSH 1. Extra cost (potatoes)
Fertiliser
6000 x 3
Seeds
3000 x 3
Sub - total18 000
9 000
27 0001. Extra revenue 120 000 2. Cost saved (Maize)
Fertiliser
4000 x 3
Seeds
1200 x 312 000
3 6002. Revenue fore gone 90 000 Sub total 15 600 TOTAL 42 600 TOTAL 210 000 - With a reason, what advice can you give to Mr. Mwangi? (1mk)
-
- Draw up a partial budget for Mr. Mwangi’s farm. (6mks)
- The diagram below shows a maize stalk infected by a certain pest .Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the pest ( 1mrk)
- Maize stalk borers (Buseola fusca)
- Apart from maize, two other crop attacked by the pest named above ( 2marks)
- Sorghum
- Sugar cane
- Rice
- Give two cultural measures that can be applied to control the pest (2mrks)
- Early planting.
- Rogueing.
- Burning infested maize crop remains after harvesting.
- Use of appropriate pesticides at funnel of each plant
- Identify the pest ( 1mrk)
-
- Describe five advantages of rotational grazing (5mrks)
- Livestock make maximum use of pastures.
- Reduces the build-up of pest and diseases.
- Animal waste is distributed evenly in all fields or paddocks.
- Pasture area is given time to regrow before it is grazed on again.
- Excess pasture can be harvested for conservation.
- It is possible to apply fertiliser in portion of the pastures which are not in use. Reseeding and weeding can also be done.
- Explain eight ways in which soil fertility can be maintained (8mrks)
- Control of soil erosion.
- The measures to control soil erosion aims at promoting good water infiltration and reducing runoff. Includes: terracing, contour cultivation, strip cropping, cut-off drains and planting cover crops.
- Crop rotation.
- Practice of growing crops of different families on the same piece of land in an orderly sequence.
- Helps to control crop pests, diseases and weeds.
- Ensures maximum utilization of soil nutrients by growing a variety of crops which have different nutrient requirements.
- Legumes in a rotation programme improves the soil nitrogen.
- Control of soil pH.
- Most living organisms do well at a pH around neutral.
- Extreme pH inhibit the activities of living organisms.
- Proper drainage.
- Can be done by breaking hard layers impeding drainage. Where poor drainage is as a result of poor soil structure and texture, water channels can be used.
- Weed control.
- The weeds compete with crops for growth resources such as: nutrients, soil moisture, space and sunlight.
- Some weeds acts as alternate hosts of crop pests and diseases.
- Intercropping and mixed cropping.
- Intercropping offers a better ground cover thus smothering weeds and controlling soil erosion.
- Legumes intercropped with cereals fix nitrogen which is used by the cereal crops.
- Minimum tillage.
- Over cultivation destroys the soil structure leading to soil erosion. Therefore unnecessary land operations should be avoided.
- Use of manure.
- Supply organic matter, which on decomposition releases nutrients into the soil. This increases the water holding capacity, moderates soil pH and improves soil structure which helps to control soil erosion.
- Use of organic fertilizer.
- Chemical substances which are manufactured to supply specific plant nutrients. Once used they improves the soil fertility
- Control of soil erosion.
- Describe seven effects of weeds (7mks)
- Compete with crops for nutrients spacing ,light, moisture lowering yield e.g. MacDonald’s eye
- Some are parasitic e.g. wihhweed
- Low quality of produce e.g. Mexican marigold lowering quality of milk/pigweed seeds in finger millet
- Poisonous to both man and livestock e.g. Dahira stramonium, Bracken fern
- Allirnate hosts for pests and diseases e.g. mallow weed –for cotton strainer
- Some are allelopallic/hinder germination e.g. Mexican marigold
- Block irrigation channel e.g. salvinia/water hyacinth
- Affect fishing and navigation-salvinia and water hyacinth
- Lower quality of pasture e.g. manyatta grass
- Reduce workers efficiency/irritate e.g. double thorn, shnging nelthe, devil’s horse whip
- Describe five advantages of rotational grazing (5mrks)
-
- Describe five importance of agro -forestry in soil and water conservation (5mrks)
- Protect the soil below from raindrop erosion by reducing the force with which it falls onto the ground.
- Provide shade and reduce loss of moisture through evaporation.
- Acts as windbreaks.
- The roots of trees bind soil particles together.
- Reduces speed of running water thus reducing its erosive power.
- The leaves decay to supply humus which improves soil structure and increases water infiltration into the soil.
- Explain six reasons for pruning coffee. (6mrks)
- To regulate bearing. Unpruned coffee produces a heavy crop in one season and a light one in the next season.
- To remove old and unproductive branches.
- To make harvesting easy by regulating the height of trees.
- Open pruning facilitates penetration of sprays.
- There is economic use of sprays.
- To open up the bush and bush and allow air circulation. This removes Micro-climate suitable for pest and disease organisms.
- Describe 6 ways in which labour productivity can be improved on a farm (6mrks)
- Training worker e.g. in F.T.C’s, during field days, Agricultural shows, through demonstrations and workshops.
- Measuring farm operations to supplement the labour force.
- Providing incentives to workers such as attractive wages, free protective wear, housing, medical facilities, proper feeding, rewarding good workers. Et.c
- Supervising and counseling workers.
- Mechanizing farm operations.
- Creating good operator - worker relationships.
- Assigning specific tasks to the labor force.
- Outline three effect of over application of nitrogenous fertilizer (3mrks)
- Delayed maturity due to excessive vegetative growth at the expense of reproductivegrowth.
- Causes excessive succulence making plants liable to pest damage.
- Causes lodging in cereals.
- Causes blossom end rot in tomatoes.
- Describe five importance of agro -forestry in soil and water conservation (5mrks)
-
- Describe the procedure of silage making (8mrks)
- The silo is prepared before harvesting the crop.
- The crop is cut at the appropriate stage (8-10 weeks for re-growths) and wilted for 6- 12 hours to about 65-75% moisture content.
- The crop is chopped up and put into the silo, compacting it every 10-12cm layer.
- The silo should be filled as rapidly as possible, preferably in less than two days. The ensiled materials should have a ‘ridge’ appearance when ensiling is complete.
- Temperatures in the silo should be checked regularly during the ensiling process. If it is higher than 32.2, water should be added and compaction reduced. If it is below this, compaction should be increased and dry materials or molasses added.
- The ensiled materials is covered with polythene sheet or a layer of dry grass to prevent it from water and air.
- The silo is covered with a thick layer of soil.
- A trench is dug all round the silo to drain off rain water.
- Discuss Cabbage production under the following subheading
- Varieties and example in each (2mks)
- Early maturing varieties.
- Sugar loaf
- Mukuki.
- Golden acres.
- Gloria hybrid.
- Copenhagen market. (2x ½ =1 mk)
- Late maturing varieties.
- Early drum-head.
- Savoy cabbage.
- Prize drum-head
- Perfection.
- Surc-head (2x ½ =1 mk)
- Early maturing varieties.
- Nursery establishment (4mks)
- Should be in an area where Brassica family crop has not been grown or the last 3 years.
- Nursery bed should be prepared to a fine tilth removing all roots, stones and perennial weeds.
- Shallow drills 10cm apart are made
- seeds are evenly drilledcover lightly. (4x1=4mks)
- Field management practices (3mks)
- Top dressing.
Top dress at 20-25 cm high with one teaspoonful of SA or CAN and repeat 3-4 weeks after the first top dressing. - Weeding.
The field should be kept weed free and hand weeding is done. Do not break the leaves during weeding as it interferes with head formation. - Pest control
Pest like Aphids and cutworms should be comtrolled using appropriate insecticide - Disease control
Diseases like black rot,damping off and downy mildew should be controlled using appropriate methods
( State ½ ,explain ½ )
- Top dressing.
- Varieties and example in each (2mks)
- Outline importances of a nursery in crop production (3mks)Facilitates production of many seedlings in a small area.
- Routine management practices are easily and timely carried out than in main seedbed.
- Facilitates raising of small seeds which develop into strong seedlings that are easily transplanted.
- Ensures transplanting of only the healthy and vigorously growing seedlings.
- Facilitates transplanting of seedlings that are already established thus reducing period taken in the field.
- Excess seedlings from the nursery may be sold thus becoming source of income to the farmer.
- Makes it possible to provide the best conditions such as fine tilth levelled field and shade.
(3x1=3mks)
- Describe the procedure of silage making (8mrks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mathioya Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students