INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper consists of two sections A and B.
- Non-programmable silent electronic calculators may be used.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY.

QUESTIONS
SECTION A: (25MARKS)
- State one property of image formed by a pinhole camera. (1mk)
- Other than density, state another factor that affect the speed of sound in a solid. (1mk)
- A radio wave has a frequency of 3MHz and travels with a velocity of 3.0 x108 m/s. Calculate its wavelength. (2mks)
- Draw a circuit diagram to show P-N junction diode in the reverse biased mode. (2mks)
- Explain why the walls of studio are padded with woolen materials (1mk)
-
- Define the term ‘’radioactivity’’ (1mk)
- The figure below shows a radioactive element placed in an evacuated glass chamber. The element produces alpha,beta and gamma emissions. The three emission pass through an electric field
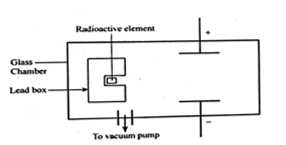
Complete the diagram to show the path of each of the emissions. (3mks)
- Explain why radio waves signals are easier to receive in a place surrounded by hills. (2mks)
- State two ways of minimizing electrical power losses during transmission of electric power. (2mks)
- Give a reason why convex mirror is preferred to a plane mirror for use as a driving mirror (1mk)
- State two ways of minimizing local action in a simple cell. (2mks)
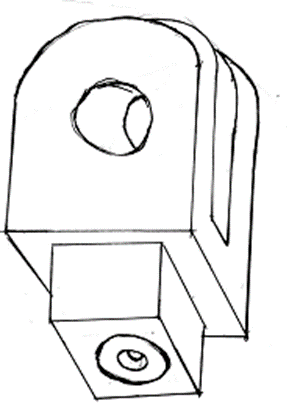
- The figure below shows a defect of vision being corrected by concave lens placed infront of the eye.
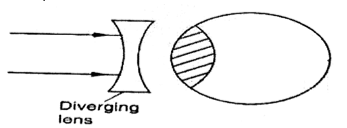
- Name the defect. (1mk)
- Complete the rays to show the effect of the lens. (2mks)
- State one use of microwaves . (1mk)
- Determine the speed of light in water given that the speed of light in air is 3.0 x 108m/s and the refractive index of water is 1.33 (3mks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section.
-
- State the Ohm’s law (1 mk)
- Give one factor that affect the resistance of a metallic conductor. (1mk)
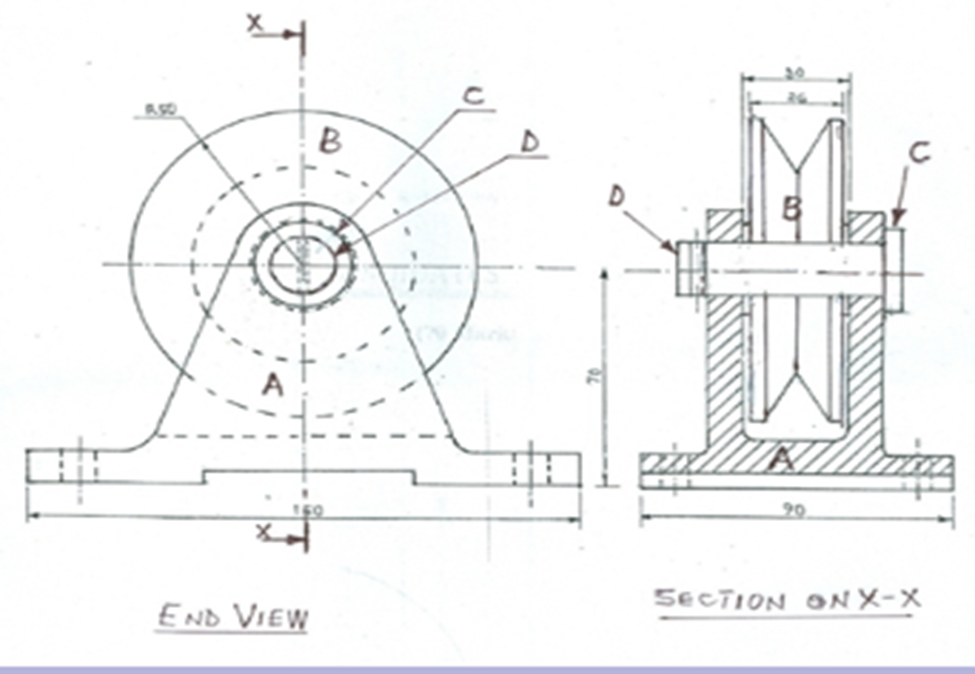
- The figure below shows three resistors connected to 12V supply of internal resistance of 0.2Ω.
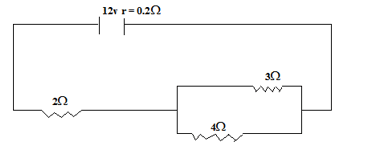
Calculate- The effective resistance. (3mks)
- The total current in the circuit. (2 mks)
-
- Define the term ‘ doping’ (1 mk)
- Briefly explain how silicon is used to make an p-type semi-conductor. (3 mks)
- State one application of a diode. (1mk)
-
- Why is the cap of the gold leaf electroscope circular? (1mk)
- A match stick is lit near the cap of a charged electroscope.State and explain the observation made. (2mks)
- State one factor that affects the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor.(1mk)
- A 10µF capacitor is charged to potential difference of 300V and isolated.It is then connected in parallel to a 5µF capacitor.Calculate:
- The resultant potential difference. (3mks)
- The total energy in the two capacitors after connection. (3mks)
-
- State the Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
- Give two factors that affect the magnitude of the induced em.f (2mks)
- A transformer with primary coil of 400 turns and secondary coil 200 turns is connected to 240 V a.c mains.
- Calculate the secondary voltage . (2mks)
- If the primary current is 3.0 A and secondary is 5.0A.Calculate the efficiency of the transformer (3mks)
- State how the following are minimized in a transformer . (2mks)
- Hysteresis loss
- Eddy currents
- Explain why the alternating voltage is used in a transformer. (1mk)
-
- Define the term ‘work function’ (1mk)
- Distinguish between thermionic emission and the photoelectric emission. (1mk)
- State one factor that determines the velocity of photoelectrons produced on the metal surface when light shine on it. (1mk)
- The threshold wavelength of a photoemissive surface is 5.55x10-7 m.(Take speed of light C=3.0x108 m/s,plancks constant h=6.63 x10-34 Js and mass of an electron Me=9.1x 10 -31kg.) Calculate:
- Its threshold frequency (3mks)
- The workfunction of the surface (3mks)
- The maximum speed with which a photoelectron is emitted if the frequency of the radiation is 6.2 x1014 Hz (3mks)
-
- State one similarity between cathode rays and X-rays. (1mk)
- Give two uses of X-rays in medicine (2mks)
- In a T.V set magnetic fields are preferred for use as deflection system instead of the electric field. Explain (1mk)
- The figure below represent a cathode ray oscilloscope (C.R.O).
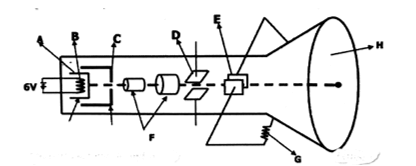
- Name the parts labelled A and C (2mks)
A…………………………………………
C………………………………………… - What is the function of part labelled D (1mk)
- Explain how electrons are produced in the C.R.O. (1mk)
- State the reason why the part labelled F has variable potential difference. (1mk)
- Give a reason why the tube is evacuated. (1mk)
- Name the parts labelled A and C (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A: (25MARKS)
- State one property of image formed by a pinhole camera. (1mk)
real
inverted/ upside down - Other than density, state another factor that affect the speed of sound in a solid (1mk)
temperature - A radio wave has a frequency of 3MHz and travels with a velocity of 3.0 x108 m/s.Calculate its wavelength. (2mks)
V=f/λ λ=3.0 x108/3.0x 106 =100m
λ =V/f - Draw a circuit diagram to show P-N junction diode in the reverse biased mode. (2mks)

- Explain why the walls of studio are padded with woolen materials (1mk)
Wollen materials absorb most of the energy of incident sound waves preventing reflection of sound waves (echoes) -
- Define the term ‘’radioactivity’’ (1mk)
It’s the spontaneous radom emission of particles from the nucleus of an unstable nuclide - The figure below shows a radioactive element placed in an evacuated glass chamber. The element produces alpha,beta and gamma emissions.The three emission pass through an electric field
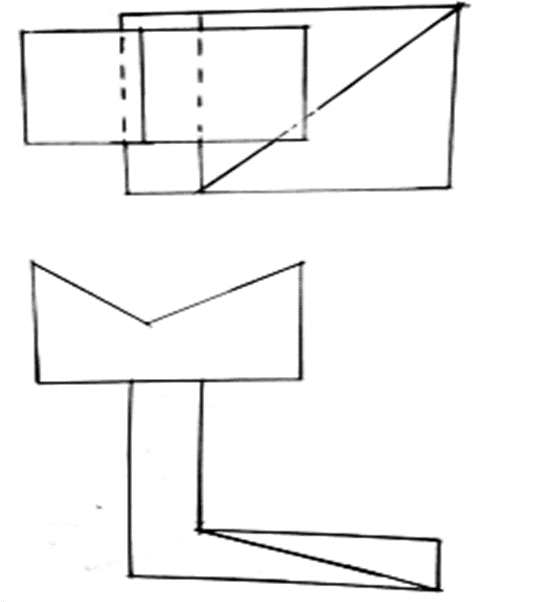
Complete the diagram to show the path of each of the emissions. (3mks)
- Define the term ‘’radioactivity’’ (1mk)
- Explain why radio waves signals are easier to receive in a place surrounded by hills. (2mks)
Radio waves have longer wavelengths hence easily diffracted around the hills. - State two ways of minimizing electrical power losses during transmission of electric power. (2mks)
Stepping up the voltage
Using thick wires - Give a reason why convex mirror is preferred to a plane mirror for use as a driving mirror (1mk)
Provide wide field of view
Forms upright images - State two ways of minimizing local action in a simple cell. (2mks)
- Use of pure zinc metal plate
- Coating zinc plate with mercury
- The figure below shows a defect of vision being corrected by concave lens placed infront of the eye.
- Name the defect. (1mk)
Shortsightedness/Myopia - Complete the rays to show the effect of the lens. (2mks)
- Name the defect. (1mk)
- State one use of microwaves. (1mk)
Cooking/heating in micro ovens
Radar communication - Determine the speed of light in water given that the speed of light in air is 3.0 x 108 m/s and the refractive index of water is 1.33 (3mks)
Refractive index =Velocity in air/ Velocity in water = 3.0 x 108/Vw = 1.33
Vw= 2.256 x 108m/s
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- State Ohms law (1mk)
States that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the p.d across it provided the temperature and other physical conditions are kept constant - Give one factor that affect the resistance of a metallic conductor. (1mk)
Temperature -Cross-sectional area of conductor
Length of the conductor - The figure below shows three resistors connected to 12v supply of internal resistance of 0.2Ω.
Calculate- The effective resistance. (3mks)
R= 4X3/(4+3)=2+0.2
=12/7+2.2= 3.914Ω - The total current in the circuit. (2 mks)
V=IR
I=V/R= 12/(3.914)= 3.066A
- The effective resistance. (3mks)
-
- Define the term ‘ doping’ (1 mk)
Addition of impurities to a pure semi-conductor to improve its electrical conductivity. - Briefly explain how silicon is used to make an p-type semi-conductor. (3 mks)
Silicon is doped with boron/trivalent atom.
three electrons bond covalently leaving a hole.
holes are the majority charge carriers and electrons the minority charge carriers. - State one application of a diode. (1mk)
Rectification.
- Define the term ‘ doping’ (1 mk)
- State Ohms law (1mk)
-
- Why is the cap of the gold leaf electroscope is circular? (1mk)
To ensure uniform distribution of charges - A match stick is lit near the cap of a charged electroscope.State and explain the observation made. (2mks)
The leaf of the electroscope falls/collapses/leaf divergence decreases.
The flame ionizes the air around the cap.The opposite charges to the one on the electroscope are attracted neutralizing the charges hence discharging. - State one factor that affects the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor. (1mk)
Area of overlap
Distance between the plates
Dielectric material between the plates - A 10µF capacitor is charged to potential difference of 300V and isolated.It is then connected in parallel to a 5µF capacitor.Calculate:
- The resultant potential difference. (3mks)
Q=CV (10x 10-6 +5x10-6)V2=3.0 x10-3
=10x 10-6 x300 1.5x10-5 xV2= 3.0x10-3
=3.0x 10-3C V2=(3.0x10-3)/(1.5x 10-5) = 200V
C1V2+C2V2=3.0x10-3 - The total energy in the two capacitors after connection. (3mks)
W=1/2 xCV2
W=1/2x 10x10-6x2002+ 1/2x5x10-6x 2002
=0.2+0.1 =0.3J
- The resultant potential difference. (3mks)
- Why is the cap of the gold leaf electroscope is circular? (1mk)
-
- State Farady’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
States that the magnitude of induced em.f is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage. - Give two factors that affect the magnitude of the induced em.f (2mks)
strength of the magnetic field
number of turns in the coil
rate of change of magnetic flux - A transformer with primary coil of 400 turns and secondary coil 200 turns is connected to 240 a.c mains.
- Calculate the secondary voltage . (2mks)
Ns/Np=Vs/Vp 400/200=Vs/240 Vs=400x240/200= 480V - If the primary current is 3.0 A and secondary is 5.0A.Calculate the efficiency of the transformer. (3mks)
Power output=240x3=720W Efficiency= (power output)/(power input) x100%
Power input =480x 5=2400W =720/2400x100% =30%
- Calculate the secondary voltage . (2mks)
- State how the following are minimized in a transformer. (2mks)
- Hysteresis loss - using a core of a soft magnetic material eg soft iron
- Eddy currents - laminating the core
- Explain why the alternating voltage is used in a transformer. (1mk)
It can stepped up or stepped down.
- State Farady’s law of electromagnetic induction. (1mk)
-
- Define the term ‘work function’ (1mk)
Minimum amount of energy of radiation/light required to dislodge an electron from the surface of a metal - Distinguish between thermionic emission and the photoelectric emission. (1mk)
Thermionic emission is the process of emitting electrons from the metal surface due to heat energy while photoelectric effect is the process of emitting electrons from the metal surface by electromagnetic radiation of sufficient frequency/energy. - State one factor that determines the velocity of photoelectrons produced on the metal surface when light shine on it. (1mk)
Frequency/wavelength/energy of the radiation - The threshold wavelength of a photoemissive surface is 5.55x10-7 m.(Take speed of light C=3.0x108 m/s,plancks constant h=6.63 x10-34 Js and mass of an electron Me=9.1x 10-31kg.) Calculate:
- Its threshold frequency (3mks)
fo=C/λO fo=(3.0x108)/(5.55x10-7) fo=5.405 x1014Hz - The workfunction of the surface (3mks)
Wo =hfo
=6.63x10-34 x 5.405x1014
=3.584 x10-19 J
- Its threshold frequency (3mks)
- The maximum speed with which a photoelectron is emitted if the frequency of the radiation is 6.2 x1014 Hz (3mks)
hf=hfo +1/2MeV2 1/2MeV2=(6.63x10-34x6.2x1014) -3.584x10-19=5.266x10-20J
1/2MeV2=hf –hfo V= √(5.266X10-20X2)/(9.1X10-31) =3.402X105m/s
- Define the term ‘work function’ (1mk)
-
- State one similarity between cathode rays and X-rays. (1mk)
Both travel in straight line at the speed of light. - Give two uses of X-rays in medicine (2mks)
Sterilize surgical equipments
Killing cancerous cells/radiotherapy
Radiography - In a T.V set magnetic fields are preferred for use as deflection system instead of the electric field. Explain (1mk)
Magnetic fields provide a wider deflection compared to electric fields. - The figure below represent a cathode ray oscilloscope (C.R.O).
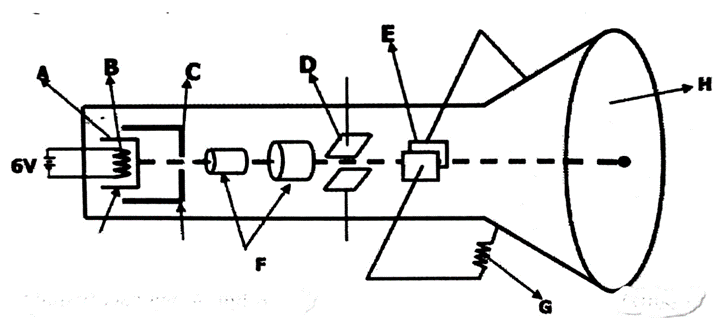
- Name the parts labelled A and C (2mks)
A-Cathode
C-Grid - What is the function of part labelled D (1mk)
used for vertical deflection of the electron beam - Explain how electrons are produced. (1mk)
Thermionic emission-when the cathode is heated electrons on its surface gain enough energy to enable them break loose from the force of attraction from the nuclei./the filament heats up the cathode, causing the electrons to boil off or be emitted from surface. - State the reason why the part labelled F has variable potential difference. (1mk)
To focus/converge the electron beam on the screen. - Give a reason why the tube is evacuated. (1mk)
To prevent electrons from losing energy due to collision with air particles.
- Name the parts labelled A and C (2mks)
- State one similarity between cathode rays and X-rays. (1mk)
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Nginda Girls Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
