Questions
Instructions to Candidates
- Answer all the questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C.
SECTION A. (30 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section in the spaces provided
- State four disadvantages of extensive farming. (2 marks)
- State four human factors that lead to low crop production. (2 marks)
- State four characteristics of soil that influence crops planted. (2 marks)
- State four factors that influence the number of secondary cultivation. (2 marks)
- Mention four reasons for ridging in crop production. (2 marks)
- State four practices that encourage minimum tillage. (2 marks)
-
- Name three non-chemical methods of water treatment. (1½ marks)
- State four advantages of trickle irrigation. (2 marks)
- State four importance of organic matter in sandy soil. (2 marks)
- Name four types of records kept by a poultry farmer. (2 marks)
-
- Name two forms in which nitrogen element is absorbed by plants. (1 mark)
- Name any two methods of harvesting agro forestry trees. (1 mark)
-
- State four importance of nursery practice in vegetable crop production. (2 marks)
- Name three vegetative propagation material used to propagate pineapples. (1½ marks)
- State four effects of excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer on growing crops. (2marks)
- State four cultural ways of controlling nematodes in a field of bananas. (2 marks)
- Distinguish between Pricking out and Rogueing. (1 mark)
SECTION B: (20 MARKS.)
Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
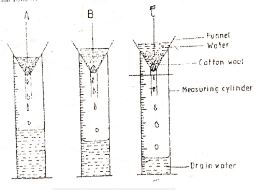
- The diagram below illustrates an investigation on property of soil samples labeled A, B, and C
- If the levels of water drained in the diagram were observed after two hours, name the property of soil being investigated. (1 mark)
- What is the relationship between the soil property named in (a) above and the size of soil particles. (1 mark)
- Which soil sample would be suitable for growing paddy rice? (1 mark)
- Name the type of soil. (2 marks)
A
C
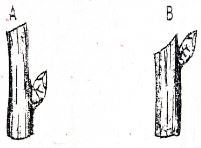
- Use the diagram below that show pruned plants after budding to answer the questions that follow
- Which diagram shows the correct pruning cut? (1mark)
- Explain why the other cutting is wrong? (1 mark)
- State three importance of pruning coffee. (3 marks)
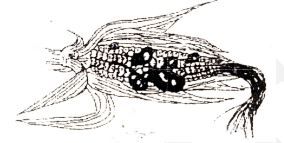
- Use the diagram below that show maize cob attacked by a disease. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the crop disease illustrated above. (1 mark)
- A part from maize name other two crops attacked by the same disease. (2 marks)
- State two control measure of the disease in (a) above. (2 marks)
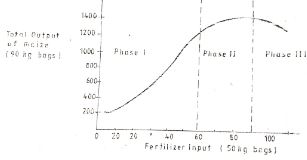
- Below is a graph representing the law of diminishing return. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Explain what would happen to each of three zones marked I, II, and III in relation to fertilizer input to beans output. (3 marks)
- Which is the rational zone among three zones and why? (2 marks)
SECTION C: (40 MARKS).
Answer any TWO questions from this section in the spaces provided after question 21.
-
- Describe five agencies involved in marketing of Agricultural products. (10 marks)
- Give six practices carried out in the field that control maize diseases. (6 marks)
- State four importance of irrigation. (4 marks)
-
- Outline five farming activities which may encourage soil erosion. (5 marks)
-
- Describe harvesting of cotton (5 marks)
- Explain the precaution during harvesting of sugarcane. (3 marks)
- Describe the production of carrots under the following sub – headings.
- Seedbed preparation (3 marks)
- Field management (4 marks)
-
- State seven factors that influence seed rate during planting. (7 marks)
- Outline five factors necessary for proper functioning of farmers’ co-operative societies in Kenya. (5 marks)
- Outline eight ways farmers can overcome risks and uncertainties in a farming business. (8 marks)
Marking Scheme
- Four disadvantages of extensive farming
- Law output
- Land is underutilized
- Done where land is not limited
- Can//not use land to get loans
- Low profit per unit area
- Poor quality produce
- No land improvement
- High spread of pests and diseases
- Four human factors that lead to low crop production
- Low level of education
- Poor health
- Poor economy
- Lack of market force
- Poor government policy
- Cultural and religious belief
- Four characteristics of soil that influence crops planted
- Nutrients available
- Soil PH
- Drainage
- Water holding capacity
- Air movement
- Soil depth
(4×2=2mks)
- Four factors that influence the number of secondary cultivation
- Size of planting material
- Land topography
- Soil moisture
- Condition of soil ciods
- Capital available
- Population of weeds
(4×2=2mks)
- Four reasons for ridging
- Encourage tuber expansion
- Control soil erosion
- Improve drainage
- For easy harvesting tuber crops
- Four practices that encourage minimum tillage
- Use of herbicides
- Mulching
- Cover cropping
- Slashing/uprooting/ grazing animals on weeds
-
- Three non chemical methods of water treatment
- Filtration
- Boiling
- Sedimentation
- Geration
- Four advantages of trickle irrigation
- Require little water
- Use water under low pressure
- Discourage fungal diseases
- Control weeds between rows
- Can be used to apply soluble fertilizer
(4x1/2= 2mks)
- Three non chemical methods of water treatment
- Four importance of organic matter in sandy soil
- Increase water holding capacity
- Improve soil fertility after decomposition
- Provide food and shelter to micro-organisms when fresh Improve soil structure after decomposition
- Butter soil pits after decomposition
- Reduce the toxicity of plant poison due to chemical and fertilizer application after decomposition
- Pack color of humus increase soil temperature that make crops grow faster (4 x 1/2= 2mks)
- Four types of records kept by a poultry farmer
- Egg production
- Inventory
- Feeding
- Health
- Marketing Labour
(4 x 1/2= 2mks)
-
- Two forms nitrogen element is absorbed by plants
- Nitrate ions (NO-3)
- Ammonium ions (NH+4)
(2x1/2= 1mk)
- Two methods of harvesting Agro forestry trees
- Pruning
- Lopping
- Pollarding
- Coppicing
- Two forms nitrogen element is absorbed by plants
-
- Four importance of nursery practice
- Production of many seedlings in a small area
- Easy to carry management practices
- Easy to provide the best condition for growing of crops
- Facilitating the planting of small seeds into strong seedlings
- Easy to select healthy seedlings for transplanting
- Facilitating planting of already established seedlings
- Excess seedlings can be sold
(4x)/2= 2mks)
- Three vegetative propagation material of pineapples
- Crown
- Slip
- Suckers
- Four importance of nursery practice
- Four effects of excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer on growing maize
- Lodging excessive / succulence weakening of stems
- Scorching / burning of leaves
- Delayed maturity
- Excessive foliage growth
- Encourage causes blossom end rot
- Four cultural ways of controlling nematodes in a field of bananas
- Plant resistant tourant varieties
- Remove and burn infected plants / held hygiene
- Crop rotation
- Plant Mexican marigold in the field
- Trim roots of suckers before planting
- Pricking out and Rogueing
- Pricking out is uprooting some seedlings in an overcrowded nursery and planting them in a second nursery bed while rogueing is uprooting and destroying infected plants with a disease (mark as a whole lmk)
-
- Soil porosity / water holding capacity (1mk)
- The smaller the size of the particles the greater the force of holding capacity (lmk)
- Sample C
-
- A Sandy soil
- C Clay soil
-
- A
- A-Too close to the bud
- B- Sloping wrong way
- 3 importance of pruning coffee
- Remove diseased and unwanted parts
- Cropping
- Facilitate picking
- Easy penetration of chemical spray
- Remove micro-climate for disease coming microorganisms e. g CBD (3mks)
- A
-
- Smut (1mk)
- Any cereal crop and sugarcane (2mks)
- Two control measure
- Hot water treatment
- Use certified seeds
- Crop rotation Field hygiene (2mks)
-
- Zone 1: An input of fertilizer results in an increased output in bean production
Zone 2: Any increase in input results in a decreased output of beans till it reaches a maximum le decreased output reaches zero
Zone 3: Any further increase in fertilizer input results in a negative output of beans I e decline (3mks) - Zone 2 because the output reaches maximum (2mks)
- Zone 1: An input of fertilizer results in an increased output in bean production
-
- Intenerant traders / middumen: buy produce from farmers and resell
- Processors or manufacturing companies: Buy produce to process
- Wholesalers: Buy produce in bulky from farmers or processors and resell
- Brokers or commission agents: Act on behalf of other businessmen for a fee or commission Co-operative societies and union: Buy farmers produce locally
- Marketing boards: Buy produce from farmers (state 1mk, explanation 1mk)
- Six practices that control maize diseases
- Crop rotation: Break life cycle of disease causing organisms
- Rogueing: Prevent spreading
- Plant disease free plants: Prevent introduction of pathogens
- Close seasons: Break life cycle of pathogens
- Early planting / timely: Crops establish faster before attack
- Weed control: Prevent them harboring some pathogens
- Use resistant varieties: Prevent attack by pathogens
- Chemical application: Kill pathogens
- Clean equipments: Reduce contamination with disease causing organisms
- Quarantine: Prevent introduction of pathogen on farm
- Destroy crop residues: Minimize spread
Control vectors: Minimize spread of pathogens
- Importance of irrigation
- Enables crop production during dry seasons
- Enable to reclaim and land for production
- Supplement rainfall for crop production
- Sustain proper growth of crops which require plenty of water e g rice
- Create favorable temperature for proper plant growth
- Facilitate supply of fertilizer in irrigation water / fertilization
- Make possible to grow crops in special structure I e green houses
- Increase crop yield
- Maximize utilization of resources where land is ferble but no water
- Source of employment in areas where it is used extensively
- Promote crop production for export
- Control pests like moles and aphids
- Intenerant traders / middumen: buy produce from farmers and resell
-
- Five farming activities which may encourage soil erosion
- Continuous cropping
- Burning of vegetation
- Ploughing along the slope
- Deforestation
- Proper plant nutrition:
- Ploughing along the river banks
- Cultivating when soil is too dry
- Overgrazing / overstocking
- Flooding / over irrigation
- Over cultivation / pulverizing the soil (5mks)
-
-
- Procedure of harvesting cotton
- Start 4 month after planting
- Have two containers Done when balls are dry
- Pick as soon as first ball open
- Sorting is done as you harvest grade AR (Safi) and BR (fifi)
- Avoid contamination / avoid sisal bags (Smks)
- Precautions during harvesting sugarcane
- Bunt cane should be cut immediately after burning
- Cut cane be delivered to factory within the first 24 hours
- Cut cane at ground level (3mks)
-
- Describe the production of carrots under the following sub-headings
- Seedbed preparation
- Prepare during dry season
- Clear vegetation
- Plough / dig deeply to eradicate all seeds
- Harrow to a moderate filth / fine / appropriate filth
- Field management
- Thinning
- Weed control
- Top dressing
- Spray appropriate pesticides to control pests
- Spray appropriate fungicide to control diseases
- Water during dry seasons (4mks)
- Seedbed preparation
- Five farming activities which may encourage soil erosion
-
- Seven factors that influence seed rate
- Intended use of the crop: Fodder more seeds
- Germination percentage: How germination more seeds
- Method of planting: Broadcasting more seeds
- Number of seeds per hole: Two or more require more seeds
- Soil fertility: Fertile soil more seeds
- Size of crop: Tall spreading crops less seeds
- Spacing: Close spacing more seeds
- Seed purity: Impure seeds more seeds
- Crop stand: Pure stand more seeds (state & explanation 7mks)
- Five factors necessary for proper functioning of farmers co-operative societies
- Availability of adequate funds, capital invue for members
- Training of personnel or availability of advisory services on managerial skills
- Loyalty on the part of all farmers co-operators and officials to support their organization
- Proper and accurate record keeping and accountability for all operations
- Efficiency with which produce from farms are marketed
- Honesty on the part of personnel with regard to the handling of cooperative finances
- Timely payment of farmers dues (5mks)
- Eight ways farmers can overcome risks and uncertainties
- Diversification / growing a variety of crops or having various enterprises: If one fails he can rely on the other
- Taking insurance policy: Incase of failure the enterprises are covered
- Inventory marketing / strategizing farming: keeping farm products and selling at time when prices are favorable
- Flexible enterprises: Engaging in enterprises that can be stopped or started early as conditions change
- Rationing of inputs: Using just sufficient inputs such that in case of losses the costs are toohigh
- Using more certain husbandry practices: Use practices that the farmer is sure of and has used in the past
- Contracting: Making arrangement with marketing agencies in advance that change in prices after the arrangement do not change the price of farmers produce
- Selecting more certain enterprises: Select enterprises that have done well in the area / tried through research
- Adopting modern methods of production: I e irrigation, planting resistant varieties (8mks)
- Seven factors that influence seed rate
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Bondo Joint Mocks Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students