Instructions to candidates
- Answer ALL questions
- All workings MUST be clearly shown where necessary
QUESTIONS
- Name the organelle that performs each of the following functions in a cell
- Protein synthesis (1mark)
- Transport of cell secretions (1mark)
-
- Define the term ‘parthenocarpy’ (1mark)
- Name two plant growth hormones that promote parthenocarpy (2marks)
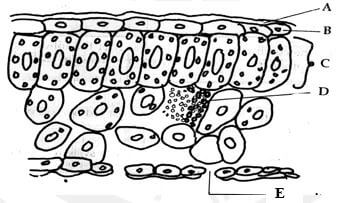
- The diagram below shows a longitudinal section of mammalian skin
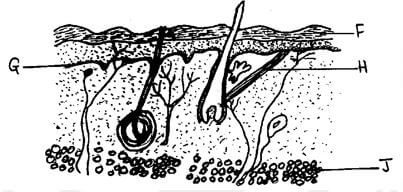
- Name the parts labelled F and G (2marks)
F
G - State one function of each of the parts labelled H and J (2marks)
H
J
- Name the parts labelled F and G (2marks)
-
- State two characteristics used to divide the phylum Arthropoda into classes (2marks)
- Name the class with the largest number of individuals in the phylum Arthropoda (1mark)
- The diagram below represents a longitudinal section of a fruit
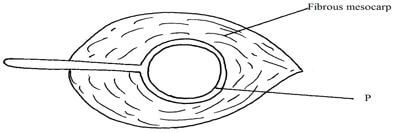
- Identify the mode of dispersal (1mark)
- Describe two adaptations of the fruit to its mode of dispersal (2marks)
-
- What causes the following diseases?
- Diabetes mellitus (1mark)
- Diabetes insipidus (1mark)
- An individual shows the symptoms for diabetes mellitus, how would you determine in the school laboratory whether they are positive for the condition? (2marks)
- What causes the following diseases?
-
- Give two examples of natural selection in action (2marks)
- List two features that make man the most dominant species on earth (2marks)
- Study the diagram below of a neurone in human being
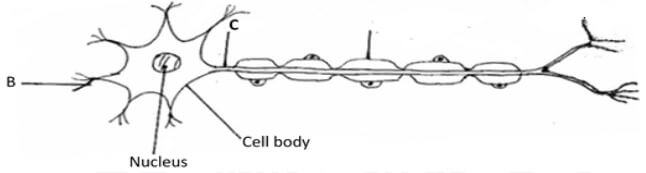
- Identify the neurone (1mark)
- Name the part labeled B (1mark)
- Study the diagram of the mammalian tooth below and answer the questions that follow
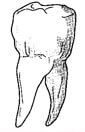
- Identify the tooth (1mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in (a) above (1mark)
- State one adaptation of the tooth to its function (1mark)
- It was found that during germination of pea seeds 93cm3 of carbon (iv) oxide was produced while 91cm3 of oxygen was used up
- Calculate the respiratory quotient (RQ) of the reaction taking place (2marks)
- Explain why it is difficult to measure respiratory quotient in plants during the day (1mark)
- The diagrams below represent two types of bacteria species that causes some human diseases
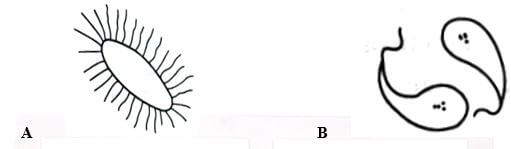
Identify each bacterium and state the disease it causes (4 marks)
A:
Disease it causes:
B:
Disease it causes: -
- What is metamorphosis? (1mark)
- What is the biological significance of metamorphosis to an insect? (2marks)
- Study and complete the table below (3mks)
Feature
Monocot
Dicot
a) Number of stamens
b) Arrangement of vascular bundle in stem
c) Type of root
- The diagrams below show embryos of certain vertebrates animals Study them and answer the question that follows
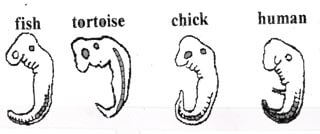
- Mention two observable structural features in these embryos that suggest that they have a common ancestral origin (2marks)
- What phenomenon in organic evolution is exhibited by these diagrams of embryos? (1mark)
- What is meant by the terms? (2marks)
- Hypogynous flower
- Dichogamy
- What is the main difference between the phloem tissues of sub divisions Gymnospermaphyta and Angiospermaphyta (1mark)
- State two ways in which the skin of a frog is adapted for gaseous exchange (2marks)
- What would be the effect of the following treatments on the nerve transmission?
- Inducing the axon with metabolic inhibitors (1mark)
- Removing myelin sheath from a nerve fiber (1mark)
- Give one reason why blood leaving the lungs may not be fully oxygenated (1mark)
- What is the importance of retina in vision? (2marks)
- The diagram below represents a simple endocrine feedback mechanism in human male
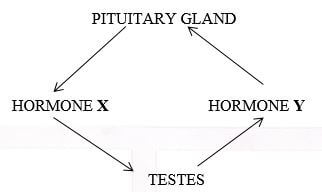
- Name the hormone labelled X (1mark)
- State two differences that may be observed between a normal male and one who is incapable of producing hormone labelled Y (2marks)
-
- Name the cartilage found between the bones of the vertebral column (1mark)
- State the function of the cartilage named in (a) above (1mark)
- The cells shown below were obtained from two different plant cells which were immersed in 2% and 25% salt solutions

- Which of the two cells A and B was immersed in 2% salt solution? (1mark)
- Comment on the nature of 25% salt solution in relation to the cell sap (1mark)
- What biological phenomenon leads to the observation made in A (1mark)
- Name one structures found in the cortex of the kidney (1mark)
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of a leaf
- Name the part labelled B (1mark)
- State the function of the part labelled C (1mark)
- State two difference between xerophytic and hydrophytic leaves (2marks)
Xerophytic
Hydrophytic
-
- Distinguish between gaseous exchange and respiration (1mark)
- Explain the disadvantages of anaerobic respiration in plant roots (2marks)
-
- Suggest the significance of the following adaptations in bony fish
- Flexible vertebral column (1mark)
- Presence of swim bladder (1mark)
- State two features which reduce resistance in fish during swimming (2marks)
- Suggest the significance of the following adaptations in bony fish
- State two protective feature of human eye (2marks)
- State two differences between photosynthesis and respiration (2marks)
Photosynthesis
Respiration
- Explain why malaria cannot be transmitted through blood transfusion (2marks
MARKING SCHEME
-
- ribosome
- golgi apparatus / bodies
-
- fruit formation without fertilization
- auxins
gibberillim
-
- F cornified layer
G malpighian layer - H contracts and relax to raise and lower hair follicles
J storage of fats; // insulation against heat loss
- F cornified layer
-
- number of body parts
number of legs
presence and number of antennae
- number of body parts
-
- water
- has fiber mesocarp which store air to enable it to float
has tough seed coat which is impermeable to water
-
-
- insufficient / less insulin secrteions
- insufficient / less secretions of antiduretic hormone
- take urine sample from the patient and put in a test tube
add benedicts solution
then boil ( then record the colour change)
-
-
- resistance against insectivcides and antibiotics
industrial melanism - ability to communicate through speech
upright posture
a modified forelimb into hand/ arm with opposable thumb for manipulation of tools
- resistance against insectivcides and antibiotics
-
- motor neurone
- receptor dendrite
-
- premolar
- has two roots
has cusps - has wide top surface to increase surface area for grinding / chewing
has cuspsfor grinding / chewing
-
- R.Q = vol of carbon (IV) oxide produced = 9.3 cm3 = 1.02198
volume of oxygen consumed 9.1 cm3 - oxygen produced during photosynthesis is used for respiration and co2 produced in respiration is utilized in photosynthesis
- R.Q = vol of carbon (IV) oxide produced = 9.3 cm3 = 1.02198
- A: salmonella typhi
causes typhoid
B: Vibrio cholerae
cause cholera -
- developmental changes in the body form of arthropods / organism in the course of its life cycle from egg to adult form
- enables an organism to grow in size and complexity
enable an organism to explore different ecological niche
-
feature monocot dicot number of stamens in multiples of threes in multiples of 4s or 5s arrangement of vascular bundle in stem scattered arranged in Q ring type of root fibrous root system tap root system -
- have a tail
have a notochord - comparative embryology
- have a tail
-
- a flavour with superior ovary with other floral parts before the ovary
- a condition in which male and female floral parts mature at different times
- gymnospermaphyla - lacks companion cells
angiospermaphyta - have companion cells - moist to dissolve respiration gases
thin epithelium to offer a shortened diffusion distance for gases
highly vascularized to transport the respiratory gases -
- stops nerve transmission
- lower speed of nerve transmission
- blockage of alveoli / air sacs
infection of the breathing system ;
high pumping speed of the heart - retina contains photoreceptors calls (rods & cornea)
which are sensitive to different light intensities -
- intestinal cell stimulating hormone; Rj; abrrr
- absence of beards
less masculine
shrewed voice
sterility
-
- intervertebral disc
- shock absorber
reduce friction between the vertebrae
allows flexibility of the v/column
-
- B
- hypertonic
- plasmolysis
- proximal convolutes tubule ; bowmans' capsule
distal convoluted tubule ; glomerulus -
- upper-epidermis / upper epidermal cell
- photosynthesis ; site for photosynthesis
-
xerophytes hydrophytic thick cuticle thin cuticle few sunken stomata
leaves reduced in sizemany exposed stomata
leaves are broad
-
- gaseous exchange is the passage of respiratory gases across respiratory surface while respiration is the chemical breakdown of foods (in cells) to release energy;
- lower rate of ion uptake by active transport due to low energy output; // ethanol produced poisons the tissues leading to their death
-
-
- allows body to more from side to side / bending
- air filled to make fish bouyant / keep fish a float / allows change in depth
- streamlined body
inflexible head
scales overlapping ; pointing backwards
muscus on the skin
bowed scales
-
- eyeball within features sockets / orbit for protection from mechanised injuries
eyebrows prevents sweat from entering the eyes
larenchymal gland secrete tears which is antiseptic
eyelids prevents entry of dusts / small particles into the eye -
photosynthesis respiration scam in the chloroplast occurs in the mitichondria / cytoplasm co2 is used up co2 is given out o2 is released o2 is used up glucose is formed glucose is used up - its a vectorborne disease; parasites are transmitted from sick individual to a healthy one through bites of infected female anapheles mosquito;
Download Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Maranda Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
