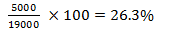SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
- Identify two hard wood tree species in Kenya. (2 mks)
- Give two ways in which tree harvesting in Kenya differ from that of Canada. (4 mks)
-
- Name two tourist attractions along the Kenyan coast. (2 mks)
- State two physical factors that attract tourists in Switzerland. (2 mks)
-
- Name two exotic breeds of dairy cattle reared in Kenya. (2 mks)
- State three physical conditions that favour dairy farming in Kenya. (3 mks)
-
- Name two prairies provinces of Canada where wheat is grown on large scale. (2mks)
- Give three physical conditions that favour large scale wheat farming in prairies provinces of Canada. (3 mks)
-
- What is a polder? (2 mks)
- Name three crops grown in the polders. (3 mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- The table below shows the number of tourists who visited Kenya from various parts of the world in 2005 and 2006. Use it to answer questions (a) and (b).
Place of origin
No. of tourist per year
2005
2006
Europe
Africa
Asia
North America
Australia & New Zealand
All other countries
942,000
120,000
97,000
94,000
19,000
29,000
965,000
154,000
128,000
103,000
24,000
41,000
Total
1,301,000
1,415,000
-
- Which continent had the highest increase in the number of tourist visiting Kenya between 2005 and 2006. (2 mks)
- Calculate the percentage increase of tourist from Australia & New Zealand between 2005 and 2006. (2 mks)
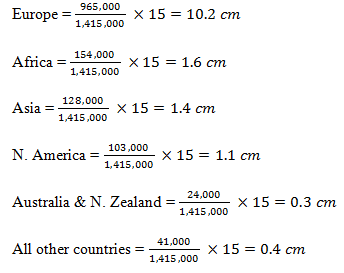
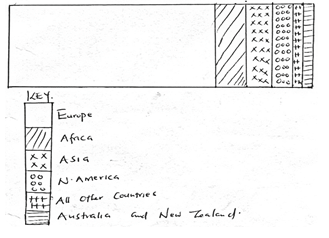
- Draw a divided rectangle of 15cm long to represent the number of tourist that visited Kenya in 2005. Show your working. (10 mks)
-
- State two advantages of using divided rectangle to represent geographical data.(2 mks)
- Give four reasons why in 2005 and 2006 there were more tourist visiting Kenya from Europe compared to those from other part of world. (4 mks)
- Give five reasons why domestic tourism is being encouraged I n Kenya.
-
-
- The table below shows the quantity of minerals produced in Kenya in tonnes between year 2001 and 2005. Use it to answer questions a (i) and (ii).
Minerals/year
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
Soda ash
297,780
304,110
352,560
353,835
360,161
Fluorspar
11,885
85,015
80,201
117,986
109,594
Salt
5,664
18,848
21,199
31,139
26,595
Others
6,093
7,000
4,971
6,315
8,972
Source: Survey 2006- Calculate the average annual production of soda ash over the 5 year period. (2 mks)
- Calculate the total mineral production for the year 2003. (1 mk)
- Give three uses of soda ash. (3 mks)
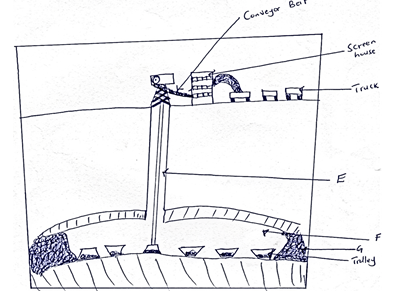
- The diagram below shows shaft mining.
- Name the parts marked E, F, G. (3 mks)
- State two problems associated with shaft mining. (2 mks)
- Explain four ways in which gold mining has contributed to the economy of South Africa. (8 mks)
- Explain three negative effects of mining on the environment. (6 mks)
- The table below shows the quantity of minerals produced in Kenya in tonnes between year 2001 and 2005. Use it to answer questions a (i) and (ii).
-
- Name three cocoa growing areas in Ghana. (3 mks)
-
- Outline the stages involved in the processing of cocoa from harvesting to the time it is ready for export. (6 mks)
- List four problems experienced by cocoa farmers in Ghana. (4 mks)
- State four physical conditions necessary for growing of cocoa. (4 mks)
- You intend to carry out a field study on agricultural activities around your school.
- State four preparations that you would make for your study. (4 mks)
- Give four following activities you would carry out after the field study. (4 mks)
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation. (2 mks)
- State three methods used in reclaiming land in Kenya. (3 mks)
- State three methods used to control tsetse flies in Lambwe valley in Kenya. (3 mks)
-
- Explain four physical conditions favouring rice growing in MweaTebere Irrigation Scheme. (8 mks)
- Describe the stages in the reclamation of land from the sea in Netherlands. (7 mks)
- Name two major projects involved in reclaiming land in Netherlands. (2 mks)
-
-
- Define fisheries. (2 mks)
- Name two countries in Southern Africa that are important for marine fish production. (2 mks)
- Explain four factors that favour fishing in Japan. (8 mks)
- Describe purse seining as a method of fishing. (6 mks)
-
- State four problems experienced in the marketing of fish in Kenya. (4 mks)
- State three ways in which the Kenya government is promoting fishing industry in the country. (3 mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- Hardwood tree species in Kenya.
- Camphor
- Meru oak
- Elgon teak
- Mahogany
- Mvule/Mvuli
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Ways in which tree harvesting in Kenya differs from that of Canada.
- In Kenya tree harvesting is carried out throughout the year while in Canada harvesting is carried out in winter and early spring.
- In Kenya harvesting is done selectively while in Canada clear cutting or indiscriminate cutting of tree is carried out
(Any 2 x 2 = 4 mks)
- Hardwood tree species in Kenya.
-
- Tourist attractions along the Kenyan coast.
- Historical sites/Fort Jesus/Gedi ruins/Vasco da Gama pillar
- Sand beaches
- Warm tropical climate
- Varied culture along the coast
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Physical factors that attract tourists in Switzerland.
- Glaciated features/hanging valleys
- Snowcapped Alps mountain
- The glittering lakes
- Warm summer/cold winter
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Tourist attractions along the Kenyan coast.
-
- Exotic dairy cattle breeds reared in Kenya.
- Friesian
- Ayrshire
- Jersey
- Guernsey
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Physical conditions favouring dairy farming in Kenya.
- Availability of rich and nutritious grass in the highlands
- Cool temperatures in the highlands that are conducive for dairy farming
- Availability of reliable water supply which favour growth of pastures and water for animals
- The landscape is gently sloping for easy grazing of the animals
- There is high rainfall for growth of pasture
- The dairy farming areas are free of tsetse fly/diseases, so there is little expenses in maintaining and treating of animals
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Exotic dairy cattle breeds reared in Kenya.
-
- Prairies provinces of Canada where wheat is grown on large scale.
- Albrta
- Manitoba
- Saskachewan
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Physical conditions favouring large scale wheat farming in the prairies provinces of Canada.
- Extensive land that allow cultivation on a large scale
- Presence of prairies soil/dark brown chenozens
- Undulating landscape that allows use of farm machinery/mechanization
- Suitable climate with frost free peiod/warm summers which allows timely ripening and harvesting/sunny summers
- The area receives moderate rainfall 1560mm annually which is suitable for wheat growing
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Prairies provinces of Canada where wheat is grown on large scale.
-
- What is a polder?
Polder is land reclaimed from the sea (2 mks) - Crops grown in the polders.
- Rye
- Barley
- Oat
- Wheat
- Flowers
- Tomatoes
- Sugar beet
- Potatoes
- Fodder crops
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- What is a polder?
SECTION B
-
-
- Highest increase in number of tourist.
Africa (2 mks) - % increase in number of tourist visiting Kenya between 2005 and 2006 from Australia and New Zealand.
- Divided rectangle working/calculations.
DIVIDED RECTANGLE SHOWING TOURIST TO KENYA IN 2006
Marking
Segment 6 x 1 = 6 mks
Calculations1/2mark @ = 3 mks
Tittle = 1 mk
10 mks
- Highest increase in number of tourist.
-
- State two advantages of divided rectangle to represent geographical data.
- Give clear visual impression of individual components
- Easy for comparison
- Can be used to represent a wide range of data
- Easy to draw
- Easy to read/interpret
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Reasons why in 2005 and 2006 there were more tourists visiting Kenya from Europe.
- There are many direct flights from European capitals to Kenya
- Aggressive marketing for tourism in Europe
- Europe has had long historical ties with Kenya/good relations
- European countries encourage package tours to Kenya
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- State two advantages of divided rectangle to represent geographical data.
- Give reasons why domestic tourism is being encouraged in Kenya.
- Expose Kenyans to a wide variety of recreation facilities
- To make use of tourist facilities during low tourist seasons
- Ensure Kenyans become familiar with different parts of the country
- To make Kenyans appreciate the country’s national heritage/artifacts/culture/wildlife
- Enhance circulation of money within the country/promote domestic trade
- Create employment to the country
(Any 5 x 1 = 5 mks)
-
-
-
- Average annual production of soda ash.
1668446 ÷5=333689.2 tonnes - Total production of minerals for year 2003.
458931 Tonnes(1mk) - Three uses of soda ash.
- It is used as a raw material for making glass
- It is used in making detergents
- It is used in some chemical industries
- It is used as water softener
- It is used in paper industries
- It is used in desulphurising steel
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Average annual production of soda ash.
-
- Parts marked.
E – Main shaft/vertical shaft
F – Tunnel/Horizontal tunnel
G – Mineral ore/Rock bearing mineral
(3 x 1 = 3 mks) - Problems associated with shaft mining.
- Sometimes mines get flooded with subterranean water
- Occasional emissions of poisonous gases in mines
- Dust produced cause respiratory diseases
- Sometimes tunnels collapse causing death of miners
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Parts marked.
- Explain four ways in which gold mining has contributed to the economy of South Africa.
- Earns foreign exchange which is used to improve other sectors of economy
- Gold provides raw materials for industries that make jewelry and other high valued items promoting industrial expansion
- Gold as a medium of exchange in the world is used in South Africa as means of paying international debts
- Gold mining industry generate employment opportunities which raises the standard of living
- Gold mining lead to development of towns in the Rand and Orange free state creating demand for agricultural product
- Mining of gold has led to expansion of infrastructure such as transport and communication which have created linkages between mining towns and other parts of the country
- Gold mining has led to development of industries, mining skills that are useful in other sectors
(Any 4 x 2 = 8 mks)
- Three negative effect of mining of environment.
- Dumping of rock waste has led to loss of biodiversity/destruction of natural vegetation
- Dereliction of land with dumping of waste is an eye sore/destroys natural beauty of land
- Pollution of area by noise, blasts, smoke, water pools are all health hazards
- Mining disrupts water table which may lead to water shortage
- Mining takes up land that would be used for agriculture thus interfering with food production
- Mining displaces human settlement
(Any 3 x 2 = 6 mks)
-
-
- Name three cocoa growing areas in Ghana.
- Accra
- Kumasi
- Takoradi
- Tema
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
-
- Outline the stages involved in the processing of cocoa from harvesting to the time its ready for export.
- Pods are harvested using sharp pointed knives
- Pods are collected and piled at a certain place
- Pods are opened with sharp knives and beans scooped out by hands
- Beans are put in heaps on mats and covered with banana leaves
- Beans are allowed to ferment for 5 – 6 days during which the juicy pulp drains away
- Fermented beans are washed and cleaned
- Beans are spread on table covered with mats to dry in hot sun
- Beans are turned frequently as they dry and slowly they turn brown
- Dry beans are put in sacks and sent to harvest buying centre
- At the centre the dry beans are weighed and graded ready for export
Sequence should be followed (Any 6 x 1 = 6 mks)
- List four problems experienced by cocoa farmers in Ghana.
- Pest and diseases which destroy crops
- Fluctuation of prices in the world market which discourage the farmers
- Low prices paid of the crop discourage farmers
- Strong hamattan winds destroy crops/strong winds
- Inadequate labour during harvesting
- Poor means of transport make it difficult for farmers to deliver the crop in time
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- Outline the stages involved in the processing of cocoa from harvesting to the time its ready for export.
- State four physical conditions necessary for growing of cocoa.
- High temperature throughout the year/average must be over 21oc to 30oc
- High rainfall not less than 1000 – 2100 mm evenly distributed throughout the year
- Deep fertile well drained soils/can withstand wide variety of soils
- Low altitude of up to 700m above sea level
- Seedling must be sheltered from strong winds
- High relative humidity
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
-
- Four preparations that you would make for study.
- Seeking permission from relevant authority
- Preparing students into groups
- Formulating objectives and hypothesis
- Conducting reconnaissance/pre-visit
- Identifying/collecting relevant tools/equipment
(Any 4 x 1 = 1 mk)
- Give four follow – up activities.
- Analyzing photographs/data collected
- Writing reports
- Displaying photographs
- Displaying collected samples
- Holding class discussion
- Consulting the teacher
- Reading further
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- Four preparations that you would make for study.
- Name three cocoa growing areas in Ghana.
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and rehabilitation.
Land reclamation is the process by which unproductive land is made useful for agriculture and settlement whereas land rehabilitation is the process of restoring land to its former productive state (2 mks) - Methods of land reclamation in Kenya.
- Irrigation
- Draining swamps
- Controlling pests e.g. tsetse fly
- Afforestation
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Methods of controlling tsetse flies in Lambwe valley.
- Sterilizing the male fly
- Bush spraying
- Bush clearing
- Creation of buffer zones
- Killing of the hosts
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
-
- Physical factors favouring rice growing in MweaTebere.
- Constant/plenty water supply from rivers Thiba and Nyamindi
- Black cotton soils which are capable of retaining water
- Gently sloping land making it possible for irrigation allowing water to flow by gravity
- Extensive land for expansion
- Warm climate which favours growth of rice
(Any 4 x 2 = 8 mks)
- Stages in the reclamation of land from the sea in Netherlands.
- Protecting dykes/sea walls are constructed to enclose the part of the sea to be reclaimed
- Ring canals are constructed on the interior side of the dykes
- Pumping stations are installed to pump out sea water from the area enclosed by the dykes
- Reeds are planted to help dry out the soil
- Drainage ditches are made on the land being reclaimed
- Drainage pipes ae laid below the soil
- The area is divided into rectangular portions using inner dykes and canals
- Soils are treated with chemicals to lower salinityThe drained land is flushed with fresh water to remove salt from the soil
- Infrastructure is laid down
(Any 7 x 1 = 7 mks)
- Major projects involved in reclaiming land in Netherlands.
- Zuyder Zee project
- Delta plan project
(2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Physical factors favouring rice growing in MweaTebere.
- Differentiate between land reclamation and rehabilitation.
-
-
- Define fisheries.
Fisheries are water bodies where exploitation of aquatic organisms is carried out(2 mks) - Name two countries in Southern Africa that are important for marine fish production.
- South Africa
- Angola
- Namibia
(Any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
- Define fisheries.
- Explain four factors that favour fishing in Kenya.
- The cool waters are ideal for fish breeding because of abundant supply of planktons
- The coast has many off shore islands which provide sheltered inlets ideal for establishment of fishing port/villages
- The indented coastline provides secure breeding ground for fish
- The meeting/convergence of warm kurosiwo and cold siwo ocean current results in upwelling of sea water thus bringing minerals for the planktons from the sea bed to surface
- Most settlement are found along the coast and main occupation of people is fishing
- Japanese had advanced technology used in fishing, processing and preserving fish
- Japan has large population that provides ready market for fish
- Shallow continental shelf allow light in the sea bed for growth of micro-organism which are food for fish
(Any 4 x 2 = 8 mks)
- Describe purse seining as a method of fishing.
- It uses two boats, one larger and small one
- It uses large net
- The net has floats on top and weights at the bottom to keep it in a vertical position while in water
- The net has a string along its bottom edge
- The fishermen begin by locating a shoal/area rich in fish
- The small boat drags the net to enclose the area that has fish
- The string at the bottom of the net is pulled to close the net at the bottom and trap the fish
- The net is pulled out of water and fish is hauled into the large boat for preservation and transportation to the shores
(Any 6 x 1 = 6 mks)
-
- Four problems experienced in marketing of fish in Kenya.
- Some fishing areas are far from market and roads are poor therefore fish go bad
- Fishermen lack appropriate storage and preservation of fish
- There are limited local market due to cultural beliefs
- External market are limited by strict regulation/competition from other producers
- Limited number of fish species limits the market
(Any 4 x 1 = 4 mks)
- Three ways in which the Kenya government is promoting fishing industry in the country.
- Fishermen are given loans
- Fishermen are encouraged to form cooperatives
- Research are carried out/restocking of over-fished areas with fingerlingsThere is standardization of size of nets used for fishing
- Restriction of fishing in some areas/specific area where fish breeds
- Laws have been enacted against water pollution to protect fish
- Clearance of water hyacinth from the fresh water fisheries
(Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- Four problems experienced in marketing of fish in Kenya.
-
Download GEOGRAPHY PAPER 2 - KCSE 2019 STAREHE PRE MOCK EXAMINATION (WITH MARKING SCHEME).
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students