INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- The paper consists of two section A and B
- Answer all question in section A
- In section B answer question SIX and any other TWO questions

QUESTIONS
SECTION A: ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. 25 MARKS
-
- Give two types of environments. [2marks]
- State three major branches of practical geography. [3marks]
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate. [2marks]
- Give three benefits of humidity in the atmosphere. [3marks]
- Study the diagram below and answer questions that follow
.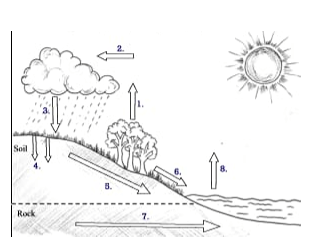
- Identify the process labeled 3 and 6. [2marks]
- State the force that is responsible for process 5. [1mark]
- Highlight two factors that influence process 4. [2marks]
-
- Give two causes of river rejuvenation. [2marks]
- Identify three features that result from river rejuvenation. [3marks]
- The diagram below shows some features of wind deposition. Study it to answer questions that follows
- Identify part marked K, L and M [ 3marks]
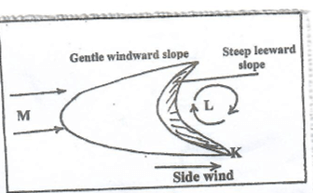
- State two factors that influence deposition of materials by wind in deserts. [2marks]
- Identify part marked K, L and M [ 3marks]
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of KISUMU EAST 1: 50000 [SHEET 116/2] provided to answer the following questions.
-
- Apart from the type of map you are using state any other two types of maps. [2marks]
- Identify two vegetation in the area covered by the map [2marks)
- Name two methods used to represent relief in the area covered by the map. [2marks]
-
- In what hemisphere does Kisumu East lie? [1mark]
- Measure the distance of the section of railway line west of Easting 00 to Kisumu station, give your answer in kilometers. [2marks]
- Identify two forms of land transport in Kisumu east. [2marks]
-
- Describe relief of the area covered by the map. [3marks]
- Describe the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map [4marks]
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represent 20m draw a cross section along northing 98 from Easting 96 to Easting 02. [4marks]
On it mark and label the following. [3marks]
River Nyangori
Dry weather road
Steep slope.
-
-
- Define the karst scenery. [2mark]
- Explain three factors that influence the formation of features in limestone area. [6marks]
- Give three reasons why there are few settlements in the karst landscape. [3marks]
- Describe how the following features are formed.
- Grikes and Clints. [4marks]
- Swallow holes. [4marks]
- You are supposed to carry out a field study of an area eroded by underground water.
- Give three reasons why you would need a working schedule. [3marks]
- Name two erosional features you are likely to identify during the study. [2marks]
- State three recommendations that you could make from your study to assist the local community to rehabilitate the eroded area. [3marks]
- Define the karst scenery. [2mark]
-
-
- Define the term earthquakes. [1mark]
- State three types of earthquakes depending on the depth of focus. [3marks]
- Differentiate between the intensity and magnitude of an earthquake. [2marks]
- Highlight three causes of vulcanicity. [3marks]
- State two types of magma. [2marrks]
- State three factors that influence the shape and type of volcanic features formed. [3marks]
- Describe how hot springs are formed. [5marks]
- Explain three ways in which volcanic features positively influence human activities. [6marks]
-
-
- Different between derived and cultivated vegetation. [2marks]
- Explain how the following factors influence vegetation distribution in Kenya.
- Living organism. [2marks]
- Precipitation. [2marks]
- The map below shows the globe distribution of vegetation. Study and use it to answer the questions that follow.
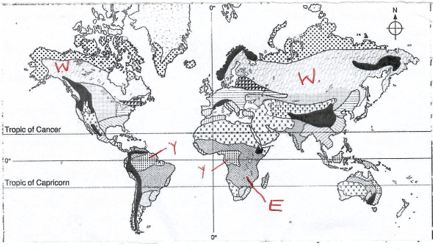
- Identify the vegetation labelled, W and Y [2marks]
- Describe the adaptive characteristics of the vegetation labelled E on the map. [6marks]
- Your class is planning to undertake a field study on vegetation in Mt. Kenya Forest`,
- State four preparations you would carry out. [4marks]
- Give three sampling techniques you would use. [3marks]
- Identify four problems you are likely to encounter during the actual field study. [4marks]
-
-
- what is continental shelf? [2marks]
- State two characteristics of the continental shelf. [2marks]
-
- state two types of islands. [2marks]
- Give three sources of ocean salts. [3marks]
- Give two reasons why water salinity is lower in areas around the equator seas than further away in the tropics. [2marks]
-
- Give two types of tides. [2marks]
- Using a well labelled diagram, describe how a wave break. [4marks]
- Use the diagram below to answer questions that follow.
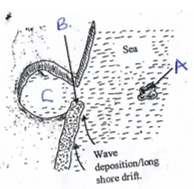
- identify the parts labeled. A, B and C. [3marks]
- Your class carried out a field study on the coastal landforms
- State two features of lowland submerged coasts that you identified. [2marks]
- Give three reasons why you needed a route map. [3marks]
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A: ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. 25 MARKS
-
- Give two types of environment. . [ 2marks]
- Physical environment.
- Human environment.
- State three major branches of practical geography. [3marks]
- Statistical methods
- Maps and map work
- Field work
- Photography interpretation
- Give two types of environment. . [ 2marks]
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate [2marks]
- Weather is the state of the atmosphere of a given place over a short period of time WHILE climate is average weather conditions of a place recorded over a long period of time.
- Give three benefits of humidity in the atmosphere [3marks]
- Regulation of temperature in the atmosphere
- helps in the development of storms in the atmosphere.
- It indicates the potential of the atmosphere to hold moisture and the formation of precipitation.
- Helps in regulation of human body temperature
- Differentiate between weather and climate [2marks]
- Study the diagram below and answer questions that follow.
- Identify the process labeled 3 and 6. [2marks]
3------ Precipitation. /rainfall
6-------- Surface run-off. - State the force that is responsible for process 5. [1mark]
- Force of gravity/ gravitational force.
- Highlight two factors that influence process 4. [2marks]
- Amount of water already in the soil.
- Porosity and the structure of the soil
- The type of the soil.
- The amount and seasonal changes in the vegetation cover
- Identify the process labeled 3 and 6. [2marks]
-
- Give two causes of river rejuvenation. [2marks]
- Unequal regional subsidence of the land along the river.
- Vertical erosion by the river may expose resistant rock which creates Knick points hence renewing its erosive activity.
- Regional uplift which increase the gradient along the river course and makes the river renew its erosive activity.
- Fall in the sea level
- Increased discharge due to river capture or precipitation
- change in the rock resistance from hard bedrock to soft bedrock
- Identify three features that result from river rejuvenation. [3marks]
- Rejuvenation gorges.
- Rejuvenation terraces
- Abandoned meanders. /meander score
- Incised/ingrown/entrenched meanders.
- Knick points/rejuvenation head
- Give two causes of river rejuvenation. [2marks]
- The diagram below shows some features of wind deposition. Study it to answer questions that follows
- Identify part marked.
- K Horn 1mark
- L Eddy currents 1mark
- M Prevailing winds 1 mark
- State two factors that influence deposition of materials by wind in deserts. [2marks]
- Vegetation cover /obstacles on desert surface
- The strength and direction of wind
- The nature of desert surface.
- The weight of the load carried.
- Changes / variation in weather conditions.
- Identify part marked.
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of KISUMU EAST 1: 50000 [SHEET 116/2] provided to answer the following questions.
-
- Apart from the type of map you are using state any other two types of maps. [2marks]
- Sketch Map
- Atlas maps
- Identify two vegetation in the area covered by the map (2mks)
- Scattered trees
- Papyrus swamp vegetation
- Scrub vegetation
- Name two methods used to represent relief in the area covered by the map. [2marks]
- Use of contours.
- Use of trigonometric stations.
- Rock outcrop/symbols.
- Apart from the type of map you are using state any other two types of maps. [2marks]
-
- In what hemisphere does Kisumu East lie? [1mark]
- Southern hemisphere
- Measure the distance of the section of railway line west of Easting 00 to Kisumu station, give your answer in kilometers. [2marks]
6.6 - ± 0.1 km - Identify two forms of land transport in Kisumu east. [2marks]
- Road transport.
- Railway transport.
- In what hemisphere does Kisumu East lie? [1mark]
-
- Describe relief of the area covered by the map. [ 3marks]
- There is a col to the northern part of the area covered by the map.
- The northern part of the area covered by the map is steeply sloping as indicated by closely
Packed contours. - The east is a plain / Kano plain /plateau
- The lowest area is to the south west /which is about 1140m above sea level.
- The highest is Nyando escarpment /1852m above sea level.
- The is numerous river valley these have steep of the highlands are broad in the lowland.
- There is a basin to the south western part of the area covered by the map.
- Describe the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map [4marks]
- There is dense settlement in Kisumu town e.g. this may be due to access of social amenities.
- There is linear settlement in the plantation this could be due to government policy.
- There is linear settlement along some roads for easy movement.
- The land immediate to the west of the escarpment has many settlements because it is gently sloping / undulating
- Hills has few settlements on the North eastern side because the land has steep slopes.
- There is dispersed settlement in Nyando escarpment due to rugged terrain/steep slopes
- Describe relief of the area covered by the map. [ 3marks]
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm represent 20m draw a cross section along northing 98 from Easting 96 to Easting 02. [4marks]
On it mark and label the following. [3marks]
River Nyangori
Dry weather road
Steep slope.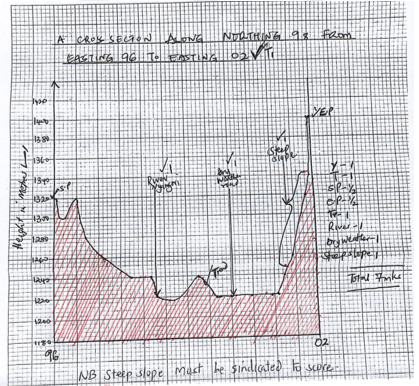
-
-
- Define the karst scenery. [2mark]
- is a landscape of chalk /limestone/dolomite rock made of surface and underground features formed by the carbonation /solution process.
- Explain three factors that influence the formation of features in limestone area. [6marks]
- Deep water table far below the limestone rock surface to allow the formation of the karst features.
- Presence of thick limestone rocks to allow solubility by rain water.
- Hard and well jointed rocks to allow water to percolate for carbonation process to take place.
- Hot-humid /high temperatures and moderate rainfall to facilitate chemical weathering
- Give 3 reasons why there are few settlements in the karst landscape. [3marks]
- Areas are rocky hence unsuitable for human activities.
- Have thin soils which is unsuitable for agriculture.
- Have rugged surfaces hence unsuitable for settlement.
- Have inadequate water supply as most water sink underground.
- Have poor vegetation cover.
- Explain three factors that influence the formation of features in limestone area. [6marks]
- is a landscape of chalk /limestone/dolomite rock made of surface and underground features formed by the carbonation /solution process.
- Describe how the following features are formed.
- Grikes and Clints. [4marks]
- Rain water absorbs carbon IV oxide to form weak carbonic acid.
- The water percolates through the joints in the limestone rock and react with limestone to form a solution of calcium bi-carbonate.
- The rock is dissolved which enlarge the joints.
- The joints become deeper and wider to form gullies/ valleys called grikes.
- The gullies are separated by ridges called clints. 4marks.
- Swallow holes. [4marks]
- Rain water absorbs carbon IV oxide to form weak carbonic acid.
- The water percolates through the joints in limestone rocks and react with calcium bi-carbonate
- The solution process enlarges the vertical joints to form deep vertical holes from the surface into the underground caves/caverns called sink holes.
- Rain /river water may disappear underground through this hole to form a swallow hole. 4 marks.
- Grikes and Clints. [4marks]
- You are supposed to carry out a field study of an area eroded by underground water.
- Give three reasons why you would need a working schedule. [3marks]
- To ensure all planned activities are carried out/ no important area is forgotten
- To save on time programmed for the field study.
- To ensure well-coordinated field study among students.
- To avoid being distracted to unintended activities
- to ensure the objectives of the filed study are achieved.
- To ensure no important area is forgotten
- Name two erosional features you are likely to identify during the study. [2marks]
- Expose rocks/inselbergs/tors
- Ridges/clints
- Gullies/wadis/grikes/dry valleys
- State three recommendations that you could make from your study to assist the local community to rehabilitate the eroded area. [3marks]
- Building gabions
- Constructing terraces
- Planting tress / planting cover crops
- Adapting farming methods that allow soil conservation/contour ploughing /strip cropping 3 marks
- Give three reasons why you would need a working schedule. [3marks]
- Define the karst scenery. [2mark]
-
- Define the term earthquakes. [1mark]
- An earthquake is a sudden and rapid earth movements which cause vibrations in the rocks of the earth’s crust./It is the trembling and shaking of the crustal rocks caused by shock waves originating from the interior of the earth.
- State three types of earthquakes depending on the depth of focus. [3marks]
- Shallow focus earthquakes.
- Intermediate focus earthquakes.
- Deep focus earthquakes.
- Differentiate between the intensity and magnitude of an earthquake and give a scale used to measure each. [2marks]
- intensity of an earthquake is how strong or hard an earthquake shakes the ground and it is measured using the rossi-forrel /Mercalli scale WHILE magnitude is the amount of energy given off by an earthquake and is measured using the Richter scale . ans. 2marks.
- Define the term earthquakes. [1mark]
-
- Highlight three causes of vulcanicity. [3marks]
- High pressure in the interior /mantle layer which released by earth movements.
- High interior temperatures cause the solid rocks to melt and change into molten materials.
- Underground water coming into contact with hot magma /hot volcanic rocks –water is heated and change into gaseous under pressure to form steam jets /geysers and hot springs.
- Earth movements /folding /faulting/earthquakes which cause rocks to crack forming fissures, joints and vents /pipes through which molten material or magma comes out.
- State two types of magma. [2marrks]
- Acidic /viscous magma
- Basic magma
- Ultra-basic magma
- Intermediate magma
- State three factors that influence the shape and type of volcanic features formed. [3marks]
- Type of magma/lava /viscosity of magma or lava.
- Nature of eruption – quiet or violent eruption
- Type of opening used by magma such as fissures, pipes/ vents.
- Highlight three causes of vulcanicity. [3marks]
- Describe how hot springs are formed. [5marks]
- Rain water percolates through cracks /fissures and comes into contact with hot volcanic rocks /hot magma underground.
- The water is heated to form steam /vapour which expands and collect in underground chambers /sumps which contain water.
- The water in the sumps get superheated by the hot steam.
- The heated water builds up pressure that force the steam upwards through the cracks and joints/faults.
- The steam heats the ground water near the surface and force it to flow out to the surface.
- The steam near the ground surface may cool and condense to make hot water flowing out on the surface.
- The warm / hot water flows out on the surface quietly and continuously to form hot springs. 5 marks.
- Explain three ways in which volcanic features positively influence human activities. [6marks]
- Volcanic rocks weather and form well drained volcanic soils which support agriculture.
- Volcanic mountains /highlands attract high rainfall on the wind ward side which is a source of rivers that provide water for domestic use.
- Volcanic mts /highlands attract high relief rainfall that encourage agriculture and settlement
- Volcanic mts. influence formation of relief rainfall that supports forests bon mt. slopes which are exploited for timber /building and construction materials.
- Some volcanic rocks are important building and construction materials promoting industry e.g., trachyte.
- Volcanic mts. Highlands modify temperatures and make it attractive to human settlement and agricultural activities.
- Steam jets and geysers provide suitable sites for generation of geothermal power.
- Volcanic eruption from pipes with valuable minerals which are mined and sold to generate income /foreign exchange /industrial raw materials
-
- Different between derived and cultivated vegetation. [2marks]
- Derived vegetation is a plant cover that grows in an area after natural vegetation is interfered with human beings/man WHILE planted /cultivated vegetation is a plant cover which has been planted by man.
- Explain how the following factors influence vegetation distribution in Kenya.
- Living organism. [2marks]
- Bacteria/earthworms and burrowing animals improve soil fertility resulting into more vegetation growth
- Insects and birds pollinate plants enhancing their propagation.
- Bacteria and insects cause plant diseases resulting in death of some plants e.g., aphids which affect cypress in the 80s
- Large herds of wild animals can destroy vegetation through overgrazing and lead to loss of natural vegetation leading to growth of derived vegetation.
- Human beings / man, afforestation efforts by man leads to creation of planted forest /vegetation.
- Precipitation. [2marks]
- there is a high number of trees in areas with high precipitation and these areas are dominated by forest with broad leaved tress to help increase the rate of transpiration.
- Areas with moderate rainfall are dominated by grasslands.
- Areas with low rainfall have scanty vegetation with thin leaves or fleshy stems.
- High precipitation supports luxuriant growth of vegetation/ derived vegetation.
- Living organism. [2marks]
- The map below shows the globe distribution of vegetation. Study and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the vegetation labelled, W and Y [2marks]
Y ------------------------------------- Equatorial /tropical rain forest.
W--------------------------------------coniferous forest. - Describe the adaptive characteristics of the vegetation labelled E on the map. [6marks]
- The grass dries up in the dry season as a preservation measure against drought and quickly sprouts the onset of rains
- Most tress are thorny to protect them from browsing animals
- Most have long roots to tap underground water
- Most tress gave thin waxy leaves to reduce water loss through transpiration.
- Most tress are umbrella shaped to provide shade on the ground hence reduce water loss through evaporation
- Some tress such as baobab have thick fleshy stems to store water
- Some tress shed their leaves during the dry season to reduce water loss through evaporation.
- Identify the vegetation labelled, W and Y [2marks]
- Your class is planning to undertake a field study on vegetation in Mt. Kenya Forest`,
- State four preparations you would carry out. [4marks]
- seeking permission from the relevant authorities
- setting the objectives and hypothesis
- holding discussion on the topic of study
- Carrying out a pre- visit
- Reading more on the topic of study
- Prepare a working schedule
- Obtain a route map
- Gathering the relevant materials and tools for the field work etc.
- Give three sampling techniques you would use. [3marks]
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Systematic sampling
- Random sampling
- Identify four problems you are likely to encounter during the actual field study. [4marks]
- Attack by wild animals
- Presence of thick vegetation cover may hinder movement within the forest.
- Injuries from thorns
- Fatigue
- Adverse weather conditions I.e., heavy rainfall
- Difficulty in identifying types of vegetation
- State four preparations you would carry out. [4marks]
- Different between derived and cultivated vegetation. [2marks]
-
-
- what is continental shelf [2marks]
- It is the smooth, gently sloping platform which starts from the continental land mass into the ocean water and ends abruptly into the continental slope.
- State two characteristics of the continental shelf. [2marks]
- Gently sloping and fairly smooth surface.
- Shallow waters up to 180m deep.
- Most planktons which serve as food fish are found
- Narrow straight coasts but wide in indented or irregular coasts.
- Some have islands due to marine erosion and deposition.
- May have coral reefs.
- Has deposits of shingle, shells and mud.
- Some have deep valleys or canyons cut by river erosion or by faulting
- what is continental shelf [2marks]
-
- state two types of islands. [2marks]
- Continental islands
- Oceanic islands
- Coral islands
- Give three sources of ocean salts. [3marks]
- Run-off water carrying dissolved salts into the sea.
- Vulcanicity on the sea bed with the salts in magma being dissolved.
- Melt water with dissolved salts.
- Salty bed rocks dissolved by ocean water.
- Salts dissolved in rivers flowing into oceans.
- Give two reasons why water salinity is lower in areas around the equator seas than further away in the tropics. [2marks].
- Heavy rainfall resulting in many fresh water rivers that dilute salts in oceans.
- Lower evaporation due to high humidity in the atmosphere leading to lower salts concentration in water.
- state two types of islands. [2marks]
-
- Give two types of tides. [2marks]
- Perigean tides.
- Apogean tides.
- Spring tides.
- Neap tides.
- Describe using a diagram how a wave break. [4marks]
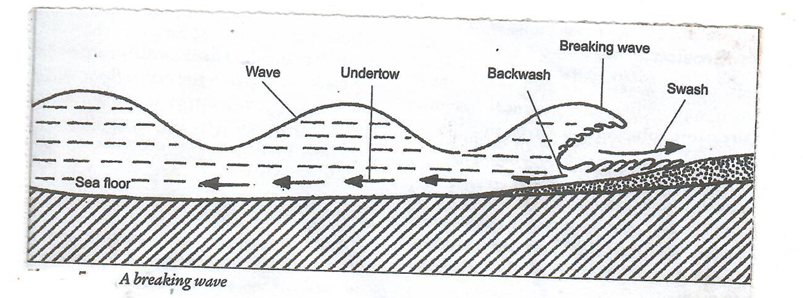
- As waves nears the coastal land the water of the shore becomes shallow.
- There is increased friction between the water and the sea bed.
- This makes the height of the wave to reduce.
- The crest of the wave surges forward suddenly which is called wave breaking.
DIAGRAM- 2marks
EXPLANATION- 2marks
- Give two types of tides. [2marks]
- Use the diagram below to answer questions that follow.
- identify the parts labeled.
- A An island [1mark]
- B A spit [1 mark]
- C Bay [1mark]
- identify the parts labeled.
- Your class carried out a field study on the coastal landforms
- State two features of lowland submerged coasts that you identified. [2marks]
- Estuaries /estuarine coasts
- Broad continental shelf
- Fiords/fjords coast.
- Give three reasons why you needed a route map. [3marks]
- To help identify the direction to follow / to avoid getting lost.
- To help in the preparation of a working schedule.
- To help identify the location of features during the study.
- To estimate the time the filed study is likely to take.
- To help estimate the cost of study.
- State two features of lowland submerged coasts that you identified. [2marks]
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Nginda Girls Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
