INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- The paper consists of two section A and B
- Answer all question in section A
- In section B answer question SIX and any other TWO questions

QUESTIONS
SECTION A: Answer all questions in this section.25MKS
-
- State two formations in which mineral ores occurs. (2mks)
- Give three reasons why coal resource in the Mui basin Kitui County has not been commercially exploited. (3mks)
-
- What is mixed farming? (2mks)
- Give three advantages of mixed farming. (3mks)
-
- What is energy crisis. (2marks)
- Identify three causes of energy crisis. (3marks)
-
- Name two forest reserves in Kenya. (2marks)
- State three characteristics of Equatorial rainforests. (3marks)
-
- State three human factors favoring tourism in Switzerland. (3marks)
- Define eco-tourism. (2marks)
SECTION B (75MARKS)
Answer question SIX and any other TWO questions
- The table below shows the various modes of transport used by tourists visiting Kenya between
the years 2006 and 2009. Use it to answer the following questions.
Mode of transport
No. of tourists.
Road
2006
2007
2008
2009
100,000
50,000
150,000
200,000
Air
600,000
650,000
700,000
800,000
Water
200,000
150,000
100,000
50,000
-
- state two reasons why tourists preferred air transport over the other modes of transport over the period. (2marks)
- Calculate the percentage increase in the number of tourists between the year 2008 and 2009. (3marks)
- Using a scale of 1cm to represent 100 000 tourists, draw a compound bar graph to represent the number of tourists who visited Kenya using the different mode of transport. (9marks)
-
- Explain three roles played by transport in the economy of Kenya. (6marks)
- Name one high way created in Africa to ease transport across the continent. (1mark)
- Form four students from Kibutha high school visited Kisumu airport for a field study.
- Identify two methods they used to record their data. (2marks)
- Give two follow up activities they engaged in. (2marks)
-
-
-
- What is land reclamation. (1mark)
- State five benefits which Kenya derives from irrigation farming? (5marks)
- Explain three factors that led to the successful establishment of Perkerra irrigation scheme. (6marks)
- Give four problems facing the perkerra irrigation scheme. (4marks)
- Name three crops grown under irrigation in perkerra. (3marks)
- Explain three reasons why horticulture is more developed in the Netherlands than Kenya. (6marks)
-
-
-
- What is industrialization? (2 marks)
- State three reasons why some industries consider regular supply of water as the main reason for their location. (3 marks)
- Outline four similarities between Jua Kali industry in Kenya and cottage industry in India. (4mks)
- Explain three factors that have influenced the location of iron and steel industry in the Ruhr region of Germany in the 19th century. (6 marks)
- You intend to carry out a field study of a heavy manufacturing industry;
- State three effects of the industry on the environment you are likely to observe (3 marks)
- Design a working schedule you would use during the day of study (4 marks)
- State three reasons why it is important to prepare a working schedule for the study. (3 marks)
-
-
-
- What is unfavorable balance of trade. (2marks)
- Outline five measures a country can adopt to reduce unfavorable balance of trade. (5marks)
- Explain five benefits that Kenya derives from participating in international trade. (10marks)
-
- State three non-agricultural exports from Kenya. (3marks)
- State five problems facing developing countries in international trade. (5marks)
-
-
-
- What is an environmental hazard? (1mark)
- Apart from floods list three other environmental hazard. (3marks)
- Explain four ways in which air pollution affects the environment. (8marks)
- Explain four incidents that may lead to noise pollution in urban areas. (8marks)
- Students from Kangema carried out a field study on floods at Kano plains.
- State two objectives for their study. (2marks)
- State three ways in which residents of Kano plains are affected by floods that students observed. (3marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A.(25 MARKS)
-
- State two formations in which mineral ores occurs (2mks)
- Some occur as alluvial / placer deposits.
- Some occur in beds/seams
- Some occurs as weathering products
- Some as veins and lodes
- Give three reasons why coal resource in the Mui basin Kitui County has not been commercially exploited. (3mks)
- Inadequate capital to invest in coal mining.
- The low coal demand in the local market
- The coal reserves are found far from the potential market; the remote location of the resource.
- Availability of cheaper alternative sources of energy e.g. oil, electricity.
- Poor quality of coal
- Low quantities of coal reserves.
- Disputes over compensation/resettlement of affected citizens.
- State two formations in which mineral ores occurs (2mks)
-
- What is mixed farming? (2mks)
- Type of agriculture where crops are grown and livestock kept in the same farm.
- Give three advantages of mixed farming. (3mks)
- It provides security to the farmer, if crops fail, livestock sustains the farmer.
- Some of the crops grown are fed to the animals
- Animals provide organic manure to enrich the soil.
- What is mixed farming? (2mks)
-
- Define energy crisis 2marks
- A situation where demand for oil and its products outstrips the supply and as result the prices goes up as well as the prices of all other products
- Identify three causes of energy crisis. (3marks)
- Over-reliance on petroleum and its products.
- High oil prices due to sharp rise in oil demand.
- Economic and political sanctions
- Uncertainties in oil supplies to consumers.
- Rapid depletion of oil reserves.
- Conflict in the Middle East especially between Israel and Palestine.
- Define energy crisis 2marks
-
- Name two forest reserves in Kenya. (3marks)
- Arabuko sokoke
- Shimba hills
- Mt. Kenya forest
- Kakamega forest
- Mau forest
- Aberdare forest
- State three characteristics of Equatorial rainforests. (3marks)
- Closely set trees with three distinct canopies.
- There is less undergrowth on the forest floor due to light being obstructed by canopies.
- Trees take long time to grow.
- Trees have large trunks with buttress roots (radiating wall like roots).
- Trees have broad leaves to increase the surface area for efficient transpiration due to high precipitation.
- There is varied number of plants species over a small portion.
- Trees are tall, have smooth stems and straight trunks.
- Some trees are evergreen shedding a few leaves at a time while others
- Name two forest reserves in Kenya. (3marks)
-
- State three human factors favoring tourism in Switzerland (3marks)
- It has Excellent infrastructural facilities with a well-developed network of roads, railways, electrified rail cars and cable cars which enable tourists to travel easily to centres of attraction.
- The policy of neutrality which makes people from all the parts of the world to feel at home while there.
- Diversity of languages of Europe are spoken which makes it possible for tourists to get excellent services in the country.
- Define eco-tourism. (2marks)
- Environmentally friendly tourism or tourism emphasizing environmental conservation where tourists and local communities are involved in enjoying nature as well as conserving it.
- State three human factors favoring tourism in Switzerland (3marks)
SECTION B: (75 MARKS)
-
-
- state two reasons why tourists preferred air transport over the other modes of transport over the period.(2marks)
- It is faster over long distances
- It is more comfortable over long distances
- It experiences less traffic congestion
- operates on fixed time schedule hence travelers can plan their journeys in advance. (2marks)
- Calculate the percentage increase in the number of tourists between the years 2008 and 2009.
1,050,000 – 950,000 = 100,000
100,000/ x 100
950,000
= 10.526%/10.53%/10.5% - Using a scale of 1cm to represent 100 000 Draw a compound bar graph to represent the data.
Mode of transport
No. of tourists.
Air
2006
2007
2008
2009
600 000
650 000
700 000
800 000
Water
200 000
15000
100 000
50 000
Road
100 000
50 000
150 000
200 000
- state two reasons why tourists preferred air transport over the other modes of transport over the period.(2marks)
-
COMPOUND BAR GRAPPH SHOWING THE NUMBER OF TOURIST WHO VISITED KENYA BETWEEN 2006 AND 2009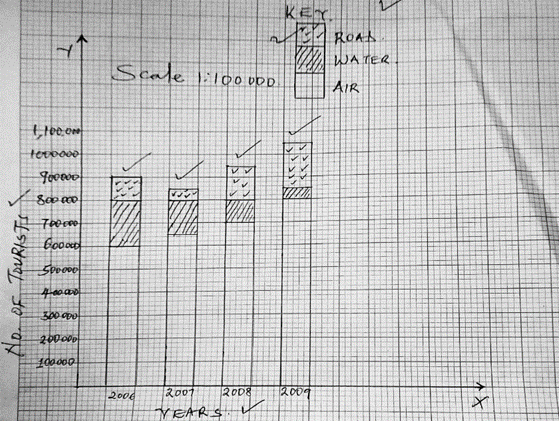
- TITLE – 1mk
- KEY- 1mk
- Y and X axis- 2mks
- BARS- 1mk each- Total 4mks
- SCALES- 1mk
-
- Explain any three roles played by transport in the economy of Kenya. (6marks)
- Influences the movement of raw material/finished products affecting location/distribution of economic activities/exploitation of resources.
- Makes movement of goods/services possible hence expanding the market.
- Creates employment opportunities reducing unemployment/improving the living standards.
- Enables the movement of tourists to/in exchange used to import goods into the country.
- Earns revenue to the government through taxation which is used to develop the country/put up facilities/ other sectors of economy.
- Leads to urbanization.
- Name one highway created in Africa to ease transport across the continent. (1mark)
- Great North Road
- Trans-African highway
- Trans-Saharan highway
- Trans Africa Tripoli – l
- Tripoli - Lagos
- Dakar – Ndjamena
- Lagos – Nouakchott
- Explain any three roles played by transport in the economy of Kenya. (6marks)
- Form four students from Buchenya secondary school visited Kisumu Airport for a field study.
- Identify two methods they used to record their data. (2marks)
- Note taking
- Video recording
- Filling questionnaires
- Taking photographs.
- Tallying
- Sketching.
- Give two follow up activities they engaged in. (2marks)
- Compile notes
- Discuss findings.
- Draw better diagrams/maps
- Display photographs.
- Making models.
- Identify two methods they used to record their data. (2marks)
-
-
-
- Two methods of reclamation. (2marks)
- Irrigation
- Tsetse fly control
- Planting of trees / afforestation
- Flood control
- Two methods of swamp drainage. (2marks)
- Construction of drainage pipes.
- Digging open ditches / canals.
- Pumping out water.
- Two methods of reclamation. (2marks)
-
- Two rivers that supply water to Mwea. (2marks)
- Thiba River
- Nyamindi river
- Murubaru river.
- Factors influencing establishment of Mwea irrigation scheme. (8marks)
Topography- The gently sloping /undulating land makes it possible for water to flow by gravity onto / out of the irrigated land.
- The gently sloping land allows for mechanization which allows large areas to be put under cultivation.
Soils - Presence of black cotton soil which retains water for a long time suitable for cultivation of rice.
Population - The area was originally sparsely populated which enabled large areas to be put under cultivation üü / very few people were displaced thus it as cheaper to start the scheme.
Government policy - There was need to keep political detainees busy / use them to provide free labour. This made the colonial government to set up Mwea where scheme there was a large detention camp.
- Two rivers that supply water to Mwea. (2marks)
-
- Three areas of Zuider zee project. 3marks
- North Eastern folder
- South Flavoland
- East flavoland
- Markerward
- Wie ringer meer polder.
- Four differences between land reclamation in Kenya and Netherlands. (8marks)
- In Kenya the reclaimed land is relatively small while areas reclaimed in the Netherlands are large.
- In Kenya irrigation is used as a means of reclaiming dry areas while irrigation in the Netherlands is used to lower salinity of the soil in reclaimed lands.
- In Kenya simple methods like digging canals ditches to drain water from the land while in the Netherlands highly advanced methods like draining land from the sea/ creating a polder are used.
- In Kenya dykes are used to control water floods while in the Netherlands dykes protect the reclaimed land from invasion by the sea.
- In Kenya land is reclaimed from marginal areas and swamps while in the Netherlands it is from the sea.
- Drought resistant crops are planted in marginal areas while in the Netherlands hardy crops lie oats, barley is planted in the polders.
- In Kenya there is low market for irrigated crops while in the Netherlands there is a large market for irrigated crops.
- Three areas of Zuider zee project. 3marks
-
-
- What is industrialization? (2marks)
- It is the process / pace at which a country / community sets / establishes industry. It is the process of change from primary to secondary to tertiary production. It is the level of industrial production.
- State three reasons why some industries consider regular supply of water as the main reason for their location. (3marks)
- Water is used for constant cooling of the machines to avoid damage by heat.
- In some industries, water is used for cleaning the raw materials/ to improve the quality of the final products/coffee industry.
- Some industries use water as a cheap means of transport.
- Some industries require water as a medium through which they dispose of their waste products.
- In coffee factories, water is used for grading coffee berries.
- Some industries use water to provide power to turn their machines.
- Some industries use water as the main raw materials / brewing industry / soft drink industry.
- What is industrialization? (2marks)
- Outline four similarities between Jua kali industry in Kenya and cottage industry in India. (4marks)
- Both are operated by small individuals / groups
- Sometimes they are both practiced as part time
- Both of their products are sold in the local market / some can be exported
- They both use simple equipment.
- They both use basic / simple skills in craft.
- They both use local / recycled raw materials.
- They both require little capital investment to begin.
- They are both widespread in the country / in urban centers.
- They are mostly operated in open sheds / homes. / Simple enclosure.
- They are both labour intensive.
- In most cases, they are both owned by families.
- Explain three factors that have influenced the location of iron and steel industry in the Ruhr region of Germany in the 19th century. (6marks)
- Presence of other industries in the region such as food and textile provided industrial inertia.
- Availability of coal / iron ore / limestone from within the region / Rhine Valley provided raw materials needed in the industry.
- The Dense and affluent population in Western Europe / Germany provided ready market for iron and steel.
- Rich merchants and companies such as Kotile AC/ Krupp group provided capital for the establishment / development / of industries.
- Presence of negotiable rivers such as Rhine/ Ruhr / Lipper /Wupper / Escher provided cheap means of transport for the bulky raw materials / finished products.
- Coal from the Ruhr region / imported petroleum provided power required in the industry.
- River Rhine / Ruhr / Lipper / Wupper / Escher provided water required for cooling machines in the industry / raw materials in the industry.
- The local population had acquired skills in the iron working / availability of local skilled labor which formed the foundation of iron and steel industry.
- You intend to carry out a field study of a heavy manufacturing industry;
- State three effects of the industry on the environment you are likely to observe. (3marks)
- Smoke from chimneys polluting air / air pollution.
- Garbage heaps as a result of solid industrial waste polluting soil.
- Industrial discharge polluting water bodies / soil / biodiversity.
- A lot of noise causing noise pollution.
- Design a working schedule you would use during the day of study. 4marks
Time
Activity
8:00-8:10 AM
· Assemble equipment
8:10-8:20AM
· Depart for the area of study
8:20-10:00AM
· Arrive at the area of study
10:00-10:15 AM
· Report to the authorities
10:15-1:00 PM
· Embark on data collection
1:00-2:00 PM
· Break for lunch
2:00-4:00PM
· Resume on data collection and recording
4:00-4:05 PM
· Report back to the authorities
4:05-5:30 PM
· Departure to school
- State three reasons why it is important to prepare a working schedule for the study. (3marks)
- It gives ample / enough time to each activity so that no activity is forgotten.
- It provides the framework that guides the research team to work within the scope of the topic.
- It reduces the tendency to waste time forcing the research team to work within the allocated time.
- It provides the basis for evaluating the research while still in progress.
- It provides an estimate of the time required for the study.
- State three effects of the industry on the environment you are likely to observe. (3marks)
-
-
- What is unfavorable balance of trade (2marks)
- An economic situation where a country’s visible exports earn less than what the country pays for its visible imports/when a country spends more money to pay for imports than it earns from exports
- Outline five measures a country can adopt to reduce unfavorable balance of trade (5mks)
- Establish and protect import substitution industries
- Production of high-quality products to attract international market
- Diversification of industrial, agricultural and service industries
- Develop alternative sources of energy to reduce on heavy oil imports
- Restrict importation of luxurious commodities
- Expansion of market for local products abroad
- Economic integration to acquire trade partners to widen market for exports
- What is unfavorable balance of trade (2marks)
- Explain five benefits that Kenya derives for participating in international trade. (10marks)
- Disposal of surplus products by selling them to foreign
- Kenya earns foreign exchange from exporting products to other countries
- Kenya is able to import essential commodities e.g., machinery, medicine which are not produced locally
- Inter trade has helped Kenya to specialize in production for which its best suited e g cash crop farming
- International trade creates employment opportunities to traders and personal involved in trading activities
- The government of Kenya collects revenue e g trade license fee, custom duty from international trade
- Enables Kenya to acquire technology from foreign trading partners
- International trade makes Kenya to have friendly trade partners who often assist the country when in need
-
- State three non-agricultural exports from Kenya. (3marks)
- Soda ash
- Fluorspar
- Tourism/cash transfer/insurance
- State five problems facing the developing countries in international trade (5mks)
- Poor terms of trade due to their cheap primary exports compared to costly imports of finished products
- Overdependence on primary products which are at the mercy of natural factors e g weather
- Fluctuation of world prices for developing world export commodities negatively affecting their income and economy
- Stiff competition for world market and production of synthetic fibres
- Trade restricts imposed by developed countries negatively affect developing countries negatively affect developing countries
- Inadequate transport and communication facilities limit trade with other countries
- Smuggling of goods across borders denies the country revenue and traders opportunities for genuine business
- Political instability/insecurity in third world countries which hinder trade
- Low level of technology and productivity leading to limited international market for products
- Poor bargaining power on international trade issues which often leaves them disadvantaged against developed countries
- State three non-agricultural exports from Kenya. (3marks)
-
-
-
- what is an environmental hazard (1mk)
- A danger or disaster within the environment due to natural or human factors that have negative effects on the environment.
- Apart from floods list three other environmental hazards (3mks)
- Lightning
- Pests/disease
- Drought
- Earthquakes
- Volcanic eruption
- Windstorm
- Pollution (land/air)
- Fire
- Floods
- Landslides
- what is an environmental hazard (1mk)
- Explain four ways in which air population affects the environment (8marks)
- Gases emitted from industries contain substances which corrode roofs of houses and metal surfaces
- Some gases from factories contain substances which make plants to wilt and animals to die
- Inhalation of smoke and soot particles leads to discomfort and irritation of respiratory system
- Smoke and soot discolor buildings and plants making them look ugly
- Gases emitted from factories may contain poisonous substances which may lead to poor health of people when inhaled
- Smock and smog reduce visibility the atmosphere which may cause accidents in transport sector
- Some gases released into the atmosphere combine with moisture to form acid rains harmful to life
- Gases or excess carbon dioxide increase the temperature of affected areas due to depletion of ozone layer
- Explain four incidents that may lead to noise pollution in urban areas. (8marks)
- High pitched music played in night clubs, dance halls, public vehicles, bars and churches
- Repeated hooting from motor vehicles along main roads in town, bus stops etc
- Roaring aircraft especially during the takeoff and launching
- High intensity sounds produced by some animals e g barking dogs
- Shouting by touts and hawkers operating within towns
- Loudly cheering fans during sports/ social activities
- Reveling machines, grinding mills and steel rolling industries which produce a lot of noise
- Excessively loud laughter, singing, wailing and quarreling by people
- Students from Musingu carried out a field study on floods at Kano plains
- State two objectives for their study (2marks)
- To find out relief of the areas prone to floods (Kano plains)
- To find out causes of floods on Kano plains
- To find out the effects of floods on the residents of Kano plains
- To find out measures being undertaken to control floods on Kano plains
- State three ways in which residents of Kano plains are affected by floods that the students observed (3mks)
- Destruction of property belonging to the people
- Loss of lives as people drown and die
- Floods destroy transport and communication lines
- Displacement/evacuation of people from their homestead
- Transmission and spread of waterborne diseases during floods
- Food shortage/hunger as the floods destroy crops on farms and food stores
- State two objectives for their study (2marks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Nginda Girls Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
