INSTRUCTIONS
- This paper contain two sections; Section I and Section II.
- Answer all the questions in section I and II. In the spaces provided
- All workings and answers must be written on the question paper in the spaces provided below each question.
- Marks may be given for correct working even if the answer is wrong.
- Calculators and KNEC Mathematical tables may be used EXCEPT where stated otherwise.
- Show all the steps in your calculations, giving your answers at each stage in the spaces below each question.

QUESTIONS
SECTION A 25 Marks
- The figure1 below shows three point source of light with an opaque object placed between them and the screen
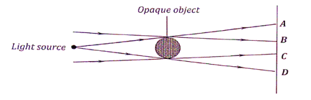
State and explain the nature of shadow formed a long B and C (2marks) - The diagrams below show a positively charged acetate strip and a negatively charged polythene strip freely suspended and isolated.
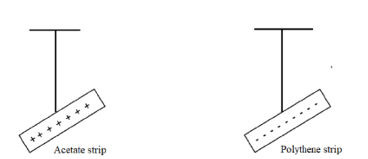
Two rods X and Y are brought up in turn to these strips. X attracts the acetate strip but repels the polythene strip. Rod Y does not repel either the acetate or the polythene. State the type of charge on each rod.
X...(1 mark)
Y....(1 mark) -
- State any one way of reducing the magnetic force of attraction of a magnet (1mark)
- Show the direction of the magnetic field in the conductor carrying current shown below. (1mark)
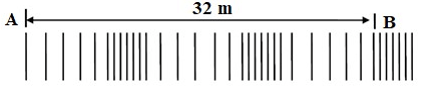
- The diagram below shows waves generated from a tuning fork. If the wave takes 0.1 second to move from point A to B. determine the frequency of the wave. (2marks)
- Other than current state one other factor that affect the magnitude of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field. (1mark)
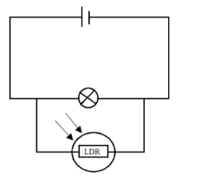
- A student connected the set up below in the laboratory. Explain the observation made on the bulb when the set-up below is taken to a dark room (1 mark)
- A radioactive carbon – 14 decays to nitrogen by beta emissions as shown.
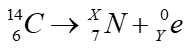
Determine the values of X and Y in the equation
X=…………………………………….. …………………….. (1mark)
Y = …………………………………………………………… (1mark) -
- state the reason for topping up a lead-acid accumulator with distilled water. (1mark)
- State one quatity that is used to determine whether accumulators require charging or not. (1mark)
- Figure 8 shows wave fronts of water waves approaching a concave surface.
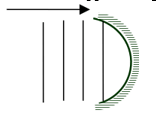
- Complete the diagram to show the wave fronts formed after striking the surface. (1 mark)
- What is the effect on velocity of the above if it moves from shallow to deep region (1marks)
- A person standing 110 m from the foot of a cliff claps his hands and hears a sound 0.75 seconds later. Find the speed of sound in air. (2 marks)
- Figure 9 below shows light travelling from more optically dense to less optically dense medium.
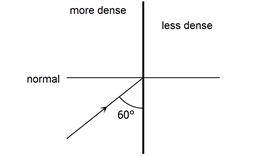
- On the same diagram, sketch a ray to show the direction of the refracted ray. (1 mark)
- If the refractive index of the denser medium is 1.42, calculate the angle of refraction. (2marks)
- Eleven (11) images are formed when two mirrors are inclined at an angle between them. Determine the size of angle between the inclined mirrors (2 marks)
-
- The figure10 below is part of electromagnetic spectrum.
A Visible light UV
Name one detector of A (1 mark) - Define focal length of a curved reflecting surface (1 mark)
- The figure10 below is part of electromagnetic spectrum.
SECTION B 55 MARKS
-
-
- State any one condition necessary for two sources of waves to be coherent ( 1 mark)
- A student walking on a straight perpendicular to two coherent signal generators hears alternating loud and soft sounds. Explain why at some point the sound heard is softer (1mark)
- Explain why radio wave signals are easier to receive than TV waves signals in a place surrounded by hills. (1mark)
- In an experiment using a ripple tank the frequency, f of the electric pulse generator was reduced to one third of its original value. How does the new wave length compare with the initial wavelength? (1mark)
- In a double slit interference experiment, explain the effect on the appearance of the fringes of:
- Reducing the separation of the slits but keeping the width of each slit constant. (1mark)
- Making each of the two slits wider but keeping the slit separation constant. (1mark)
- The figure 11 below shows wave fronts before and after passing through an opening.
State what would be observed on the pattern after passing the opening if the wavelength of the wave is increased. ( 1 mark)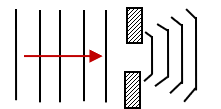
-
-
- The figure 12 below shows a X-ray tube.
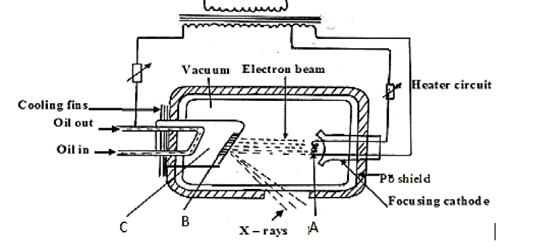
- Name the part labelled C (1 mark)
- State the property of the material labelled B on the diagram which makes it suitable for use in the X-ray tube. (1 marks)
- Why is C inclined at an angle of 45o? (1 mark)
- State the adjustment that can be made to vary
- The quality of X-rays (1 mark)
- The quantity of the X-rays. (1 mark)
- An x-ray tube has an accelerating potential of 100KV. Determine the maximum frequency of the x-rays produced.(Plank’s constant = 6.63 10 -34 Js, e = 1.6 × 10-19C) (2 marks)
- In a CRO, waveform given below was displayed on the screen when the sensitivity at the Y plate was10V/cm and time base set at 20 milliseconds/cm.
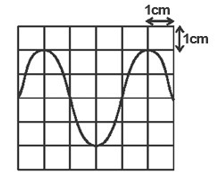
Determine:- The peak voltage (2marks)
- The frequency of the signal (2marks)
- The figure 12 below shows a X-ray tube.
-
- 226 88 Ra decays into 222 86 Rn by emission of an alpha particle. Write a nuclear equation for the decay (1 mark)
-
- What do you understand by the term half-life of a radioactive substance? (1 mark)
- A G.M tube registers 20 counts. When a radioactive source is brought close to it, it registers 3220 counts and 120 counts 30 hours later. What is the half-life of this substance? (2 marks)
- The figure 14 below shows a G.M tube.
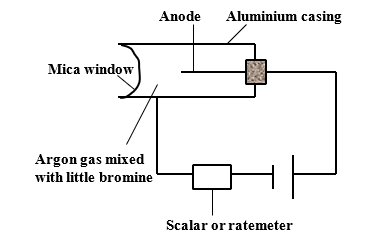
- Explain the purpose of the bromine (1 mark)
- Briefly explain how the Geiger Muller tube works to detect radiations. (2 marks)
- When beta and alpha radiations are passed through a magnetic field, the beta radiations are deflected more than the alpha radiations. Give a reason for this observation. (1 mark)
- The figure below is a circuit with two identical bulbs and components, Diodes 1 and 2.
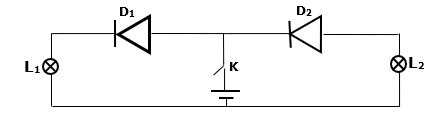
- State and explain the observation made when switch K is closed. (2marks)
- On the axes provided below, sketch the graph of output voltage against time for a full wave rectifier (1mark)

- A capacitor is now connected across the output. Explain its effect on the output. (1mark)
-
- You are provided with a rheostat, 2 cells, a voltmeter, an ammeter, a switch and a fixed resistor.
- Draw a circuit diagram that can be used to verify Ohm's law. (2 marks)
- Describe how the above set up can be used to determine Ohms law. (3marks)
- Study the circuit diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
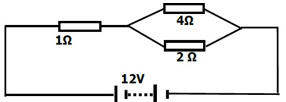
Calculate the current through the 4Ω resistor (3 marks) -
- An electrical emersion heater is rated as 240V, 500W. What does this information mean? (1mark)
- Calculate the resistance of the element used in the heater. (2marks)
- You are provided with a rheostat, 2 cells, a voltmeter, an ammeter, a switch and a fixed resistor.
-
- A ray of light travelling from water to glass makes an angle of incident of 30°. Find the angle of refraction in the glass. Refractive index of water=4⁄3 . Refractive index of glass= 3⁄2 (2 marks)
- State one necessary and sufficient condition for total internal reflection to occur (1mark)
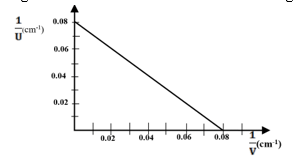
- The graph below shows the variation of 1/V and 1/U in an experiment to determine the focal length of the mirror. Determine the focal length. (2marks)
- The figure below shows a human eye defect.
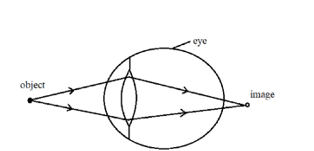
- State one possible cause of this defect. (1 mark)
- On the diagram, show how the defect is corrected. (1 mark)
-
- A bar magnet is moved into a coil of an insulated copper wire connected to a zero- centre-galvanometer as shown below
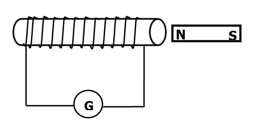
- Show on the figure above the direction of the induced current in the coil (1 mark)
- State what is observed on the galvanometer if the south pole of the magnet was moved into and then withdrawn from the coil. (1 mark)
- A transformer has 800 turns in the primary and 40 turns in the secondary winding. The alternating voltage connected to the primary is 240V and current of 0.5.A. If 10% of the power is dissipated as heat within the transformer, determine the current in the secondary coil. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a three-pin plug.
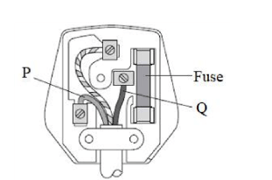
- Name the colour code of conductors Q (1 mark)
- Why is the earth pin longer than the rest in the three-pin plug shown above? (1 mark)
- Give one advantage of a circuit breaker instead of a fuse in domestic wiring. (1mark)
- State one modification can be done to the fuse wire to give it a higher rating? (1mark)
- A bar magnet is moved into a coil of an insulated copper wire connected to a zero- centre-galvanometer as shown below

MARKING SCHEME
- The shadow along BC is a umbra (total shadow)
All the rays of light from the point sources towards the region BC are blocked by the opaque object and therefore cannot reach the screen √ 1mark - X-Negative charges √ 1mark
Y-Neutral √ 1mark -
- Hitting while facing east-west direction
- Heating while facing east-west direction
- Inserting in a solenoid with a.c current facing east-west direction
-
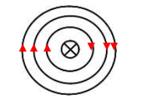
- Hitting while facing east-west direction
- 2.5 ƛ= 32
1 = 1×32/ 2.5
ƛ = 12.8?√
V=32/ 0.1 = 320 M⁄S
f = V⁄λ =320× 2.5/ 32
=25Hz√ 1mark - Length of the conductor within the magnetic field
- Magnetic field strength
- Angle between the conductor and magnetic field lines √ 1mark
- Brightness of the bulb increases.
- The resistance of the LDR increases when the intensity of the light increases this causes more current to flow through the bulb.
- X=14 Y=-1 √ 1mark (No half mark)
-
- To replace the water which has evaporated , and help in maintenance the level of electrolyte above the plates
- To restore the relative density of the acid
-
- When the e.m.f of the cell drops below 1.8V
- When the relative density of the acid falls below 1.12. √ 1mark
-
-
-
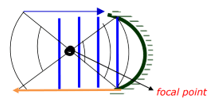
- speed increases √ 1mark
-
- In 0.75 seconds, the sound has traveled 220 m
Speed = distance/ time
speed= 220m/ 0.75s =293.3 m⁄s
1mark (correct substitution)
1mark (correct answer with units -
-
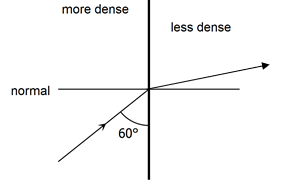
- Sin C=1/n=1 /1.42=0.7042 C=44.76° √ 1mark
-
- n=360/ɵ 11=360/ɵ-1 ɵ=30° √ 1mark
-
- Solid state diodes, crystal detectors,
- It is the distance from the pole of the mirror to its principal Focus,√
-
-
- The two waves have same frequency or wavelength
Have equal or comparable amplitudes
Have constant phase difference - This is due to destructive interference of sound waves, where sound waves meets out of phase
- The two waves have same frequency or wavelength
- Radio waves are easily diffracted around hills than T.V waves since radiowaves have longer wavelengths.
- The wavelength increases three times
since v = f λ
Let λ1 be initial wavelength and λ2 be final wavelength Then v = λ1f and v = λ2f/3
Since v is constant, λ1f = λ2f/3 Hence λ2 = 3λ1 This means that the λ increases three times -
- Width of the fringes gets increased if the distance between the slits (d) is decreased and thus we get wider fringes.
- Intensity of light emitted by the slits increases as the width of the slit is increased. Thus, more brighter fringes are formed at the screen on increasing the width of the slits.
- waves would appear more circular.
-
-
-
- Anode / copper anode√
- High melting point√
- To direct x rays out of the tube through the window√
-
- Varying the accelerating voltage (increasing / decreasing the accelerating voltage√
- Increasing or decreasing (varying) the heating current at the cathode √
- k.e = eV =hf
= 100000 × 1.6 × 10−19√
= 1.6 × 10−14 J
ƒ=2.413 ×1019Hz√
-
-
y - gain × no.of divisions
10 v⁄cm×2cm =20v - Time base = 4 × 20 =80ms
= 0.08√ f
=12.5 Hz√
-
-
-
- f
22688 Ra → 22286Rn + 42 He -
- The time taken for half the number of nuclides initially present in a radioactive sample to decay/ Is the time taken for the activity to decrease to half of the initial value of radioactivity nuclei present to decay.
- initial =3220 - 20
final =120 - 20
100 = 3200 (1⁄2) 30/t
(1⁄2)5 = (1⁄2) 30/t
5= 30⁄t
-
- To absorb Kinetic. Energy of the ions hence preventing secondary ionization / Quenching agent
- when a radioactive substance is placed in front of the window, the emitted radiations enter the tube through the window ionizing the gas inside. The negative ions moves towards the central anode while positive ions moves to the cathode;thus a discharge is suddenly obtained between anode and cathode and registered as current by counter.
- alpha particles are heavier than beta particles.
-
- L1lights while L2 does not light. D1is connected in forward bias, which allows current to pass through while D2 is connected in reverse bias, which does not allow the flow of current.
-
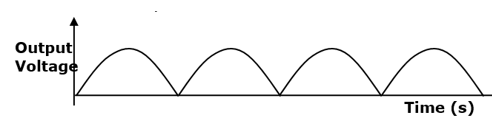
- Smoothen the output voltage. √ 1mark
- f
-
-
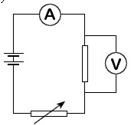
-
- Vary the voltage using the variable resistor and record the corresponding values of voltage and current
- Repeat for several values of current and voltage and tabulate
- Plot a graph of P.d against current. The graph is a straight line with positive gradient. Showing that current through a conductor is directly proportional to the P.d across it.
- RT=R1+R1R2 /R1+R2 =1+8/6=2.333Ω
IT=12/2.333=5.144
Curent across 4Ω Resistor I=2⁄6 x5.144
=1.715 A -
- That the appliance operates at a voltage of 240 volts. When it is operating normally, the electrical power outputs is 500 watts i.e. 500J of electrical energy is converted to other useful energy per unit time.
- R = V²/P R = 240²/500 = 115.2Ω √ 1mark
-
-
-
sin i/ sin r =wng
sin 30/Sin r=3/2 x 3/4 r=26.390 - Light must move from an optically denser to optically less dense medium.√
The incidence angle in an optically denser medium must be greater than the critical angle - 1/f=intercepts f1=1/0.08=12.5 cm f2=1/0.08=12.5 cm;
f=(12.5+12.5)= 12.5 cm -
- Longer focal length√ Shorter eyeball√
-
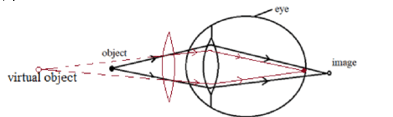
-
-
-
-
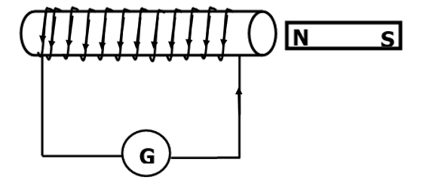
- The pointer deflects in one direction and comes back to zero. √When magnetic fields cut through the conductor, emf is induced which makes the current to flow and the pointer deflect but comes back to zero when there is no relative motion between the coil and the magnet√
-
- NG/ Np = Vs/ Vp
40/ 800 = Vs/√ 240
Vs=40+240/800
=12V
vsls/ vplp× 100=90
ls= 0.9×240×0.5/12 =9À -
- Q– Red / Brown
- To open the blinds√
- To earth the appliance before current start flowing√
- It breaks the circuit instantaneously, whereas the wire fuse takes time to melt down.
It is reset for use once the fault has been corrected, as opposed to the wire fuse which has to be replaced. - By using a thicker fuse wire. √ 1mark
-
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Wahundura Boys Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
