INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in the section
SECTION A (30MARKS)
Answer All the questions in this section
- Give two ways in crop rotation helps in weed control. (1mark)
- Differentiate mixed cropping and intercropping. (2marks)
- Give four advantages of intensive farming system. (2marks)
- Name three practices that help to attain optimum crop population after planting. (1½marks)
- Give two reasons why tsetse fly control is considered a land reclamation process. (1mark)
- Explain how leaching leads to loss of soil fertility. (1mark)
- Outline four observable indicators of economic development of a nation. (2marks)
- Give four methods of farming. (2marks)
- State four factors that should be considered when selecting a crop to grow in an area. (2marks)
- Identify four roles of calcium in crops. (2marks)
- Give two benefits of using certified seeds. (1mark)
- Give four benefits of tissue culture in crop propagation. (2marks)
- Give two ways in which mulching helps in water conservation. (1mark)
- Apart from tomatoes, name four examples of fruits and vegetables. (2 marks)
- Distinguish hardening and hardening off as applicable in crop production. (2marks)
- Give four ways of improving labor productivity in the farm. (2marks)
- What is production function? (1mark)
- Suggest five symptoms of viral infection in crops. (2½marks)
SECTION B 20 MARKS
(Answer ALL the questions in this section)
- The diagrams below illustrate field pest of maize. Study them and answer the question that follows.


A B- Identify the pest labeled (2marks)
- Give one cultural method of controlling pest A (1 mark)
- Give the damage caused by the pest B (2marks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.

- Name the structure above (1mark)
- Give two ways in which the above structure helps in soil and water conservation. (2marks)
- State two reasons why the above structure is not commonly used as a soil conservation method. (2marks)
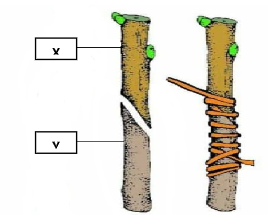
- Below is an illustration of crop propagation. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the method of propagation above. (1mark)
- Identify the parts labelled (2marks)
- Give two advantages of the propagation method. (2marks)
- The table below shows the format of a farm record. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Date Disease symptoms Livestock affected Drugs used Cost of treatment Remarks - Identify the record illustrated above. (1mark)
- State four uses of the record illustrated above. (4marks)
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any two questions from this section.
-
- Explain five causes of land fragmentation. (5marks)
- State five factors that can encourage soil erosion. (10marks)
- State any five methods of harvesting agroforestry trees. (5marks)
-
- State and explain four ways of classification of herbicides. (8marks)
- State and explain any six human factors that influence agriculture (12marks)
-
- Explain five ways in which a farmer can adjust to risk and uncertainties (10marks)
- Discuss any five factors that promote the rooting of cuttings. (10marks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Breech of birth is a presentation during parturition where the hind legs of a new born come out first. (1mk)
Description Cattle Pigs Poultry Young from birth/ hatching to weaning Calf Piglet Young female b4 first parturition Heifer Pullet Mature male for breeding boar cock -
- To stimulate growth and production
- To prevent disease attacks
- To improve feeding habits (appetite). (Any 2 x ½ = 1mk)
- Implements used for secondary cultivation.
- Disc harrow.
- Spike toothed harrow.
- Rotavator.
- Ox- tine harrow
- Chain harrow.
- Zigzag harrow.
- Sprung tine harrow. 4 x ½ =2mrks.
-
- Avoid poisoning by chemicals or lead that may be in paints.
- To discourage/avoid tainting of milk if shed is used immediately after painting
- Discourage insects from inhabiting the shed 2 x ½=1m
- Uses of wind power of the farm
- Winnowing of crops
- Driving machines e.g. wind mill 2 x ½=1m
-
- Oxytocin
- Adrenaline 2 x ½=1m
-
- Pin
- Shoe
- Head
- Stem
- Thumbscrew any 2 x1= 2m
-
- Keeps birds busy scratching, hence reduce cannibalism
- Gives comfort and warmth to the birds
- Helps in drying droppings any 2 x1= 2m
-
- Disinfect the teats
- Apply milking salve on teats
- Weigh the milk
- Cooling the milk
- Straining/ sieving the milk
- Clean utensils 4 x ½ =2mrks
-
- Mastitis
- Milk fever 2x ½= 1mk
-
- Checking the level of electrolyte and adding distilled water if plates are exposed.
- Checking specific gravity using hydrometer and adjusting accordingly.
- Cleaning the terminals if dirty.
- Recharging if the voltage is low. 4x ½ = 2mks
-
- Age of the equipment
- Wear and tear/use
- Lack of maintenance practice
- Exposure to weather/improper storage
- Obsolescence/change in technology (Any 4 x ½ = 2mks)
-
- Collect eggs regularly and frequently.
- Make nests dark
- Feed balanced diet.
- Debeak perpetual egg eaters.
- Supply green leaves to keep birds busy. Any 4x ½ =2mks
-
- Anthrax
- Black quarter/leg 2 x ½ = (1mk)
- Vaccine
- Blanthrax 1 x ½ = (½mks) Mark as a whole
-
- Flushing the tubes under high pressure to it.
- Greasing / oiling rotating parts in the pump
- Storing it to dry upside down after thorough washing 3 x ½ = 1½mks
- Advantages of jersey
- Hardly / withstand high temperatures
- Needs less food
- Excellent grazer on fairly poor pastures. ½ x 2 = 1mk
-
- Makes a vertical cut into the soil ahead of the share to separate the furrow slice from unploughed land.
- Cut any trash on the surface 2 x ½ = ( 1mk)
-
- Sahiwal
- Red poll
- Simmental
- Brown Swiss 2 x ½ = 1mk
-
-
- G-Liver fluke (Fasciola ssp)
- H -Round worms (Ascaris ssp)
- S -Tape worms (Taenia ssp) 3 x ½ =1½mks
- Internal/endoparasites. 1 x ½ = (½mk)
-
- G – Liver fluke is found in the bile duct/ gall bladder / liver.
- S -Tape worm are found attached on the wall of the small intestine.(2 x ½ = 1mk
-
- Control of fresh water snail by physically killing them.
- Control of fresh water snail by use of adding CuSo4 solution to stagnant water.
- Draining swampy areas:
- Burning swampy bushes during dry weather.
- Avoid grazing affected animals near marshy or swampy areas.
- Routine drenching with suitable. Anthelmintic.
- Rear ducks which feed on snails. 3 x ½ = (1½mks)
-
-
- Wire guard ½mk
-
- X – Cold/low temperatures thus making chicks move closer to the heat source. (1mk)
- W – Draught/strong wind from one side which makes them to move to the opposite side. 2 x1= 2m
-
Amount of maize = 15/25 x 200 = 120kg ½ m
Amount of sunflower = 10/25 x 200 = 80kg = ½ mk -
- Spark plugs
- Distributor/rotor
- Ignition coil
- Battery 4 x ½ = 2mks
-
- Produce sparks required for ignition during power production at the combustion chamber
- Distribution of electrical energy in the correct order to the various spark plugs.
- Converts low voltage from the battery to high voltage current of 6000 colts required to provide a spark at the spark plugs.(3 x 1 = 3mks)
-
- Remove carbon deposits on the spark plugs
- Replace spark plugs whereas electrons are worn –out
- Clean contact breaks
- Replace condenser regularly
- System should be kept dry
- Ignition wires should all be insulated. (3mks)
-
-
- Security : Located near homestead eg poultry house.
- Accessibility: should be connected with roads for easy of transportation of inputs/outputs
- Soil type – Should be well drained and unproductive
- Drainage / Gradient: When there is free flow of water
- Nearness to water sources eg. Vegetable nursery for easy irrigation
- Social amenities: Homesteads to be near schools, hospitals and churches
- Other infrastructure such as near roads and power lines
- View of farm (panoramic)
- Future expansion space to be left for future expansion (10 x 1 = 10mks)
- Advantage of fences
- They mark boundaries
- Keep off intruders / thieves
- Control grazing/ facilitate rotational grazing
- Prevent damage of crops by animals
- Control breeding
- Act as wind breaks
- Control of pests and diseases by preventing entry of wild and sick animals
- Live fences have aesthetic value
- Provide livestock feeds, firewood, mulch and compost manure material
- Add value to farms (5 x 1 = 5mks)
-
- Cementing the posts
- Inserting droppers between standard posts
- Supporting the corner posts with struts and strainers
- Tightening the wire strainers
- Fixing braces to support the fencing posts (5 x 1 = 5mks)
-
-
- Parts of a cattle dip and their functions
- Holding yard/assembly yard/lead in pen/concrete floor - for holding animals before dipping
- Foot bath - 4 m long 25 cm deep
- i.e. rough concrete floor
- wash feet of animals
- contains chemicals for controlling foot rot
- Lead in gang – narrow entrance
- Allows animals to jump singly into the dip tank.
- The jump / leaf in ramp
- Taken off point where the animal jump into the distance
- Dip tank / plunge dip
- Deep water tank below the ground level
- Contains acaricide
- Exit ramp
- Stairs that lead to the drinking race
- Allows animals to come out of the dip wash slowly
- Draining race / drip gang way
- Has a sloping floor towards the dip tank
- Allows dip wash to drain back to the dip tank
- Drying yard
- Animals are restrained before being released.
- Silt trap outlet
- Trap silt and dung as the dip wash floors back into the distance
- Dip tank shelter / roof
- Above the dip tank
- Lowers evaporation of dip wash
- Water tank / reservoir tank – for storing water
- Waste pit – dumping sediments from the dip tank
Stating ½ x 12 = 6mks Function ½ x 12 = 6mks
- Three differences between a petrol engine and a diesel engine (accp table format)
- A petrol engine has a carburetor while a diesel engine has an injector pump
- In a petrol engine fuel and air first mix in the carburetor while in a diesel / engine they mix in the cylinder
- In petrol engine produces little smoke / complete combustion while a diesel engine produces a lot of smoke / incomplete combustion
- A petrol engine is relatively light and suited for light duties while a diesel is relatively heavy and suited for heavy duties 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Maintenance practices of a tractor battery
- Level of electrolyte should be kept just above the plate topping is with distilled water.
- Corroded terminals should be scrapped, cleared and smeared with grease
- Should be tightly fixed in a box to avoid spillage and damage
- Battery should be fitted / connected correctly
- During long storage the battery should be emptied and kept upside down
- Generator fan belt should always be functional to ensure the battery is always charged. Any 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Methods of attaching the tractor drawn implements
- Through the draw bar
- Through hydraulic system
- Through power take off 2 x 1 = 2mks
- Parts of a cattle dip and their functions
-
- Clean and disinfect the far rowing pen
- Wash / clean and disinfectant the sow.
- Treat the sow against external parasites
- Move the sow to a furrowing pen – 3 days before furrowing
- Provide a creep area.
- Provide clean bedding maternal
- Provide bran for the sow after furrowing.
- Ensure piglest are breathing.
- Ensure piglets suckle colostrum
- Disinfect umbilical cord of piglets.
- Weigh piglets on day one to get birth weight
- Dispose the after – birth
- Dispose-off born still piglets on day 1 to attain birth weight.
Stating ½ mk + Explaining ½ mk = 12mks.
-
- Old age
- Health of a boar
- Serious injury of the boar
- When daughters are used as replacement stock / to avoid inbreeding.
- When boar is too fat and lazy.
- Poor performance of offsprings
- Lack of libido / infertile boar.
- Bad temperament
Stating ½ mk +Explaining ½ mk 8mks.
- Clean and disinfect the far rowing pen
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Maranda High School Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students