INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
- This paper consists of TWO sections A and B.
- Answer ALL questions in section A
- In section B answer question 6(compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
Section Question Maximum score Candidate score
|
Section |
Question |
Maximum score |
Candidate score |
|
A |
1 2 3 4 5 |
8 8 8 8 8 |
|
|
B |
6 7 8 |
20 20 20 |
|
|
|
TOTAL |
80 |
|

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
-
- In Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) the gene for eye color is sex-linked located on the X chromosome. The gene for red eye is dominant. A cross was made between a homozygous red-eyed female and white-eyed male. Work out the genotype of their off springs. Use R to represent the gene for red eyes.(4 marks)
- Give two reasons why the fruit fly is successfully used in genetic study. (2 marks)
- In a population, there are more males suffering from colorblindness than females. Explain. (2 marks)
- One variety of the moth, Biston betularia, has pale, speckled wings. A second variety of the same species has black wings. There are no intermediate forms. 100 moths of both varieties were released into a wood made up of trees with pale bark as shown below.
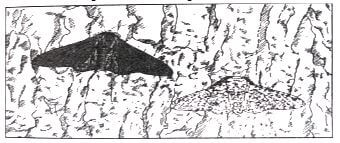
After two weeks the moths were caught and the results are shown in the table below.
Wing color of moth
Number released
Number caught
Pale, speckled
100
82
Black
100
36
- Explain the difference in the numbers of the varieties of moths caught.(2 marks)
- What would be different in the number of the varieties of moths caught if they were released in an area where the trees were darkened with soot from air pollution. (1 mark)
- Define natural selection.(2 marks)
- Explain why it is more difficult to treat malaria using chloroquine.(3 marks)
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of a broad bean seed.
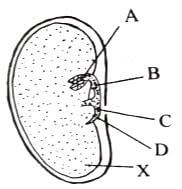
- Name the parts labelled A and B.(2 marks)
A
B - State the function of the part labeled X.(1 mark)
- Which part undergoes fastest growth to bring about epigeal germination. (1 mark)
- Name a plant hormone responsible for:(2 marks)
- Callus tissue formation
- Fruit ripening
- State two roles of water in germination. (2 marks)
- Name the parts labelled A and B.(2 marks)
- Study the homeostatic scheme below
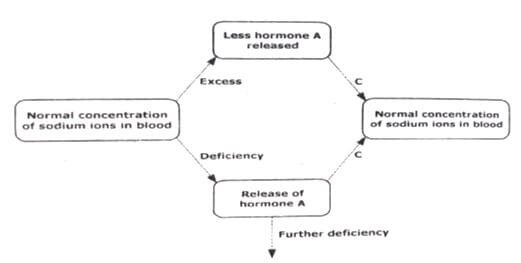
- Identify the hormone labelled A.(1 mark)
- Which gland releases hormone A.(1 mark)
- Identify two major sites of action of hormone A.(2 marks)
- Identify the mechanism labelled C.(1 mark)
- A person was found to pass large volume of dilute urine frequently.
Name the:- Disease the person was suffering from.(1 mark)
- Hormone that was deficient.(1 mark)
- Give a reason for maintaining a constant body temperature. (1mark)
- The diagram below shows a part of a plant tissue.
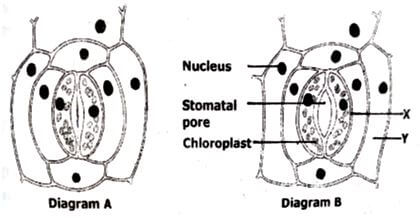
- Label each of the cell X and Y.(2 marks)
- Diagram B is drawn to show the change that has occurred in A. State the change. (1 mark)
- Explain how light could bring the change you have stated in (b) (ii) above. (4 marks)
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
- The heartbeat rate of a student was measured before and after a period of 2 minutes exercise. Immediately before and after the exercise, the student rested on a bed. The results are shown in the table below.
Time (minutes
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Beats per minute
76
76
76
107
135
95
84
84
79
77
76
76
76
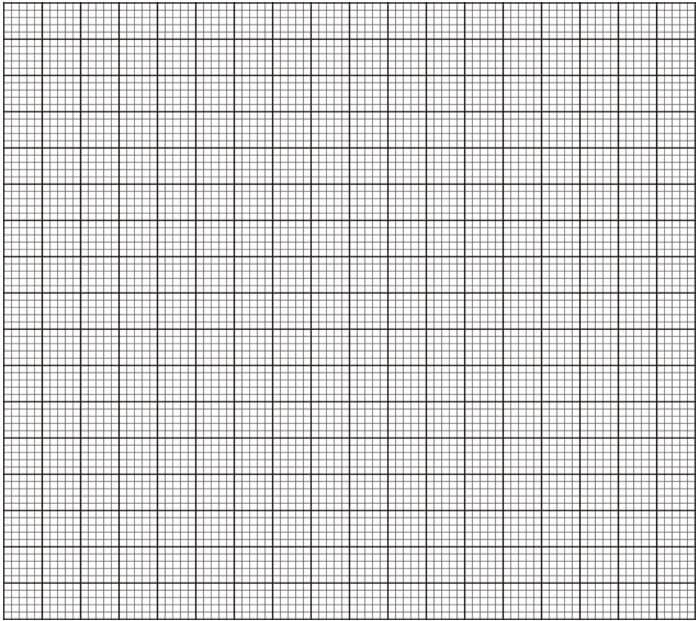
- Use the data in the table to plot the graph of heartbeat per minute against time. (6 marks)
- Explain why the heart beat rate of the student rose during the period of exercise. (4 marks)
- By how many beats per minute did the heart beat rate of the student increase during the exercise period? (2 marks)
- Explain why after the exercise, the return to resting rate was gradual. (3 marks)
- Other than exercise, name two factors that increase the rate of heartbeat. (2 marks)
- Name the nerve that increases the rate of heartbeat. (1 mark)
- Explain why blood in arteries is under high pressure. (2 marks)
- Use the data in the table to plot the graph of heartbeat per minute against time. (6 marks)
-
- Describe the structure and function of the internal structure of the leaf. (15 marks)
- Describe how the stomata of xerophytes are modified to conserving water. (5 marks)
-
- Describe advantages of asexual reproduction in plants. (5 marks)
- Describe the role of the pituitary gland in the female reproductive cycle. (15 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Possible to get a large sample size as female produce large number of offspring at a time.
The flies have many contrasting observable characteristics.
They are easily bred in the laboratory with minimum requirements.
They have a short generation time hence many generations can be studies in a short period.
Their offspring can be crossed with their parents at will.
The flies are safe to handle because they do not transmit human diseases.
Mark 1st two - Males have only one X chromosome; the corresponding allele is absent on the Y chromosome;
-
- More black moths were eaten (by predators); because they were not camouflaged;
Accept the converse - More black moth caught than speckled moths;
- This is whereby nature selects those organisms that are well adapted to the prevailing environmental conditions enabling then to survive to reproductive maturity; those that are poorly adapted die young leaving no offspring and their characteristics are eventually eliminated from the population;
- (Frequent exposure to chloroquine caused the) plasmodium to mutate; developing a gene that offers resistance to chloroquine; the mutant plasmodium survives and pass the gene for resistance to their offspring; hence a population of plasmodium that are resistance arose;
- More black moths were eaten (by predators); because they were not camouflaged;
-
- A- plumule
B- Epicotyl - store food for germination
- C/ Hypocotyl
-
- cytokinins
- Ethene/ ethylene
- Activate enzymes;
medium of transport;
hydrolyze the stored food;
medium of reaction;
soften the seed coat for radicle and plumule to emerge;
any 1st two
- A- plumule
-
- Aldosterone;
- Adrenal (glands);
- loop of henle;
Colon; - Negative feedback;
-
- Diabetes insipidus;
- Antidiuretic hormone;
- to provide optimum temperature for enzymatic reactions hence optimum rate of metabolic reactions/ organism remains active throughout;
Enables organisms occupy a wide range of habitats;
Mark any one
-
- X- guard cell; rej. Guard cells
Y- Epidermal cell; rej. Epidermal cells - stoma open;
- chloroplast in the guard cells carry out photosynthesis producing sugar/glucose; sugar accumulates in the sap vacuole of guard cells increasing the osmotic pressure; water is drawn into the guard cells from surrounding epidermal cells by osmosis; the guard cells become turgid, bulge outwards and stoma opens;
- X- guard cell; rej. Guard cells
-
- Axis-2 mks
Scale -2 mks
Plotting -1 mk
Curve -1mk - to supply more oxygen and glucose to the muscle tissues; to increase energy production; for muscular contraction; faster transport of carbon (IV) oxide to excretory organs to be excreted;
- 135-96 2 = 29.5
=30 beats per minute ; rej. 29.5 beats as the final answer - (during the exercise muscles respire anaerobically producing) lactic acid which accumulates in the tissues. Heart rate remains high to supply more oxygen; to oxidize lactic acid to carbon (IV) oxide, energy and water/ transport lactic acid to the liver;
- Fever/ high temperature;
emotions/ anxiety/fear/ adrenaline; - sympathetic nerve;
- blood from the heart is pumped into arteries under high pressure;
They have narrow lumen that maintain the high pressure of blood;
- Axis-2 mks
-
- Epidermis; secretes the cuticle; protects inner tissues from mechanical damage/entry of micro-organisms;
Cuticle; reduces excessive loss of water; protects the inner tissues from mechanical damage/ prevents entry of micro-organisms; it is transparent to allow light to penetrate through into the photosynthetic cells;
Guard cells; have chloroplasts hence carry out photosynthesis; control opening and closing of the stomata;
Palisade cells; spongy mesophyll cells; are photosynthetic cells;
Xylem; transports water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaf cells; phloem; transports manufactured food from the leaves to the rest of the plant;
Total 17 mks max 15 mks - have reduced number of stomata hence low rates of transpiration; small stomatal opening to reduce transpiration; some plants have sunken stomata; where water vapour accumulates in the pit reducing the diffusion gradient; hence lower rate of transpiration. Some plants have reversed stomatal rhythm; to prevent excessive water loss by transpiration; some plants have stomata that show midday closure; to prevent excessive water loss; total 7mks max 5mks
- Epidermis; secretes the cuticle; protects inner tissues from mechanical damage/entry of micro-organisms;
-
- Good qualities from the parents are retained in the offspring without any variation;
The plants mature faster than those produced by sexual means;
The plant depends on its own activity to reproduce;
The new plants are able to obtain nourishment from their parent plants, hence are able to survive temporarily under unsuitable conditions;
There is no wastage of large number of offspring as it does not result in indiscrimate and widespread distribution of new plants;
It makes it possible for plants that do not have the capacity for sexual reproduction to reproduce asexually; total 6mks max 5mks - The pituitary gland secrete a number of reproductive hormones which carry out various reproductive functions follicle stimulating hormone; secreted just after menstruation; to stimulate the development of graafian follicle; it also stimulates the ovarian tissues to secrete oestrogen; which controls development of female secondary sexual characteristics; causes healing and repair of the endometrium; and stimulates pituitary gland to secrete luteinizing hormone; luteinizing hormone (LH); stimulates maturation of graafian follicle; causing ovulation; LH also stimulates the corpus luteum to start secreting progesterone;
Prolactin; stimulates secretion of milk; (by the secretory cells of the mammary gland)
Oxytocin; stimulates contraction of uterine muscles during labour; to facilitate birth; it also stimulates milk let-down; total 17mks max 15 mks
- Good qualities from the parents are retained in the offspring without any variation;
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - MECS Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
