INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections: A and B
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- All working must be clearly shown.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used
- Take g=10ms-2
- Density of mercury = 13600 kg/m3
For Examiner’s Use
|
SECTION |
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
A |
1-12 |
25 |
|
|
B |
13 |
12 |
|
|
14 |
10 |
||
|
15 |
10 |
||
|
16 |
12 |
||
|
|
17 |
11 |
|
|
TOTAL |
80 |
||

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provide
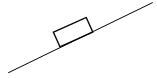
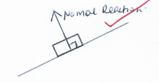
- The figure below shows a body resting on an inclined plane. Indicate the normal reaction (1 mark)
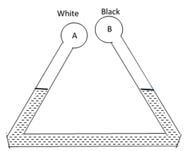
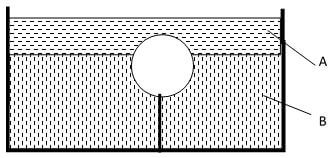
- The figure below shows two identical bulbs A and B painted white and black respectively connected with a pipe containing water at the same level at the room temperature.
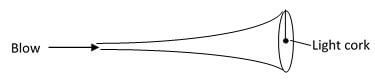
State and explain the observation made when ice cold water is poured on the bulbs (2 marks) - A boy blows through the mouth of a hollow vuvuzela as shown below. A light cork is suspended freely by a string as shown. Giving reason indicate the path taken by the cork (2 marks)
- The figure below shows a hollow metal cylindrical tin. A student used a vernier caliper and a micrometer screw gauge to determine the external and internal diameter of the tin respectively. The readings of the instruments are as shown below
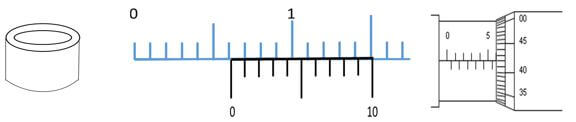
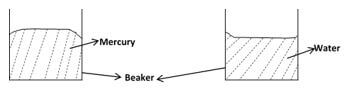
Determine the thickness of the metal used to make the tin in SI unit leaving your answer in standard form (3 marks) - The figure below shows the level of mercury and water in a beaker.
Explain the difference in the shape of the meniscus (1 mark) - When an inflated balloon is placed in a refrigerator, it is noted that its volume reduces. Use kinetic theory to explain this observation (2 marks)
- The figure below shows a solid just before being released into a liquid of the same density as the solid. On the same diagram draw the observation made when the solid is released (1 mark)
- The figure below shows a glass tumbler partly filled with water at room temperature.
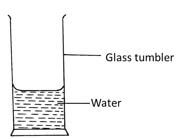
Briefly explain what happens to the stability of the tumbler when the water is heated (2 marks) - The figure below shows some air trapped in a glass tube, the tube is inverted in a dish containing mercury.
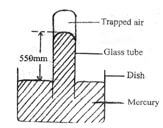
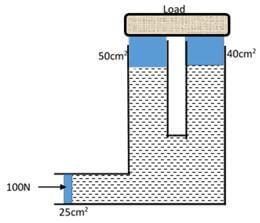
Given that the atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg and the height of mercury column in the glass is 550 mm determine the pressure of the air trapped in the tube in mm Hg. (2 marks) - The figure below shows a hydraulic machine in equilibrium while supporting a load when a force of 100N is applied one of the pistons. The cross section area of the pistons are as shown. Determine the weight of the load (3 marks)
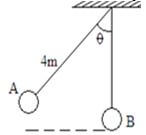
- A metal ball suspended vertically with a light string of length 4m is displaced through an angle as shown in the diagram below. The body is released from A and swings past the lowest point B. Given that its velocity at point B is 4 m/s, determine angle ϴ (3 marks)
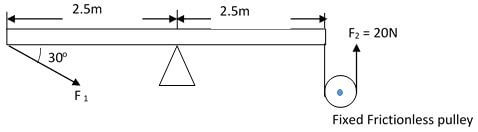
- The figure below shows a uniform bar balanced by forces F1 and F2. Determine the value of F1 (3 marks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided
-
- An object of mass 50g is dropped from a height of 80m to hit the ground below
- For the motion, on the same axes, sketch and label the graphs of : (3 marks)
- Kinetic energy against time
- Potential energy against time
- Determine how long it takes to reach the ground (2 marks)
- Determine the momentum as it hits the ground (3 marks)
- For the motion, on the same axes, sketch and label the graphs of : (3 marks)
- Engine oil licks on the ground from a lorry as it decelerates uphill. The oil drops are shown below as black dots. The time between any two drops is constant at 2sec

- On the same diagram indicate the direction of the lorry with an arrow (1 mark)
- Determine the acceleration of the deceleration of the lorry (3 marks)
- An object of mass 50g is dropped from a height of 80m to hit the ground below
- The figure below shows a system used to lift a septic slab of weight 150N by applying a force of 50N on a light bar as shown. The radii of the pulley belt wheels are as indicated in the diagram
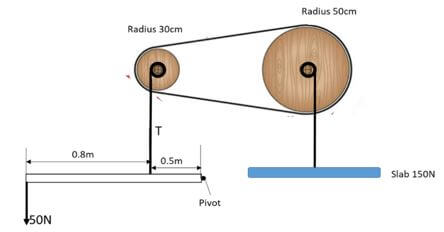
Determine- Tension T of the vertical string (3 marks)
- MA of the system (2 marks)
- VR of the system ( 3 marks)
- Efficiency of the system ( 2 marks)
-
- State three factors that affect the toughness of a spring (3 marks)
- When a mass of 120g is applied to a spring the pointer reads 6cm. A pan, in which a mass of 210g is placed, is now suspended from the spring and the pointer reads 14cm. When the 210g mass is removed from the pan the pointer reads 4cm.
- Draw a diagram or diagrams to represent the information above (1 mark)
- Determine the mass of the pan. (3 marks)
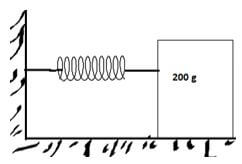
- The figure below shows a mass 200g placed on a frictionless surface and attached to a spring. The spring is compressed and released. Given that the elastic potential energy of the compressors spring is 2.7x10-2J. Determine the maximum speed with which the blocks moves after released. (3 marks)
- The sphere below has a volume of 0.1 litres. It is held with a tight string at the base with ¼ of its volume in liquid A of density 380kg/m3 while the rest is in Liquid B of density 700kg/m3. The tension of the string is 0.32N
Find- Mass of liquid A displaced (2 marks)
- Mass of liquid B displaced (2 marks)
- Upthrust experienced by the sphere (2 marks)
- Mass of the sphere (3 marks)
- Density of the sphere (3 marks)
- A girl joins two 20g masses A and B on a string and whirls them in a vertical circle Centre O of radius 50cm as shown below. The bodies maintained an angular velocity of 10 Rad-s
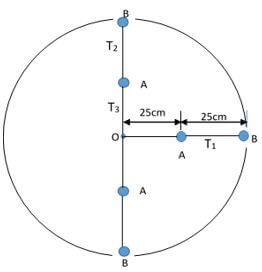
Determine:- The linear velocity of body A (2 marks)
- Centripetal acceleration of Body B (2 marks)
- The tension of the string
- T1 (2 marks)
- T2 (2 marks)
- T3 (3 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in the spaces provide
- The figure below shows a body resting on an inclined plane. Indicate the normal reaction (1 mark)
- The figure below shows two identical bulbs A and B painted white and black respectively connected with a pipe containing water at the same level at the room temperature.

State and explain the observation made when ice cold water is poured on the bulbs (2 marks)- level of water in side B rises while on side A lowers
- Black bulbs emits heat at a higher rate than the white. Air on side B contracts more causing the change of level as indicated
- A boy blows through the mouth of a hollow vuvuzela as shown below. A light cork is suspended freely by a string as shown. Giving reason indicate the path taken by the cork (2 marks)

air passes A at a higher speed than B.
Pressure lower at A greater pressure at B pushes the cork as shown - The figure below shows a hollow metal cylindrical tin. A student used a vernier caliper and a micrometer screw gauge to determine the external and internal diameter of the tin respectively. The readings of the instruments are as shown below

Determine the thickness of the metal used to make the tin in SI unit leaving your answer in standard form (3 marks)
standard form
external diameter = 0.61 cm
internal diameter = 5.50
+ 0.42
5.92 mm
thickness = external diameter - internal diameter
2
= 6.1 mm - 5.92mm = 0.09 mm
2
= 9 x 10-5 m - The figure below shows the level of mercury and water in a beaker.

Explain the difference in the shape of the meniscus (1 mark)- for mercury C >A and for water A>C
- When an inflated balloon is placed in a refrigerator, it is noted that its volume reduces. Use kinetic theory to explain this observation (2 marks)
- A heat escapes molecules looose Kinetic energy
- Molecule slow down making the balloon to shrink
- The figure below shows a solid just before being released into a liquid of the same density as the solid. On the same diagram draw the observation made when the solid is released (1 mark)
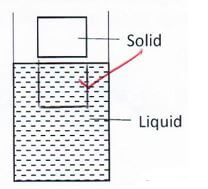
- The figure below shows a glass tumbler partly filled with water at room temperature.

Briefly explain what happens to the stability of the tumbler when the water is heated (2 marks)- stability reduces
- when heated water expands at a higher rate than glass. It rises raiasing the egg
- The figure below shows some air trapped in a glass tube, the tube is inverted in a dish containing mercury.

Given that the atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg and the height of mercury column in the glass is 550 mm determine the pressure of the air trapped in the tube in mm Hg. (2 marks)
- GP + CP = Atm
GP = atm - CP
= 760 - 550
210 mmHg
- GP + CP = Atm
- The figure below shows a hydraulic machine in equilibrium while supporting a load when a force of 100N is applied one of the pistons. The cross section area of the pistons are as shown. Determine the weight of the load (3 marks)

F1 = F2
A1 A2
100 = F2
25 90
F2 = 100 x 90 = 360N
25 - A metal ball suspended vertically with a light string of length 4m is displaced through an angle as shown in the diagram below. The body is released from A and swings past the lowest point B. Given that its velocity at point B is 4 m/s, determine angle ϴ (3 marks)
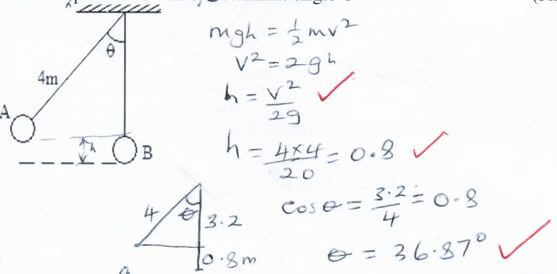
- The figure below shows a uniform bar balanced by forces F1 and F2. Determine the value of F1 (3 marks)
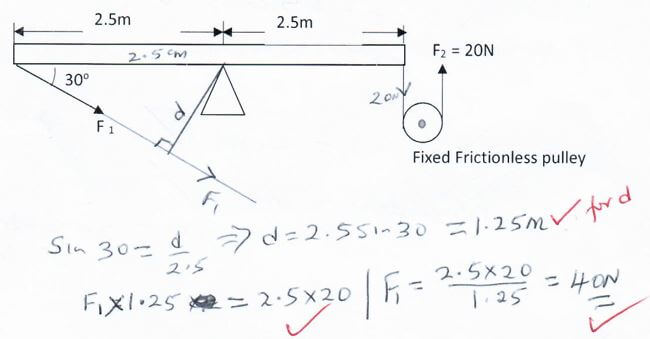
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided
-
- An object of mass 50g is dropped from a height of 80m to hit the ground below
- For the motion, on the same axes, sketch and label the graphs of : (3 marks)
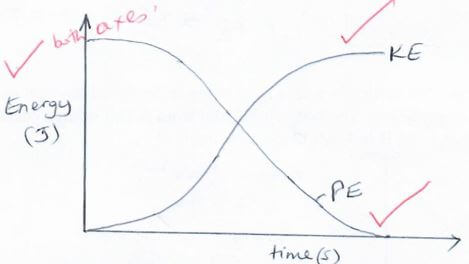
- Kinetic energy against time
- Potential energy against time
- Determine how long it takes to reach the ground (2 marks)
- h = 1/2gt2
80 = 1/2 x 10t2
t2 = 16
t = 45 seconds
- h = 1/2gt2
- Determine the momentum as it hits the ground (3 marks)
- v = gt
v = 10 x 4
momentum = mv
0.05 x 40 = 20kgm/s
- v = gt
- For the motion, on the same axes, sketch and label the graphs of : (3 marks)
- Engine oil licks on the ground from a lorry as it decelerates uphill. The oil drops are shown below as black dots. The time between any two drops is constant at 2sec

- On the same diagram indicate the direction of the lorry with an arrow (1 mark)
- Determine the acceleration of the deceleration of the lorry (3 marks)
- u = 120/4 = 30m/s
v = 80/4 = 20 m/s
a = v - u
t
a = 20 - 30 = -1.25 m/s2
4 x 2
d = 1.25 m/s2
- u = 120/4 = 30m/s
- An object of mass 50g is dropped from a height of 80m to hit the ground below
- The figure below shows a system used to lift a septic slab of weight 150N by applying a force of 50N on a light bar as shown. The radii of the pulley belt wheels are as indicated in the diagram

Determine- Tension T of the vertical string (3 marks)
- f1d1 = f2d2
50 x 1.3 = T x 0.5
T = 130N
- f1d1 = f2d2
- MA of the system (2 marks)
- MA = L/E = 150/50 = 3
- VR of the system ( 3 marks)
- VR = VR1 X VR2
1.3 x 50 = 4.333
0.5 30
- VR = VR1 X VR2
- Efficiency of the system ( 2 marks)
- eff = MA x 100
VR
Eff = 3/4.333 x 100 = 69.23%
- eff = MA x 100
- Tension T of the vertical string (3 marks)
-
- State three factors that affect the toughness of a spring (3 marks)
- no of coils or length of the spring
- cross section area of the spring
- materials making the string
- When a mass of 120g is applied to a spring the pointer reads 6cm. A pan, in which a mass of 210g is placed, is now suspended from the spring and the pointer reads 14cm. When the 210g mass is removed from the pan the pointer reads 4cm.
- Draw a diagram or diagrams to represent the information above (1 mark)
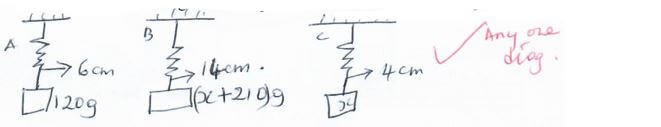
- Determine the mass of the pan. (3 marks)
- comparing A and B
e = 8
mass = x + 210 - 120
= (90 + x)g - Comparing A and C
e = 2 cm
mass = (120 - x)g - Combining
90 + x = 120 - x
8 2
90 + x = (120 - x)4
90 + x = 480 - 4x
5x = 390
x = 78g
- comparing A and B
- Draw a diagram or diagrams to represent the information above (1 mark)
- The figure below shows a mass 200g placed on a frictionless surface and attached to a spring. The spring is compressed and released. Given that the elastic potential energy of the compressors spring is 2.7x10-2J. Determine the maximum speed with which the blocks moves after released. (3 marks)

- EPE = KE
2.7 x 10-2 = 1/2 x 0.2v2
v2 = 0.27
v = 0.5196m/s
- EPE = KE
- State three factors that affect the toughness of a spring (3 marks)
- The sphere below has a volume of 0.1 litres. It is held with a tight string at the base with ¼ of its volume in liquid A of density 380kg/m3 while the rest is in Liquid B of density 700kg/m3. The tension of the string is 0.32N

Find- Mass of liquid A displaced (2 marks)
- volume of sphere = 100cm3
volume of liquid A = 1/4 x 100 = 25cm3
mass of A = Fv = 0.38 x 25 = 9.5g
- volume of sphere = 100cm3
- Mass of liquid B displaced (2 marks)
- volume of B = 100 - 25 = 75
mass of B = fv = 0.7 x 75 = 52.5g
- volume of B = 100 - 25 = 75
- Upthrust experienced by the sphere (2 marks)
- upthrust = weight of fluids displaced
= 0.095 + 0.525
= 0.62N
- upthrust = weight of fluids displaced
- Mass of the sphere (3 marks)
- T = u -mg
0.32 = 0.62 - mg
mg = 0.62 - 0.32 = 0.3N
m = 0.30/10 = 0.03kg or 30 g
- T = u -mg
- Density of the sphere (3 marks)
- f = m/v = 30/100 = 0.3g/cm3 or 300 g/m3
- Mass of liquid A displaced (2 marks)
- A girl joins two 20g masses A and B on a string and whirls them in a vertical circle Centre O of radius 50cm as shown below. The bodies maintained an angular velocity of 10 Rad-s

Determine:- The linear velocity of body A (2 marks)
- a = rw
a = 0.25 x 10
= 2.5 m/s
- a = rw
- Centripetal acceleration of Body B (2 marks)
- a = rw2
a = 0.5 x 102
= 50 m/s2
- a = rw2
- The tension of the string
- T1 (2 marks)
T1 = mrw2 or T1 = ma
= 0.02 x 50
= 1N - T2 (2 marks)
T2 = mrw2 - mg
1 - 0.2
= 0.8N - T3 (3 marks)
TA = mrw2 - mg
0.02 x 0.25 x 102 - 0.2
0.5 - 0.2 = 0.3 N
T3 = T2 + TA
0.8 + 0.3 = 1.1N
- T1 (2 marks)
- The linear velocity of body A (2 marks)
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Bunamfan Post Mock 2021 Exams.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

