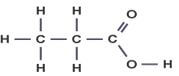
INSTRUCTIONS
- Answer all questions
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary
|
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 |
14 |
|
|
2 |
14 |
|
|
3 |
10 |
|
|
4 |
10 |
|
|
5 |
11 |
|
|
6 |
12 |
|
|
7 |
10 |
|
|
TOTAL SCORE |
80 |

QUESTIONS
- The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent actual symbols of the elements.
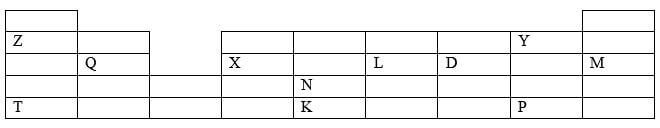
- To which chemical family does element M belong? (1 mark)
- Giving a reason, compare the following;
- Atomic radius of T and K (2 marks)
- Boiling point of Y and P (2 marks)
- Physical state at room temperature (25 ºC) of an oxide of Q and an oxide of L (2 marks)
- An element W forms a stable ion with the formula W2+. The ion of W has an electron configuration similar to the electron configuration of an atom of M
- Write the electron configuration of an atom of W. (1 mark)
- Place element W in its position on the grid (1 mark)
- Identify the element from the grid that; (1 mark)
- Has the lowest first ionization energy (½ mark)
- Forms an amphoteric oxide (½ mark)
- G is a metallic element in the same group Z and less reactive than T. Draw a dot (O) and cross(X) diagram showing how element G and D combine (1 mark)
- The table below gives the atomic and ionic radii of three elements P, Q and R. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
Element
Atomic radius
Ionic radius
P
0.099
0.181
Q
0.157
0.095
R
0.133
0.216
- Identify the element that is a good conductor of electricity. (1 mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in e(i) above (1 mark)
- In an experiment to investigate the molar enthalpy of displacement of copper (II) ions, 25 cm3 of 0.1M copper (II) sulphate solution was reacted with zinc powder. The temperature of the solution was recorded after every minute for 2 minutes. On the 3rd minute, 6g of zinc was added to the solution. The mixture was stirred with a thermometer and temperature was recorded after every minute for an additional 6 minutes. The results were recorded in the table below.
Time in minutes
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Temperature (0C)
25.0
25.0
25.0
X
28.6
28.3
28.0
27.7
27.5
27.1
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature (y– axis) against time (x – axis) (3 marks)
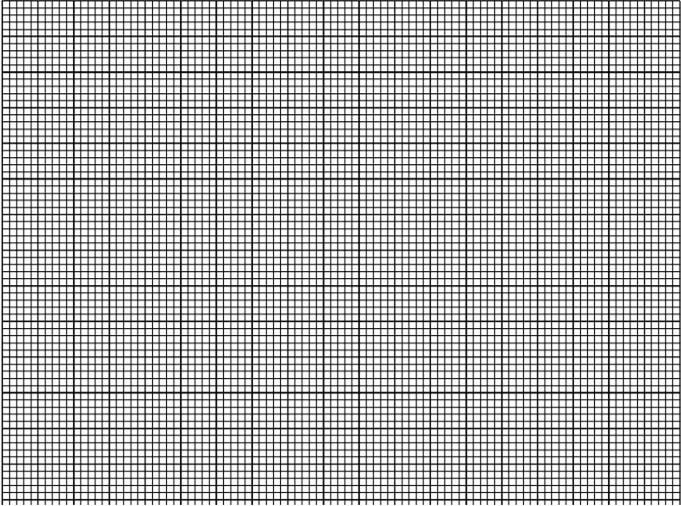
- Use your graph to determine the temperature change (1 mark)
- Calculate the;
- Enthalpy change for the reaction (density of solution = 1g/cm3, specific heat capacity = 4.2 kJ/Kg/K) (2 marks)
- Moles of copper (II) ions displaced, given that the zinc powder was in excess (1 mark)
- Molar enthalpy of displacement of copper (II) ions (2 marks)
- A similar reaction was carried out using the copper (II) sulphate solution and metal Q in place of zinc powder. The molar enthalpy change was found to be – 201kJ/mol.
- Compare the reactivity of element Q and zinc. (1 mark)
- Explain your answer in d(i) above (1 mark)
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of temperature (y– axis) against time (x – axis) (3 marks)
-
- Name the following compounds; (2 marks)
- An organic compound has the molecular formula C5H12.
- To which homologous series does the compound belong? (1 mark)
- Define isomers (1 mark)
- Draw and name two isomers of the compound. (2 marks)
- In an experiment, ethanol was reacted with acidified potassium manganate (VI) to form product T
- Identify the product T (1 mark)
- Name the process of converting ethanol to product T (1 mark)
- State the observation made when;
- Acidified potassium manganate (VII) is added to ethanol (1 mark)
- Sodium carbonate is added to solution T (1 mark)
- An organic compound L has the formula CH3CH2CH2COOCH3.
- To which group of organic compounds does it belong to. (1 mark)
- Identify the two substances that react to give the compound above (2 marks)
- Name the following compounds; (2 marks)
- The set – up below was used to prepare sulphur (IV) oxide in the laboratory. Study it and use it to answer the questions that follow.
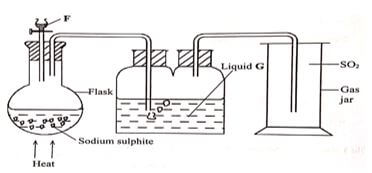
- Identify (1 mark)
- Liquid F
- Liquid G
- State the role of liquid G (1 mark)
- State and explain two observations made when moist blue litmus paper is put in the gas jar. (2 marks)
- Sulphur (IV) oxide is used industrially in the manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid.
- Name the process (1 mark)
- Identify two raw materials used in the process named above (1 mark)
- Name the most suitable catalyst used (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction in the catalytic chamber (1 mark)
- State and explain the observations made when concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the following
- Glucose (1 mark)
- Hydrated cobalt (II) chloride (1 mark)
- Identify (1 mark)
-
- Define the following terms; (3 marks)
- Deliquescence
- Strong acid
- Saturated solution
- Starting with lead (II) oxide, describe how you can obtain a dry sample of lead (II) sulphate in the laboratory. (3 marks)
- Study the flow diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
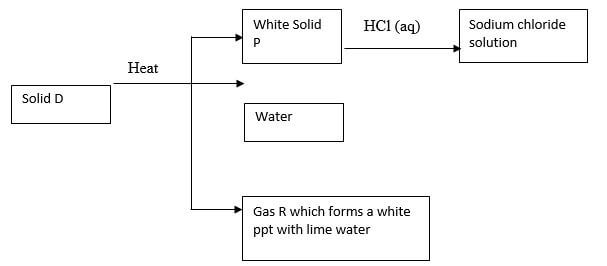
- Identify the following (1 ½ marks)
- Solid D
- White solid P
- Gas R
- State and explain the observation made when lead (II) nitrate is added to sodium chloride solution (1 ½ mark)
- Identify the following (1 ½ marks)
- Study the equation below and answer the question that follows
H2O2 (l) + H2O (l) ⇌ H3O+ (aq) + HO2- (aq)
Giving a reason, identify the;- Acid (1 mark)
- Base (1 mark)
- Define the following terms; (3 marks)
- The set up below was used to isolate nitrogen from a sample of air. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
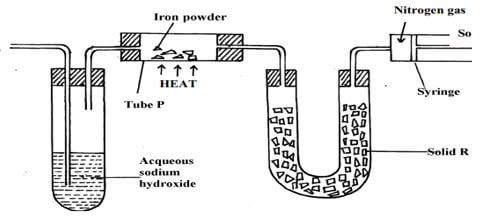
- Name solid R and state its role (2 marks)
Name
Role - Identify the substance removed in the; (2 marks)
- Boiling tube
- combustion tube
- Write an equation for the reaction in the boiling tube (1 mark)
- Explain what would happen if iron powder is replaced with magnesium powder (1 mark)
- Name the impurity collected in the syringe (1 mark)
- State two uses of nitrogen gas (1 mark)
- Ammonia gas is prepared in the lab by reaction of ammonium chloride with solid F
- Name solid F (1 mark)
- Name the most suitable substance used to dry ammonia gas (1 mark)
- State two physical properties of ammonia gas (2 marks)
- Name solid R and state its role (2 marks)
-
- The diagrams below represent allotropes of carbon
Allotrope X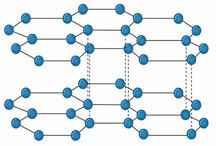
Allotrope Y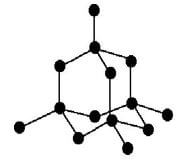
- Define allotropes (1 mark)
- Identify allotrope (2 marks)
X
Y - Using structure and bonding, explain one physical difference between the two allotropes (2 marks)
- Carbon reacts with excess oxygen to form a gaseous oxide of carbon
- State the nature of the oxide formed (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction (1 mark)
- 400g of carbon was burnt in limited oxygen gas. Calculate the volume of the gaseous product formed at R.T.P (C=12.0, O=16.0, Molar gas volume at RTP=24,000 cm3) (3 marks)
- The diagrams below represent allotropes of carbon

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Noble gases √1
-
- T has a bigger atomic radius or K has a smaller radius √1
K has a higher nuclear charge hence a greater pull of electrons - Y has a lower boiling point √1
it has a smaller atomic radius √ ½ hence weaker intermolecular forces of attraction √ ½ - oxide of Q is a solid as it has strong ionic bonds
oxide of L is a gas since it has molecular structure with weak van der waal’s forces.
- T has a bigger atomic radius or K has a smaller radius √1
-
- 2.8.8.2
- Group II, period 4
-
- T
- X
-
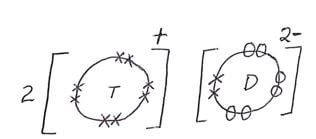
-
- Q
- It is a metal hence has delocalized electrons
-
-
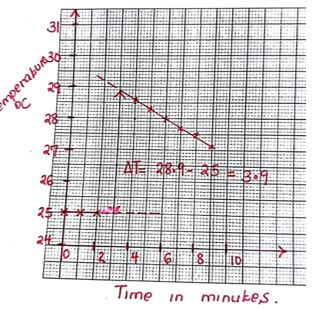
- 28.9 – 25.0 = 3.9 0C +or – 1
-
- 0.025 x 4.2 x 3.9 = 0.4095 kJ
- (25 x 0.1)/1000 = 0.0025 moles
- (1 x 0.4095)/0.0025
= – 163.8 kJ/Mol
penalize ½ for missing state symbol
-
- Q is more reactive than zinc
- A more reactive metal gives a higher molar enthalpy of displacement
- graph
X½ Y½ P1 L1
-
-
-
- propanoic acid
- Ethan – 1,2 – diol
-
- alkanes
- Compounds with the same molecular formular but different structural formula
-
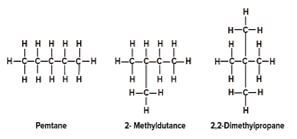
-
- ethanoic acid
- oxidation
- purple KMnO4 changes from purple to colourless effervescence
-
- esters
- Butanoic acid and methanol
-
-
-
- Hydrochloric acid
- concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- To dry the gas
- Moist blue litmus changes to red √ ½ then white √ ½
Sulphur (IV) oxide is acidic √ ½ and has bleaching properties √ ½ -
- Contact process
- sulphur/ zinc sulphide/lead (II) sulphide √ ½
oxygen / air √ ½ - Vanadium (V) oxide
- 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2SO3 (g)
-
- glucose changes from white to black√ ½
Glucose is dehydrated to carbon √ ½. Removes chemically combined water - hydrated cobalt (II) chloride changes from pink to blue √ ½
it loses its water of crystallisation √ ½
- glucose changes from white to black√ ½
-
-
-
- A process by which a solid absorbs moisture and dissolves to form a solution
- a substance which completely dissociates in solution to form many hydrogen ions
- a solution which cannot dissolve any more solute at a particular temperature
- Add lead (II) oxide to dilute nitrc (V) acid until in excess. √ ½ Filter to obtain lead (II) nitrate solution as filtrate. √ ½ Add sodium sulphate to the filtrate. √ ½ Filter to obtain lead sulphate as residue.√½Wash residue √ ½with distilled water and dry it√ ½
-
- sodium hydrogencarbonate
sodium carbonate accept formulae
carbon (IV) oxide (accept formula) - white precipitate
lead (II) chloride is insoluble
- sodium hydrogencarbonate
-
- H202 – It donates a proton to form HO2-
- H2O – It accepts a proton to form H3O+
-
-
- Anhydrous calcium chloride
It dries the gas formed -
- carbon (IV) oxide
- oxygen
- CO2(g) + NaOH(aq) →NaHCO3(aq)
or
CO2(g) + NaOH(aq) →Na2CO3(aq)+H2O(l) - Magnesium would react with nitrogen gas and it would not be collected
- Argon
- Nitrogen gas is also used to provide an unreactive atmosphere. It is used in this way to preserve foods and in bulbs
Manufacture of ammonia
Refrigeration of semen -
- Calcium hydroxide
- Calcium oxide
- soluble in water
Easily liquiefies under pressure
Less dense than air
Irritating smell
Colourless
- Anhydrous calcium chloride
-
-
- Allotropes are different forms of an element that exist in the same physical state
- X- Graphite
Y – Diamond - Diamond is very hard since it has covalent bonds between atoms throughout the structure while graphite is soft and slippery since it has weak van der waal’s forces between layers.
Diamond is a poor conductor of electricity since all its valence electrons are used in bonding while graphite is a good conductor since it has delocalised electrons
-
- acidic
- C (s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
- moles of carbon =
400/12 = 33.33 moles √1
Mole ratio C:CO = 1:1 √ ½
Moles of CO=33.33 √ ½
1 mole → 24,000 cm3
33.33 moles → 800,000 cm3
Or 800 L√1
-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - MECS Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students