INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and Index Number in the spaces provided above.
- This paper consists of two sections. Section A and section B.
- Answer ALL questions in section A in the spaces provided. In section B answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
-
- What is meant by the following terms?
- Protandry ( 1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Self sterility ( 1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Protandry ( 1mark)
- The diagram below shows a stage during fertilization in a plant
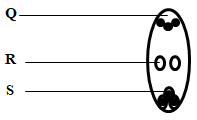
- Name the parts labelled Q,R and S (3 marks)
Q……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
R…………………………………………………………………………………………….……….
S…………………………………………………………………………………………………….. - State two functions of the pollen tube (2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Name the parts labelled Q,R and S (3 marks)
- On the diagram label the microphyle. (1mark)
- What is meant by the following terms?
- Explain what happens to excess amino acids in the liver of humans. (3marks)
- ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Which portions of the human nephron are only found in the cortex? (3 marks)…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
-
- What would happen if a person produced less antidiuretic hormone? (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - What term is given to the condition described in C (i) above? (1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- What would happen if a person produced less antidiuretic hormone? (1 mark)
-
-
- What is meant by the term biological control? (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Give an example of biological control. (1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- What is meant by the term biological control? (1mark)
-
- What is eutrophication? (3marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - What are the effects of eutrophication? (3 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- What is eutrophication? (3marks)
- Name a substance that is responsible for acid rain. (1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
-
- Leaves are the organs of photosynthesis. The following diagram shows what happens in a plant leaf during photosynthesis
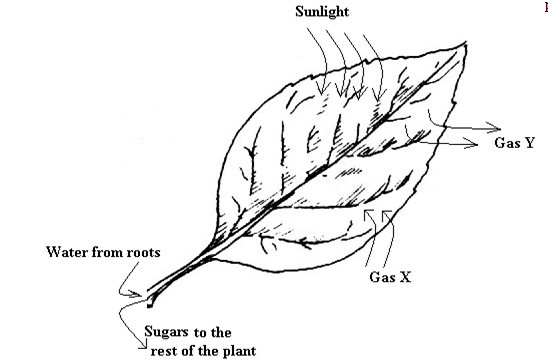
- Give two ways in which leaves are adapted to absorb light. (2 marks)………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Name the gases labelled X and Y. ( 2marks)
X………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Y……………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Name the tissue which transport:
- Water in to the leaf. ( 1 mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. - Sugars out of the leaf. (1 mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- Water in to the leaf. ( 1 mark)
- Explain why it is an advantage for the plant to store carbohydrates as starch rather than as sugars.
(2marks)………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Some millet seeds were socked in water for two days. They were then broken into small pieces and placed on the surface of agar containing starch. After two days it was found that the agar no longer contained starch.
- Suggest how the test for starch in the agar was carried out. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Explain why there was no starch in the agar after two days. (2marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Why was it necessary to soak the seeds? (1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Why were the millet seeds broken into small pieces? (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………...……. - State the observation that would be made if the seeds had been soaked in boiling water? ( 1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Suggest a control experiment that would have been suitable. ( 2marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………...………….
SECTION B:
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
- Suggest how the test for starch in the agar was carried out. (1 mark)
- A research was carried to determine the trend of growth of some boys and girls.Their average mass in kilograms was taken separately for a period of 20 years and tabulated as shown in the table below.
Age Average mass of boys (kg) Average mass of girls (kg) 0 2.5 2.5 2 11.5 11.5 4 15.0 16.0 6 18.5 19.3 8 22.1 27.1 10 25.1 27.1 12 27.5 30.5 14 37.0 35.5 16 44.0 44.0 18 46.9 52.0 20 48.5 55 
- On the same axis draw a graph of the average mass of the girls and boys against age. (7marks)
- From the graph , determine the;-
- Mass of boys at the age of 11 years. (1 mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Growth rate of girls between ages 13 and 15. ( 3 marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Mass of boys at the age of 11 years. (1 mark)
- Account for the change in the mass of girls during the age stated in (ii) above. (2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Explain the trend observed in the curves for both boys and girls. ( 2 marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Why do girls above 10 years require in take of food that is richer in iron than boys of the same age?
(2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… - Part from using average mass to estimate growth in human beings, name two other parameters that can be used. (2 marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Describe how the various parts of the human digestive system are adapted to their functions. (20 marks)
-
- State the causes of air pollution. (5 marks)
- State how air pollutants affect organisms hence state how air pollution should be controlled.
(15 marks)




MARKING SCHEME
-
- Protandry: condition in which stamen/anthers of a flower mature before the carpels/pistils/stigma;(1 mark)
- Self sterility; pollen grains from anthers of a flower fail to germinate on the stigma of the same flower ; (1 mark)
-
- Q- Antipodal cells/embryo sac wall;
R - Polar nucleus/nuclei;
S - Egg call/ovum 3 marks - Secrete enzymes that digest the stigma/style/ovary tissue;
Offer passage for male nuclei to the ovum; 2 marks
- Q- Antipodal cells/embryo sac wall;
- Award if correctly shown in the diagram; 1 mark
-
- Excess amino acids are deaminated/amino group is removed/amino group is converted in to ammonia; ammonia combines with carbon(iv) oxide(in the ornithine cycle) to form urea; carbohydrate group is converted into glucose for respiration/glycogen for storage;
2NH3+CO →CO (NH3)2 +H2O 3 marks - Glomerulus; Bowman’s capsule; proximal convoluted tubule; distal convoluted tubule; 3 marks
-
- Production of large amounts of dilute urine/diuresis; 1mark
- Diabetes inspidus; 1mark
- Excess amino acids are deaminated/amino group is removed/amino group is converted in to ammonia; ammonia combines with carbon(iv) oxide(in the ornithine cycle) to form urea; carbohydrate group is converted into glucose for respiration/glycogen for storage;
-
-
- Using a living organism to regulate/control/reduce/check the population of another organism;
1mark - Catscontrolling mice; beetles controlling water hyacinth; fish in ponds controlling mosquito larvae;
Majimoto ants controlling scales; goats controlling weeds in plantations; any 1 (1mark)
- Using a living organism to regulate/control/reduce/check the population of another organism;
-
- eutrophication is enrichment of water bodies with nitrates/phosphates/ammonium ions/sulphates/nutrients; due to discharge of sewage/domestic effluents/kitchen wastes containing detergents/run off water containing fertilizers; leading to rapid growth of surface plants/algae bloom/aquatic plants/phyloplanktons;
Acc symbols for ions (aq) must be present.
Rej kitchen wastes alone
Reg domestic wastes 3 marks - (Proliferation of plants) block light from reaching plants underneath which will not photosynthesise; the plant die and decompose leading to depletion of oxygen/lack of oxygen ;( as a result) animals also die/suffocate (to death); Reg organisms die 3 marks
- eutrophication is enrichment of water bodies with nitrates/phosphates/ammonium ions/sulphates/nutrients; due to discharge of sewage/domestic effluents/kitchen wastes containing detergents/run off water containing fertilizers; leading to rapid growth of surface plants/algae bloom/aquatic plants/phyloplanktons;
- Nitrogen (IV) oxide; sulphur (IV) oxide;
Acc Nitrogen Dioxide and sulphur dioxide
Reg oxides of sulphur and nitrogen
-
-
-
- Broad and flat to absorb maximum light;
- Have chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll for trapping light;
- Transparent cuticle to allow light to pass through;
- Palisade cells are near the upper surface for optimum absorption of light; 2 marks
- X - Carbon (IV) oxide;
Y – Oxygen; -
- Xylem;
- Phloem;
- Starch is insoluble in water; hence osmotically inactive; this reduces the effect on absorption of water
-
-
- Iodine solution was poured on the agar; 1 mark
- Millet seeds produced amylase; that converts starch to maltose2 marks
- To activate the enzymes; 1 mark
- To increase surface area for exposure of enzymes; 1 mark
- Starch would not be digested since the enzymes would be denatured by boiling;
- Placing millet seeds that have not been soaked; in water on the agar/boiled millet seeds on the agar;
2 marks
-
-
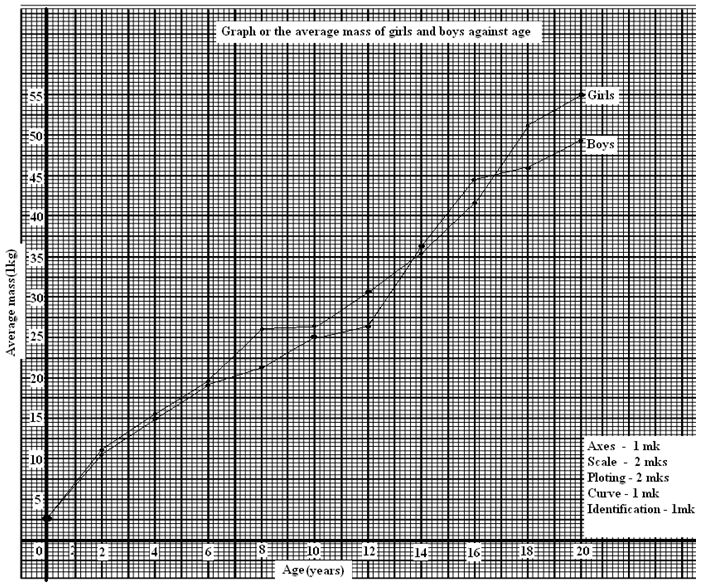
-
- 26 kgs± 0.5;
- Girls 15 yrs - 39
Girls 13 yrs - 33
6
6 ÷ 2; = 3.0 kg/year;
- Girls at adolescence grow faster; there is an increase in the size of hips and breasts;
- Girls generally grow faster than boys /boys grow slowly compared to girls; but later after puberty they grow more steadily.
- Girls above ten years begin the menstruation cycle; they need more iron to replace the blood lost during menstruation;
- Height of the body; volume of the body;
-
- Mouth;
- With teeth for chewing to increase the surface area for digestion and easy swallowing
- Has salivary gland which secrete saliva to soften and lubricate food for easy swallowing
- Has muscular tongue to turn food sideways for proper mixing with saliva and chewing
- Rolls food in to boluses and pushes them down the gullet
- Saliva has saliva amylase to initiate digestion of starch;
Oesophagus; - Has circular and longitudinal muscles to propel food in to the stomach by peristalsis
Stomach; - Has cardiac sphincter muscles to allow/regulate food into the stomach
- Pyloric sphincter to retain food for digestion in the stomach
- With gastric glands that secrete mucus to protect wall of the stomach from digestive enzymes; enzymes pepsin and rennin to digest proteins;hydrochloric acid to kill bacteria in food;and provide optmum PH for protein digestion,activation of pepsnogen
- With muscular walls whose contaction churn/mix chyne with digestive enzymes.
Duodenum - With brunners glands in its walls to produce alkaline fluid and mucus
- Has crypts of lieberkuhnwhose cells produce digestive enzymes
- Is connected to the pancrease and the liver which supply pancreatic juice and bile respectively
- Bile emulsifies fats and neutralizes the acid from the stomach. Pancreatic juice contains digestive enzymes/pancreatic lipase, pancreatic amylase and Trypsin that acts on lipids, starch/amylase and proteins respectively.
Ileum - Long to allow complete digestion and absorption of food
- With villi and microvilli to increase surface area for digestion and absorption
- Folded to increase surface area for digestion and absorption
- Narrow to keep digested food in contact with epithelium to reduce distance over which food diffuses
- With moist inner surface to enhance absorption of nutrients
- With epithelical cells continuously replaced
- Has lacteals for fat transportation
- Has muscular walls for peristaltic movement of food
Colon - Folded to increase surface area for absorption of water and mineral salts
- With muscular walls for peristaltic movement of undigested food
Rectum; - Secretes large amounts of mucus for lubrication to aid defecation
Anus - With muscular sphincter to control defecation
- Causes of air pollution
- Sulphur and nitrogen dioxide ;; from industries
- Carbon (iv) oxide ( from combustion of fuels in industries and motor vehicles);
- Dust and smoke (from quarries and factories)
- Radio active radiations(from atomic and nuclear plants)
- Agricultural chemicals used as sprays;
- Noise from factories and vehicles;
mark any five
Effects on organisms - Sulphur dioxide/nitrogen dioxide/dust/smoke/carbon iv oxide and agricultural sprays cause respiratory diseases; and irritate respiratory systems;
- Nitrogen dioxide /sulphur dioxide combine with atmospheric moisture to form acidic rainfall which is corrosive; poisonsplants; lower metabolic activities/photosynthesis; acidic soils destroy vegetation.
- Dust/ smoke reduce amount of light reaching on the plant lowering photosynthesis;
- Carbon II oxide is a respiratory poison/combine with haemoglobin reducing oxygen carrying capacity of red blood cells;
- Carbon iv oxide causes green house effect by forming a layer around the earth’s atmosphere/insulate the earth causing global warming/ change of climatic patterns;
- Radioactive radiation causes mutation and cancer;
Control methods - Erect factories and power generating station from residential areas;
- Build factories with chimneys to discharge waste gases up the ground;
- Educate people on dangers of air pollution;
- Filtration of waste gases to remove poisonous pollutants before being discharged into the air;
- Use of alternative less polluting fuels like hydroelectric power/lead free fuels;
- Use smokeless fuels in houses and factories;
- Banning manufacture and use of chemical weapons;
- Impose heavy fines on air pollutors; (like factories)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 2 Kenya High Post Mock Exams 2020 - Questions and Answers.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

