INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consist of six questions
- Answer any five questions in spaces provided.
- Candidates should answer the question in English.
Business studies paper 2
-
- Explain FIVE factors that may discourage entrepreneurship development in a country.
(10 marks) - Inflation rate in Kenya is reported to have hit 10%. Explain five non-monetary measures the Kenyan government may put in place to control the above trend
(10 marks)
- Explain FIVE factors that may discourage entrepreneurship development in a country.
-
- Outline five benefits that may accrue to a business as a result of computerization on its operations
(10marks) - The following transactions were extracted from the books of Lureko Traders in the month of June 2019
Required;DATE TRANSACTION June 4 Sold goods on credit to Biyang Kshs. 14,000 and Wendo Kshs. 17,000 June 7 Bought goods on credit from Panyako Kshs. 43,000 June 10 Biyang returned goods worth Kshs. 3,000 June 12 Purchased goods on credit from Shabiri Kshs. 64,000 and Akoyi Kshs. 28,000 June 18 Goods worth Kshs. 5,000 and Kshs. 2,000 were returned to Panyako and Shabiri respectively June 22 Goods sold on credit to Biyang Kshs. 6,000, Mwaura Kshs. 10,000 and Cheloti Kshs. 11,000 June 28 Goods returned by Mwaura Kshs. 1,000
Prepare the relevant books of original entry.
(10 marks)
- Outline five benefits that may accrue to a business as a result of computerization on its operations
-
- Explain FIVE goals of economic development
(10 marks) - Explain Five advantages of specialization to a firm.
(10 marks)
- Explain FIVE goals of economic development
-
- Outline Five differences between general insurance and life assurance
(10 marks) - Define the following terms as used in international trade
- terms of trade
(2 marks) - balance of trade
(2 marks) - balance of payment
(2 marks) - trade liberalization
(2 marks) - export processing zone
(2 marks)
- terms of trade
- Outline Five differences between general insurance and life assurance
-
- Explain FIVE factors for the decrease in the supply of maize in the Kenyan Market.
(10marks) - Explain Five reasons that may influence the government to start a parastatal include.
(10marks)
- Explain FIVE factors for the decrease in the supply of maize in the Kenyan Market.
-
- Explain Four circumstances under which a firm may be located near the market for its products.
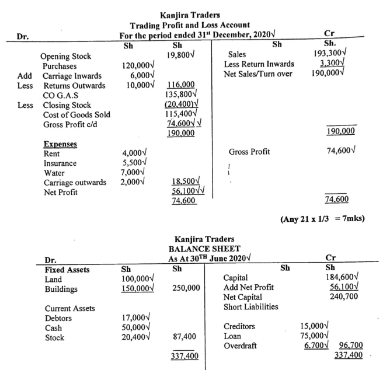
(8 marks) - The following information was extracted from Kanjira Traders as at 31st Dec, 2020.
Kanjira Traders
Trial Balance
As At 31st December 2020
Kshs. Kshs.
Opening stock 19,800
Purchases 120,000
Sales 193,300
Returns outwards 10,000
Returns inwards 3,300
Carriage inwards 6,000
Rent 4,000
Land 100,000
Insurance 5,500
Loan 75,000
Creditors 15,000
Debtors 17,000
Cash 50,000
Overdraft 6,700
Buildings 150,000
Water 7,000
Capital 184,600
484,600 484,600
Additional information- Stock on 31st December, 2020 was Kshs. 20,400.
- Carriage outwards was Kshs. 2,000
Required;- Prepare Kanjira Trading, profit and loss account.
(7 marks) - A balance sheet as at 31st December, 2020.
(5 marks)
- Prepare Kanjira Trading, profit and loss account.
- Explain Four circumstances under which a firm may be located near the market for its products.
MARKING SCHEME
-
(10mks)- Unfavorable government policy/ imposing high taxes- which discourage production of certain commodities/increase the cost of production.
- Poor entrepreneurial/culture/lack of adequate role models- in the society to inspire/motivate the would be entrepreneurs
- Inadequate/lack of market- due to low purchasing power/high level of poverty/low incomes.
- Poor transport (network) infrastructure/Utilities- making it difficult/expensive to access row materials/market/accept relevant examples of poor infrastructure/utilities as a mention.
- Insecurity (in some areas)- that discourage entrepreneurs from investing/getting raw materials/ accessing the markets in such areas.
- Inadequate natural resource (endowment/raw materials/land)- leading to low production/Accept examples of inadequate natural resources as a mention.
- In availability/Inaccessibility inappropriate technology- that leads production of poor quality/non-competitive goods.
- Political instability - may create unconducive/harsh/unfavorable environment for entrepreneurs to invest.
- Unfair/unhealthy competition- Which makes investment very expensive/uncompetitive/from cheap/interior imports.
- Limited access to capital/inadequate capital/credit/finance is costly/hard to access- which make it difficult to start to run business.
- Corruption/poor governance- which increases the cost of doing business. xii). Poor education/training - leading to lack of skills to start /run business
- Unfavourable/negative cultural practices - leading to poor/negative consumption/practices/choices/discouraging starting /running of business.
- Bureaucracy/red-tapes/legal control- making it complex/expensive/difficult to start/run business.
- (10mks)
- Reducing Government spending thereby reducing the amount of money in circulation
- Raise income tax which reduces the consumers' disposable income.
- Reduce tax on production/lower tax rates on imports to lower the cost of production/to lower the prices of subsequent goods and services.
- Subsidise production to keep production cost low hence lower prices of goods and services. v). Government to produce commodities that are in short supply to ensure supply matches with demand.
- Wage control to avoid increase in production cost that leads to increase in prices.
- Restricting imports to take care of control imported inflation.
- Price control whereby the government tames business people who keep increasing prices of commodities as a result of desire to increase profit margins.
- Export control to avoid shortages that arise leading to price hike
- Restricting terms of hire purchase/credit terms of sale in order to reduce the consequent demand for commodities.
-
- (10mks)
- Computers speed up operations thus saving on time.
- Output by computers is presentable
- Computers can store large volume of information and for a long time.
- Computers can be used to process large amount of transactions/prepare ledger accounts/payroll.
- It enhances accuracy/efficiency thereby minimizing losses/wastage.
- It facilitates communication from one point to another (through LAN-local area network)
- It economizes on space and materials as computers have large internal storage capacity/compact removable storage devices.
- It is used to curb fraud through efficient storage of records/easy to retrieve/ trace records.
- It has enhanced communication/research through internet/intranet/website.
- It has enabled establishment of paperless hence enhancing neatness in the office
- Reduced /loss of government revenue earned from import/export not exported
Naming =1mk, otherwise= 2mksx5=10mks
- PURCHASES JOURNAL
DATE DETAILS FOLIO INVOICE NO AMOUNT 2019 JUNE 7 Panyako 006 43,000 JUNE 12 Shabiri 007 64,000 JUNE 12 Akoyi 008 28,000 135,000
SALES JOURNAL
DATE DETAILS FOLIO INVOICE NO. AMOUNT 2019 June 4 Biyang 001 14000 June 4 Wendo 002 17000 June 22 Biyang 003 6000 June 22 Mwaura 004 10,000 June 22 Cheloti 005 11,000 58,000
SALES RETURNS JOURNAL
PURCHASES RETURNS JOURNALDATE DETAILS FOLIO CREDIT NOTE NO. AMOUNT 2019 June 10 Biyang 011 3,000 June 28 Mwaura 012 1,000 4,000
DATE DETAILS FOLIO CREDIT NOTE NO AMOUNT 2019 June 10 Biyang 013 5000 June 28 Mwaura 014 2000 7000
- (10mks)
-
- (10mks)
- To diversify the economy- to avoid overreliance on one sector of the economy.
- To correct balance of payment deficit- through enhanced/diversification of a country's exports/establishing export substitution industries.
- To alleviate poverty - by empowering people economically making them productive.
- To curb unemployment - thus improving peoples living standards
- To reduce income iequalities- through provision of basic services to the disadvantaged / through affirmative action/subsidizing the poor.
- To conserve the environment- production should not be at the expense of current and future generation/should be sustainable.
- To provide basic human needs- such as housing /food/suitable education/health facilities to the disadvantaged citizens.
- To improve infrastructure - to enhance economic activities / ease the movement of factors of production.
- Promotion of balanced regional development-
- To provide a wide variety of goods- to widen consumers choice.
- To enhance international understandings/relations with other countries - thereby promoting international peace.
- To develop social infrastructure- through education training.
- (10mks)
- Workers carryout production tasks that they are best suited for thus increasing their efficiency.
- Repetition of the same task overtime reduces fatigue as workers use less effort to perform assigned tasks.
- The quantity of output per worker is longer since their efficiency is high
- The quality of output is high because division of labour encourages employment of specialization.
- Use of machines results in mass production hence toners production costs which can translate into lower prices of goods / services.
- It encourage innovation/invention/improvement of skills in their areas of production.
- It saves our production time since workers do not have to more from one task to another.
- Ease in planning/organizing/coordinating work/workers, hence greater production efficiency.
(Naming -1mk, otherwise - 2mksx5= 10mks)
- (10mks)
-
- (10mks)
General insurance Life insurance Deals with property Deals with life Is a protection plan Is a saving plan Is a short term contract/ require periodical renewal Is a long term contract / no renewal Has no surrender value Has got a surrender value Insured must have insurable interest Assured may not have insurable interest Cannot be assigned/ nominated to anybody Can be assigned / nominated to a beneficiary Don't have maturity date Has maturity date Is not a security/ collateral for obtaining loan Can be used as security collateral for obtaining loan Value of policy/ premium depends on the value of property Value of policy / premiums depends on ability to pay Risk insured may never happen at all The risk must happen -
- terms of trade - refers to the ratio of a country's export price index and import price index in the current year compared to the basic year
(2 marks) - balance of trade - refers to the difference between visible export and visible imports of a county over a period of one year
(2 marks) - balance of payment - refers to the difference between both visible and invisible export and visible and invisible imports as well as capital inflow and outflow over a period of one year
(2 marks) - trade liberalization - is the removal/reduction of trade restrictions/ barriers to allow free trade between /among countries
(2 marks) - export processing zone - are economic zones set aside by government to allow importation of duty free raw material for the manufacture of export goods
(2 marks)
- terms of trade - refers to the ratio of a country's export price index and import price index in the current year compared to the basic year
- (10mks)
-
- (10mks)
- The low price of maize - less is supplied at lower price due to less profit/high cost of production.
- High cost of production -.which makes production difficult/unsuitable/not attractive.
- Poor level of technology-leading to production of poor quality/quantity goods
- High price of complimentary goods- which makes farmers to produce the complimentary good at the expense of Maize lowering its production.
- Poor government policy/increased taxation on input/decreased subsidy- which increases the cost of production /makes production unattractive/unsuitable.
- Exits of firms from the industry- leads to a decrease in overall production
- Shortage of inputs/fertilizers/ seeds- hence low production/supply.
- Future expectations of price increase - hence restrict supply to supply in future when the price is high.
- Poor/bad weather/natural factors- leading to poor harvest hence low supply.
- Time- maize take time to manure/grow/be ready for consumption.
(Any 5x2=10mks)
- (10mks)
- To provide strategic goods and services to its citizens at low prices/which cannot be left in the hands of private investors.
- To increase revenue collection through proceeds of the firms
- To reduce foreign dominance by venturing in investments by foreign investors.
- To take care of business ventures that require a large initial capital that the private investors cannot afford.
- To take care of sensitive ventures (such as sell of fire arms which cannot be left in th hands of the private investors.
- To implement government manifestos such as creation of employment for its citizens.
- To provide goods and services with low returns/profits hence avoided/neglected by private investors.
- To promote competition with the private sector in society to ensure responsiveness to consumer needs.
- To regulate business activities in order to prevent consumer exploitation.
- To address special needs in society which could not be addressed by the private investors.
- To stimulate economic development by creating an enabling environment eg by creating an enabling environment e.g by creating easy access to credit
(Naming -1mk, otherwise -2mks x 5 = 10mks)
- (10mks)
-
- (10mks)
- Where a firm is producing perishable goods that need reach consumers before going bad.
- The firm could be producing fragile products to avoid loss emanating from breakages during transportation.
- Where the market for the product is concentrated in one area.
- The firm's products could be bulky hence cumbersome to transport.
- Where raw materials are cheaper to transport than final products.
- Where a firm produces bulky goods that would be cumbersome/expensive to transport far places.
-
(Any 10 x 2 = 5mks)
- (10mks)
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Catholic Diocese of Kakamega Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
