INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- This paper consists two sections A and B.
- All working MUST be clearly shown.
- Non-programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC Mathematical tables may be used.
Take g = 10Nkg-1
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section in the spaces provided
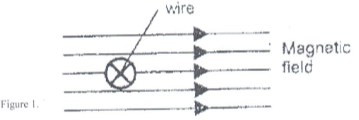
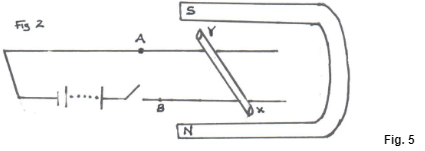
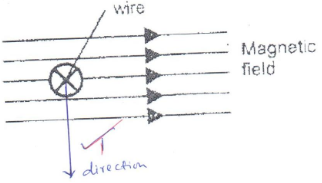
- The figure 1 shows a wire in a magnetic field. A current is switched on to flow through the wire in the direction shown. State the direction of motion of the wire. (1mk)
- In a textile industry, the machines experience electrostatics forces at certain points. Suggest one method of reducing these forces. (1mk)
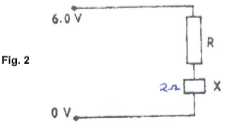
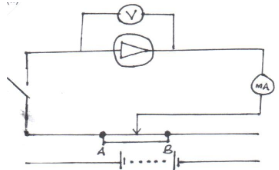
- When the device X is connected in the circuit below, the voltage across it is 0.14V.
Calculate the value of the resistance R. (2mks) - Four bars of metal W, X, Y and Z are tested for magnetism. X attracts both W and Y but not Z. Z does not attract W, X or Y. W and Y sometime attract one another and sometimes repel one another. What conclusion can you draw about? (2mks)
- Bar W
- Bar X
-
- An observer watching a fireworks displays sees the light from an explosion and hears the sound 4 seconds later. How far was the explosion from the observer? (Speed of sound in air 330m/s). (3mks)
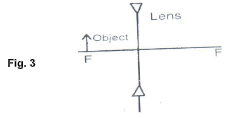
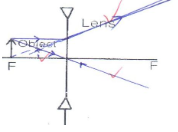
- A vertical object is placed at the focal point F of a diverging lens as shown in figure 3.
Sketch a ray diagram to show the image of the object. (2mks)
- If the focal length of the lens above is 10cm. Calculate its power. (2mks)
- At what part of the cathode ray tube would the time base be connected? (1mk)
- A heater of resistance R1 is rated P watts, V volts while another of resistance R2 is rated 2P WATTS, V/2 volts. Determine R1/R2. (2mks)
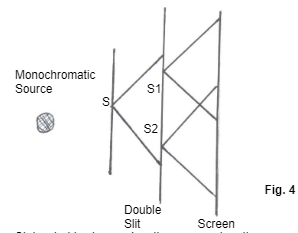
- The figure below shows an experimental arrangement. S1 and S2 are narrow slits.
State what is observed on the screen when the source is: (3mks)- Monochromatic
- White light
Use the diagram below to answer question 10.
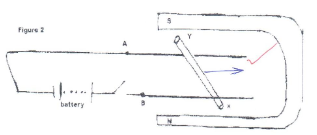
- An un-insulated copper wire XY lies over the fixed wire A and B connected to a battery. When the key in the circuit is closed, the rod XY moves. In which direction does the wire XY experience the force? (Indicate using an arrow) (1mk)
- When is the force on the wire XY greatest? (1mk)
- State and explain the effect of reducing the EHT in an X-ray tube on the X-rays produced. (1mk)
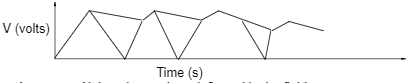
- The graph below shows the variation of capacitance of a capacitor with voltage supplied across it.
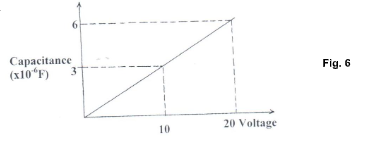
Use the graph to determine the quantity of charge stored in the capacitor. (3mks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section in the spaces provided
-
-
- State the meaning of the statement diode characteristic. (1mk)
- Sketch a circuit diagram that can be used to investigate p-n junction diode characteristics. (2mks)
- Define the term acceptor atom as applied in semiconductor. (1mk)
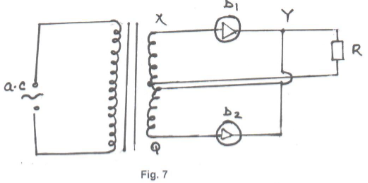
- Study figure 7 below and use it to answer questions that follow.
- Briefly explain how the circuit works to produce a rectified alternating current.(3mks)
- Draw on the diagram to show the position of the capacitor. (1mk)
- State the functions of the capacitor in the circuit. (1mk)
- Sketch the graph of the output as seen on a CRO screen. (1mk)
-
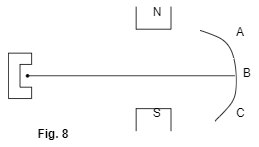
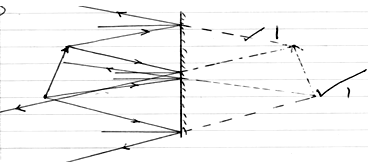
- Figure 8 below shows an experimental set up in a vacuum for investigating the effect of a magnetic field on the radiation emitted by a radio-active source.
The background radiation at the place is 5 counts per minute. The detectors are placed a positions A, B and C respectively. Results obtained are shown in the table below.
Positions A B C Counts/min 480 5 400 - Use the table to explain which of the three types of radiations are emitted from the source. (2mks)
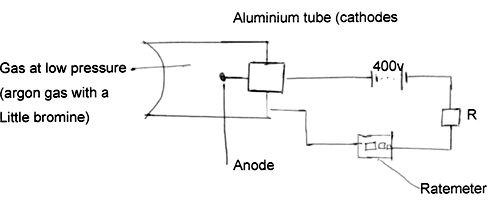
- Figure 9 below shows the features of a Geiger-Muller (G.M) Tube used for detecting radiation.
- State the use of Argon gas and Bromine. (1mk)
- Argon gas
- Bromine
- Explain how radiation from the source is detected by the tube. (4mks)
- State one use of radio activity in medicine. (1mk)
- State the use of Argon gas and Bromine. (1mk)
- The box contains names of seven parts of electromagnetic spedrium.
Radio waves Microwaves Infra-red Visible light Ultra violet X-rays Gamma rays - State the order in which they have been written. (1mk)
- The parts are all transverse waves. State one other property which they all have in common. (1mk)
- A photocell has a cathode made of caesium metal when a monochromatic radiation is shone on the cathode photoelectrons are emitted. A graph of kinetic energy against frequency is drawn as shown in figure 10.
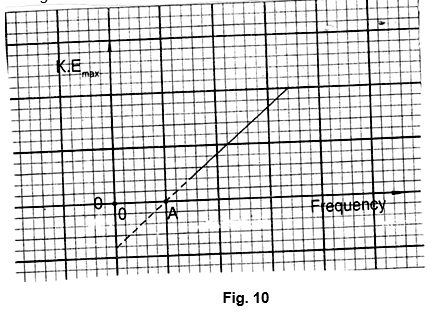
- Use the graph to answer the questions below.
- What is the unit of the slope? (1mk)
- What physical quantity is represented by point A? (1mk)
- Lithium metal has a higher work function than caesium. On the same axes, sketch the graph of lithium. (1mk)
- What does the term Monochromatic mean? (1mk)
- The maximum Kinetic energy of the electrons emitted from a metallic surface is 1.6 x 10-19J when the incident radiation is 7.5 x 1014Hz. Calculate the minimum frequency of radiation for which electrons will be emitted.
(A planck’s constant = 6.6 x 10-34Js) (3mks)
- Use the graph to answer the questions below.
-
- Refraction is the bending of light as it travels from one media to another. State the cause of the bending. (1mk)
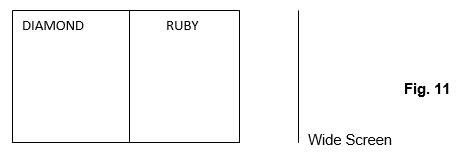
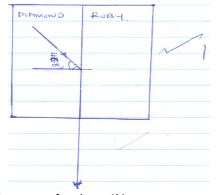
- The figure 11 below shows two adjacent solids of materials Diamond and Ruby.
The refractive index of Diamond is 2.4 and that of Ruby is 1.75.- Find the refractive index of Ruby with respect to diamond. (3mks)
- Draw an accurate ray from diamond such that no light is incident on the screen. (3mks)
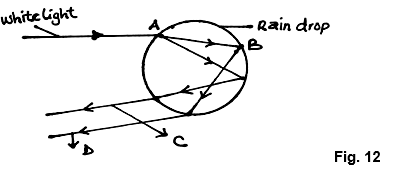
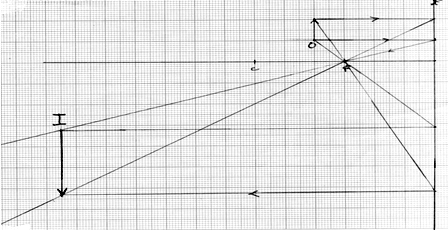
- The figure 12 below shows white light incident on a rain drop.
- State what happens at A and B. (1mk)
- State the colour of rays C and D. (2mks)
-
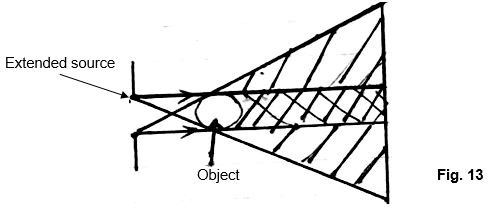
- The figure 13 shows shadow formation using an extended source of light.
State the effect on the umbra as the object is moved away from the screen when:- Diameter of the hole is the same as the diameter of the object. (1mk)
- The diameter of the object is smaller than the diameter of the hole. (1mk)
- The diameter of the object is greater than the diameter of the hole. (1mk)
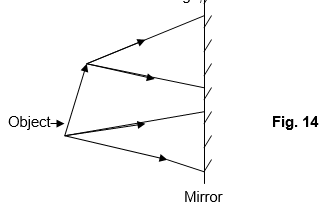
- The figure 14 shows an object infront of a plane mirror. Complete the diagram to show the location of the image,
- The graph below shows an object O placed in front of a concave mirror of focal length 30cm.
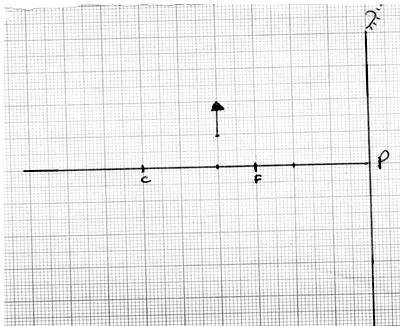
Construct ray diagrams to show the position of the object. (3mks) - Give one feature that makes Parabolic Mirrors suitable for use as car head lights.(1mk)
- The figure 13 shows shadow formation using an extended source of light.
-
- Appliances which draw current from a ring’s main circuit have a third cable connected to the earth. Give a reason why? (1mk)
- In a lighting circuit the wires used are relatively thinner than those of a cooker circuit. Give an explanation for this. (1mk)
- A transformer with 6000 turns in the primary circuit and 300 turns in the secondary circuit has its primary circuit connected to a 400V a.c. source. A heater connected to the secondary circuit produces heat at the rate of 600W. Assuming that the transformer is 100% efficient determine:-
- The voltage in the secondary circuit. (3mks)
- The current in the primary circuit. (2mks)
- The current in the secondary circuit. (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Earthing machines using spikes.✔1
- P.d across R = 6 – 0.14
I = 0.14 = 0.07Amps✔1
2
R = V = 6 – 0.14
I 0.07
= 83.71Ω✔1 -
- Permanent magnet. ✔1
- Magnetic material. ✔1
-
- Distance = speed x time
= 330 x 4
= 1320m -
- Distance = speed x time
- P = 1 ✔1 = 1 = -10 Diopters✔1
F -0.1 - X – Plates✔1
- R1 = V2
P
R2 = (V/2)2
2P
R1 = V2 + V2
R2 P 8P
= 8 -
- Fringes of light
- Central white fringe and fringes of different colours on either side of the central fringe.
- To the right✔1
- When the wire is positioned at right✔1 angles to the magnetic field.
- Soft x-rays✔1 are produced because lower EHT results in slowly moving electrons hence✔1 low energy electrons.
- Q = CV
The area under✔1 the graph gives the energy stored in the capacitor.
Area = 6 x 10-6 x 20✔1
= 1.2 x 10-4J✔1 -
- A graph of current against voltage,
- The atoms that introduce holes in the pure semiconductors.
-
-
- During the first half cycle D1 is forward biased while D2 is reverse biased.
- The path taken by current is D1, Y R Z.
- During the next half-cycle D2 is forward biased while D1 is reverse biased and the path of the current is Q D2 Y R Z.
- During both cycles, current flows through the resistor in the same direction.
-
- Smoothen the output signal.
-
-
-
- Position A - Alpha – heavy, less deflected in the field.
- B - Gamma – no deflection just a ray
- C - Beta – lighter, deflected more in the field.
-
-
- Argon gas – ionized by the radiation.
- Bromine – quenching agent.
-
- When a radioactive substance is placed in front of the window, the emitted radiations enter the tube through the window and ionize the argon gas.
- The negative ions move towards the anode while the positive ions move towards the cathode.
- As ions accelerate, they collide with more particles on their paths, resulting in further ionization (Avalanche of electrons).
- A pulse current flow. A corresponding pulse voltage is registered across the resistor R.
- These currents can be amplified and if passed through a loudspeaker, clicks are heard – or a rate meter.
-
- Used to monitor the function of thyroid gland.
- Used to trace blood clots.
- Used to kill harmful tissues such as cancerous cells.
-
-
- Increasing wavelength / reducing frequency.
- Travel at the speed of light c.
-
-
-
- Joules second (Js)
- Thresh-hold frequency
- See graph
- Radiation with simple wavelength.
- K.E = hf – hfo
= 1.6 x 10-19 = 6.6 x 10-34 x 7.5 x 1014 – 6.6x10-34fo
6.6 x 10-34 fo = 3.35 x 10-19
6.6 x 10-34 6.6 x 10-34
fo = 5.0758 x 1014Hz.
-
-
- Change in velocity. ✔1
-
- dηR = dηa . aηR✔1
1 x 1.75✔1
2.4
= 0.729167✔1
OR
dηR = ηR
η1
= 1.75 = 0.7292
2.4 - Rηd = Rηa . aηd
1 x 2.4
1.75
= 1.371
Rηd = 1
Sin c ✔1
Sin c = 1
Rηd
c = sin-1 1/Rηd
= sin-1 (1/1.371) or sin-1 (1.75/2.4)
= 46.8°✔1
- dηR = dηa . aηR✔1
-
-
- At A light undergoes refraction. ✔½
- At B light undergoes total internal refraction. ✔½
-
- C - Violet✔1
- D – Red ✔1
-
-
-
- The umbra✔ remains the same.
- The umbra becomes smaller. ✔
- The umbra becomes greater. ✔
-
-
- Produces parallel beam of light. ✔1
-
-
- To earth the device to avoid electrocution. ✔1
- Lighting circuit draws a smaller current than cooker circuit. ✔1
-
- VP = NP ✔1
VS NS
VS = VPNS
NP
= 400 x 300✔1
6000
= 20V✔1 - Power input = Power output
600W = IP x 400V
IP = 600
400
= 1.5A✔1 - P = ISPS
600 = IS x 20
IS = 600✔1
20
= 30A✔1
- VP = NP ✔1
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students