INSTRUCTIONS:
- Answer ALL the questions
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
Question |
Maximum Score |
Candidates score |
|
1 |
13 |
|
|
2 |
15 |
|
|
3 |
11 |
|
|
4 |
10 |
|
|
5 |
10 |
|
|
6 |
10 |
|
|
7 |
11 |
|
| Total Score |
80 |

QUESTIONS
- The grid below represents the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of elements.
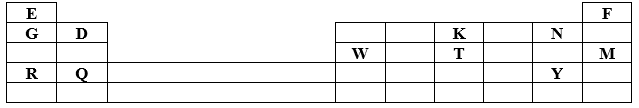
-
- Which letter represents an element that is least reactive? (1 mark)
- Why are elements D and Q referred to alkali earth metals? (1 mark)
- How does the atomic radius of W and T compare? Explain. (2 marks)
- Select two letters representing elements that would react most explosively. (2 mark)
- Write the equation showing how Y forms its ion. (1 mark)
- Write the formula of:-
- Chloride of D. ( ½ mark)
- Nitrate of W. ( ½ mark)
- What type of bonding exists between;
- G and N. ( ½ mark)
- K and Y. ( ½ mark)
- Explain why melting point of Y is higher than N. (1 mark)
- The 1st, 2nd and 3rd ionization energies (in KJ/mol) of elements G and R are given below.
Element
1st I.E
2nd I.E
3rd I.E
G
520
7,300
9,500
R
420
3,100
4,800
- Define the term ionization energy. (1 mark)
- Apart from the decrease in energy levels, explain the big difference between 1st and 2nd ionization energies. (1 mark)
- Calculate the amount of energy in KJ/mol for the process. (1 mark)
R(g) → R3+(g) + 3e-
-
-
- The scheme below shows some organic reactions. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
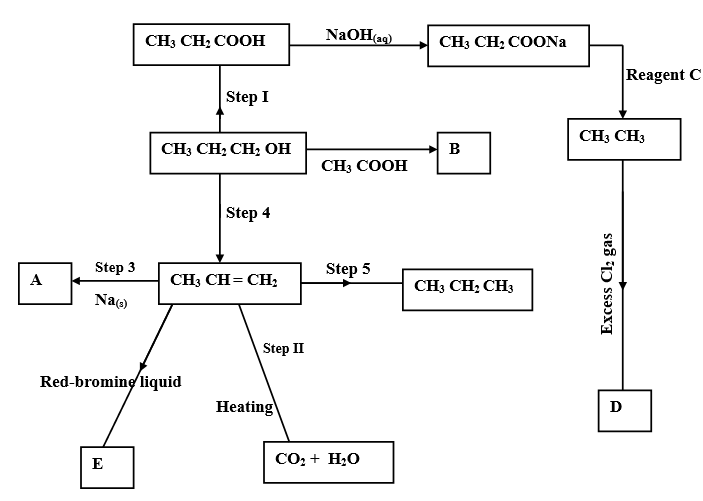
- Write the formula of compounds. (2 marks)
- B
- A
- Name the type of reaction, reagent and conditions for the reactions of the following steps.
- Step 1: (2 marks)
Type
Reagent - Step 4: (2 marks)
Type
Reagent - Step 5: (2 marks)
Type
Reagent
- Step 1: (2 marks)
- Name reagent C.
- Draw and name the structural formula of D. (2 marks)
- Name the structure E. (1 mark)
- Give one property of compound B. (1 mark)
- Write the formula of compounds. (2 marks)
- Polymers and fibres are either synthetic or natural.
- Give two examples of synthetic fibres and polymers. (1 mark)
- A polymer is formed whose formula is;
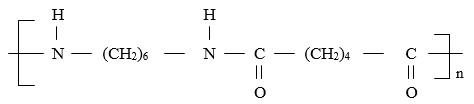
Draw the structural formula of the monomers. (2 marks)
- The scheme below shows some organic reactions. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow.
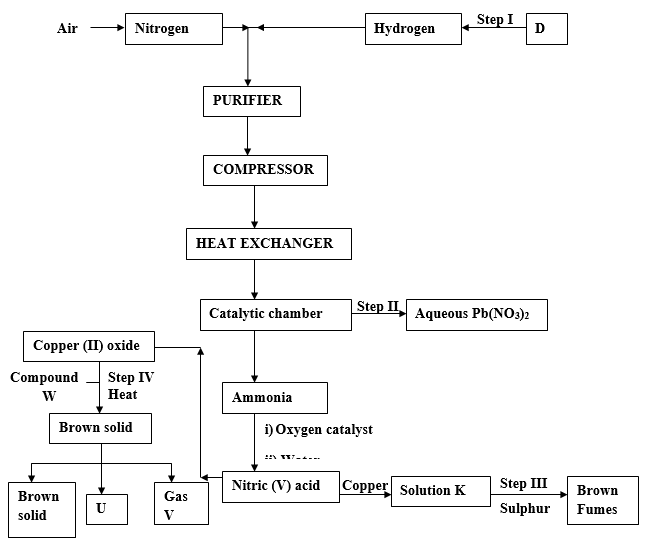
- Name the impurities removed by the purifier. (2 marks)
- What is the work of the heat exchanger? (1 mark)
- Write down the chemical equation for the reaction taking place where Nitric (V) acid is formed. (1 mark)
- Name;
- Compound W. (1 mark)
- Substance U. (1 mark)
- Gas V. (1 mark)
- Write down the formula of compound P. (1 mark)
- Other than manufacture of ammonia write down one other use of Nitrogen. (1 mark)
- Calculate the mass of Nitrogen in 6.6g of Ammonium Sulphate. (H = 1, S = 32, O = 16). (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents a paper chromatogram of pure substances W, X, Y and Z.
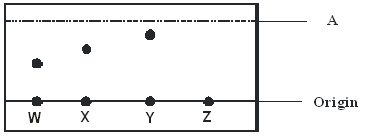
- Name A. (1 mark)
- Explain why substance Y moves faster from origin than X. (1 mark)
- Explain the observation made on substance Z in the chromatogram. (1 mark)
- The relationship between pressure and volume of a fixed mass of a gas was studied at 25°C. The data was recorded as shown in table below.
Volume (dm3)
0.5
1
2
3
Pressure (atmosphere)
6
3
1.5
1
Product of volume and pressure
- Complete the table by calculating the products of volume and pressure. (2 marks)
- Using the data comment on the relationship between volume and pressure of fixed mass of gas at constant temperature. (1 mark)
- Use the information below to answer the questions that follow.
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ΔH1 = -393.5 Kj/mol-1
H2(g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O(g) ΔH2 = -285.8 Kj/mol-1
C2H5OH (l) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) ΔH3 = -1370 Kj/mol-1- Define the term heat of formation. (1 mark)
- Calculate the heat of formation of ethanol. (3 marks)
-
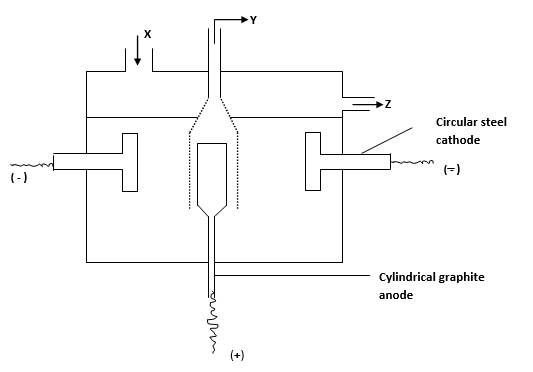
- Sodium is extracted in the Downcell shown below.Name Y. (1 mark)
- Down’s cell must operate at high temperature of about 600°C. Explain. (2 marks)
- Explain why anode is made of graphite instead of steel though it’s a better conductor. (1 mark)
- State the purpose of steel diaphragm. (1 mark)
- The set up below was used to prepare and collect dry sample of gas G. During the experiment, cleaned magnesium ribbon was strongly heated before heating the wet glass wool.
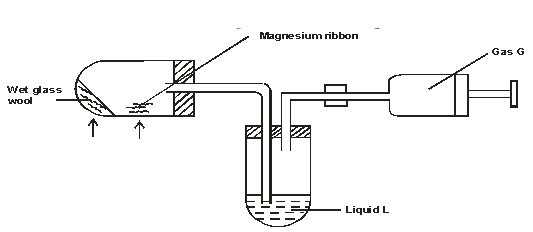
- Why was the magnesium ribbon cleaned before it was used? (1 mark)
- State the observations that would be noted in the reaction tube. (1 mark)
- Name;
- Gas G. (1 mark)
- Suitable liquid L. (1 mark)
- Write equation of reaction in the reaction tube. (1 mark)
-
- Study the standard electrode potential below and answer the questions that follow.
The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements.
M2+(aq) + 2e- → M(s) Eθ = -0.76V
N2+(aq) + 2e- → N(s) Eθ = -2.37V
2P+ + 2e- → 2P(s) Eθ = +0.80V
R2+ + 2e- → R(s) Eθ = - 0.14V- The standard electrode potential of Fe2+ is -0.44 volts. Select the element which would be best to protect iron from rusting. (1 mark)
-
- Calculate the Eθ value for cell represented as M(s) / M2+(aq) // P+(aq) + P(s). (2 marks)
- Draw the electrochemical cell represented in b(i) above. (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents an experiment by a student using electrodes A and B.
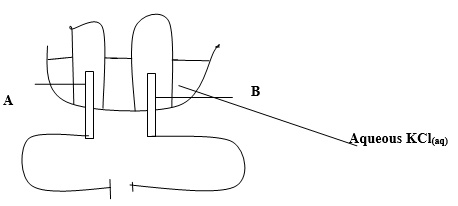
- Name the products at the electrodes. (1 mark)
- Write equation of reaction at each electrode. (1 mark)
- During purification of copper by electrolysis, 1.48g of copper was deposited when a current was passed through aqueous copper (II) sulphate for 2½ hours. Calculate the amount of current that was passed. Cu = 63.5 and 1 Faraday = 96500C. (3 marks)
- Study the standard electrode potential below and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Define the term solubility. (1 mark)
Temp oC
0
8
20
40
60
80
Solubility in g/100g of the H2O
254
225
140
80
25
10
- Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
- Plot a graph of solubility in g/100g of water of copper (II) sulphate against temperature. (4 marks)
- From the graph,
- How does the solubility of Copper (II) sulphate vary with temperature? (1 mark)
- Determine solubility of Copper (II) sulphate in g/100g water at 35°C. (1 mark)
- If 30g of Copper (II) sulphate are dissolved in 100g of water at 30cC, is the resulting solution saturated, supersaturated or unsaturated. (1 mark)
- A saturated solution of copper (II) sulphate is cooled from 70°C to 20°C.
- Should the mass of copper (II) sulphate be reduced or increased for the solution to remain saturated. (1 mark)
- Determine the mass in (iv) (a) above. (2 marks)
- Plot a graph of solubility in g/100g of water of copper (II) sulphate against temperature. (4 marks)
- Define the term solubility. (1 mark)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- F
- Abudant in earth crust ½ and reacts with water to form alkalines solutions
- W is bigger than T1 OR T is shorter than W. This is because of increased nuclear charge across the period
- R 1 and N1 or N1 and R1
- Y + e → Y-1
-
- DCl2
- W (NO3)3
-
- Ionic ½ / electrovalent
- Covalent
- Y is liquid while N½ is a gas. N is a molecular compound with van der waals forces while Y is a liquid with strong covalent bonds
-
- Energy required to remove an electron from an atom in gaseous form
- The 2nd electron is being removed from a stable energy level
- 420 + 3,100 + 4,800 = 8,320
-
-
-
-
- B – CH3COO CH2 CH2 CH3
A – CH3 CH2 CH2 Na
- B – CH3COO CH2 CH2 CH3
-
- Type – oxidation
Reagent – Acidified KMno4 / K2 Cr2 O71 - Type – Dehydration
Reagent – Conc H2SO41 - Type – Hydrogenation
Reagent – presence of Nickel catalyst
- Type – oxidation
- NaoH
- 2 dibromopropane
- Has a sweet smell
-
-
- Polythene
- Polychloro ethane
-
-
-
- carbon IV oxide
- Dust particles
- Water vapour etc
any one
- Heat reactants OR Cool reactants
- 4NO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + O2(g) → 4HNO3(aq)
- W – Ammonia gas
U – Water
V – Nitrogen gas - NH4NO31
- Used in light bulbs1 OR Used in storage of semen
- Mass of (NH4)2SO4 = 28 + 8 + 32 + 64 = 132
if 28g 132g
? 6.6
= (6.6 ×28)/132
=1.4g
-
-
- Solvent front
- Y is more soluble than X 1 or Y has a lower absorption power
- Z is insoluble in the solvent
-
- Volume
Pressure
Product 3.0½ 3.0½ 3.0½ 3.0½ - Volume is inversely proportional to pressure
- Volume
-
- Heat change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements
- 2C + 3H2 + ½ O2 → C2 H5 OH
⇓
2 CO2 + 3 H2O
ΔHf + Δ H3 = 2 ΔH2 + 3H2(g)
ΔHf + Δ H1 = 3 ΔH2 – ΔH3
= (2 x 393.5) + (3x – 285.8) + 13701
= -787 + -857.4 + 13701
= 274.4 KJ Mol-1
-
-
- Chlorine gas
- To maintain sodium chloride in molten form to allow ions to be mobile to conduct electricity
- Carbon in graphite is resistant to attack by chlorine
- To prevent chlorine from mixing with sodium to form sodium chloride
-
- To remove magnesium oxide layer on the surface
- Bright white flame / light or white powder
-
- Hydrogen gas
- concentrated sulphuric
- Mg(s) + H2O(g) → MgO(s) + H2(g)
-
-
-
- element N ½, it has the lowest reduction potential and would thus get easily oxidized at the expense of iron ½
-
- Eθ = E reduction – E oxidation ½
Eθ = 0.80 – (-0.76)
Eθ = +1.56 ½
- Eθ = E reduction – E oxidation ½
-
- At A = oxygen gas ½
at B = Hydrogen gas ½ - At electrode A
4OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) + O2 + 2e-1
At electrode B
2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g)
- At A = oxygen gas ½
- CU 2+ (aq) + 2e- → CU(s)
Therefore 63.5g of copper requires 193,000C
1.48g = ?
= (1.48g ×193,000)/63.51
= 4498.2677 C
Since Q = It
Then I = Q/t = 4498.2677/(2 1/2 ×3600)1 = 0.4998075
= 0.499807 5 Ampheres
-
-
- The maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in 100g of water at a given temperature
-
- Axes
Plots
Curve - Solubility decreases as temperature increases
- Unsaturated
-
- increase
- 70°C = 16.0g
20°C = 140
∴ Mass = 140 – 16g
= 124
- Axes
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Achievers Joint Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
