INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper has two sections: A and B.
- Answer all the questions in section A.
- Answer question 6 and any other two questions from section B.
Section A
Answer all the questions in this section
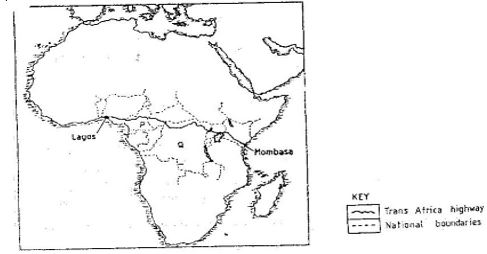
- The map below shows the Trans- Africa highway from Mombasa to Lagos. Use it to answer question (a)
- Name the countries marked P and Q. (2mks)
- State three reasons why it is difficult to transport goods from Mombasa to Lagos along the highway (3mks)
-
- Give three reasons why hardwood tree species in Kenya are in danger of extinction (3mks)
- State two ways in which softwood forest in Kenya differ from those of Canada. (2mks)
-
- A part from rural – rural migration, list three other types of migrations in Kenya. (3mks)
- Give two causes of rural – rural migration in Kenya (2mks)
-
- Name two rivers in Kenya which cause large scale flooding ( 2mks)
- State three methods through which floods can be controlled. (3mks)
-
- Name three types of beef cattle reared in Argentina. (3mks)
- Give two ports in Argentina through which processed beef is exported to overseas markets (2mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
- The table below shows the quantity of minerals produced in Kenya in tonnes between years 2001 and 2005. Use it to answer questions (a) (i) and (ii).
Mineral/Year 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Soda ash 297,789 304, 110 352, 560 353, 835 360, 161 Fluorspar 11,885 85,015 80, 201 117, 986 26, 595 Salt 5,664 18,848 21,199 31,139 26,595 Others 6,093 7,000 4,971 6,315 8,972 TOTALS 321,431 414,973 458,931 509,275 422,323 -
- Calculate the average annual production of soda ash over the 5 years period. (2mks)
- Using a scale of 1cm represent 100,000 tonnes, draw proportional circles representing total mineral production for years 2001, 2002, and 2004. Use diameter method. (7mks)
- State two uses of soda ash (2mks)
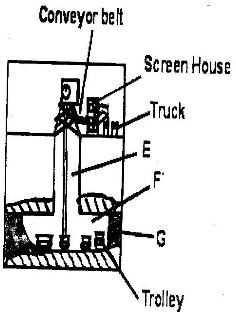
- The diagram below shows shaft mining.
- Name the parts marked E, F and G. (3mks)
- State two problems associated with shaft mining. (2mks)
-
- State three negative effects of mining on the environment (3mks)
- Explain three ways in which gold mining has contributed to the economy of South Africa. (6mks
-
-
-
- Name two historical sites on the Kenyan coastal region that attracts tourists (2mks)
- Explain the differences between the tourist attractions in East Africa and Switzerland under the following sub- headings
- Climate (2mks)
- Culture (2mks)
- Explain four benefits that Kenya derives from tourism (8mks)
- Explain three measures that Kenya should take in order to attract more tourists (6mks
- Some students carried out a field study on inland tourist sites.
- Identify two sampling techniques the students may have used during the study. (2mks)
- Give three advantages of sampling the area of study. (3mks)
-
-
-
- State five problems experienced in irrigation farming in Kenya (5mks)
- Explain three conditions that favour irrigation farming in Kenya (6mks)
- Describe the stages in the reclamation of land from the sea in the Netherlands (6mks)
- Explain four benefits of land reclamation in the Netherlands (8mks)
-
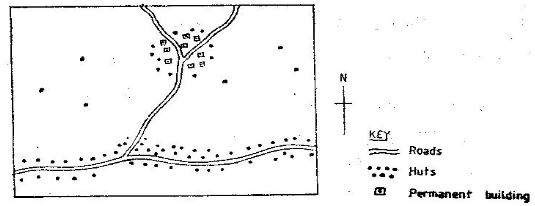
- Study the map below and answer the questions that follow
- Name the main settlement pattern in:
- The northern part of the map. (1mk)
- The southern part of the map. (1mk)
- State four factors that led to the development of Kisumu town (4mks)
- List five functions of New York City (5mks)
- Explain four problems facing urban centres in Kenya (8mks)
- You intend to carry out a field study in the nearby urban center
- State three reasons why you will conduct a pre-visit to the area of study (3mks)
- Give three advantages of studying the nearby urban center through field work. (3mks)
- Name the main settlement pattern in:
-
-
- Define the term international trade (2mks)
- Name three major imports from Europe to Kenya (3mks)
- State four factors that influence external trade in Kenya (4mks)
- Explain four ways through which Kenya will benefit from the renewed East Africa Cooperation ( 8mks)
- Explain four negative effects of international trade (8mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
- The map below shows the trans-Africa highway from Mombasa to Lagos. Use it to answer question (a)
- Name the countries marked P and Q.
- P - Cameroon
- Q - Democratic Republic of Congo (2x1=2mks)
- State three reasons why it is difficult to transport goods from Mombasa to Lagos along the highway
- Political differences/hostilities between the countries through which the highway passes
- There are civil wars in the region
- Tarrifs charged at the border increase transportation costs
- Parts of highway are incomplete/impassable during wet seasons
- Different currencies are used
- Long distance covered
- Language barrier (Any 3x1=3mks)
- Name the countries marked P and Q.
-
- Give three reasons why hardwood tree species in Kenya are in danger of extinction
- High demand for hard wood has led to over – exploitation.
- Population pressure on land has led to increased cutting of trees to provide land for farming and settlement.
- The time taken for the hardwood trees to mature does not match the rate at which they are being exploited.
- Indusrialisation/ Mordernisation leads to deforestation to create space
- Prolonged drought/ climate change which dries up some trees (Any 3x1=3mks)
- State two ways in which softwood forest in Kenya differ from those of Canada.
- Softwood forest in Canada are more extensive than those in Kenya
- Softwood trees species in Kenya are Exotic while those in Canada are indigenous.
- There is a wider variety of softwood tree species in Canada than is in Kenya. (2x1=2mks)
- Give three reasons why hardwood tree species in Kenya are in danger of extinction
-
- Apart from rural – rural migration, list three other types of migrations in Kenya.
- Rural-urban
- Urban-Urban
- Urban-Rural
- International
- Regional (3x1=3mks)
- Give two causes of rural – rural migration in Kenya
- Population pressure which leads to landlessness hence migration
- Insecurity in some areas make some people to migrate to more secure areas.
- Establishment of large plantation and irrigation schemes attract people from neighboring areas as they search for employment
- Natural catastrophes such as floods cause people to move to more secure higher grounds.
- Pastoral communities migrate from one rural area to another in search of pasture and water for their livestock.
- Drought and famine sometimes cause people to migrate in search of food
- Marriages/Inter-marriages (Any2x1=2mks)
- Apart from rural – rural migration, list three other types of migrations in Kenya.
-
- Name two rivers in Kenya which cause large scale flooding
- Nyando
- Nzoia
- Tana
- Kuja/Gucha
- Yalla
- Ewaso Nyiro (Any2x1=2mks)
- State three methods through which floods can be controlled.
- Construction of dams/check dams which help reduce velocity of rivers
- Construction of dykes/ artificial levees which restrict outflow of rivers
- Construction of diversion channels/canals which diverts flooded waters
- Planting of vegetation/forest in the river catchment areas to reduce the surface run-off and increase seepage.
- Clearing drainage system/channels to facilitate easy flow of water. (Any 3x1=3mks)
- Name two rivers in Kenya which cause large scale flooding
-
- Name three types of beef cattle reared in Argentina.
- Hereford
- Aberdeen Angus
- Holando Argentina
- Zebu
- Charolais (Any 3x1=3mks)
- Give two ports in Argentina through which processed beef is exported to overseas markets
- Buenos Aires
- La Planta
- Bahia Blanca (Any 2x1=2mks)
- Name three types of beef cattle reared in Argentina.
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
- The table below shows the quantity of minerals produced in Kenya in tones between years 2001 and 2005. Use it to answer questions (a) (i) and (ii).
-
- Calculate the average annual production of soda ash over the 5 years period. (2mks)
= 1668455 ÷ 5 = 333691 Tonnes - Using a scale of 1cm represent 100,000 tonnes, draw proportional circles representing total mineral production for years 2001, 2002, and 2004. Use diameter method.
Year Diameter (cm) Radiu (cm)
2001 = 321431 ÷ 100,000 = 3.214 1.607
2002 = 414973 ÷ 100,000 = 4.149 2.074
2004 = 509275 ÷ 100,000 = 5.092 2.545
NB/ Marks distribution- Each correct culculated radius 1mk x 3= 3mks
Each circle 1mk x 3 = 3mks
Title 1mk Total 7mks
- Calculate the average annual production of soda ash over the 5 years period. (2mks)
- State two uses of soda ash
- It is a raw material for making glass
- It is used in making detergents
- It is used in some chemical industries /petroleum refining
- It is used as a water softener/water treatment
- It is used in desulphurising steel
- It is used in paper industries. (Any2x1=2mks)
- The diagram below shows shaft mining.
- Name the parts marked E, F and G.
- E- Main shaft/vertical shaft
- F- Tunnel/horizontal shaft/Gallery
- G- Mineral ore (Each 1mk = 3mks)
- State two problems associated with shaft mining.
- Sometimes, mines get flooded with sub terrain water.
- There is occasional emission of poisonous gases in the mines
- The dust produced causes respiratory diseases
- Sometimes tunnels collapse causing deaths of miners. (Any 2x1=2mks)
- Name the parts marked E, F and G.
-
- State three negative effects of mining on the environment
- Pollution of air/ water/ land/ noise
- Dereliction of land/ ugly surface/ land slide scars
- Disruption/ lowering of the water table
- Loss of biodiversity/ plants and animals
- Leads to soil erosion/ degeneration of soils (Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Explain three ways in which gold mining has contributed to the economy of South Africa.
- Gold fetch high prices, thus it earns foreign exchanger which is used to improve other sectors of the economy.
- Gold provides raw materials for industries that make jewellery and other highly valued items thus promoting industrial expansion.
- Gold as a medium of exchange in the world is used in South Africa as a means of paying international debts.
- Gold mining industry has generated employment opportunities, which raises the standard of living of the people
- Gold mining has led to development of towns in the Rand and the Orange Free State creating a large demand for agricultural products.
- Mining of gold has led to the expansion of infrastructure such as transport and communication
- Mining of gold has stimulated the provision of social amenities like hospitals, schools .
- Gold mining has led to the development of industrial mining skills that are useful in other sectors of the economy.
(Any 3x2=6mks)
- State three negative effects of mining on the environment
-
-
-
- Name two historical sites in the Kenyan coastal regions that attracts tourists
- Fort Jesus-in Mombasa Island
- Gedi ruins – near Watamu
- Vasco dagama pillar in malindi
- Museum – with Swahili people /artefacts
- Arab architectural designs in Lamu
- Shimoni caves. (Any2x1=2mks)
- Explain the differences between the tourist attractions in East Africa and Switzerland under the following sub- headings
- Climate- While the climate of East Africa is warm and sunny most of the year, encouraging sun bathing in Switzerland there are cold winters which enable winter sports and hot summers that expose beautiful sceneries (2x1=2mks)
- Culture - In East Africa, there are varied/ a diversity of African cultures while in Switzerland the main culture is European (2x1=2mks)
- While the climate of East Africa is warm and sunny most of the year, encouraging sun bathing in Switzerland there are cold winters which enable winter sports and hot summers that expose beautiful sceneries (2x1=2mks)
- Name two historical sites in the Kenyan coastal regions that attracts tourists
- Explain four benefits that Kenya derives from tourism
- Development of tourists facilities provide employment opportunities, raising the standards of living.
- Tourists pay for the variety of services offered from which Kenya gains foreign exchange /revenue
- Tourists provide a ready market for trade items such as handcrafts and other curios.
- The need for more agricultural products for tourists in hotels and lodges has stimulated the growth of agriculture and other related industries
- The need for improved transport and communication has led to the promotion of infrastructure of tourist sites which also benefits the local people
- Establishment of national parks and museums as tourist attractions has enabled Kenya to protect/ preserve natural environment and its rich cultural heritage
- Tourism encourages cultural exchange which promotes international understanding ( any 4 x 2 = 8mks)
- Explain three measures that Kenya should take in order to attract more tourists
- Improving infrastructure/ roads/ airports/ communications to all tourists- sites in order to make them easily accessible.
- Improving security to ensure the safety of the tourists is guaranteed
- Marketing the country more aggressively in order to make it more known/ improve the image of the country abroad
- Establishing a diversity of tourists attractions to avoid depending entirely on the traditional attractions and reduce competition with other tourists destinations
- Establishing/ modernizing tourist facilities in areas that have high potential such as Coastal Kenya where such facilities are inadequate.
- Intensify marketing of domestic tourism to reduce reliance on foreign tourists. (Any 3 x 2 = 6mks)
- Some students carried out a field study on inland tourist sites
- Identify two sampling techniques the students may have used during the study.
- Stratified
- Random
- Systematic
- Clustered (Any2x1=2mks)
- Give three advantages of sampling the area of study.
- To save on time
- To reduce bias
- To allow for detailed study
- To reduce cost (Any3x1=3mks)
- Identify two sampling techniques the students may have used during the study.
-
-
- State five problems experienced in irrigation farming in Kenya
- Siltation of canals/ pipes/ reservoirs
- High rate of evaporation
- Salinization of the soil
- Presence of pests
- Clogging up of canals by water weeds
- Presence of waterborne diseases/ bilharzias
- Fluctuating regimes of rivers/ inadequate water for irrigation
- Poor marketing strategies
- Land tenure problems
- Low pricing for the crops
- Delayed payments
- Mismanagement of the schemes
- Expensive farm inputs / inadequate capital (Any5x1=5mks)
- Explain three conditions that favour irrigation farming in Kenya
- Gently sloping land which permits flow of water by gravity hence reducing the cost of pumping water to the fields.
- Presence of clay soil/ black cotton soils which retain water for longer use by crops
- Presence of river/ reservoirs/ lake which provide regular water supply/ permanent/ constant making it possible to irrigate land throughout the year
- High temperatures throughout the year which allows multiple cropping/ continuous farming activities throughout the year
- Availability of large tracts of land makes the project viable
- Sparsely populated land reduces cost of resettlement (Any3x2=6mks)
- State five problems experienced in irrigation farming in Kenya
- Describe the stages in the reclamation of land from the sea in the Netherlands
- Protective dykes/ sea walls are constructed enclosing the part of the sea to be reclaimed
- Ring canals are constructed
- Pumping stations are installed to pump out sea water from the area enclosed by the dyke
- Water is pumped out of the area enclosed by the dyke
- Reeds are sown to reduce the salinity in the soils
- Drainage ditches and more pumping stations are made on the land being reclaimed
- Drainage pipes are laid below the soil
- The area is divided into regular portions using inner dykes and ring canals
- Soils treated with chemical to lower salinity
- The drained land is flushed with fresh water to remove salt from the soil
- Pumping out water from the polders is a continuous process to prevent water from accumulating (6mks)
NB Sequence must be followed
- Explain four benefits of land reclamation in the Netherlands
- Reclamation creates more land for agriculture / settlement
- Reclaimed land has improved agricultural output hence more food
- More raw materials for industries have been produced
- Land reclamation has resulted in improved fresh water supply for domestic and industrial use/ irrigation
- Construction of dykes/ walls around the polders has helped control floods/ sea invasion
- Construction of dykes and canals has improved road transport network/shortening distance
- Reclamation has created sceneries that have become tourists attractions
- Improved social amenities such as schools, stadia have been built.
- Reclamation and associated activities have created more employment opportunities and improved the standard of living of citizens
(Any4x2=8mks)
-
- Study the map below and answer the questions that follow
- Name the main settlement pattern in:
- The northern part of the map.
- Nucleated/ clustered/ dense (1mk)
- The southern part of the map.
- Linear (1mk)
- The northern part of the map.
- State four factors that led to the development of Kisumu town
- Kisumu grew as the terminus for Kenya- Uganda railway
- It grew as large port handling the regional lake trade.
- The high population in the surrounding areas provided the required labour force.
- Early Asian settlement in the area led to commercial development
- It was a regional headquarters for colonial administration.
- Water for domestic and industrial use was readily available in the area.
- It has rich agricultural hinterland providing food and industrial raw material.
- The development of industries has attracted people to the town/fishing industry (Any 4 x1 = 4 mks)
- List five functions of New York city
- Banking / Financial center.
- Industrial center
- Fashion center
- Transport and communication center
- Headquarters of U.N
- Leading trade center/stock exchange center
- Educational center
- Cultural center (Any5x1= 5mks)
- Explain four problems facing urban centres in Kenya
- The rapid growth of population has led acute shortage of houses.
- There is serious traffic congestion during rush hours especially in major towns. This leads to loss of time/fuel
- The heaps of uncollected garbage cause health hazard as they can lead to epidemics.
- Towns have a large unemployed population which is idle and encourages crime and immoral practices.
- The urban centers suffer from perennial water shortages due to increased number of consumers
- There is poor sewage system in some parts of the towns. This causes a health hazard.
- The rapid growth of population has lead serious headache in planning for services
- The rapid growth of population has led to inadequate provision of health, education services.
- Pollution of the air/ noise caused by vehicles/ industries which causes health hazard. (Any4x2=8mks)
- You intend to carry out a field study in the nearby urban center
- State three reasons why you will conduct a pre-visit to the area of study
- To be used to prepare a route map
- To determine the suitability of the area for the study
- To be able to formulate appropriate objectives for the study
- Preparation of work schedule
- To be able to decide on appropriate data collection methods
- To find out possible problems likely to be experienced during the field study
- To seek permission for the visit
- To determine appropriate tools to be carried for the study
- To determine the possible cost to be incurred during the study (Any3x1=3mks)
- Give three advantages of studying the nearby urban center through field work.
- It enables one to get firsthand information
- It makes learning real
- It enables one to share information
- It enables one to retain information learned /make learning memorable
- It enables one to apply skills acquired in class (Any 3x1=3mks)
- State three reasons why you will conduct a pre-visit to the area of study
- Name the main settlement pattern in:
-
-
- Define the term international trade
- International trade -Is the exchange of goods and services between different countries (2mks)
- Name three major imports from Europe to Kenya
- Machinery
- Capital equipment
- Pharmaceutical products /medicine
- Fertilizers
- Automobiles
- Spare parts
- Textiles goods (Any3x1=3mks)
- Define the term international trade
- State four factors that influence external trade in Kenya
- Government policy/government legislation/imposition of tariffs on imports.
- Demand for goods both locally and outside Kenya
- Variation of natural resources/ goods / quality of goods
- Availability of transport and communications
- The purchasing power
- The level of industrialization
- Quota system/tariffs/ trade restrictions imposed on Kenya’s imports (Any 4x1 =4mks)
- Explain four ways through which Kenya will benefit from the renewed East African Cooperation
- There will be improved access to raw materials for industrial development
- The expanded market will attract new investments from local and foreign sources which will lead to expansion of industries/more earnings
- There will be exchange of research findings/training which will help in economic development
- There will be improved negotiating powers in the international arena
- There will be improved transport links between member countries which will facilitate faster movement of goods and people
- There will be increased employment opportunities raising the standards of living
- There will be mutual political understanding between member’s countries enhancing trade
- There will be free movement of people/lobour within the region hence exchange of skills (Any 4x2 =8mks)
- Explain four negative effects of international trade
- Overspecialization/overdependence on a particular item is risky incase of a fall in the prices in the world market.
- Imported items may become a threat to the local industries leading to closure of some of the
- Some imported goods e.g expired goods or substandard goods may have adverse effects on the citizen
- If a country depends on another, it may sometimes have to tolerate some undesirable gestures from such countries
- There may be over-exploitation of natural resources leading to their depletion e.g. minerals.
- Provide a chance for dangerous drugs to enter the country (Any 4x 2=8mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Lainaku II Joint Mock Examination 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students