INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections A and B
- Answer all questions in section A
- In section B, answer question 6 and any other two questions.
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- Give three characteristics of comets (3 marks)
- Give two effects of rotation of the earth on its own axis (2 marks)
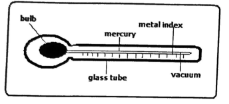
- The diagram below shows a weather measuring instrument.
- Identify the instrument (1 mark)
- Describe how the instrument works (4 marks)
-
- State three natural causes of earthquakes (3 marks)
- Give two effects of earthquakes in built up areas (2 marks)
-
- Name three types of sand dunes (3 marks)
- Give two reasons why wind is the dorminant agent of erosion in deserts (2 marks)
-
- Name two surface features in a karst landscape (2 marks)
- Give three reasons why there are few settlements in a karst landscape (3 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section.
- Study the map of Kisumu East 1:50,000 (Sheet 116/2) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What is the title of the map (1 mark)
- Convert the scale of the map to a statement scale (2 marks)
- What is the magnetic variation of the map extract (1 marks)
-
- Identify two vegetation in the area covered by the map (2 marks)
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map (2 marks)
- Name two relief features in grid square 0686 (2 marks)
- Describe the settlement of the area covered by the map (5 marks)
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represents 20m, draw a cross section along Northing 98 from Easting 96 to Easting 02. (1 mark)
On the cross-section, mark and label:- River Nyang'ori (1 mark)
- Dry weather road (1 mark)
- Steep slope (1 mark)
- Calculate the Vertical Exaggeration of the cross section (2 marks)
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represents 20m, draw a cross section along Northing 98 from Easting 96 to Easting 02. (1 mark)
-
-
-
- What is folding (2 marks)
- State two factors that influence the folding process (2 marks)
- Describe the formation of an overthrust fold (6 marks)
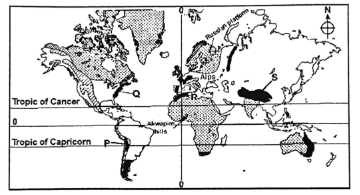
- The map below shows the location of some fold mountains.
- Name the mountain ranges marked P, Q, R and S (4 marks)
- Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding (3 marks)
- Explain four significance of fold mountains to human activities (8 marks)
-
-
- Define river capture (2marks)
- Name two features resulting from river rejuvenation (2marks)
- Explain three ways through which a river erodes (6marks)
- Explain three negative effects of rivers to the human environment (6 marks)
- Students from your class conducted a field study on a river in its old stage.
- State three reasons why they would require a route map
- Identify four characteristics of the river they would have observed
- State three follow up activities they would have been involved in
-
-
- What is natural vegetation? (2 marks)
- Identify the temperate grasslands found in the following countries.
- Russia (1 mark)
- Argentina (1 mark)
- Australia (1 mark)
-
- Describe the characteristics of the tropical rainforest (8 marks)
- Explain three ways in which the desert vegetation adopts to the environmental conditions of the region
(6 marks)
- Explain three causes of the decline of the areas under forests in Kenya (6 marks)
-
-
-
- What is an ocean
- Name two ocean currents along the western coast of Africa
- Explain three reasons why the ocean water temperature varies
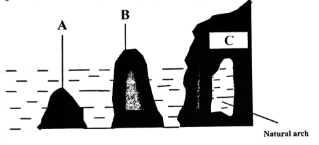
- The diagram below shows some coastal features resulting from wave erosion.
Name the features marked A, B, C and D (4 marks) - Describe how an offshore bar is formed (5 marks)
-
- Name three types of coral reefs (3 marks)
- Give three conditions necessary for coral growth
-
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- Give three characteristics of comets
(3 marks)
(Any 3x1-3mks)
- Made up of frozen gases and dust/small rocky particles
- They have a head and a tail
- They cross orbits followed by planets
- They move along oval-shaped orbits
- They orbit around the sun
- Give two effects of rotation of the earth on its own axis
(2 marks)
- Causes day and night
- Causes deflection of winds and ocean currents
It causes rising and falling of ocean tides - Causes time difference between longitudes/ causes a difference of one hour between meridians 15° apart
- Give three characteristics of comets
- The diagram below shows a weather measuring instrument.
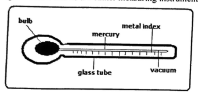
- Identify the instrument
- Maximum thermometer
(1 mark)
- Maximum thermometer
- Describe how the instrument works
(4 marks)
(Any 4x1= 4mk)
- When temperature rises, the mercury expands
- The mercury pushes the metal index forward
- When temperature falls, the mercury contracts leaving the metal index behind
- The maximum temperature reached is read at the end of the index that was in contact with the mercury last
- Identify the instrument
-
- State three natural causes of earthquakes
(3 marks)
- Collision of tectonic plates
- Energy release in the mantle
- Violent volcanic eruptions
- Gravitative pressure
- Give two effects of earthquakes in built up areas
(2 marks)
(Any 2x1=2mks)
- Loss of life (human, animal and plant)
- Disruption of transport and communication lines
- Outbreak of fires
- Avalanches and landslides may occur covering build up areas
- Tsunamis may drown coastal settlements
- State three natural causes of earthquakes
-
- Name three types of sand dunes
(3 marks)
(Any 3x1=3mks)
- Barchans
- Seif dunes
- Transverse dunes
- Give two reasons why wind is the dorminant agent of erosion in deserts
(2 marks)
- Presence of loose and unconsolidated dry particles in the desert
- Scanty vegetation that leaves the surface exposed to wind erosion
- Strong tropical storms present in deserts
- Name three types of sand dunes
-
- Name two surface features in a karst landscape
(2 marks)
(Any 2x1=2mks)
- Grikes and clints
- Swallow holes/ sink holes
- Dolines
- Uvala
- Polje
- Limestone gorges
- Give three reasons why there are few settlements in a karst landscape
(3 marks)
(Any 3x1=3mks)
- Rugged landscape hindering settlement/ construction of houses
- Scarcity of water since streams disappear underground/ few surface streams
- Presence of thin soils that discourage farming
- Rocky landscape that discourage settlement
- Name two surface features in a karst landscape
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section.
-
- Study the map of Kisumu East 1:50,000 (Sheet 116/2) provided and answer the following questions.
- What is the title of the map
(1 mark)
EAST AFRICA 1:50,000 (KENYA) - Convert the scale of the map to a statement scale
1 cm rep 50,000 cm
50,000 = 0.5Km
100,000
1 cm rep 0.5 km or 1 cm rep km
(2 marks) - What is the magnetic variation of the map extract
(1 mark)
20321
- What is the title of the map
-
- Identify two vegetation in the area covered by the map
(2 marks)
- Scattered trees
- Papyrus
- Scrub
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map
(2 marks)
34°451 - 35°00'E - Name two relief features in grid square 0686
(2 marks)
- Ditch
- River valley
- Plain (Kano plain)
- Identify two vegetation in the area covered by the map
- Describe the settlement of the area covered by the map
(5 marks)- The south western part has few settlements
- There is dense settlement on the western part of the area covered by the map
- The area has many nucleated settlements
- Nyando escarpment has few settlements
- There is linear settlement along all weather road loose surface
- There are few settlements in the plantation
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represents 20m, draw a cross section along Northing 98 from Easting 96 to Easting 02
(5 marks)
On the cross-section, mark and label:
- River Nyang'ori
(1 mark) - Dry weather road
(1 mark) - Steep slope
(1 mark)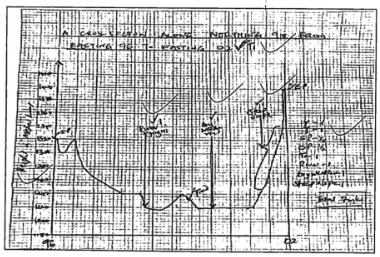
- River Nyang'ori
- Calculate the Vertical Exaggeration of the cross section
V.E = Vertical scale
Horizontal scale
= 1 ÷ = 1
2,000 50,000
= 1 X 500,000
2,000 1
= x 25
(2 marks)
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represents 20m, draw a cross section along Northing 98 from Easting 96 to Easting 02
- Study the map of Kisumu East 1:50,000 (Sheet 116/2) provided and answer the following questions.
-
-
- What is folding
A process of crustal distortion which causes the rocks to bend upwards or downwards. (2 marks) - State two factors that influence the folding process (2 marks)
- Rock type/ flexibility or elasticity of a rock
- Strength or intensity of the compressional force
- Temperature mwithin rocks/high temperatures
- Describe the formation of an overthrust fold (6 marks)
- Layers of crustal rocks are subjected to intense compressional forces
- Intense folding results in formation of an overfold
- Continued compression due to increased pressure causes the overfold to fold further into a recumbent fold
- When pressure is very great, a fracture occurs in the recumbent fold along which a thrust plane develops
- The upper part of the recumbent fold slides forward along the thrust plane over the lower part
- This results in the formation of an overthrust fold
- What is folding
- The map below show the location of some fold mountains.
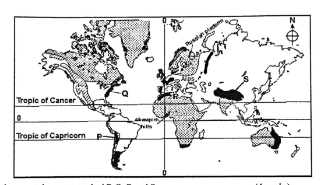
- Name the mountain ranges marked P, Q, R and S
(4 marks)
P - Andes
Q - Appalachian
R - Atlas
S - Himalayas - Apart from fold mountains, name three other features resulting from folding
(3 marks)
- Rolling plains
- Ridges and valleys
- Intermontane basin
- Intermontane plateau
- Name the mountain ranges marked P, Q, R and S
- Explain four significance of fold mountains to human activities
(8 marks)- Fold mountains are sources of rivers that provide water for the generation of H.E.P/domestic use/irrigation/industrial use.
- Fold mountains are often forested and provide timber which is used in the building & construction
industry/medicine/aesketic/wildlife habitat. - Some fold mountains have exposed valuable mineral deposits which are mined thus boasting mining industry
- The windward side of fold mountains receive high rainfall which encourages agriculture
- Leeward sides of fold mountains receive low rainfall hindering agriculture/ promote pastoralism
- Fold mountains act as barriers to construction of transport and communication lines
- Fold Mountains are a tourist attraction which brings foreign exchange.
- Fold Mountains act as protective barriers during war.
-
- State two factors that influence the folding process
- The nature of rocks
- Strength of compressional forces
- Describe the formation of an overthrust fold
- State two factors that influence the folding process
-
-
- Define river capture
(2 marks)
- River capture is the diversion of the head waters of one river into the system of an adjacent but more powerful river
- Name two features resulting from river rejuvenation
(2 marks)
- Knick points
- River terraces
- Incised meanders / Intrenched / abandoned incised meander
- Rejuvenation gorges
- Explain the three ways through which a river erodes
(6 marks)
- Attrition - As rock materials are transported downstream, they constantly collide against each other. The materials gradually wear down and reduce in size
- Abrasion/corrasion - As solid rock materials are transported downstream, they are hurled against the banks and dragged along the river bed chipping off/ scouring pieces of rock from the banks and river bed
- Solution/corrosion - Soluble rocks within the channel are dissolved
- Hydraulic action - the power of waves remove loose rock particles from the river bank. The water also enters cracks/ crevices leading to compressed air action which breaks up the rocks.
- Explain three negative effects of rivers to the human environment
(6 marks)
- When rivers flood, they destroy a lot of property
- Rivers may flood leading to loss of human lives
- Wide, deep rivers are barriers to transport especially where bridges have not been constructed
- Rivers can be a medium of spreading waterborne diseases when the water get contaminated
- Some rivers are habitats to dangerous animals which may attack human beings and destroy crops
- Students from your class conducted a field study on an old stage of a river.
- State three reasons why they would require a route map
(3marks)
- To help identify the direction to follow
- To help prepare a working schedule
- To help identify location of features for study
- To help estimate distances to be covered
- To help estimate the time the field study is likely to take.
- Identify three characteristics of the river they would have observed
(3 marks)
- Low speed
- Brown water
- River brands
- Meanders
- Distributaries
- Differed tributarie
- State three follow up activities they would have involved in after the field study (3marks)
- Reading more on the topic
- Displaying photographs / items collected
- Asking /answering question
- Writing reports
- Discussing with the rest of the class
- Analyzing/assessing the information collected against the hypothesis.
- State three reasons why they would require a route map
- Define river capture
-
-
- What is natural vegetation?
(2mks)
- It is the plant cover that grows wildly on the earth's surface without interference from man and animal.
- Identify the temperate grasslands found in the following countries
- Russia - Steppes (1mk)
- Argentina - pampas (1mk)
- Australia - Downs. (1mk)
- What is natural vegetation?
-
- Describe the characteristics of the tropical rainforest
(8mks)- Consist of mixed variety of trees species
- Trees shed their leaves at different times of the year because of the varied tree species/ they are evergreen
- Forest has little or no undergrowth since canopies block much light from reaching the ground
- Forest has numerous lianas/ epiphytes which compete for light
- Some trees have buttress roots for strong anchorage
- Trees form three distinct canopies
- Trees have broad leaves to provide large surface area for transpiration
- Trees are tall, straight, smooth trunks due to competition for sunlight
- There is little or no undergrowth because little light reaches the ground
- Most trees have shallow and extensive roots which tap nutrients lying near the surface
- Contain wide variety of species which are closed together in mixed stands
- Most trees are hardwood and take long to mature.
- Leaves have drip tips to allow rain water to drip down easily
- Explain three ways in which the desert vegetation adopts to the environmental conditions of the region.
(6mks)
- Some plants have thick/fleshy/succulent leaves to enable them store water.
- Some have long roots to tap the ground water
- Some plants have no leaves/ have thin /spiky/ waxy/needy-like leaves to reduce transpiration
- Some plants have shiny surfaces to reflect light.
- Some plants have short lives/seeds that take short time to mature to be able to survive short rains
- Leaves have stomata on the lower surface to reduce the rate of transpiration
- Some have reversed stomatal rhythm to reduce the rate of transpiration
- Describe the characteristics of the tropical rainforest
- Explain three causes of the decline of the areas under forests in Kenya.
(6mks)
- Areas of forests are destroyed by accidental and sometimes intended fires.
- Diseases caused by pest and parasites attack mainly the planted forests causing many trees to dry up.
- Human activities /settlements/logging have destroyed many forest areas.
- Over-exploitation leads to depletion of certain tree species.
- Government policy of degazetting of some forests made people free to clear many forested areas.
- Prolonged drought leads to degeneration of forests some of which take long to recover
-
-
-
- What is an ocean
(2 marks)
A vast body of salty water on the earth's surface that surrounds a continent - Name two ocean currents along the western coast of Africa
(3 marks)
- Benguela
- Guinea
- Canary
- What is an ocean
- Explain three reasons why the ocean water temperature varies
(6 marks)
- The location of oceans - Oceans located in the tropics have high temperature while those located in high latitude areas have low temperature
- Ocean currents - Cold ocean currents cause low temperatures in the oceans when they flow while warm ocean currents cause warm temperatures
- Ocean depth - Temperature of surface water in oceans located in the tropics is high while the temperature of water at the bottom is low
- The diagram below shows some coastal features resulting from wave erosion. Name the features marked A, B and C
(3 marks)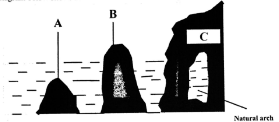
A - Stump
B - Stack
C - Headland - Describe how an offshore bar is formed
(5 marks)
- On a gently sloping shore, the waves start breaking offshore at low tide
- At high tide, waves deposit materials on land where they form a beach
- A large amount of pebbles and sand is deposited at this point
- As the tide drops, waves keep on breaking offshore and deposition continues
- The ridge of deposits grow higher
- The ridge runs almost parallel to the shoreline
- Continued deposition builds a ridge which eventually is exposed at low tide. - This forms an offshore bar
-
- Name three types of coral reefs
(3 marks)
- Fringing reef
- Barrier reef
- Atoll
- Give three conditions necessary for coral growth
(3 marks)
- Warm water/ temperature between 25°-29°
- The water should be clear
- The water should be saline
- Shallow water/ 10-60m
- Plentiful supply of plankton on which polyps feed
- Polyps must be submerged
- The water should be well oxygenated
- Name three types of coral reefs
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Catholic Diocese of Kakamega Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students