CONFIDENTIAL
- FORM THREE: Use The Map Of KIJABE 1: 50,000 For QUESTION 6
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and admission number in the spaces provided at the top of the page
- Answer all the questions in section A.. In section B answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- All answers must be written in the answer booklet provided.
- This paper consist of 5 printed pages.
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no question is missing.
QUESTIONS
-
- State how the corriolis force affects the direction of wind. (2 marks)
- Give three characteristics of cumulonimbus clouds (3 marks)
- The table below shows the mean monthly rainfall and temperature for station
Describe the climatic characteristics represented by the mean monthly rainfall and temperature table station X. (5 marks)Months
J
F
M
A
M
J
J
A
S
O
N
D
Mean monthly rainfall (mm)
15
8
8
13
31
51
51
51
28
25
18
20
Mean monthly temperature (0C)
-22
-18
-12
-1
4
10
11
11
5
-11
-18
-22
-
- What is an earthquake (2 marks)
- Identify the scales used to measure (2 marks)
- The intensity of earthquake
- The magnitude of earthquake
-
- Name two types of boundaries according to the plate tectonic theory (2 marks)
- Give three effects of the movement of tectonic plates. (3 marks)
-
- State three conditions that influence the process of solifluction in mass wasting . (3 marks)
- Give two negative effects of mass wasting on the physical environment (2 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and ANY OTHER TWO questions from this section.
- Study the map of Kijabe 1;50, 000 (Sheet 134/3) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- What type of map is the Kijabe (1 mark)
- In which hemisphere is the area covered by the Kijabe Map located? (2 marks)
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the Kijabe Map. (2 marks)
-
- Covert the linear scale of the map into a statement. (2 marks)
- Give six figure grid reference of trigonometrical station 2610. (2 marks)
- On the graph paper provided, reduce the area enclosed by Eastings 34 to 40 and Northings 91 to 97 by a scale factor of 2 (3 marks)
- On the new map, accurately mark the following;
- All weather road bound surface (1 mark)
- Forest guard post (1 mark)
- Githoito plantation (1 mark)
- Give the new scale of the reduced map (2 marks)
- On the new map, accurately mark the following;
- Describe the vegetation of the area covered by the map (4 marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, explain two factors influencing trade in the area covered by the map (4 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between faulting and folding. (2 marks)
- Name five features formed as a result of faulting. (5 marks)
- The world map below shows the location of some fold mountains. Use it to answer question (a) (i)
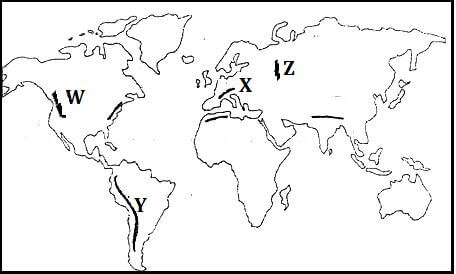
- Identify the fold mountains marked W, X, Y and Z (4marks)
- Citing relevant examples, explain how Fold Mountains were formed according to the plate tectonics theory. (6 marks)
- Explain the effects of Fold Mountains on the following
Transport. (2 marks)
Agriculture. (2 marks)
Tourism. (2 marks)
Mining. (2 marks)
-
-
- Describe the following wind erosion processes
- Abrasion (2 marks)
- Deflation (2 marks)
- Use the diagram below to answer the following questions.
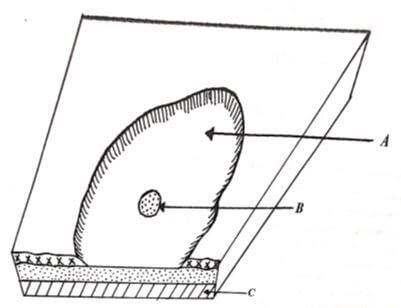
- Name the feature marked A and B (2 marks)
- State three significance of feature A to the human environment (3 marks)
- Using a well-labelled diagram, explain how the following features are formed.
- Canyon (6 marks)
- Zeugen (6 marks)
- State four characteristics of a barchan (4 marks)
- Describe the following wind erosion processes
-
-
- Define a coastline (2 marks)
- Give three types of a coral reef (3 marks)
- Using a well labelled diagram describe the formation of the following coastal landforms.
- A Tombolo (6 marks)
- Off-shore bar (6 marks)
-
- Give three factors that determine the size of a wave in the open sea. (3 marks)
- State three uses of coral reefs (3 marks)
- Students from Mombasa high school carried out a field study along the coastline of Indian Ocean. Give the reason for carrying the following items (2 marks)
- Stop watch
- Camera
-
-
-
- State three characteristics of a maximum thermometer. (3 marks)
- Explain how a maximum thermometer is used to measure temperature (6 marks)
- Describe
- How lake Victoria influences the temperature of the surrounding region. (4 marks)
- How south east trade wind. Influence temperature at the coast. (2 marks)
-
- Explain two ways in which vegetation adapts to hot climate. (4 marks)
- Describe the characteristics of equatorial climate (6 marks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
- state how the corriolis force affects the direction of wind. (2mks)
- In the northern hemisphere it deflects winds to the right while in the southern hemisphere it deflects wind in the left.
- Give three characteristics of cumulonimbus clouds (3mks)
- They are made of water droplets at the lower level and ice crystals at the upper levels
- They have great vertical extent
- They are big, heavy and black
- The top spreads out into an anvil
- They are associated with heavy rainfall/thunder and lighting
Any 3 x 1 = 3 marks
- state how the corriolis force affects the direction of wind. (2mks)
- The table below shows the mean monthly rainfall and temperature for station
Describe the climatic characteristics represented by the mean monthly rainfall and temperature table station X. (5mks)J
F
M
A
M
J
J
A
S
O
N
D
Mean monthly rainfall (mm)
15
8
8
13
31
51
51
51
28
25
18
20
Mean monthly temperature (0C)
-22
-18
-12
-1
4
10
11
11
5
-11
-18
-22
- Temperatures are low throughout the year
- January records the lowest temperature of -22º
- June, July and August record the highest temperatures of 11º
- The annual range of temperature is great 33ºc
- The region experiences low rainfall throughout the year (319mm)
- Lowest rainfall of 8mm is received in February and March
- Region experience rainfall throughout the year.
- The highest amount of rainfall 51mm is experience in June and August.
Any 5 x 1 = 5 marks
-
- What is an earthquake (2mks)
- It is a sudden earth movement that causes vibration within the earth’s crust. (1x2 =2mks)
- Identify the scales used to measure
- The intensity of earthquake
- Mercalli scale/Rossi-Forel scale (1x1mk= 1mk)
- The magnitude of earthquake
- The Ritcher scale (1x1mk = 1mk)
- The intensity of earthquake
- What is an earthquake (2mks)
-
- Name two types of boundaries according to the plate tectonic theory (2mks)
- Constructive/extension/divergent boundary
- Destructive/compression/conservative boundary
- Transform/conservative boundary (any 3x1mk = 3mks)
- Give three effects of the movement of tectonic plates. (3mks)
- Causes folding
- Occurrence of vulcanicity
- Occurrence of earthquakes
- Causes continental drift
- Causes structural adjustment/movement of rocks (Any 3x1mk = 3mks)
- Name two types of boundaries according to the plate tectonic theory (2mks)
-
- state three conditions that influence the process of solifluction in mass wasting (3mks)
- The presence of a gentle slope
- The occurrence of alternating warm and cold season
- Presence of a permafrost layer/frozen ground/bedrock
- Unconsolidated saturated weathered materials/debris
(Any 3 x 1mk) = 3 marks
- Give two negative effects of mass wasting on the physical environment (2mks)
- Destruction of vegetation
- Blockage of rivers/disruption of flow of rivers
- Exposure of land to agents of soil erosion
- Loss of life
- Leads to formation of scars on the land/derelict land
(Any 2 x 1m) = 2 marks)
- state three conditions that influence the process of solifluction in mass wasting (3mks)
-
-
- What type of map is the Kijabe
- Topographical map (1mk)
- In which hemisphere is the area covered by the Kijabe map located
- Southern hemisphere (2mks)
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map
- 36˚ 30’E to 36˚ 45’E (2mks)
N/B To score, Units i.e degrees and minutes
East must be present
- 36˚ 30’E to 36˚ 45’E (2mks)
- What type of map is the Kijabe
-
- Convert the linear scale of the map into a statement
- show the calculations
- 2cm rep 1km (2mks)
- Therefore 1cm rep 0.5km√
- Give six figure grid reference of trigonometrical station 2610
- 377938 ± 1
- Convert the linear scale of the map into a statement
-
- Reduce the area enclosed by Eastings 34 to 40 and Northings 91 to 97 by a scale factor of 2
Reduction of the area bound by Eastings 34 to 40and Northings 91 to 97 of Kijabe map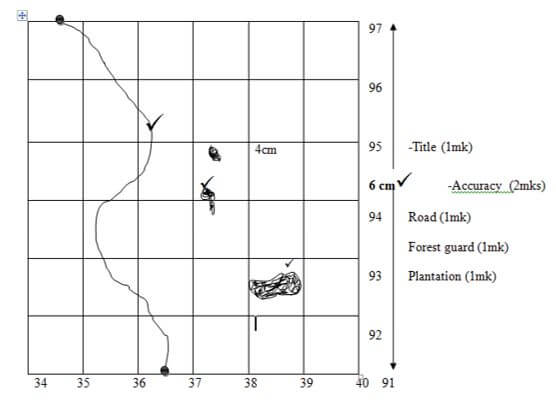
- New scale
- 1/(50,000) X 1/2 = 1/100,000 1: 100, 000 (2mks)
- Reduce the area enclosed by Eastings 34 to 40 and Northings 91 to 97 by a scale factor of 2
- Describe the vegetation of the area covered by the map (4mks)
- The main types of vegetation are forests, scrub, woodland
- The forest is on the eastern parts of the area
- There is thicket, scattered trees
- Scattered trees between grid reference 3401 to 3700
- Bamboo forest 378970 to 382970 (any 4x1mk=4mks)
- Citing evidence from the map, explain two factors influencing trade in the area covered by the map (4 mks)
- Establishment of roads and railways enables movement in and out of the area
- Presence of numerous shops, which provide opportunities for trading.
- Presence of settlement which suggests availability of market for the variety of goods and services.
- The variety of economic activities such as quarrying, farming shows that the area is productive which encourage trade. (any 2x2mks= 4mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between faulting and folding. (2 marks)
- Folding is the process through which young sedimentary rocks bend upwards or downwards due to compressional forces whereas faulting is the process through which crustal rocks fracture due to tectonic forces such as tension, compression or shear.
- Name five features formed as a result of faulting. (5 marks)
- Rift valleys
- Fault blocks (Block mountains and Horsts)
- Tilt blocks
- Escarpments/fault scarps
- Fault steps
- Depressions
- Differentiate between faulting and folding. (2 marks)
- The world map below shows the location of some fold mountains. Use it to answer question (a)(i)

- Identify the fold mountains marked W, X, Y and Z (4 marks)
- W – Rockies
- X – Alps
- Y – Andes
- Z – Ural
- Citing relevant examples, explain how Fold Mountains were formed according to the plate tectonics theory. (6 marks)
- When an oceanic plate meets a continental plate the edges of the sediments and materials at the margins into fold mountains e.g. Andes and Rockies
- Fold Mountains are also formed when two continental plates meet squeezing the materials in between into Fold Mountains e.g. Himalayas Atlas and Alps. (4mks for explanation, 2mks for examples 1 in each case)
- Identify the fold mountains marked W, X, Y and Z (4 marks)
- Explain the effects of Fold Mountains on the following
- Transport. (2 marks)
- Fold mountain scenery acts as a barrier to easy construction of roads, railways and pipelines thus making it difficult to access some regions due to ruggedness.
- Agriculture. (2 marks)
- Leeward slopes of some fold mountain ranges receive dry winds leading to arid conditions. This discourages crop farming but favours ranching and transhumance
- Windward slopes of most fold mountains receive high orographic rainfall which supports crop farming
- Tourism. (2 marks)
- Fold mountain scenery and snow-capped slopes are important tourist attractions with some slopes favouring winter sports such as skiing and ice skating, e.g. Swiss Alps
- Mining. (2 marks)
- Along some slopes of some Fold Mountains, valuable minerals were exposed thus are exploited for various economic uses e.g. copper and tin along the Andes slopes in Bolivia and Chile.
- Transport. (2 marks)
-
-
- Describe the following wind erosion processes
- Abrasion (2mks)
- Rocks materials carried by wind scour, grind and polish desert rock surface causing undercutting of rock surface
- Deflation (2mks)
- Wind moves over jointed and soft rocks desert surface dry. Loose materials like dust and fine sand are scooped/rolled on the ground and the lifted to the air by wind.
- Abrasion (2mks)
- Use the diagram below to answer the following questions.
- Name the feature marked A and B (2mks)
- A deflation hollow
- B an oasis
- State four significances of feature A to the human environment (4mks)
- Contain oasis which are sources of water to the nomadic community
- Has some feature like oasis which attract settlement and agriculture.
- The feature is a barrier to transport and communication
- The features and other associated ones attract tourists who in turn bring in foreign exchange
- Name the feature marked A and B (2mks)
- Using a well-labelled diagram, explain how the following features are formed
- Canyon
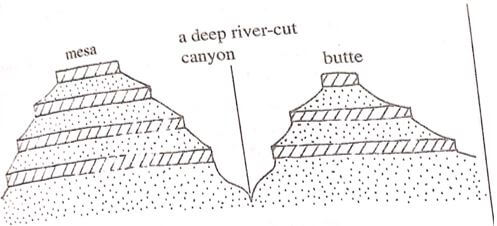
- Diagram – 2mks
- Text- 4mks
- A river originates from wetter areas and flows to arid area.
- Vertical erosion occurs on the river valley through abrasion
- The valley is deepened over a period of time. This leads to the formation of a deep steep sided gorge known as Canyon
- Zeugen (6mks)

- Diagram- 2mks
- Text- 4mks
- Rocks with alternating hard and soft rocks that lie horizontally are attached by mechanical weathering.
- Cracks form on the land rock layer
- Wind abrasion acts on the cracks deepening them
- The soft rocks layer is eroded at a faster rate.
- This leads to the formation of a flat-topped ridge which is separated from another by a furrow. The ridge is known as Zeugen.
- Canyon
- State four characteristics of a barchans (4mks)
- It lies at right angles to the prevailing winds
- It has two horns
- It may have a height of 25m and a width of 4m
- It has a gentle windward side and a steep leeward side
- Barchans migrates towards the direction of the prevailing winds
- Barchans occur in groups (any 4x1mk= 4mks)
- Describe the following wind erosion processes
-
-
- Define a coastline (2mks)
- It is a line reached by the highest storms, waves or demarcated by a cliff.
- Name three types of a coral reef (3mks)
- Fringing reef
- Barrier
- A toll
- Define a coastline (2mks)
- Using a well labelled diagram describe the formation of the following coastal landforms.
- A Tombolo (6mks)
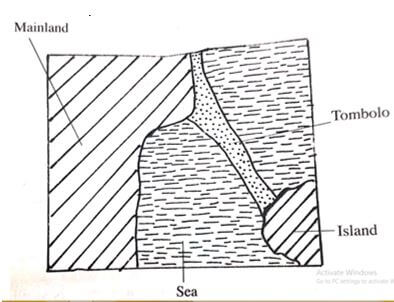
- Diagram – 2mks
- Text- 4mks
- Sand and shingle is deposited from a headland seaward by a long shore drift
- Continued deposition leads to accumulation of sand towards an island forming a spit
- With tie a bar of shingle/sand with one end attached to the mainland and the other to an island is formed. This bar is known as Tombolo
- off-shore bar (6mks)
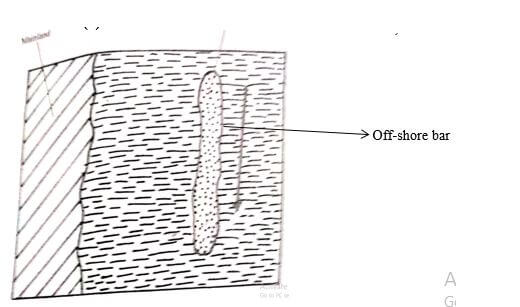
- Diagram- 2mks (mainland and offshore bar labeled)
- Text- 4mks
- Waves break long before they reach the shore on a raised part of the sea bed.
- As the waves break, they scoop out sand and shingle from the floor of the sea.
- The sand is thrown forward and is deposited on the raised sea bed
- With more deposition a ridge of sand and shingle that lies parallel to the shore and which is visible during low tide is formed. This is known as an off shore bar.
- A Tombolo (6mks)
-
- Give three factors that determine the size of a wave in the open sea. (3mks)
- Distance between two successive crests
- The energy of the walls
- Height of the waves i.e distance from crest to trough
- Steepness of the wall
Any 3 x 1mk = 3 marks
- State three uses of coral reefs (3mks)
- Coral rocks are cut into blocks and are used for building houses by local people.
- Coral limestone is used as a raw material eg at Bamburi, to manufacture cement
- The coral rocks at Watamu and Wasini Island attracts tourists who bring in foreign currency.
Any 3 x 1 = marks
- Students from Mombasa high school carried out a field study along the coastline of Indian Ocean.
- Give the reason for carrying the following items (2mks)
- Stop watch – to determine the rate which the waves break
- Camera – to take photograph of various features
- Give three factors that determine the size of a wave in the open sea. (3mks)
-
-
-
- State three characteristics of a maximum thermometer. (3mks)
- It has a narrow graduated glass tube
- The glass tube is filled with mercury
- It has metal index
- Explain how a maximum thermometer is used to measure temperature (6mks)
- During the day temperature rises
- The temperature heat the mercury in the glass tube
- The mercury expand and pushes the metal index along the glass tube
- When the temperature fall the mercury contractor
- It leaves the metal index behind
- The maximum temperature of the day is obtained by leading the scale at the end of the index which was in contact with the mercury.
- State three characteristics of a maximum thermometer. (3mks)
- Describe:
- How Lake Victoria influences the temperature of the surrounding region (4mks)
- During the day the land around lake Victoria is heated faster than the water, a cool breeze blows from the lake towards the land lowering the temperatures
- At night the land cools faster than the lake warm air rises from the lake and spreads to the adjacent land raising the temperatures
Any 2 x 2mks = 4 marks
- How south east trade wind. Influence temperature at the coast. (2mks)
- The south east trade winds blow over the warm Mozambique currents. They become warm and raise the temperature of the costal lands.
2 x 2mks = 2 marks
- The south east trade winds blow over the warm Mozambique currents. They become warm and raise the temperature of the costal lands.
- How Lake Victoria influences the temperature of the surrounding region (4mks)
-
- Explain two ways in which vegetation adapts to hot climate. (4mks)
- Some grass dries off during the hot summer and sprout when it rains
- Some plants are deciduous and shed their leaves during hot summers
- Some plants have thick leaves to store water.
- Some have long/deep tap roots to reach underground water (any 2x2mks = 4mks)
- Describe the characteristics of equatorial climate -(6mks)
- Temperatures are high throughout the year (270) since the region receives high isolation.
- Rainfall in the afternoon, since by this time the ground has received maximum heating leading to formation of clouds.
- Rain is accompanied by thunder and lightning due to presence of cumulonimbus clouds
- Diurnal range of temperature is small 3ºc due to thick cloud cover which prevents temperatures from rising too high or falling very low
- Skies are usually cloudy because of rapid convection due to high temperatures.
- Region experiences double maxima rainfall regime due to the sun been overhead the equator at two times in the year.
- Has permanent low pressure belt due to intense heating
- Explain two ways in which vegetation adapts to hot climate. (4mks)
-
Download Geography Questions, Answers and Confidential - KCSE 2022 Pavement Form 4 Trial 1 Pre-Mock Examination.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

