INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Scientific calculators may be used.
-
- Define the term isomerism. (1mark)
- Draw and name two isomers of C4H10 (2 marks)
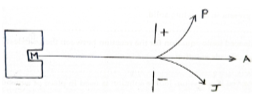
- The figure below shows the behavior of emission from a radioactive isotope M. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Explain why isotope M emits radiations (1 mark)
- Name the radiations labeled P and J (1 mark)
- Explain why radiation A is not deflected (1 mark)
- 13.68g of aluminium sulphate were dissolved in 600cm3 of water, calculate the concentration of the sulphate ions in the solution. (Al=27,S=32,O=16) (3 marks)
-
- Using an equation explain the observation made when concentrated nitric (V) acid is added into a beaker containing copper turnings. (2 marks)
- What property of nitric acid is shown in the equation above? (1 mark)
- An element Z is atomic number 13, Z reacts with both oxygen and chlorine. Explain why the oxide of Z has a melting point of 1020°C while the chloride of Z sublimes at 124°C (2marks)
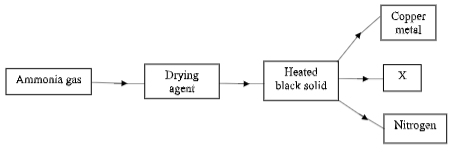
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follows.
- Name a suitable drying agent used in the process above (1mark)
- Describe one chemical test for ammonia gas (1mark)
- Name substance X (1mark)
- Lead (II) nitrate solution forms a white precipitate when reacted with sodium hydroxide. The precipitate dissolves in excess sodium hydroxide to form a colourless solution.
- Identify;
- The white precipitate …………………………………………… (1mark)
- Colourless solution ……………………………………………… (1mark)
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of the colourless solution (1mark)
- Identify;
- The set up below shows the investigation of the effect of a certain gas on heated iron powder. Use the diagram to answer the questions that follow.
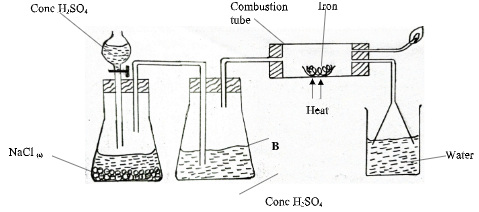
- State the observation made in the combustion tube. (1mark)
- State and explain the difference in the observation made if chlorine gas was used instead of the gas produced in the set up above. (2marks)
- Identify the amendment that would be made in the set up above when chlorine gas is to be used.(1 mark)
- Describe one chemical test that can be used in a school laboratory to distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid. (2mark)
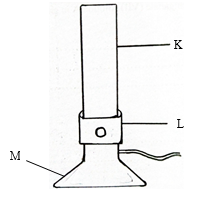
- The diagram below shows a piece of heating apparatus. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the parts labeled L and M (2marks)
- State the function of the parts labeled K (1mark)
- Hydrazine gas N2H4 burns in oxygen to form nitrogen gas and steam.
- Write a balanced chemical equation when hydrazine burns in oxygen (1mark)
- Use the bond energies given below to calculate enthalpy change for the reaction in (a) above. (3marks)
Bond Bond energy (kJmol−1) N ≡ N 944 N − N 163 N − H 388 H − H 496 O = O 463
- A form four students accidentally mixed the following: iron filling, sodium chloride, aluminium chloride and copper (II) oxide. Describe how the student can obtain a pure sample of sodium chloride crystal. (3marks)
- Explain how a student can prepare a crystal of silver nitrate in the school laboratory starting with silver metal. (3marks)
- Use the standard electrode potential below to answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements.
Half –cell reactions Eθ Volts
A2+(aq) + 2e−A(s) − 2.72
B2+(aq) + 2e−B(s) − 2.72
C+(aq) + e−C2(g) 0.00
D2+(aq) + 2e−D(s) +0.34
F2(aq) + 2e−F−(aq) +2.44
- Identify element C (1mark)
- Draw a well labeled diagram for the electrochemical cell formed when the half cells of A and B are combined. (3marks)
- Carbon (II) oxide was passed over heated lead (II) oxide in a combustion tube as shown in the diagram below.
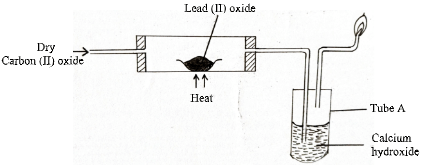
- State the observation made in tube A (1mark)
- Write a well-balanced chemical equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube. (1mark)
- Graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon:
- Name one other element that exhibits allotropy (1mark)
- Give a reason why graphite is an ideal lubricant than ordinary oil (1mark)
-
- State the Grahams’ law of diffusion (1mark)
- In an experiment 60cm3 of a gas Q diffuse through a porous plate in 10 seconds. Another gas P diffuse through the same plate in 30 seconds. Given that the density of gas Q is 1.25g/cm3, calculate the density of gas P. (3marks)
- An element Q reacts with excess oxygen to form a yellow solid.
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between Q and water. (1mark)
- State one observation made when Q reacts with water (1mark)
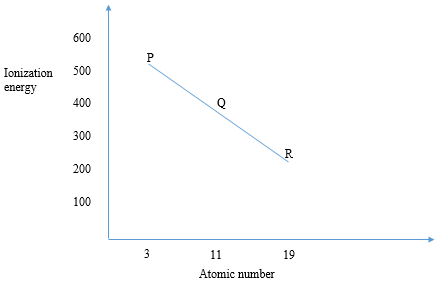
- Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
- What is meant by the term ionization energy? (1mark)
- What is the general name given to the group in which elements P,Q and R belong to (1mark)
- Explain why R has the lowest ionization energy (1mark)
- Hydrogen chloride gas was bubbled into three boiling tubes A, B and C containing methylbenzene, distilled water and excess sodium hydroxide solution respectively. A piece of magnesium ribbon was then added into each boiling tube. State and explain the observations made in boiling tubes A and B. (3marks)
Boiling tube Observation Explanation A B - An element C reacts moderately with an acid to produce hydrogen gas. It also reacts with steam to form a black solid and hydrogen gas.
- State the name of the name of the product formed when C is exposed to moist air (1mark)
- Write the equation for the reaction between C and steam. (1mark)
- The figure below represents extraction of sulphur by frasch process.
- Identify the substance carried through pipe X (1mark)
- State two properties of molten sulphur that make it possible for sulphur to be extracted by the method shown above. (2 mark)
- Explain why sulphur is not extracted by open cast mining method. (1mark)
- The set up below was used by Anthony a form four student who wanted to electroplate his metallic cup with silver. He passed a current of 2A for 2 hours.
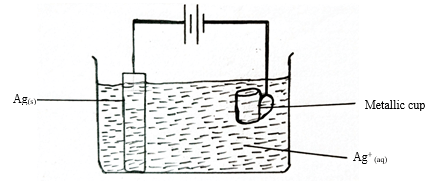
- If the initial mass of the cup was 98g, determine the mass of the cup after the 2hours (1F=96,500C Ag=108) (3marks)
- State one importance of electroplating (1mark)
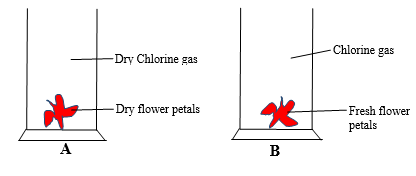
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- State and explain the observations made in gas jar A and B (3marks)
- Write the chemical equation that occurs in gas jar B (1mark)
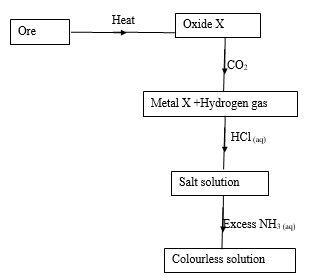
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follows.
- Name the chief ore from which metal X is extracted (1mark)
- Name the main cation in the colourless solution (1mark)
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction between the oxide of X and carbon (II) oxide when heated. (1mark)
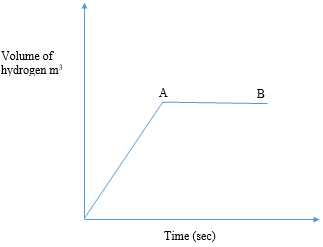
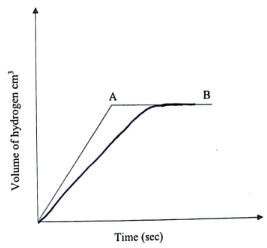
- In an experiment magnesium ribbon was reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid and the volume of hydrogen gas produced with time recorded. The graph below shows the volume of hydrogen gas produced against time.
Explain the following observations:- The curve is steep at the beginning (2mark)
- The curve flattens at region AB (1mark)
- On the same axis plot the curve that would be obtained if the acid used was ethanoic acid in place of hydrochloric acid (1mark)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Is the occurence/ existence of compunds with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
-
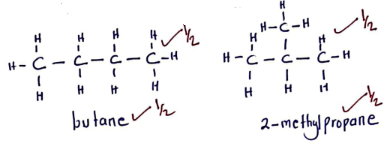
Award for the name only if the structure is correct
-
- It is unstable
-
- Beta
- Alpha
- Has no change
- 1 mole → 324g
? → 13.68g
13.68 = 0.04moles
342
0.04 moles → 600cm3
? → 1000cm3
1000 × 0.04
600
= 0.06667moles/L
0.06667 × 3
= 0.2moles/L -
- Cu(s) + 4HNO3(l) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + H2O(l)
(brown) (blue) (brown) - Oxidation
- Cu(s) + 4HNO3(l) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO2(g) + H2O(l)
- The oxide of Z has giant ionic structure with strong ionic bonds while the chloride of Z has molecular structure where the molecules are held by co-ordinate bonds.
-
- Calcium Oxide reject formula
- Dip a glass rod in concentrated hydrochloric acid and introduce it into a gas jar containing ammonia. A white fumes of ammonium/chloride are formed.
- Water reject formula
-
- Lead (II) hydroxide // Pb(OH)2 (s)
- Sodium tetrahydroxoplumbate (II) // Sodium plumbate
- Pb(OH)2(s) + 2OH−(aq) → [Pb(OH)4]2−(aq)
-
-
- Grey solid changes to green
- When chlorine gas is used grey solid changes to brown. Chlorine reacts with heated iron to form brown Iron (II) Chloride.
- Add Manganese (IV) Oxide to the reactants and heat
Accept an amendment that will produce Cl2
- In two boiling tubes containing ethanol and ethanoic acid separately, add Sodium hydrogen carbonate. Effervescence occurs with ethanoic acid while no effervescence with ethanol.
Accept other correct methods -
-
- Colar
- Base
- A pathway where laboratory gas and air mox and move to the top for burning.
-
-
- N2H4(g) + O2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
-
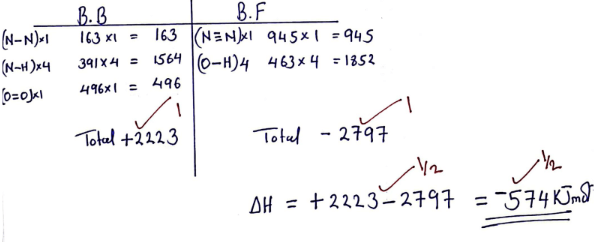
-
- Put the mixture on a flat surface and use a magnet to remove iron fillings
- Put the remaining mixture in a glass beaker and cover with a watch glass containing ice cold water. Heat the mixture to sublime aluminium chloride
- Add water to the remaining mixture and stir sodium chloride dissolves. Filter to obtain sodium chloride as filtrate. Heat the filtrate to saturation, cool to form crystals. Pour the mother liquor and dry between filter papers.
-
- Burn silver metal in air form Silver Oxide.
- In a beaker containing dilute nitric (V) acid add silver oxide little by little while stiring until in excess.
- Filter to remove unreacted silver oxide. Heat the filtrate to saturation. Cool to form crystals pour the mother liquor and dry the crystals between filter paper.
-
- Hydrogen Accept H Reject Hydrogen gas
-
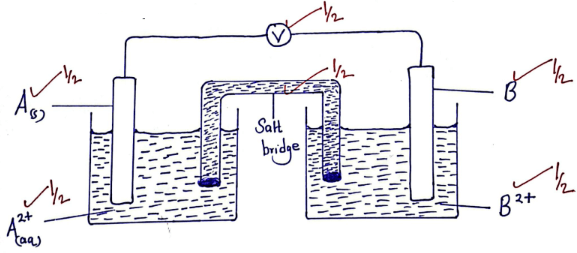
-
- White precipitate formed
- PbO(s) + CO(g) → Pb(s) + CO2(g)
-
- Sulphur, Phosphorus, Oxygen
- Graphite has giant atomic structure with strong covalent bonds thus high melting point than ordinary oil.
-
- At constant temperature and pressure the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density.
-
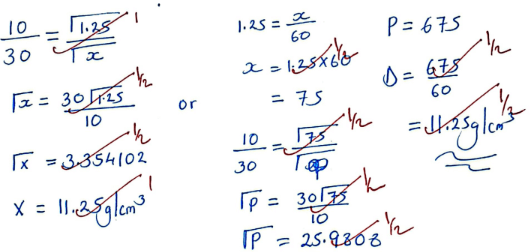
-
- 2Q(s) + H2O(l) → 2QOH(aq) + H2(g) OR 2Na(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
-
- Darts on water surface
- Forms a silvery ball
- Produces a hissing sound
-
- Minimum energy required/absorbed when an atom loses an electron from outermost energy level in gaseous state.
- Alkali metals
- Has largest atomic radius thus low nuclear force of attraction
-
Boiling tube Observation Explanation A No effervescence bubbles Hydrogen chloride gas does not ionize in methly benzene since HClg is polar while methylbenzene is non-polar B Effervescence/ Bubbles HClg is polar thus ionizes in water which is polar to form H+ which reacts with Mg to form H2(g) -
- Hydrated Iron (III) Oxide
- 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
-
- Hot compressed air
-
- Relatively low melting point
- Insoluble in water/ unreactive with water
- The sulphur deposit are found deep munderground and the soil layers are weak hence may collapse
-
- Q =It
= 2 × 2 × 60 × 60
=14,400C
Ag+(aq) + e− → Ag(s)
96,500C → 108g
14,400C → ?
108 × 14,400
96,500
= 16.1161g
98 + 16.1161
= 114.1161g -
- Prevent rusting
- Improve appearance
- Q =It
-
-
Gas jar Observation Explanation A Colour of flower petals is retained Dry chlorine gas has no effect on dry flower petals B Flowers petals are bleached white Chlorine dissolves in H2O to form HOCl which bleaches the flower petals by oxidation - HOCl(aq) + Dye → HCl(aq) + [Dye + O]
-
-
- Zinc blend
- Tetraamine zinc (II) ion
- ZnO(s) + CO(g) → Zn(s) + CO2(g)
-
- High concentration of reacting particles hence more fruitful collision thus high rate of reaction
- Reacting particles are depleted // reaction has gone to completion.
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mokasa II Joint Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students