QUESTIONS
- You are provided with:
Acid
2.0M sodium hydroxide solution labelled solution B
A labelled solution A
Solution C containing 25.0g per litre of an alkanoic acid
You are required to:- Prepare a dilute solution of sodium hydroxide solution B.
- Determine the:
- Molar mass of the alkanoic acid
- Reaction ratio between sodium hydroxide and acid A
Procedure 1
Using a pipette and pipette filler, place 25cm3 of solution B in to a 250.0 ml volumetric flask. Add about 200cm3 of distilled water. Shake well. Add more distilled water up to the mark. Label this solution D. Retain the remaining solution B for use in Procedure 2. Fill the burette with solution C. Using a clean pipette and pipette filler, place 25cm3 of solution D into a 250 ml conical flask. Add two drops of phenolphthalein indicator and titrate with solution C. Record your results in Table 1. Repeat the titration two more times to complete the table. (4 marks)
Table 1
Determine the:I II III Final burette reading Initial burette reading Volume of solution C (cm3) added - Average volume of solution C used.
- Concentration of solution D in moles per litre.
- Concentration of the alkanoic acid in solution C in moles per litre. (1 mole of the acid reacts with 3 moles of the base).
- Molar mass of the alkanoic acid.
Procedure 2
Fill a clean burette with solution A. Place 5 cm of solution A in to a 100ml beaker. Measure the initial temperature of solution A in the beaker and record in Table 2. Using a 50 ml measuring cylinder, measure 25 cm of solution B. Add it to solution A in the beaker and immediately stir the mixture with a thermometer Record the maximum temperature reached in Table 2. Repeat the experiment with other sets of volume of solutions A and B and complete the table.
Table 2 (5 marks)
Volume of solution A (cm3) 5 9 13 17 21 25 Volume of solution B (cm3) 25 21 17 13 9 5 Maximum temperature (°C) Initial temperature (°C) Change in temperature, ΔT - On the grid provided, plot a graph of AT (vertical axis) against the volume of solution A. (3 marks)
- From the graph determine the volume of solution A which gave the maximum change in temperature
- Determine the volume of solution B that reacted with the volume of solution A.
- Calculate the:
- Ratio between volume of solution A and B that neutralized one another.
- Concentration in moles per litre of the acid in solution A. (Assume that the volume ratio is the same as the mole ratio).
- You are provided with solid E. Carry out the following tests and write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place about one half of solid K in a test-tube and heat it strongly. Test any gases produced with both red and blue litmus papers.
Observations Inferences - Place the rest of solid in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm3 of distilled water. Divide the resulting solution into five portions. To the first portion, add lead(li) nitrate
Observations Inferences - To the second portion add dilute Nitric (IV) acid.
Observations Inferences - To the third portion add barium nitrate
Observations Inferences - To the fourth portion add aqueous ammonia till in excess
Observations Inferences - To the fifth portion add sodium hydroxide dropwise till in excess
Observations Inferences
- Place about one half of solid K in a test-tube and heat it strongly. Test any gases produced with both red and blue litmus papers.
- You are provided with solid F Carry out the tests below write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided
- Place all of solid F in a test-tube and add 6cm of sodium hydroxide solution
Observations Inferences - Place the solution obtained in a above in a boiling tube add about 10cm3 of 2M dilute hydrochloric acid drop wise, filter the mixture and retain the residue for tests below. Wash the residue with about 10 cm3 of distilled water. Dry the residue Between filter papers.
Place about one third of the dry residue n metallic spatula and bum ton a Bunsen burner flame.
Observations Inferences - Place all the remaining residue in to a boiling tube. Add about 10 cm of distilled water and shake Divide the mixture into two portions:
- To the first portion add two drops of bromine water
Observations Inferences - To the second portion, about 5 cm of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid and then about 5 cm3 of ethanol. Warm the mixture.
Observations Inferences
- To the first portion add two drops of bromine water
- Place all of solid F in a test-tube and add 6cm of sodium hydroxide solution
CONFIDENTIAL
In addition to the fittings and chemicals found in the Chemistry laboratory, each candidate will require the following:
- One 50ml burette
- 25ml pipetle and pipette filler
- Two 250ml conical flasks
- Thermometer (-10°C -110°C)
- 3 labels
- One 250cmvolumetric flask
- About 500cm of distilled water in a wash bottle
- 100ml plastic beaker
- 50ml measuring cylinder
- 10ml measuring cylinder
- 10mls of absolute ethanol
- Filter funnel
- Two filter papers
- Two boiling tubes
- 1 blue and 1 red litmus paper
- About 150cm3 solution A
- About 150cm3 of solution B
- About 70cm3 of solution C
- 0.5g of solid E
- 0.5g of solid F
- Six test tubes in a rack
- 12cm of 2M HCI
- A dropper
- Metallic spatula
Access to the following:
- Acidified potassium manganate (VII) supplied with a dropper
- Bunsen burner
- Phenolphthalein indicator supplied with a dropper
- 2M sulphuric (VI) acid supplied with a dropper
- Bromine water supplied with a dropper
- 2M NaOH supplied with a dropper
- 2M aqueous ammonia supplied with a dropper
- 2M hydrochloric acid
- Aqueous lead (II) nitrate supplied with a dropper
- Aqueous barium nitrate supplied with a dropper
- Dilute nitric (V) acid
NOTES AND PREPARATIONS
- Solid Eis Hydrared Ammonium Aluminium sulphate
- Solid F is Benzoic Acid 3.
- Solution A: measure about 500ml of distilled water and place in a one litre volumetric flask then add the 172cm of concentrated hydrochloric acid carefully and top up to the mark. (2M HCI)
- Solution is prepared by dissolving 800g of the Sodium hydroxide pellets in about 500cm of water then diluting to one litre. (2.0M NaOH)
- Solution C is prepared by dissolving 25.0g of anhydrous citric acid, C&H:0(COOH) R.F.M = 192 in about 500cm of water then diluting to one litre

MARKING SCHEME
-
I II III Final burette reading 13.5 13.5 13.5 Initial burette reading 0.0 0.0 0.0 Volume of solution C (cm3) added 13.5 13.5 13.5 - 13.5 + 13.5 + 13.5 = 13.5cm3
3 - M1V1 = M2V2
2 x 25 = M2 x 250
M2 2 x 25 = 0.2M
250 - If 0.2 moles ⇒ 100cm3
? ⇒ 25cm3
25 x 0.2 = 0.005
1000
moles of c = 0.005 = 0.0017moles
3
if 0.0017moles 13.5cm3
? = 1000cm3
1000 x 0.0017 = 0.1259m
135 - If 0.1259 moles = 25g
1 mole = ?
1 x 25 = 198.57
0.1259 - 15cm3
- 30 - 15 = 15cm3
- 15/15 : 15/15 = 1:1
- moles 15 x 2 = 0.03
1000
0.003 - 15
? - 1000
= 2M
moles of A = 0.003
Table 2
Volume of solution A (cm3) 5 9 13 17 21 25 Volume of solution B (cm3) 25 21 17 13 9 5 Maximum temperature (°C) 24.0 27.5 30.0 39.5 27.5 24.0 Initial temperature (°C) 20.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 20.0 Change in temperature, ΔT 04.0 07.5 10.0 10.5 7.5 4.0 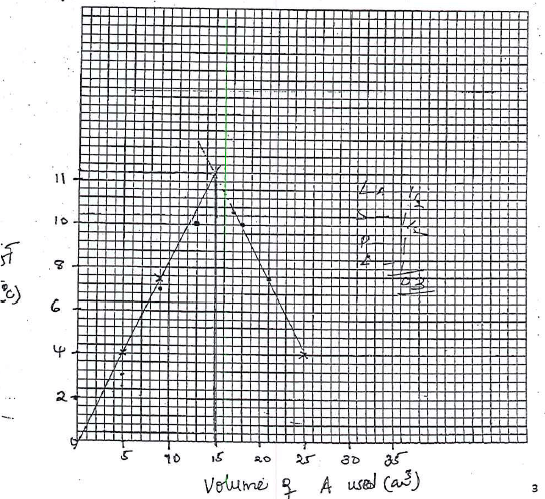
- 13.5 + 13.5 + 13.5 = 13.5cm3
Observations Inferences a) red litmus changes to blue and blue litmus remains blue
colourless liquid
b) white ppt
c) No bubbles
d) White ppt
e) White ppt insoluble
f) White ppt solubleH4+ (tied to red turns blue)
Hydrated salt (tiied to colourless liquid)
SO2-4 SO25-3 CO2-3 Cl Br present
SO42- , Cl, Br present
SO42- present;
Mg2+ Al3+ present
Al3+ present
Observations Inferences a)Solid F dissolves to form a colourless solution
b)Burns with a yellow sooty flame
c)i)Yellow bromine water is not decolorized
ii) pleasant smella)Solid F is acidic
b)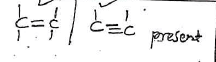
c)i)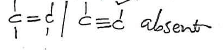
ii)R-COOH present
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Alliance Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
