INSTRUCTIONS:
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- This paper consists of 10 printed pages.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.

QUESTIONS
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the element.
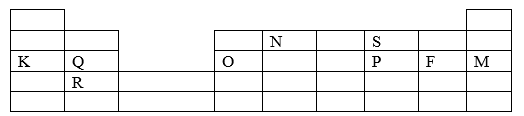
- What name is given to the group of elements to which Q and R belong? (1 mark)
- Write the formula of the compound formed when Q and P combine. (1 mark)
- Name the type of bond formed in (b) above. (1 mark)
- How does the atomic radii of O and P compare? Give a reason. (2 marks)
- Draw a dot (.) and cross (x) diagram for the compound formed between N and F. (1 mark)
- Explain how you would obtain a pure sample of the carbonate of K from its mixture with Lead carbonate powder. (2 marks)
- Give one use of element M. (1 mark)
- The melting point of M is -189°C lower than that of F -102°C. Explain this difference in their melting points. (2 marks)
- The list below shows the formulae of some organic compounds. Use letters T1 to T6 to answer the questions that follow.
T1 – CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
T2 – CH3CH2CH2COOC2H5
T3 – CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
T4 – CH3CH2CH2COOH
T5 – CH3CH2CHCH2
T6 – CH3CCCH3-
- Select two compounds which are not hydrocarbons (1mk)
- Would decolorize both bromine water and acidified potassium manganite (VII) (1mk)
- Would produce hydrogen gas when reacted with potassium metal (1mk)
- Select a compound which would produce bubbles of a gas when reacted with sodium carbonate. (1mk)
-
- Identify the compound that is likely to undergo additional polymerization.
Give a reason for your answer. Using two molecules show how polymerization occurs.- Compound (1mk)
- Reasons (1mk)
- Polymerization (1mk)
- Name the process by which compound T2 is formed and identify the compounds that were used to form it.
- Process (1mk)
- Compounds (1mk)
- Identify the compound that is likely to undergo additional polymerization.
-
-
- What is meant by the term molar enthalpy of combustion? (1mks)
- The enthalpies of combustion of carbon, hydrogen and ethanol are given below.
C(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ∆ H = -393kJmol-1
H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O (l) ∆H = - 286 kJmol-1
Enthalpy of combustion of ethanol ∆H = -1369kJ/ mol- Draw an energy cycle diagram that links the enthalpy of formation of ethanol to enthalpies of combustion of Carbon, hydrogen and ethanol (2 marks)
- Determine the enthalpy of formation of ethanol (2 marks)
- An experiment was carried out where different volumes of dilute nitric (v) acid and
Aqueous potassium hydroxide both at 25°C were mixed and stirred with a thermometer.
The highest temperature reached by each mixture was recorded in the table below.
Volume of nitric (V) acid (cm3)
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
Volume of potassium hydroxide cm3
36
32
28
24
20
16
12
8
4
Highest temperature of mixture
19.8
22.2
24.6
27.0
27.0
25.0
23.0
21.0
19.0
- Plot a graph of highest temperature (vertical axis) against volume of nitric(v) acid. (horizontal axis) 3mks
- Using your graph, determine the;
- Highest temperature reached ( 1 marks)
- The volume of the acid that reacted when the highest temperature is reached. (1marks)
- The amount of heat liberated during the neutralization process
(Specific heat capacity is 4.2Jg-1K-1 and the density of solution is 1.0gcm-3 (2 marks) - The molar enthalpies of neutralization for dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric (v) acid are -55 kJmol-1 while that of ethanoic acid is -52.2kJ/mol. Explain this observation. (1mks)
- Plot a graph of highest temperature (vertical axis) against volume of nitric(v) acid. (horizontal axis) 3mks
-
- The standard electrode potentials for the elements chloride and magnesium are:
Cl2 (aq) + 2é → 2Cí(aq) Eθ= +1.36V
Mg2+ (aq) + 2é → Mg(s) Eθ= –2.36V- Which one for the two elements will act as an oxidizing agent? Explain your choice. (2 marks)
- Calculate the electromotive force of a cell where the overall reaction is:
Cl2(aq) + Mg(s) → MgCl2(aq) (1mark)
- The table below gives the standard electrode potentials for divalent metals represented by the letters P, Q, R and S (not their symbols of elements). Use it to answer the question that follow.
Metal Eθ (volts)
P +1.50
Q +0.44
R +0.34
S –0.76- Which one of the metals cannot be displaced from a solution of its ions by any other metals in the table? Explain. (2 marks)
- Metals P and Q were connected to from a cell as shown in the diagram below.
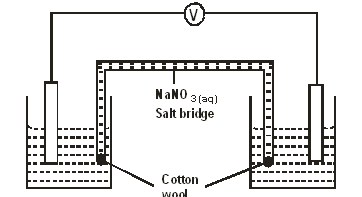
- On the diagram label the metals P and Q , the flow of electrons and indicate the ions in solution (2 marks)
- Write equations (half equations) of the reactions taking place at the electrodes.
- Electrode P (1 mark)
- Electrode Q (1 mark)
- State two functions of the salt bridge. (2 marks)
- What must be observed about the choice of a salt bridge? (1 mark)
- A metallic couple of the metal S and Z produced a voltage of +1.71volts.
(Assume that S has the higher negative electrode potential)- Calculate the standard electrode potential for metal Z. (1 mark)
- Arrange the metals P, Q, R and Z in their decreasing order of reactivity. (1 mark)
- The standard electrode potentials for the elements chloride and magnesium are:
- The flow chart below shows some reactions starting with lead (II) nitrate. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
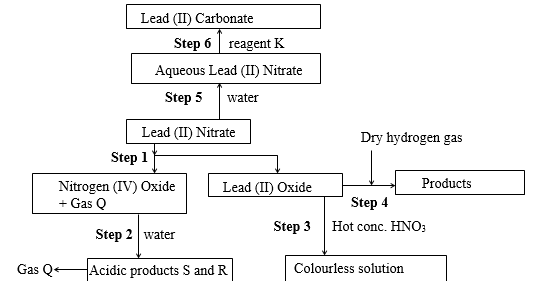
-
- State the conditions necessary in Step 4 (1mk)
- Identify
- Reagent K (1/2mk)
- Gas Q (1/2mk)
- Acidic products S and R. (1mk)
- Write
- The ionic equation for the reaction in step 6. (1mk)
- The equation for the reaction in Step 4. (1mk)
- The use of materials made by Lead in roofing and water pipes is being discouraged. State
- Two reasons why these materials have been used in the past. (2mks)
- One reason why their use is discouraged. (1mk)
- The reaction between Lead (II) Nitrate and sulphuric (vi) acid starts and stops immediately. Explain (2mks)
-
-
- A student was supplied with a colourless liquid suspected to be water.
- Describe one chemical test that could have been used to show that the liquid was water (2mk)
- How could it have been shown that the liquid was pure water? (1mk)
- The flow chart below shows the various stages of water treatment. Study it and answer the questions that follow
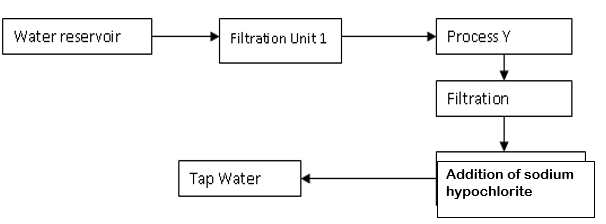
- Which substances are likely to be removed in filtration unit I? (1mk)
- What is the purpose of process Y (1mk)
- What is the purpose of the addition of sodium hypochlorite (1mk)
- It was confirmed that magnesium sulphate was present in the tap water
- What type of hardness was present in the water? (1mk
- Explain one method that can be used to remove the water hardness. (2mks)
- The set-up below was used to collect gas F, produced by the reaction between water and calcium metal.
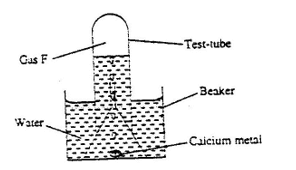
- Name gas F (1mk)
- At the end of the experiment, the solution in the beaker was found to be a weak base. Explain why the solution is a weak base. (2 marks)
- Give one laboratory use of the solution formed in a beaker. (1 mark)
- A student was supplied with a colourless liquid suspected to be water.
-
-
- Name the allotropes of sulphur (1mk)
- Sulphur is mined using the Frasch process which uses super-heated water at 170°c and hot compressed air.
- Explain how water at 170°c is obtained. (1mk)
- State one role of the super-heated water (1mk)
- State and explain what happens when wet petals of red flowers are put in a gas jar full of sulphur (iv) oxide (2mark
- Write an equation for the reaction of sulphur (IV) oxide and concentrated Nitric (V) acid. (1mark)
-
- Name the catalyst used in contact process (1mark)
- An equilibrium exists as
2SO2(g) + O2(g)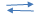 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)
State and explain what happens if- More oxygen is added to the system (2 marks)
- Pressure is decreased (2 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Alkaline earth metals (1mk)
- Q2P2 → QP – NB: metal should be followed by a non-metal and not vice versa. (1mk)
- Ionic bond. (1mk)
- The atomic radius of P is smaller than that of O. P has higher/stronger nuclear
force of attraction than O. P has more number of protons than O.
NB: Comparative words MUST be used. (2mk) -
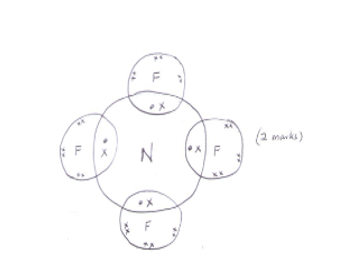
NB: outermost electrons in the atoms of F must be shown (1mk) - Add water to the mixture of K carbonate and lead carbonate and stir. K carbonate
dissolves while lead carbonate does not.
Filter to obtain K carbonate solution as a filtrate and lead carbonate as the residue.
Evaporate the filtrate to obtain crystals of carbonate of K
Wash the residue with distilled water and dry between filter papers. (2mks) - Used in light bulbs to provide an inert environment to prevent oxidation.
NB: reject used to make light bulbs.
Used as an insulator in arch – welding. (1mk) - M is a monoatomic gas while F is a diatomic gas; the Van der waal forces in M are weaker than in F hence the low m.p.t (2mks)
-
-
- T2 , T3 , T4 any two (1mk)
- T5 and T6 (1mk
- T3 and T4 (1mk)
- T4 (1mk)
-
- T5 or T6 (1mk)
- Reason: it is unsaturated (1mk)
- Polymerization (1mk)
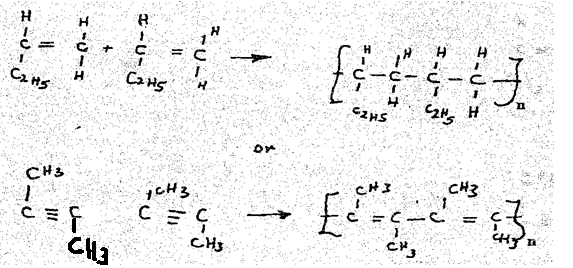
-
- Process: Esterification
- Compounds (1mk)
- Butanoic acid (CH3CH2CH2COOH)
- Ethanol (C2H5OH)
-
-
- The amount of heat liberated when one mole of a substance is burnt completely in excess oxygen.
rej- heated in oxygen
rej- heated required to burn ….
NB: burning must be complete -
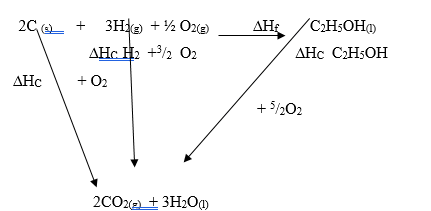
-
Correct energy cycle with arrows pointing right 1mk
Balancing all the equations – 1mark
NB: If an energy level diagram (axis labelled) is drawn with correct arrows award. (1marks - ∆H1 = ∆H2 + ∆H3
2(-393) + 3(-286) = ∆H2 + - 1369
∆Hf =∆H2 = -786 + - 858 + 1369 kJmol-1 (J) must be capital
= -275 kJ/Mol (2mks)
Penalize ( ½ marks) if units missing.
Penalize ( ½ mark if –ve sign is missing.
-
-
-
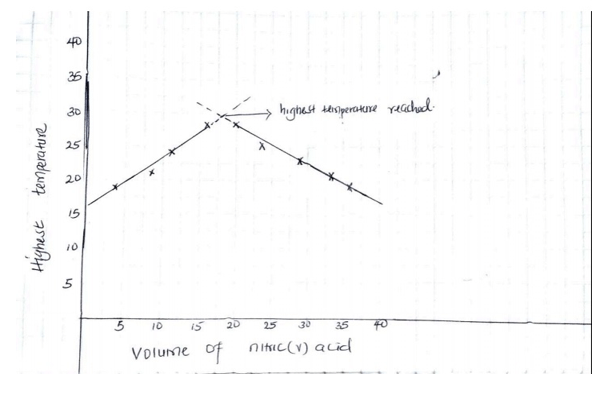
NB: Straight lines ½ mk each with extrapolation
Plotting 1mk
Axis label ½ mk each- xoC – must be read from the extrapolated value from the graph. (1 mk)
- Vcm3 – must be read from the graph correctly. ( 1 mk)\
- ∆H = MC∆T
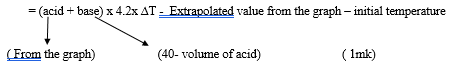
NB: final answer must have –ve sign otherwise penalise (½ mk) (1mk) - Ethanoic acid is a weak acid therefore heat is used to ionize it before neutralization occurs.
-
- The amount of heat liberated when one mole of a substance is burnt completely in excess oxygen.
-
-
- Cl2 1 mk It has a positive standard electrode potential hence a higher tendency to gain electrons 1mk
- Cl2(aq) + 2é→ 2Cl-(aq) Eθ = +1.36V
Mg(s) → Mg2+ (aq)+ 2é Eθ = +2.36V
Eθ = +3.72
Eθ = +3.72V
-
- Metal S: 1mk it has the highest negative e.m.f hence a high oxidizing power therefore low tendency to gain electrons and be displaced1 mk
-
-
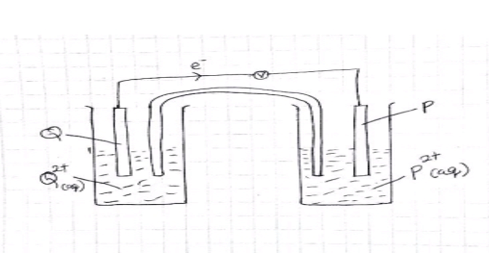
- P: P2+ (aq)+ 2é → P(s)
Q: Q(s)→ Q2+ (aq)+ 2é - It completes the circuit 1 mk
It ensures electrical neutrality and balance of ions between the two cells 1 mk - The salt in the bridge should not react with ions in the solution
-
-
- Eθ cell = Eθ reduction - Eθ oxidation
+1.71 = Z – – 079
Z = +1.71 – 0.76
= + 0.95V - Q, R, Z, P (1 marks)
- Eθ cell = Eθ reduction - Eθ oxidation
-
-
-
- Heat
-
- K2CO3 //Na2CO3 // (NH4)2 CO3 // Names 1/2
- Oxygen 1/2
-
-
- Pb2+ (aq) + CO2-3 (aq) → PbCO3 (s)(1mk)
PbO (s) + H2 (g) → Pb (s) + H2O (l)
- Pb2+ (aq) + CO2-3 (aq) → PbCO3 (s)(1mk)
-
- Cheap / corrosion resistant /durable any two
- Lead is poisonous / harmful
- The reaction produces insoluble lead (II) sulphate which coats the surface if Lead (II) Nitrate preventing further reaction.
-
-
- When blue anhydrous cobalt (II) chloride paper is dipped in a sample of the liquid, it turns to pink√.
White anhydrous copper (II) sulphate turns to blue√ when sample of the liquid is added. - When the liquid is heated to boil, its boiling point is 100°C at sea level/one atmosphere pressure√.
When the liquid is cooled to solidify, its freezing point is 0°C at sea level/one atmosphere pressure√.
When the density of liquid is determined it is 1gcm-3 at 4°C √
- When blue anhydrous cobalt (II) chloride paper is dipped in a sample of the liquid, it turns to pink√.
-
- Large solid particles like rock/sang√
- Causes small suspended particles to settle√.
- To kill germs/microorganisms√
-
- Permanent hardness√
- Addition of sodium carbonate√ that precipitates Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions
Distillation√ to remain with MgSO4 / CaSO4 as residue√.
Use ion-exchange permutit√ which will remove Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions√.
-
- Hydrogen/H2√
- Calcium hydroxide is slightly soluble√ in water. It is partially dissociated into few Ca2+ and OH-(aq) ions. √
- Test for the presence of CO2 gas√
Preparation of ammonia gas.
-
- Name the allotropies of sulphur (1mk
Rhombic sulphur√½
Monoclinic sulphur √½ - Sulphur is mined using the Frasch process which uses super-heated water at 1700c and hot compressed air.
Explain how water at 1700c is obtained. (1mk)
Heating water at 10 atmosphere pressure √1mk
OR
Heating water at high pressure.√1mk
State one role of the super-heated water (1mk)
To melt the sulphur deposits√1mk - State and explain what happens when wet petals of red flowers are put in a gas jar full of sulphur (IV) oxide (2marks)
The red petals turn white√1mk
Sulphur (IV) oxides bleaches the flower petals √1mk - Write an equation for the reaction of sulphur(IV) oxide and concentrated Nitric (V) acid (1mark)
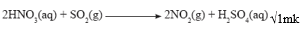
-
- Name the catalyst used in contact process (1mark)
Vanadium (V) oxide √1mk
OR
Platinum√1mk - An equilibrium exists as
2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g)
2SO3(g)- Because adding more oxygen increase the concentration of reactants in the forward reaction√1mk
- Equilibrium moves to the left 1mk decrease in pressure leads to increase in volume/no of molecules therefore equilibrium moves to the side with decreased number if molecules
- Name the catalyst used in contact process (1mark)
- Name the allotropies of sulphur (1mk
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Wahundura Boys Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
