INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of TWO sections A and B.
- Answer ALL the questions in section A and B in the spaces provided.
- All working MUST be clearly shown.
- Non programmable silent calculators may be used.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
Constant: g=10N/kg or 10m/s2

QUESTIONS
SECTION A: (25 MARKS)
- The figure below shows a section of a meter rule used to measure length of a piece of wood.
Find the length of the wood (2marks)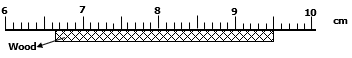
- The diagram below shows a capillary tube immersed in water.
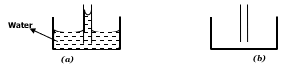
- Make a sketch on the figure alongside (b) to show the appearance of the capillary tube if it was inserted in mercury. (1 mark)
- Explain the difference if any between figure (a) and (b) above (2 marks)
- Explain why a partially inflated balloon released at sea level would become fully inflated at a higher altitude. (1mark)
- A catapult is used to project a stone of mass 40.0g vertically upwards to a height of 50.0m.
Calculate the amount of elastic potential energy initially present in the catapult. (2marks) - A turning effect of force depends on the magnitude of the force. State any other factor that determines the moment of a force (1mark)
- Mercury is usually preferred over water for use as a barometric liquid. Give a reason for this. (1mark)
- State the property of Freon that makes it suitable for use as refrigerant. (1mark)
- Other than the mass of ice, State another physical quantities that remain constant while pure ice is being converted to water. (1mark)
- Giving a reason, explain why it’s advisable for luggage carrier compartment to be put under the seats than at the roof tops of the buses. (1 mark)
- Other than angle of banking, state any other factor that affects the critical velocity of a vehicle negotiating a bend. (1 mark)
- A balloon filled with argon gas of volume 200 cm3 at the earth’s surface where the temperature is 20°C, and the pressure 760mm of mercury. If it is allowed to ascend to a height where the temperature is 0°C and the pressure 100mm of mercury, calculate the volume of the balloon. (2marks)
- It is a common behavior for a high jumper to slightly flex their knees just before landing. Explain the importance of this behavior from your knowledge of physics. (1mark)
- The figure below shows a manometer containing water. Air is blown across the mouth of one tube and the levels of the water changes as shown.
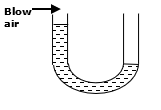
Explain why the level of water in the left limb of manometer is higher. (2 marks) - The figure below shows a uniform rod AB of weight 20N pivoted at A.
If the system is in equilibrium, determine the weight W shown. (3marks)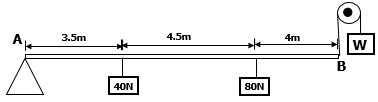
- A cemented floor feels cold to the feet, but a woolen carpet on the same floor feels warm. Explain this. (1mark)
- The diagram below shows an arrangement used to determine the upper fixed point of ungraduated thermometer.
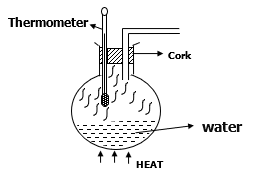
- Why is the bulb of thermometer not dipped in the water? (1mark)
- Explain how the sensitivity of a thermometer can be improved. (1mark)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- State Archimedes’ principle . (1 mark)
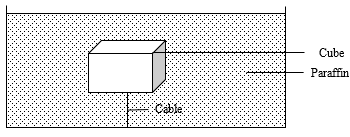
- The figure shows a cube of side 2.0 m block and of mass 4,800 kg attached to the base of a tank containing paraffin of density 800 kgm-3 by means of an inextensible and light weight cable.
Determine:- The density of the block. (2marks)
- The upthrust acting on the block. (3 marks)
- The tension in the cable. (2 marks)
- The cable is then released, and the block rises to the surface where it subsequently floats. Calculate the fraction of the block which is beneath the surface of the paraffin. (2 marks)
-
- Give two ways of increasing the boiling point of a liquid. (2 marks)
- A lagged copper calorimeter of mass 0.8 kg contains 0.6 kg of water at 22.0° C. A metal nut of mass 0.4 kg is transferred quickly from an oven at 3000 C to the calorimeter and a steady temperature of 520 C is reached by the water after stirring. Given that the specific heat capacity of copper is 400 Jkg-1K-1 and that of water is 4200 Jkg-1K-1, calculate:
- Heat gained by the calorimeter and water. (3 marks)
- Energy lost by the metal nut. (1 mark)
- The specific heat capacity of the material making the nut. (3 marks)
- An electric kettle rated 120 V, 60 W is used to melt 20 g of ice at 00C to water at 00C in 112 seconds, calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. (3 marks)
-
- A stone is thrown vertically upwards from the top of a tower 30m high, with an initial velocity of 20m/s. Determine:
- The time it takes to reach maximum height. (2marks)
- The total time which elapses before it hits the ground. (2marks)
- A string of negligible mass has a bucket tied at the end. The string is 60cm long and the bucket has a mass of 45.0g. The bucket is swung horizontally making 6 revolutions per second. Calculate
- The angular velocity (2marks)
- The angular acceleration (2marks)
- The tension on the string. (2marks)
- A stone is thrown vertically upwards from the top of a tower 30m high, with an initial velocity of 20m/s. Determine:
-
-
- During the construction of dams, the base of the dam is widened and curved. Explain.(2 marks)
- A block of density 1.60 g/cm3 and measures 3.0cm by 5.0cm by 7.0cm was placed on the ground. Determine the difference between the maximum and minimum pressure that would be exerted on the ground by the block. (3 marks)
-
- State Newton’s second law of motion (1 mark)
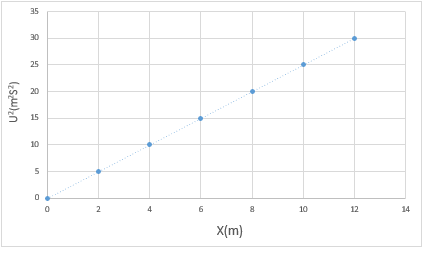
- A wooden block resting on a horizontal bench is given an initial velocity U so that it slides on the bench for a distance X before it stops. Various values of X are measured for different value of the initial velocity. The figure below shows a graph of U2 against X.
- Determine the slope S of the graph (3 marks)
- Determine the value of k given that U2= 20kX where k is a frictional constant for the surface (2marks)
- State with a reason what happens to the value of k when the roughness of the bench surface is reduced (2 marks)
-
-
-
- State the kinetic theory of gases. (1 mark)
- State the reason why it is easier to separate water into drops than to separate a solid into smaller pieces. (1mark)
-
- State Hooke’s law (1mark)
- Two identical helical springs are connected in series. When a 50g mass is hang at the end of the springs, it produces an extension of 2.5 cm. Determine the extension produced by the same mass when the springs arc connected in parallel. (3marks)
-
- State Boyle’s law. (1mark)
- Draw a suitable set up that can be used to verify Charles’s law. (3marks)
Section Question Maximum Score Candidate’s Score
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A: (25 MARKS)
- The figure below shows a section of a meter rule used to measure length of a piece of wood.
Find the length of the wood (2marks)
9.5-6.7=2.8cm correct readings√,final answer√ - The diagram below shows a capillary tube immersed in water.
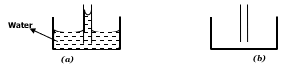
- Make a sketch on the figure alongside (b) to show the appearance of the capillary tube if it was inserted in mercury. (1 mark)
Convex meniscus, level below level in the beaker - Explain the difference if any between figure (a) and (b) above (2 marks)
In (a) the adhesive forces between the water and glass molecules are stronger than cohesive forces between the water molecules while in (b) in the cohesion forces between the mercury molecules are greater than adhesion forces between mercury and glass.
- Make a sketch on the figure alongside (b) to show the appearance of the capillary tube if it was inserted in mercury. (1 mark)
- Explain why a partially inflated balloon released at sea level would become fully inflated at a higher altitude. (1mark)
Pressure outside the balloon reduces below the pressure inside leading making it to increase in size/expansion - A catapult is used to project a stone of mass 40.0g vertically upwards to a height of 50.0 m.
Calculate the amount of elastic potential energy initially present in the catapult. (2marks)
Elastic potential=potential energy gained by the stone
= 0.04x10x50
= 20J - A turning effect of force depends on the magnitude of the force. State any other factor that determines the moment of a force (1mark)
Perpendicular distance away from the point
Angle at which the force is applied- Mercury is usually preferred over water for use as a barometric liquid. Give a reason for this. (1mark)
- Mercury has a higher density than water and therefore a shorter tube/length is required.
- State the property of Freon that makes it suitable for use as a refrigerant. (1mark)
- Highly volatile/easily evaporates.
- Other than the mass of ice, State another physical quantities that remain constant while pure ice is being converted to water. (1mark)
- Temperature of the ice
- Mercury is usually preferred over water for use as a barometric liquid. Give a reason for this. (1mark)
- Giving a reason, explain why it’s advisable for luggage carrier compartment to be put under the seats than at the roof tops of the buses. (1 mark)
- Makes the buses more stable by lowering the position of cog
- Other than angle of banking, state any other factor that affects the critical velocity of a vehicle negotiating a bend. (1 mark)
Radius of the curve
Nature of road surface/ wheels - A balloon filled with argon gas of volume 200 cm3 at the earth’s surface where the temperature is 20°C, and the pressure 760mm of mercury. If it is allowed to ascend to a height where the temperature is 00C and the pressure 100mm of mercury, calculate the volume of the balloon. (2marks)
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
V2=P1V1T2/P2 =760X200X273/293X100 =1,416.25cm3 - It is a common behavior for a high jumper to slightly flex their knees just before landing. Explain the importance of this behavior from your knowledge of physics. (1mark)
Increases the time of impact hence reduces the fatal impulsive force - The figure below shows a manometer containing water. Air is blown across the mouth of one tube and the levels of the water changes as shown.

Explain why the level of water in the left limb of manometer is higher. (2 marks)
When air is blown at high velocity, pressure above it is reduced below atmospheric pressure√
Atmospheric at the other limb is greater and therefore pushes the liquid to the left.√ - The figure below shows a uniform rod AB of weight 20N pivoted at A.

If the system is in equilibrium, determine the weight W shown. (3marks)
Clockwise moments=anticlockwise moment
(40x3.5)+ (80x8)+(20x6) = Wx12
140+640+120 = 12W
W=900/12 =75N - A cemented floor feels cold to the feet, but a woolen carpet on the same floor feels warm. Explain this. (1mark)
The cemented floor is a good conductor of heat and therefore conducts heat away from the feet. - The diagram below shows an arrangement used to determine the upper fixed point of ungraduated thermometer.

- Why is the bulb of thermometer not dipped in the water? (1mark)
Upper fixed point is the temperature of pure steam. - Explain how the sensitivity of a thermometer can be improved. (1mark)
Making the bulb walls thinner.
- Why is the bulb of thermometer not dipped in the water? (1mark)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- State Archimedes’ principle . (1 mark)
When a body is partially or fully submerged in a fluid, it experiences an up thrust force equal to the weight of the fluid. - The figure shows a cube of side 2.0 m block and of mass 4,800 kg attached to the base of a tank containing paraffin of density 800 kgm-3 by means of an inextensible and light weight cable.

Determine:- The density of the block. (2marks)
Ρ=m/v = 4,800 = 600kg/m3
23 - The upthrust acting on the block. (3 marks)
Upthust = weight of fluid displaced
=ρgV = 800X10X23 =64,000N - The tension in the cable. (2 marks)
W=mg = 4,800X10 = 48,000N
T= U- W
=64,000-48,000 =16,000N - The cable is then released, and the block rises to the surface where it subsequently floats. Calculate the fraction of the block which is beneath the surface of the paraffin. (2 marks)
Up thrust= weight of the object = 64,000N
U =ρgV
V=U/ρg =64,000/800X10 = 8m3 (the block is just submerged.)
- The density of the block. (2marks)
- State Archimedes’ principle . (1 mark)
-
- Give two ways of increasing the boiling point of a liquid. (2 marks)
Increasing pressure
Addition of impurities - A lagged copper calorimeter of mass 0.8 kg contains 0.6 kg of water at 22.0° C. A metal nut of mass 0.4 kg is transferred quickly from an oven at 300°C to the calorimeter and a steady temperature of 52°C is reached by the water after stirring. Given that the specific heat capacity of copper is 400 Jkg-1K-1 and that of water is 4200 Jkg-1K-1, calculate:
- Heat gained by the calorimeter and water. (3 marks)
Q= mcϴ Q=Mcϴ
=0.8x400x30 = 0.6x4200x30
=9,600 J =75,600J
Total = 9,600 +75,600
=85,200J - Energy lost by the metal nut. (1 mark)
85,200J - The specific heat capacity of the material making the nut. (3 marks)
Q = mcϴ=85,200J
C = 85,200/0.4x 248 =85,200/99.2 =858.87J/kg/K
- Heat gained by the calorimeter and water. (3 marks)
- An electric kettle rated 120 V, 60 W is used to melt 20 g of ice at 0°C to water at 0°C in 112 seconds, calculate the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. (3 marks)
Pt =mLf
60x112 = 0.02Lf
Lf = 60x112 = 336,000J/kg
0.02
- Give two ways of increasing the boiling point of a liquid. (2 marks)
-
- A stone is thrown vertically upwards from the top of a tower 30m high, with an initial velocity of 20m/s. Determine:
- The time it takes to reach maximum height. (2mks)
u=20
V=0
a= -10
V=u +at t=V-U/a = 0-20/-10 = 2s - The total time which elapses before it hits the ground. (2mks)
U=20
S=30
a=10
t =?
V2=u2+2as = 202+(2x10x30) =400+600 =1,000
V =√1,000 =31.63m/s
V=u+at
31.63 = 20 +10t t= 31.63-20/10 = 1.163s +4s =5.163s
- The time it takes to reach maximum height. (2mks)
- A string of negligible mass has a bucket tied at the end. The string is 60cm long and the bucket has a mass of 45.0g. The bucket is swung horizontally making 6 revolutions per second.
Calculate- The angular velocity (2mks)
6rev/s =6x2Л rad/s =12Л rds/s - The angular acceleration (2mks)
a = Ꞷ2r
= 12Л2 x0.6 = 852.734rad/s2 - The tension on the string. (2mks)
T= mꞶ2r = 0.045x852.734 =38.37N
- The angular velocity (2mks)
- A stone is thrown vertically upwards from the top of a tower 30m high, with an initial velocity of 20m/s. Determine:
-
-
- During the construction of dams, the base of the dam is widened and curved. Explain.(2 marks)
Wider base counters the greater pressure at the bottom √
Curved wall ensures even distribution of the pressure due to water√. - A block of density 1.60 g/cm3 and measures 3.0cm by 5.0cm by 7.0cm was placed on the ground. Determine the difference between the maximum and minimum pressure that would be exerted on the ground by the block. (3 marks)
Pmax=F/Amin =ρVg/Amin Pmin =F/Amax =1.6x3x5x7x10x10,000 /35x1000
= 1.6x3x5x7x10x10,000/3/15x1000 =480Pa
= 1,120Pa
Difference =1,120-480 = 640Pa
- During the construction of dams, the base of the dam is widened and curved. Explain.(2 marks)
-
- State Newton’s second law of motion (1 mark)
The rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the resultant force and take place in the direction of the force. - A wooden block resting on a horizontal bench is given an initial velocity U so that it slides on the bench for a distance X before it stops. Various values of X are measured for different value of the initial velocity. The figure below shows a graph of U2 against X.

- Determine the slope S of the graph (3 marks)
m=25 – 10/10– 4 = 15/6 = 2.5 m/s2 - Determine the value of k given that U2= 20kX where k is a frictional constant for the surface (2marks)
m=20k, k = m/20 =2.5/20 = 0.125m/s2 - State with a reason what happens to the value of k when the roughness of the bench surface is reduced (2 marks)
K would reduce since friction has reduced
- Determine the slope S of the graph (3 marks)
- State Newton’s second law of motion (1 mark)
-
-
-
- State the kinetic theory of gases. (1 mark)
Gases are made of tiny particles which are in a continuous state of motion - State the reason why it is easier to separate water into drops than to separate a solid into smaller pieces. (1mark)
Cohesive forces of attraction between a liquid are weaker than those between solid particles.
- State the kinetic theory of gases. (1 mark)
-
- State Hooke’s law (1mark)
For a helical spring or any other elastic material, the extension produced is directly proportional to the applied force provided the elastic limit is not exceeded. - Two identical helical springs are connected in series. When a 50g mass is hang at the end of the springs, it produces an extension of 2.5 cm. Determine the extension produced by the same mass when the springs arc connected in parallel. (3marks)
K=F/e =0.5/0.0125 =40N/m
Kp=20/2 =20N/m
e=F/Kp = 0.5/20 =0.025m
- State Hooke’s law (1mark)
-
- State Boyle’s law. (1mark)
Volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to pressure provided the temperature is kept constant. - Draw a suitable set up that can be used to verify Charles’s law. (3marks)
Measurement of volume and temperature
Maintenance of constant volume
Workability.
- State Boyle’s law. (1mark)
-
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Nginda Girls Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
