INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections A and B
- Answer ALL the questions in section A. in section B answer question 6 and any other TWO questions.
- All question must be answered in English.
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- What is multilateral trade (2mks)
- Give three advantages of multilateral trade. (3mks)
-
- Identify three types of subsistance farming (3mks)
- State three physical conditions favoring coffee farming in Kenya. (3mks)
-
- Other than wind, give two climatic hazard experienced in Kenya. (2mks)
- State two effects of wind as a hazard (2mks)
-
- Outline two factors considered while drawing sketch maps from photographs (2mks)
- Name two types of hypothesis (2mks)
-
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries (2mks)
-
- Name two countries in Southern Africa that are important for Maine fish production (2mks)
- List two types of traditional fishing methods (2mks)
SECTION B.
Answer question 6 and any other two from this section.
- The table below shows the number of tourists who visited National parks and Game reserve in Kenya in 2007-2008 in 000's. Use it to answer the question that follow.
National park / Game reserve Number of tourists 2007 2008 Maasai Mara 30 25 Amboseli 20 18 Tsavo 40 30 Nairobi 10 8 Sibilni 6 38 Hell's Gase 4 3 -
- Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to represent the number of tourists who visited Kenya in 2007. (6mks)
- Which Game reserve /National park had the higher decline in the number of tourists who visited Kenya for two years (2mks)
- Calculate the total number of tourists who visited Kenya for two years.
- Give three ways Kenyan government has used to improve tourism. (2mks)
-
- Explain three reasons why Switzerland receives more tourists than Kenya (6 mks)
- Differentiate tourist attractions in Kenya and those in Switzerland (6mks)
-
- The map below shows the location of some minerals in East Africa.
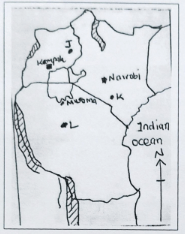
- Name the minerals mined in the areas J,K and L (3mks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals
- Mode of occurrence of minerals (4mks)
- Transport (4mks)
- Level of technology (4mks)
- Describe open cast method of mining (4mks)
- Explain three benefits of petroleum mining to the economies of middle East countries (6mks)
-
- What is forestry? (2mks)
- Differentiate forestry in Kenya and Canada under the following subheadings.
- Distribution (2mks)
- Types of forests (2mks)
- Transportation (2mks)
- Period of harvesting (2mks)
- State four measures used to conserve forests (4mks)
-
- Explain four factors that fovour the growth of natural forests on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (8mks)
- Name three indigenous hardwood tree species found in Kenyan forests (3mks)
-
- What is the meaning of the following terms as used in population.
- Population distribution (2mks)
- Population density (2mks)
-
- Give two primary sources of population data. (2mks)
- What information can be derived from a population pyramid (4mks)
-
- Describe three ways in which population in Kenya differs from that of Sweden. (6mks)
- List five consequences of a high population density in central highlands of Kenya (5mks)
- State four significance of population structure.
- What is the meaning of the following terms as used in population.
-
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation (2mks)
- What is a polder (2mks)
- List two methods used in land reclamation in Kenya (2mks)
- Explain three physical factors that influenced the location of Mwea irrigation scheme (6mks)
-
- Describe the stages involved in land reclamation in the Netherlands. (7mks)
- Compare land reclamation in Kenya and the Netherlands under the following sub-headings.
- Scale of operation (2mks)
- Agricultural output (2mks)
- Name two main projects of land reclamation in the Netherlands. (2mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- What is multilateral trade (2mks)
- Multilateral trade is an international trade that involves exchange of goods among countries (Any 1x2= 2mks)
- Advantages of multilateral trade
- Creates employment opportunities
- Enhances co-operation/ exchange of ideas/ skills.
- Country gets wider market for her goods
- A country earn foreign exchange through export
- It promotes specialization in production.
- Earns income through tariffs and duties
- Lead to improvement of roads/transport network
- Stimulates industrial growth
- Creation of wealth/capital
- Promotes quality due to competition for market (3x1=3mks)
- What is multilateral trade (2mks)
-
- 3 types of subsistence farming
- Shifting cultivation
- Sedentary subsistence agriculture
- Intensive subsistence agriculture (3x1=3mks)
- State 3 physical condition influencing coffee farming in Kenya.
- Moderate to high rainfall/(1000-2000)mm
- Moderate to high temperature (14°- 26°C)
- Gentle sloping land
- Deep well drained volcanic soils
- High altitude (610-2100)m A.S.L
- 3 types of subsistence farming
-
- Other than wind, give two climatic hazards in Kenya
- Floods
- Hail stones
- Drought
- Lightening (Any 1x2= 2mks)
- Floods
- State 2 effects of wind hazards
- Destruction of houses
- Breaking of crops /pods
- Interference with visibility
- Spreading bush fires
- Sand accumulation hinder transportation. (Any 1x2= 2mks)
- Other than wind, give two climatic hazards in Kenya
-
- Two factors considered while drawing sketch diagrams from photographs
- Orientation
- Position/location of features
- Details/features on photograph (2x1=2mks)
- State two hypothesis
- Question hypothesis
- Alternative / substancentive /positively stated
- Null hypothesis/ Negatively stated (2x1 = 2mks)
- Two factors considered while drawing sketch diagrams from photographs
-
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries
- Fishing is extraction of aquatic animals and fish from sea, ocean while fisheries are water bodies where fishing is done.
(Any 1x2=2mks)
- Fishing is extraction of aquatic animals and fish from sea, ocean while fisheries are water bodies where fishing is done.
- Two countries in southern Africa that are important for moving fish production.
- South Africa
- Angola
- Namibia
(Any 1x2= 2mks)
- List two traditional fishing methods
- Use of baskets
- Gill nets
- Use of herbs
- Harpooning/spear and arrow
- Lampara method/lamp and stick
(Any 2x1=2mks)
- Differentiate between fishing and fisheries
SECTION B
-
-
- TITLE: ADIVIDED RECTANGLUAR SHOWING THE NUMBER OF TOURISTS IN KENYA 2007.
- Which named reserve /National park had the highest decline in the number of tourist in 2008.
(1mk)
Tsavo with 10,000 tourists - Calculate total
2007 : 30,000, +20,000 + 40,000, 10,000 + 6000 + 4000 = 110,000
2008 : 25000+ 18000+30,000+8000 + 3800 + 3000 = 87,800
110,000 + 87,800 = 197,800 Tourists
(2x1=2mks)
- TITLE: ADIVIDED RECTANGLUAR SHOWING THE NUMBER OF TOURISTS IN KENYA 2007.
- 3 ways Kenyan government has used to improve tourism.
- Improved road network to tourist sites
- Improved security
- Enhanced advertisement both locally and internationally
- Encouraging investors in tourism industry
- Increased direct flights from USA and Europe to Kenya
- Curbing population of tourist sites.
-
- Explain three ways why Switzer land receives more tourist than Kenya (3x1=3mks)
- Its central location in Europe makes it easily accessible to tourist of European original while Kenyans far from Europe
- Some tourist attractions in two countries are similar hence tourist prefer visiting those that are near home in Switzerland
- Peaceful atmosphere in Switzerland encourages tourists to visit as opposed to Kenya where reports of insecurity scare tourists.
- Switzerland mounts effective marketing while Kenya has less effective.
- The well developed transport network in Switzerland, electric train provides easy access to tourist sites while in Kenya many roads are poorly maintained.
- In Switzerland tourists are charged fairly for the services while in Kenya the charges are relatively high.
- Diversity of languages spoken in Switzerland makes it possible for tourists to communicate while in Kenya few international languages are spoken.
- Advanced training of personnel in Switzerland that provides higher quality services than Kenya which is less advanced.
- NB: The two countries must be mentioned in every point to score double tick. (3x2=6mks) d
- Differentiate tourist attraction between Kenya and Switzerlands.
(3x2 = 6mks)NO. IN KENYA SWITZERLANDS 1 There is great rift valley Acaciated valleys 2 Animals in their natural habitats Animals in the Zoos 3 Coastal beaches dominates Lake beaches dominate 4 Warm climate throughout the year Winter and Summer climate alternating 5 Ice capped mountain exists Glaciated highlands exists.
- Explain three ways why Switzer land receives more tourist than Kenya (3x1=3mks)
-
-
- Name minerals mined at
(3x1 = 3)
J- Limestone
K- Soda ash/Tròna/Sodium carbonate/Salt
L- Diamond - How the following influence exploitation of minerals.
Minerals
Mode of occurrence- Minerals that occur in small quantities limit exploitation since they are of low commercial value unless the mineral is of high value.
- Large deposit is profitable to sustain mining process over along period.
- Minerals that occur near the surface are easier and cheap in extract; deep seated minerals are expensive
- Minerals close to the surface / bed/layers seams extracted using open cast method, deep minerals by underground/ shaft.
(2x2=4mks)
- Transport Efficient transport link allow easy movement /accessibility to mine site marked without delay
- Bulky minerals require cheap transport railway to reduce cost of production
- Mineral deposits in remote areas are less likely to be exploited.
(2x2=4mks)
- Level of technology.
Advanced technology improve mining operation leading to high quality and quantity.
High level of technology allows effective explorations.- Advanced technology boosts production reduce wastage.
- High level of technology reduce destruction of environment (safety of workers)
- Low level of technology limit exploitation
(2x2=4mks)
- Minerals that occur in small quantities limit exploitation since they are of low commercial value unless the mineral is of high value.
- Describe opencast mining
Unwanted materials on top of the mineral are removed by digging/quarrying
Rock minerals broken by blasting
Power shovels are used to dig up mineral deposits
The mineral is loaded into trucks to the processing plants.
(5 max 4) - Explain 3 benefits of petroleum mining East middle)
- Earn foreign exchange used to develop other sectors of the economy.
- Petroleum is used as raw materials leading to growth of related industries
- The revenue / royalties have enabled the middle east countries investments overseas to increase.
- Lead to creation of employment raising standard of living
- The proceed from petroleum mining lead to growth and expansion of settlement / urbanization.
(3x2=6mks) QT=25.
- Name minerals mined at
- Forestry is the science of planning, developing and managing forests and other related resources.
(2x1=2mks) - Differentiate forestry in Kenya and Canada under the following
- Distribution
In Kenya, small area unevenly covered while Canada large area evenly covered by forest.
(1x2= 2mks)
Forests in Canada cover most parts of the country while in Kenya, they are mainly found in Kenya Highlands - Types of forests.
In Kenya mainly planted while Canada mainly natural forests - Transportation
In Kenya transportation is mainly by use of roads and railway while Canada mainly rivers used by floating them on water sliding on frozen ground, - Period of harvesting
In Kenya harvesting is throughout the year while Canada harvesting is done in winter and early spring/summer.
(1x2=2mks)
- Distribution
- State four measures to conserve forests
(any 1x2 =2mks)- Enacting laws/ legislation to prohibit cutting trees without licenses / encroach reserves
- Establishing forest research station to research on best tree species.
- Encouraging agro-forestry
- Creation of forest reserves for indigenous trees/abetment of areas to rehabilitate forests.
- Creating public awareness/education on mass media on importance.
- Setting up Nyayo tea zones has helped to prevent encroachment.
- Introduction of afforestation and re-afforestation programme to increase area under forest.
- Support NGO'S such as greenbelt movement/ NEMA, KWS
- Encourage recycling of wood products
(4x1=4mks)
- Explain 4 factors favouring growth of natural forests on the slope of Mt. Kenya.
- High rainfall throughout the year favour flourishing growth of
- Deep,fertile volcanic soils enhance growth and anchorage.
- Gazettement of forest reserve prohibits cultivation and settlement on forest land.
- Very steep slopes discourages settlement leaving forestry as the best alternative
- Rugged terrain discourages agriculture favouring forestry
- Cool climate / temperature in Kenya highlands favours growth of trees.
- Varied altitude which favour growth of different type of trees
(4x2= 8mks)
- Three types of indigenous hardwood trees found in Kenyan forests
- Mvule
- Meru Oak
- Elgon teak
- Elgon olive
(3x1 = 3mks)
- Explain 4 factors favouring growth of natural forests on the slope of Mt. Kenya.
- Forestry is the science of planning, developing and managing forests and other related resources.
-
-
- Population distribution refers to the way people are spread out on land
- Population density is concentration of people per unit area.
(2x1=2mks)
-
- Two primary sources of population data.
- Registration of persons (by birth/death/marriage
- National census
(2x1=2mks)
- Information derived from population pyramid.
- Sample survey
- Size of population
- Different age groups
- Proportion of male to females
- The composition of sex
- Mortality ratio
- The proportion of youth/working / ageing
- Dependency ratio
- Life expectancy
(4x1=4mks)
- Two primary sources of population data.
-
- Differentiate between population in Kenya and Sweden.
- Kenya has large number of yourth below 20years while Sweden has an age population
- Kenyans population was low life expectancy while Sweden has high lifxpectancy.
- Kenya has high birth rate while Sweden was low ferenity rate.
- Kenyans high population live in rural areas while Sweden most people are in urban
- The population growth rate is high in Kenya while its low in Sweden.
(3x2=6mks)
- Five consequences of high population density in the central highlands of Kenya.
- Land fragmentation/shortage
- Shortage of food due to high demand
- Soil erosion due to clearing land for settlement
- Increased demand for basic services-food, security
- Interference with water catchment areas.
- High un employment rates
- Low per capital income / poverty
- High dependency ratio
- High population growth creates market for goods
- Congestion in towns (traffic delays/Jams)
(5x1=5mks)
- Four significance of population structure
- Helps in economic planning
- Helps in buldgeting
- Helps in calculation of dependency ratio
- Helps in calculating sex ratio
- Helps determine changes infertility and mortality over a given period of time.
- Government provision of essential basic services such a schools.
- Creation of job opportunities.
(4x1=4mks)
- Differentiate between population in Kenya and Sweden.
-
- Land reclamation is a process by which unproductive or less productive land is converted into more useful land while land rehabilitation is the restoration of land that has been destroyed / ruined misused to its former productive state. (2mks)
- What is a polder
A polder is a piece of land reclaimed from the sea (2mks)
- Two methods of land reclamation in Kenya
- Irrigation
- Afforestation
- Introduction/growing of drought resistant crops.
- Control of soil erosion
- Draining swamps in flooded areas
- Adding manure / fertilizers
(2mks)
- Three physical factors that influenced location of Mwea Irrigation scheme
- Presence of black cotton soil that retain water
- Gentle slopes/rolling plains / undulating land scape to allow water flow by gravity / for mechanization.
- Availability of water from R. Thiba/Nyaminchi Murabaru/Inadequate/Semi arid conciliation that necessitude irrigation.
- Availability of extensive land for future expansion
(6mks)
-
- Stages involved in land reclamation in the Netherland
- Dykes /Sea walls were constructed to enclose the land to be reclaimed.
- Ring sanely were constructed on interior of dykes.
- Pumping stations were installed
- Water was pumped out
- Reeds were planted to drain excess water
- Drainage pipes were laid below the soil.
- Drainage pipes were laid below the soil.
- Road network was established to facilitate movement.
- The area was subdivided into polders
- The soil was flashed with fresh water treated with chemicals to lower security
- Pumping out of water was made continues and plots leased to formers.
NB: sequence must be followed
(7mks)
- Compare land reclamation in Kenya and Netherlands under the following;
- Scale of operation in Kenya reclamation is on small scale while in Netherlands is on large scale.
(2mks) - Agricultural out put - Little out put realized in Kenya while in Netherland it has high output that leads to exports.
- Scale of operation in Kenya reclamation is on small scale while in Netherlands is on large scale.
- Stages involved in land reclamation in the Netherland
- Two main projects of land reclamation in Netherlands.
- Delta plan
- Zaiden Zee (2mks)
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Catholic Diocese of Kakamega Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
