QUESTIONS
-
- You are provided with:
- Solution A - Acidified aqueous potassium manganate(VII).
- Solution B - containing 23.5g of ammonium Iron (II) sulphate; (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2.6H20), per litre.
You are required to Standardize the potassium manganate (VII), solution A, using the ammonium iron(II) sulphate, Solution B.
Procedure - Fill the burette with solution A.
- Pipette 25.0cm of solution B into a conical flask. Titrate solution B with solution until a permanent PINK colour just appears.
- Record your results in table I below.
- Repeat the titration two more times and complete the table below.
(4 marks)Titre 1 2 3 Final burette reading (cm3) Initial burette reading (cm3) Volume of Solution A used (cm3) - Determine the average volume of solution A used.
- Calculate the concentration of the ammonium iron (II) sulphate, Solution B, i moles per litre. (RFM of (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2.6H20) = 392) (1 mark)
- Calculate the number of moles of iron(II) ions in the 25.0cm of solution B. (1 mark)
- Using the ionic equation for the reaction between manganate(VII) ions iron(II) ions given below, calculate the concentration of manganate(VII) ions solution A in moles per litre.
MnO4(aq) + 5Fe2+(aq) + 8H(aq)→Mn(aq) + 5Fe3+(aq) + 4H2O(I)
- You are provided with:
- 4.5g of solid D, Potassium chlorate in a boiling tube.
- Distilled water in a wash bottle
You are required to determine the solubility of solid D at different temperatures
Procedure- Clean the burette and fill it with distilled water.
- Place 5.0cm of distilled into the boiling tube containing solid D.
- Warm the mixture until all the solid D dissolves.
- Place the thermometer into the solution and remove it from the Bunsen burner flame.
- Stir the solution with the thermometer gently as it cools. Note the temperature at which the crystals first appear and record it in table 2 below.
- Add 5.0cm3 of distilled water into the mixture and repeat the procedure (c) -(e) above to complete table 2 below.
(6 marks)Volume of water added(cm3) Temperature at which first crystals appear (C) Mass of KCIO3 in g/100g of water 4 6 8 10 - Plot a graph of solubility of KCIO3(y-axis) against temperature at which crystals first appear. (3marks)
- State the effect of changes in temperature on the solubility of KCIO3
- From your graph, determine the solubility of KClO3 at 55°C. n(1 mark)
- You are provided with:
- You are provided with solid R. Carry out the tests below. Write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
- Place about one third of solid R in a clean dry test-tube and heat it strongly.
Observations Inferences - Place the remaining solid R in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm of distilled water and shake well. Retain the mixture for tests in (d) below.
Observations Inferences - Use about 2cm3 portions of the mixture obtained in (c) for tests (i) to (iii) below.
- Add two to three drops of aqueous barium nitrate to the mixture.
Observations Inferences - Add five drops of dilute nitric(V) acid to the mixture.
Observations Inferences - Add to the mixture, aqueous ammonia dropwise until in excess
Observations Inferences
- Add two to three drops of aqueous barium nitrate to the mixture.
- Place about one third of solid R in a clean dry test-tube and heat it strongly.
- You are provided with an IMPURE organic substance, solid Q. You are required to carry out the tests indicated below. Place a ALL of solid Q in a boiling tube. Add about 10 cm of distilled water and shake well. Divide the mixture into four equal portions in test tubes.
Observations Inferences - To the first portion, add two drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution
Observations Inferences - To the second portion, add three drops of acidified potassium dichromate(VI).
Observations Inferences - To the third portion, add all the sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Observations Inferences - Test the pH of the fourth portion using universal indicator solution provided.
Observations Inferences
- To the first portion, add two drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution
CONFIDENTIAL
INSTRUCTIONS
In addition to the fittings and apparatus found in a chemistry laboratory, each candidate will require the following:
- Each candidate
- One burette 0 – 50 ml
- One pipette 25.0 ml and a pipette filler
- One Filter funnel
- Thermometer (-10ºC – 110ºC)
- Two clean and dry 250ml conical flasks
- Six clean and dry test-tubes
- One boiling tube
- 4.5g g of solid D weighed accurately and supplied in a dry stoppered container
- About 500cm3 of distilled water supplied in a wash bottle
- One 10ml measuring cylinder
- One metallic spatula
- About 150cm3 of solution A
- About 100cm3 of solution B
- pH chart
- About 0.5g of Solid R
- About 0.5g of solid Q
- About 0.2g sodium hydrogen carbonate
- A White tile
- Test tube holder
- Access to:
- Bunsen burner
- 2M nitric(V) acid supplied with a dropper
- 0.5M Barium nitrate supplied with a dropper
- 2M aqueous ammonia supplied with a dropper
- Universal indicator solution supplied with a dropper
- Acidified potassium manganate (VII) supplied with a dropper
- Acidified potassium dichromate (VI) supplied with a dropper
Note:
- Solid D is Potassium chlorate
- Solid R is Zinc sulphate
- Solid Q is Impure Maleic acid
- Solution A is prepared by dissolving 3.16g of potassium manganate(VII) in 400cm3 of 2M sulphuric(VI) acid and making it up to one litre of solution with distilled water.
- Solution B is prepared by dissolving 23.5g of hydrated ammoniuma Iron (II) sulphate, (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2.6H2O) per litre.
- Acidified potassium dichromate(VI) is prepared by dissolving 30g of potassium dichromate(VI) in 200cm3 of 2M sulphuric(VI) acid and diluting with distilled water to 1 litre.
- Acidified potassium manganate(VII) is prepared by dissolving 3.0g of solid potassium manganate (VII) in 200cm3 of 2M sulphuric(VI) acid and diluting with distilled water to 1 litre.

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- titre 1 + titre 2 + titre 3
3
= average titre - 23.5/392
=0.05995moles per litre - 25 x answer(b)
1000
= 0.001499 - moles of A used
= 1/5 x answer
= Answer Q
Moles of A in 1000cm3
= answerQ x 1000
average titre
= correct answer
M1V1 = 5
M2V2
M2 = answer(b) x 25
5 x average titre
= correct answer
- titre 1 + titre 2 + titre 3
-
-
Volume of water added(cm3) Temperature at which first crystals appear(ºC) Mass KClO3 in g/100g of water 8 75 56.25 10 42 45.0 12 30 37.50 14 28 32.14 -
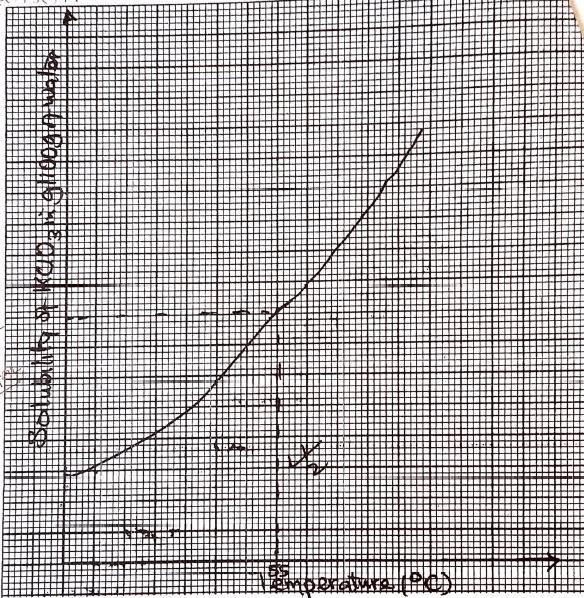
- increase in temperature increases the solubility of KClO3 / decrease in the temperature decreases the solubility of KClO3
- Showing
correct reading
-
-
| Observations | Inferences |
|
2a) colourless liquid forms on the cooler parts of the test tube residues yellow when hot and white when cold 3 dissolve to form a colourless solution |
2a) water of crystallization or hydrated salt 3) polar organic compound |
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Maranda Pre-Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

