- This paper contains Two sections: A and B
- Answer ALL the question in section A.
- In section B answer question 6 and any other two questions from Section B
- Answers to be written in the answer booklet provided
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- State three ways in which minerals occur (3 mks)
- Name any two types of underground mining (2 mks)
-
- What is a forest (1 mk)
- State any two characteristics of the tropical hardwood forests. (2 mks)
- State two main species of softwood trees mainly grown in Canada. (2 mks)
-
- State one major characteristics of non-renewable energy sources. (1mk)
- Name any two non-renewable energy sources. (2mks)
- State any two effects of charcoal burning in the environment. (2mks)
-
- What is a trading bloc. (2mks)
- State any three factors influencing trade. (3mks)
-
- Name any two pre- historic sites that are popular with tourists in Kenya. (2mks)
- State the three agencies set up by the three governments of East Africa countries to manage the game parks and take care of the wildlife. (3mks)
SECTION B
Answer question (6) compulsory and any other two questions.
- The table below shows the population for the three district of Trans–Nzoia County.
Note: Population '000' peopleDISTRICT 2008 2009 2010 2011 TRANS-NZOIA WEST 150 175 180 200 TRANS-NZOIA EAST 25 30 25 28 KWANZA 10 20 30 32 -
- Using the above information, construct a compound bar graph. Use a scale of 1cm Represent 25,000 people use the graph paper provided. (9mks)
- Draw any two conclusions from the bar graph you have constructed (2mks)
- Explain three factors causing internal migration in Kenya. (6mks)
-
- Explain three factors leading to slow population growth in some parts of East Africa. (6mks)
- State any two importance of a high population in a country. (2mks)
-
-
-
- Name 2 major towns found in the oil palm growing areas in Nigeria. (2mks)
- Explain four physical features favouring oil palm growing in Nigeria. (8mks)
- Describe the steps involved in the processing of oil palm from the time is harvested. (8mks)
-
- State four problems facing oil palm farmers in Nigeria. (4mks)
- List three uses of oil palm. (3mks)
-
-
-
- What are pelagic fish (1mk
- Give two examples of pelagic fish (2mks)
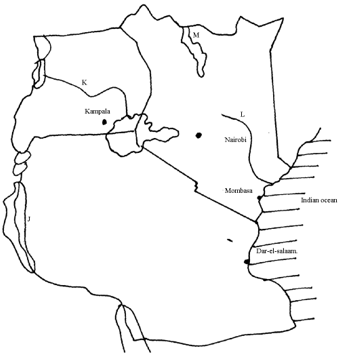
- The map below shows fishing grounds in East Africa. Use it to answer the questions that follows
- Name the fishing grounds marked J, K, L and M. (4mks)
- Explain the solutions to any four problems facing Inland fishing in East Africa. (8mks)
- Explain three factors why the Namibian Coast fishing ground is not well developed like other major fishing grounds in the world. (6mks)
- Compare fishing in Kenya and Japan under the following sub- headings.
- Market. (2mks)
- Nature of landscape. (2mks)
-
-
-
- Define land Rehabilitation (2mks)
- State four benefits of land Rehabilitation in Kenya (4mks)
-
- Explain four factors that led to the successful establishment of Pekerra irrigation scheme (8mks)
- State three problems facing Pekerra irrigation scheme (3mks)
- List four main crops grown in Pekerra irrigation scheme (4mks)
- State four advantages of irrigation farming to the economy of Kenya. (4mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between market gardening and floriculture. 2mks
- State four features of horticulture. 4mks
-
- State three physical factors that favour development of horticulture in Kenya. 3mks
- Explain why horticulture is more developed in Netherlands than in Kenya. 8mks
- State and explain four contributions of horticulture to the economy of Kenya. 8mks
-
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (25 MKS)
-
- Minerals occur in the following ways.
- Some occur in Beds, seams and layers.
- Some occur as weathered products.
- Some occur in veins and loads.
- Some occur as alluvial deposits.
- Some occur as evaporates. (any 3x1 =3mks)
- Types of underground mining.
- Deep shaft method.
- Solution method/ hydraulic.
- Adit / drift mining. (any 2)
- Minerals occur in the following ways.
-
- A forest is continuous and extensive land covered with a closed stand of tall trees, usually of commercial value. (1mk)
- Characteristics of tropical hardwood forests.
- The forest are evergreen.
- The trees are tall with straight smooth trunks and form extensive canopies.
- The trunks are large in size and bulky with protruding giant buttess roots which makes the trees difficult to cut and hull.
- They take a very long time to mature.(65-75yrs) (any 2x1=2mks)
- The main softwood tree species planted in Canada.
- Pine
- Spruce
- Forg (any 2x1=2mks)
-
- Non-renewable sources of energy are likely to be exhausted if not carefully used / extracted. ( 1mk)
- Non-renewableenergy sources.
- Fossils fuels.
- River water. (2mks)
-
- Loss of aesthetic valley / the environment looks ugly.
- Causes soil erosion because trees are cut down.
- Air pollution (increase in the amount of carbon content in air)
- Reduces visibility (smoke) (any 2x1=2mks)
-
- A trading bloc is where countries in the same geographical region join to form / team up to form a trade and economic organization. (2mks)
- Factors influencing trade.
- Availability of capital
- Availability of goods and services.
- There must be good security.
- Demand of goods.
- Availability of transport. (any 3 x1=3mks)
-
- Pre-historic sites popular with tourists in Kenya.
- Kariandusi near Gilgil.
- Olorgesailie near Magadi.
- The shores of Lake Turkana. (any 2x1= 2mks)
-
- Uganda Wildlife Authority. (UWA)
- Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS)
- Tanzania Wildlife Trust ( TWT) ( 3mks)
- Pre-historic sites popular with tourists in Kenya.
SECTION B
-
-
-
DISTRICT 2008 CT 2009 CT 2010 CT 2011 CT TRANS-NZOIA WEST 150 150 175 175 180 180 200 200 TRANS-NZOIA EAST 25 175 30 205 25 209 28 228 KWANZA 10 185 20 225 30 235 32 260
A COMPOUND BAR GRAPH SHOWING THE POPULATION
THE POPULATION OF 3 DISTRICT IN TRANS-NZOIA COUNTRY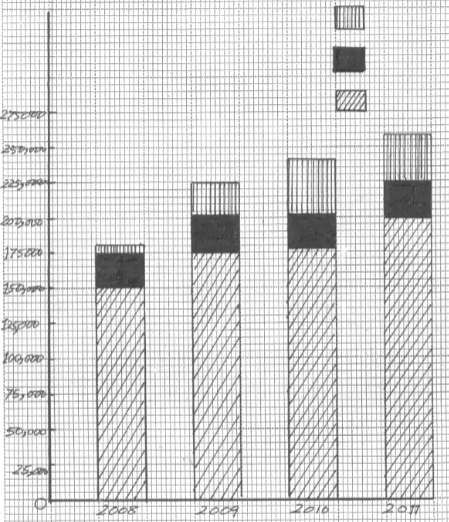
- Two conclusions from the bar graph.
- 2011 had the highest population in the country
- 2008 had the lowest population.
- The population was increasing year after year.
- Trans-Nzoia West had the highestpopulation throughout the period.
- Kwanza had the lowest population throughout the period. (any2x1=2mks)
-
- Three factors causing internal migration in Kenya.
- Pressure on land – Districts that are densely populated egKisii, Nyamira, Kakamega, Vihiga, Kiambu andNyeri do not offer enough farmland for the increasing population resulting to reduced food supplies hence some members of the population have opted to buy land elsewhere where they eventually settled.
- Better employment opportunities - School leavers usually move to urban areas in search of Jobs. People also move from one town to another to search for better paying jobs .Some people move from one farm to another to provide labour and some settle in these farms as squatters.
- Calamities – Occurrence of delisasterseg diseases, floods and drought have forced people to move to new places to get solace .Kerio plains and lower Tana and Nzoia rivers (Budalangi) suffer from periodic floods forcing people to move and only to come back when floods subside.
- Warfare – Tribal clashes in Kenya causes Temporary and sometimes permanent migration for instance during the 2007 general election disagreement , there was warfare in some parts of Rift valley where people were internally displaced.
- Government policies – whenever the government sets up a project people are displaced and settled else where like when the government started to mine Titanium in Kwale District ,people were settled elsewhere.
( any 3 factors 3mks ) (3 explained 3mks=6mks)
-
- Three factors leading to slow population growth in some parts of East Africa.
- Warfare – civil wars leads to many people being killed(woman and children) and other people move to safer places eg the civil war which occured in Uganda.
- Epidemics – when epidemics and diseases strike an area the rate of child death is high e g malaria. typhoid and measles kills children in some parts of East Africa leading to slow population growth.
- Famine – Large parts of Kenya regularly experience food shortages due to prolonged drought .Hunger kills children and very old people and the affected population is weakened and fertility rate lowered and do not contribute to population increase eg Turkana district.
- Family planning practices – many family in EA have adopted family planning and have one or two children and this has contribute to slow population growth.
- Late marriages – most people are going to school and study for many years until they complete college and begin working. This has greatly reduced the number of children such people gets.
- Emmigration – Youth move and settle to other places away from their home affecting population negatively.
- Social cultural factors – large families suffered from reduced number of children per woman because of high mortality rates among infants and children.Some customs in East Africa embrace abstention from intercourse, prolonged breat feeding and sending the wife away from the husband until the child was three and four years old leads to slow population growth.
(any 3x2=6mks)
-
- Readily available labour.
- Utilization of the available natural resources fully
- Offer readily available market for goods .
- Increase in the countriesGDP if the population is engaged in gainful employment. (any2x1=2mks)
- Three factors leading to slow population growth in some parts of East Africa.
-
-
-
- Major towns where oil palm is grown in Nigeria
- Ibadan
- Onitsha
- Calabar (any2x1=2mks)
-
- Temperature – The temperatures in Nigeria are high (over 21°c). Throughout the year and also the sunshine is plenty during ripening.
- Rainfall – The rainfall received in Nigeria is over 2000 mm and well distributed throughout the year.
- Humidity – The in high relative humidity in Nigeria is over 2000mm and well distributed throughout the year.
- Soils – The soils in Nigeria are well drained and porous and rich in humusfavoring the growth of oil palm.
- Windbreaks – There are many trees in Nigeria acting as windbreaks.
- Relief – The relief in Nigeria is undulating favouring growth of oil palm. (any 4x2=8mks)
- Major towns where oil palm is grown in Nigeria
- The branches of oil palm fruits are transported by lorries or light trains to the pioneer mills. At the mills the branches are put tube -like cages with holes all round. The cages run on rails and enter a sterilizer where the fruits are cooked by hot stream. Boiling and sterilizing ensures that the oil in the fruit does not chance to fully acids. After the fruits have been cooked they are removed from the cages and placed on a conveyor belt which moves to a stupper . In the stupper the fruits are shaken off the stalks. They are then put in digesters and cooked depulping is done in which the pericarp pulp is separated from the nut. The pulp is pressed to remove oil. The oil is left to settle in tanks for some time so that the impurities settle at the bottom of the tank. The nuts are put in grinders which cracks them to remove the kernels. The kernels may be pressed to produce kernel oil or they may be parked whole and exported for the importing countries. ( 8mks)
-
-
- Plants attacked by pests and diseases eg anthracnose , freckle, blast
- Shortage of capital.
- Shortage of food due to overdependence on oil palm.
- Lack of skills and knowledge in production of oil palm.
- Neglegence by the government
- Competition from other producing countries. (any4x1=4mks)
- Uses of palm oil.
- Cooking
- Manufactureof soap
- Manufacture of margarine
- Domestic cooking
- Lighting
- Manufacture of cosmetics
- Thatching houses / making baskets, mats and brooms. (any 3x1=3mks)
-
-
-
-
- Pelagic fish are fish communities that mainly live near the surface or at shallows depths of lakes and seas. (2mks)
- Two examples of pelagic fish.
- Herring
- Mackerel
- Sandines
- Tuna (any 2x1=2mks)
-
-
- J- Lake Malawi
- K- R. Nile
- L- R.Tana
- M – L. Turkana (4mks)
- Solution to problems facing inland fishing in East Africa.
- Inadequate capital – The government and local financial insituations should make funds available for fisher men to assist them purchase fishing equipment , refrigeration facilities and transport vans.
- Presence of dangerous animals - The KWS,UWN & TNT to capture the menacing animals and take them to the parks.
- Overfishing – Ban the use of nets with small meshes; license fishermen and start fish farms to reduce reliance of natural fishing grounds.
- Pollution of water bodies – Government to set up tough measures against pollution industries and towns to treat their effluents before releasing them in rivers and lakes.
- Inadequate transport – To develop roads leading to fresh water lakes to help them open up the market.
- Introduction of new species – T o discourage the introduction of Nile perch in other fresh water lakes.
- Presence of weeds – Local communities and the government to remove the weeds from the lakes.
- Limited market - more people to be encouraged to eat fish.
- Accidents – Fishermen to use bigger motorboats which can withstand storm.
- Lack of fish co-orperatives – Fishermen to form cooperative societies to find market.
- Lack of electricity – The government to supply power to fishing areas. Any 4well explained x2=8marks
-
- Namibian coast fishing grounds is not well developed because .
- Poor technology hence lack items like fishing vessels and other machinery.
- Shortage of capital for paying workers and buying machinery.
- Insecurity – civil war in Nambia and Angola resulting in abandonment of fishing.
- Narrow continental shelf that does not favour flourishing of planktons.
(any 3 well explained x2 =6mks)
- Comparison between Fishing in Kenya and Japan.
- Market
High population with fish eating culture offers a ready market for fishing in Japan while in Kenya most fishing grounds are found in remote areas with low Population which do not offer ready market. (2mks) - Nature of the landscape
Japan is made up of numerousislands which do not favor agriculture hence fishing is the alternative economic activity while Kenya the landscape is gently sloping and generally flat topography supporting agriculture and people neglect fishing. (2mks)
- Market
-
-
-
- Land Rehabilitation is the process of recovery of land which has been misused and destroyed through human activities such as quarrying, overgrazing, deforestation, Charcoal burning and over cultivation. (2mks)
- Four benefits of land Rehabilitation in Kenya.
- Increase in the amount of food production.
- Modification of climate.
- Reduces the rate of mosquito breeding that spread malaria because open ditches are filled.
- It controls soil erosion because trees are planted.
- Increase in the amount of land for settlement. (any 4x1=4mks)
-
- Factors which led to the successful establishment of Perkerre irrigation scheme.
- To control the seasonal floods of river Perkerra which used to devastate the area.
- To utilize the excess water of river Perkerra which used to go to waste?
- Presence of flat and gentle sloping terrain which enables easy flow of water by gravity.
- The fertile loamy soil deposited by floods reduces the use of fertilizers.
- The dry conditions of the area necessitated use of irrigation as the only way to make food production possible.(any 4 well explained x2 =8mks)
-
- Acute shortage of water.
- Siltation of canals.
- Inadequate supply of labour.
- Inadequate capital
- Limited market.
- Human diseases eg malaria and bilhazia
- Poor payment of farm produce. (any 3x1=3mks)
- Crops grown in Perkerra irrigationscheme include water melons, onions, cotton chillies and pawpaws. (any 4x1=4mks)
- Factors which led to the successful establishment of Perkerre irrigation scheme.
- Advantages of irrigation farming to the economy of Kenya.
- Offers employment to people improving their living.
- Surplus is sold to earn the country foreign exchange.
- Increase in food production for the country to sustain itself.
- Utilization of the unproductive land.
- Utilization of products from other industries / offers market for goods from industries. (any 4x1=4mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between market gardening and floriculture.
- Market gardening is the intensive cultivation of vegetables and fruits for sale in the nearest urban centre while floriculture is the cultivation of flowers for sale. 1x2 = 2mks
- State four features of horticulture.
- Small farms
- Located near communication lines
- Land is intensively farmed.
- Continuous application of manure and fertilizers.
- Located near urban centers.
- Are scientifically managed. 4 x 1 = 4mks
- Differentiate between market gardening and floriculture.
-
- State three physical factors that favour development of horticulture in Kenya.
- Abundant supply of water from lakes and rivers.
- Gentle slopes to facilitate construction of green houses.
- Warm temperatures that favour growing of horticulture products.
- Well drained soils.
- Volcanic soils / deep soils. 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Explain why horticulture is more developed in Netherlands than in Kenya.
4 x 2 = 8 mksNetherlands Kenya 1 Has higher demand for horticultural products Has low demand of horticulture products 2 Farmers have access to capital needed for horticulture farming Farmers have low capital needed for horticultural farming 3 Very high technology Poor technology 4 Well developed transport network Under developed transport network 5 Has highly skilled labour Inadequate skilled labor in production 6 There is more research into suitable methods for horticultural farming In adequate research 7 Has well organized marketing systems/ cooperatives which are favourable for horticultural farming Is under development marketing systems
- State three physical factors that favour development of horticulture in Kenya.
- States and explain four contributions of horticulture to the economy of Kenya.
- Earns foreign exchange from export.
- Creation of employment.
- Raw materials for industries e.g processing of fruits.
- Enhances development of roads/transport.
- Source of food to the population.
- Provision of social amenities in the growing areas.
- Source of income to the farmers when sold.
- Encourages land reclamation. 4 x 2 = 8mks
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students