INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all questions
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary
|
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1-28 |
80 |
QUESTIONS
- List three differences between a conductor and an electrolyte (3mks)
CONDUCTOR
ELECTROLYTE
- Describe how you can prepare ethane starting with calcium carbide and water (3mks)
- Define the following terms
- covalent bond (1mk)
- Coordinate bond (1mk)
- Draw a dot(o) and cross(x) diagram of ammonium chloride (N=14, H=1, Cl=17) (2mks)
- State two functions of a school laboratory (2mks)
- Identify substances with the following properties (1mk)
- it is an ionic compound, an electrolyte and can be used as a food additive (1mk)
- Relights a glowing splint, has a slight smell, slightly less dense than air, and fairly soluble in cold water (1mk)
- Has a density of 184 g/cm3, an oily liquid, changes blue hydrated copper (ii) sulphate to white (1mk)
-
- Define the term fermentation (1mk)
- Name the compounds formed when potassium metal reacts with (2mks)
- ethanol
- ethanoic acid
- A hydrated salt of copper has the formula CuSO4nH2O About 25g of the salt was heated until all the water evaporated If the mass of the anhydrous salt is 160g, find the value of n (Cu = 640, S = 320, O = 160, H = 1) (3 mks)
- When 100 cm3 of 05 M sulphuric acid solution, H2SO4, react with 100 cm3 of 1 M sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH, the temperature rises by 685 Kelvins (Density = 10g/cm3, specific heat capacity = 42kJkg-1K-1) Calculate the molar heat of neutralization described by the equation:
H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l) (3 mks) - Name the catalysts used in the following (3mks)
- Esterification
- Ostwald process
- Preparation of hydrogen in the laboratory
-
- State Gay Lussac’s law (1mk)
- 150cm³ of ethene were mixed with 500cm³ of oxygen and the mixture was sparked to complete the reaction If all volumes were measured at a pressure of one atmosphere and 25ºC, calculate the volume of the resulting gaseous mixture (2mks)
- The set-up below was used to prepare Nitric(V)acid
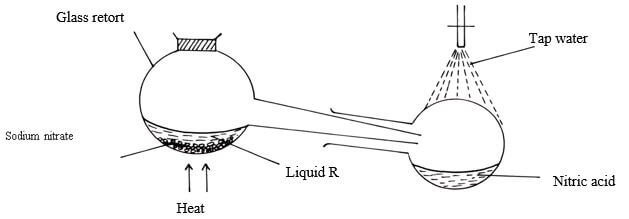
- Give the name of liquid R ( 1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in the retort flask (1mk)
- State the role of tap water (1mk)
- Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions that follow
Bond
Bond energy (KJ mol)
C-H
413
Br-Br
193
C-Br
280
H-Br
365
- Calculate the Enthalpy changes for the reaction below (2mks)
CH4 (g) + Br2 (g) → CH3Br (g) + HBr (g) - State whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic Explain (1mk)
- Calculate the Enthalpy changes for the reaction below (2mks)
- Differentiate between hydrolysis and saponification (2mks)
-
- Zeolites (Na2X) is a complex compound used to soften hard water in the ion-exchange methods according to the equation below
Ca 2+ (aq) +Na2X (aq) → CaX(s) + 2Na+ (aq)
After sometimes the Zeolites get exhausted and cease to soften water Write an equation to show how Zeolite is regenarated (1mk) - Name two other method used in softening hard water (2mks)
- Zeolites (Na2X) is a complex compound used to soften hard water in the ion-exchange methods according to the equation below
- The table below gives information about some reactions of metals A,B, C and D and their rates
Arrange the metals in order of decreasing activity (3mks)METAL
Reaction with acid
Reaction with water
Action of heat on its nitrate
A
Hydrogen evolved
No reaction
Oxide formed
B
NO reaction
No reaction
Metal formed
C
Hydrogen evolved
Hydrogen evolved
Oxide formed
D
NO reaction
NO reaction
Oxide formed
- Elements X, Y and Z have atomic numbers 9, 11 and 18 respectively
- Which element can be used in electric light bulbs? (1mark)
- Which two elements react to form an ionic compound? (1 Mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction between element B and water? (1mark)
-
- What is a universal indicator? (1mark)
- State one advantage of universal indicator over other commercial indicators (1mark)
- Explain how solid calcium sulphate can be prepared from solid samples of calcium carbonate and sodium sulphate All other reagents and apparatus are provided (3 marks)
- A heavy metal (P) was dissolved in dilute nitric acid to form a solution of compound P(NO3)2 Portions of the resulting solution were treated as follows:
- To the first portion a solution of dilute hydrochloric acid is added, where a white precipitate (S) is formed, which dissolves on warming
- The second portion is treated with two drops of 2M Sodium hydroxide solution where a white precipitate (T) is formed The white precipitate dissolved in excess sodium hydroxide to form a colourless solution
- A solution of potassium iodide is added to the third portion where a yellow precipitate (U) is formed
- When the resulting solution is evaporated to dryness and heated strongly a yellow solid (V) is formed and a brown gas (W) and a colourless gas (X) are formed
- Identify the substances P, S, T, U, V, W (3 marks)
P ........................................ U ........................................
S ........................................ V ........................................
T ........................................ W ........................................
- Identify the substances P, S, T, U, V, W (3 marks)
- Sodium thiosulphate was reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid in a round bottomed flask as shown below The gas evolved was collected by downward delivery in a gas jar
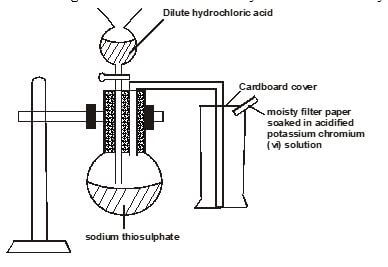
- Write an equation to show the reaction going on in the reaction in vessel(1 mark)
- State the observation noted on the filter paper Give a reason for your answer (1 mark)
- Give a reason why the filter paper soaked in the acidified potassium chromium (VI) is used at the top of the flask (1 mark)
- State one use of each of the following apparatus in the laboratory
- Conical flask (1mk)
- Desiccator (1mk)
- Crucible (1mk)
-
- Define Vulcanisation (1mk)
- What is the importance of the above defined process (2mks)
- Two gas jar containing hydrogen chloride gas and ammonia gas were close to each other as shown below
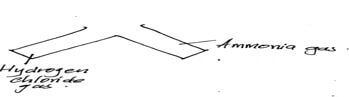
- State and explain the observation made (2mks)
- State the significance of the above experiment (1mk)
- Unknown substances had PH values as shown in the table below
State which substance is likely to be;Substance
PH values
A
6.0
B
2.0
C
8.0
- Lemon juice (1mk)
- Identify a substance that would be a better electrolyte? explain (2mk)
- The scheme below shows some reaction sequence starting with solid M
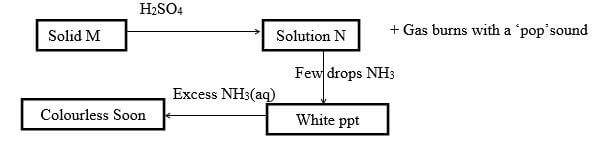
- Name solid M (1mk)
- Write the formula of a complex ion present in solution Q (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation of the reaction between lead (ii) nitrate and solution N (1mk)
- Describe how you can separate a mixture of water and hexane (3mks)
- A solid p was suspected to be a sulphate of sodium, describe the tests that would be carried out to determine whether the sold was actually sodium sulphate (3mks)
- Define the term chemistry (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
- List three differences between a conductor and an electrolyte (3mks)
Conductor
Electrolyte
solid
Molten/ aqueous
Has delocalized electrons
Had mobile ions
Remains unchanged
Decomposed by current
- Describe how you can prepare ethane starting with calcium carbide and water (3mks)
- Add water to calcium carbide in a dry flask to produce ethyne gas
- In presence of a nickel catalyst and 200oC , react excess hydrogen gas with ethyne gas to form ethane gas
- fractionate to obtain ethane gas
- Define the following terms
- covalent bond(1/2mk)
- a bond formed where the shared pair of electrons are contributed by each of the atoms forming the bond
- Coordinate bond (1/2mk)
- a special covalent bond where the shared pair is contributed to one of the atoms forming the bond
- Draw a dot and cross diagram of ammonium chloride (2mks)
- covalent bond(1/2mk)
- State two functions of a school laboratory (2mks)
- Storage of chemicals
- performing/carrying out practical’s
- Identify substances with the following properties (1mk)
- it is an ionic compound, an electrolyte and can be used as a food additive(1mk)
- Sodium chloride
- Relights a glowing splint, has a slight smell, slightly less dense than air, and fairly soluble in cold water (1mk)
- Nitrogen (ii) oxide
- Has a density of 1.18g/cm3, an oily liquid, changes blue hydrated copper (ii) sulphate to white (1mk)
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- it is an ionic compound, an electrolyte and can be used as a food additive(1mk)
-
- Define the term fermentation(1mk)
- A process in which organic material are decomposed by microorganisms with the production of ethanol, carbon (iv) oxide and heat
- Name the compounds formed when potassium metal reacts with (2mks)
- ethanol………………………………potassium ethoxide
- ethanoic acid……………………………potassium ethanoate
- Define the term fermentation(1mk)
- A hydrated salt of copper has the formula CuSO4.nH2O. About 25g of the salt was heated until all the water evaporated. If the mass of the anhydrous salt is 16.0g, find the value of n. (Cu = 64.0, S = 32.0, O = 16.0, H = 1) (3 marks)
Mass of water = 25-16 = 9 g
N=5molecules
CuSO4
H2O
mass
16
9
Molar mass
160
18
moles
16/160=0.1
9/18= 0.5
Mole ratio
0.1/0.1
0.5/0.1
1
5
- When 100 cm3 of 0.5 M sulphuric acid solution, H2SO4, react with 100 cm3 of 1 M sodium hydroxide solution, NaOH, the temperature rises by 6.85 Kelvins. (Density = 1.0g/cm3, specific heat capacity = 4.2kJkg-1K-1)
Calculate the molar heat of neutralization of sulphuric (vi) acid: (3 marks)
H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)- ΔH=MCΔT
=200/1000 x 4.2 x 6.85= -5.754kJ
1mole----------1000cm3
? -------------100cm3= 0.1moles
0.1mol---------------- 5.754
1mol-------------------? = -57.54kJ/Mol
- ΔH=MCΔT
- Name the catalysts used in the following (3mks)
- Esterification…….conc sulphiuric (vi) acid.
- Ostwald process…………………Platinum/Rhodium
- Preparation of hydrogen in the laboratory……………copper(ii) sulphate crystals
- State Gay Lussac’s law
- When gases react they do so in volumes that bears simple whole number ratios to each other and to the products if gaseous (1mk)
- 15.0cm³ of ethene were mixed with 50.0cm³ of oxygen and the mixture was sparked to complete the reaction. If all volumes were measured at a pressure of one atmosphere and 25C, calculate the volume of the resulting gaseous mixture. (2mks)
- C2H4 + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 2H2O
15cm3 45cm3 30cm3 30cm3
Resulting mixture 5cm3 excess oxygen + 30cm3 CO2 + 30 cm3 steam= 65 cm3
- C2H4 + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 2H2O
- State Gay Lussac’s law
- The set-up below was used to prepare Nitric(V)acid.
- Give the name of liquid R. ( 1mk)
- Conc sulphuric (vi) acid
- Write an equation for the reaction which takes place in the retort flask (1mk)
- NaNO3(s) + H2SO4(l) → NaHSO4(s) + HNO3 (g)
- State the role of tap water. (1mk)
- Condense nitric (v) acid fumes
- Give the name of liquid R. ( 1mk)
- Study the information given in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
- Calculate the Enthalpy changes for the reaction below (2mks)
CH4 (g) + Br2 (g) → CH3Br (g) + HBr (g)- C-H + Br-Br → C-Br + HBr
413 + 193=606 280 + 365=645
ΔH=-39kJ
- C-H + Br-Br → C-Br + HBr
- State whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic. Explain (1mk)
- Exothermic, evolves energy
- Calculate the Enthalpy changes for the reaction below (2mks)
- Differentiate between hydrolysis and saponification (2mks)
- Saponification: it’s the hydrolysis of fats/oils by an alkali by boiling
- Hydrolysis: chemical break down of a compound by reacting with water
-
- Zeolites (Na2X) is a complex compound used to soften hard water in the ion-exchange methods according to the equation below.
Ca 2+ (aq) +Na2X (aq) → CaX(s) + 2Na+ (aq)
After sometimes the Zeolites get exhausted and cease to soften water. Write an equation to show how Zeolite is regenarated. (1mk)- 2NaCl( aq) + CaX (s) → Na2X (s) + CaCl2 (aq)
- Name two other method used in softening hard water (2mks)
- Addition of ammonia
- Boiling
- Addition of sodium carbonate
- Zeolites (Na2X) is a complex compound used to soften hard water in the ion-exchange methods according to the equation below.
- The table below gives information about some reactions of metals A,B, C and D and their rates.
Arrange the metals in order of decreasing activity (2mks)METAL
Reaction with acid
Reaction with water
Action of heat on its nitrate
A
Hydrogen evolved
No reaction
Oxide formed
B
NO reaction
No reaction
Metal formed
C
Hydrogen evolved
Hydrogen evolved
Oxide formed
D
NO reaction
NO reaction
Oxide formed
- C A D B
- Elements X, Y and Z have atomic numbers 9, 11 and 18 respectively.
- Which element can be used in electric light bulbs? (1mark)
- Z
- Which two elements react to form an ionic compound? (1 Mark)
- X and Y
- Write an equation for the reaction between element B and water? (1mark)
- 2Y (s) + 2H2O(l) → 2YOH(aq) + H2 (g)
- Which element can be used in electric light bulbs? (1mark)
-
- What is a universal indicator? (1mark)
- It’s a mixture of several dyes that shows different colours depending on the strength of acids and bases
- State one advantage of universal indicator over other commercial indicators. (1mark)
- Shows the strengths of acids and bases wtte
- What is a universal indicator? (1mark)
- Explain how solid calcium sulphate can be prepared from solid samples of calcium carbonate and sodium sulphate. All other reagents and apparatus are provided. (3 marks)
- Add calcium carbonate to dilute nitric(v) acid til in excess, filter to obtain calcium nitrate solution
- Dissolve sodium sulphate in distilled water, to form sodium sulphate solution,
- Add sodium sulphate solution to calcium nitrate solution, a white precipitate is formed.
- Filter to obtain calcium sulphate as the residue and sodium nitate as the filtrate
- Wash the residue with distilled water and dry between filter papers/ sun dry
- A heavy metal P was dissolved in dilute nitric acid to form a solution of compound P(NO3)2. Portions of the resulting solution were treated as follows:
- To the first portion a solution of dilute hydrochloric acid is added, where a white precipitate (S) is formed, which dissolves on warming.
- The second portion is treated with two drops of 2M Sodium hydroxide solution where a white precipitate T is formed. The white precipitate dissolved in excess sodium hydroxide to form a colourless solution.
- A solution of potassium iodide is added to the third portion where a yellow precipitate (U) is formed.
- When the resulting solution is evaporated to dryness and heated strongly a yellow solid (V) is formed and a brown gas (W) and a colourless gas (X) are formed.
- Identify the substances P, S, T, U, V, and W. (3 marks)
- P- lead metal, S- Lead (ii) chloride, T- Lead (ii) hydroxide, U- Lead (ii) iodide, V- Lead (ii) oxide, W- Nitrogen (iv) oxide
- Identify the substances P, S, T, U, V, and W. (3 marks)
- Sodium thiosulphate was reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid in a round bottomed flask as shown below. The gas evolved was collected by downward delivery in a gas jar.
- Write an equation to show the reaction going on in the reaction in vessel.(1 mark)
- Na2S2O3(s) + 2HCl (aq) → 2NaCl (aq) + S(s) + SO2 (g) + H2O(l)
- State the observation noted on the filter paper. Give a reason for your answer (1 mark)
- The filter paper changes from orange to green
- Give a reason why the filter paper soaked in the acidified potassium chromium (VI) is used at the top of the flask (1 mark)
- Test whether the gas jar is full of sulphur (iv) oxide
- Write an equation to show the reaction going on in the reaction in vessel.(1 mark)
- State one use of each of the following apparatus in the laboratory
- Conical flask (1mk)
- Measuring approximate volume/general laboratory experiments
- Desiccator (1mk)
- Keep substances free from moisture
- Crucible (1mk)
- Heating solids that require very strong heating
- Conical flask (1mk)
-
- Define Vulcanisation (1mks)
- it is the process of hardening rubber by heating with sulphur
- what is the importance of the above defined process(2mks)
- makes rubber tougher, less flexible and less soft
- improves the quality of rubber
- Define Vulcanisation (1mks)
- Two gas jar containing hydrogen chloride gas and ammonia gas were close to each other as shown below
- State and explain the observation made (2mks)
- White dense fumes are formed; ammonia reacts with hydrogen chloride to form ammonium chloride
- State the significance of the above experiment(1mk)
- Used to test for the presence of hydrogen chloride gas
- State and explain the observation made (2mks)
- Unknown substances had PH values as shown in the table below.
State which substance is likely to be;- Lemon juice (1mk)
- A
- Identify a substance that would be a better electrolyte? explain (2mk)
- B, it’s a strong acid, or it dissociates completely to form hydrogen ions in water
- Lemon juice (1mk)
- The scheme below shows some reaction sequence starting with solid M.
- Name solid M (1mk)
- Zinc metal
- Write the formula of a complexion present in solution Q (1mk)
- [Zn(NH3)4]2+
- Write an ionic equation of the reaction between lead (ii) nitrate and solution N.(1mk)
- Pb2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq) → PbSO4(s)
- Name solid M (1mk)
- Describe how you can separate a mixture of water and hexane (3mks)
- Put the mixture in a separating funnel and wait for it to settle
- Open the tap to lease the bottom layer of water into a beaker, throw away the interphase
- Release the top layer of hexane into a different beaker
- A solid p was suspected to be a sulphate of sodium, describe the tests that would be carried out to determine whether the sold was actually sodium sulphate(3mks)
- Heat the solid,in a non-luminous flame , the solid burns in a yellow flame
- Add the solid to 2cm3 of distilled water, it dissolves
- To the resulting solution add acidified lead (ii) nitrate followed by warming, a white ppt doesn’t dissolve.
- Define the term chemistry (1mk)
- It is the study of properties ,composition, structure and changes that matter undergoes
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - MECS Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
