INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer all the questions in section A.
- In section B, answer question 6 and either question 7 OR 8
- Answers must be written in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- Candidates may be penalized for recording irrelevant information and for incorrect spellings.
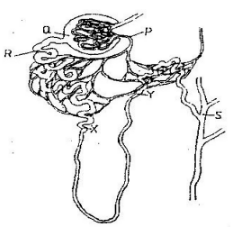
- The diagram below represents a mammalian nephron
- Name the
- Structure labele P…………………………………………………………. (1mk)
- Portion of the nephron between point X and Y………………………………. (1mk)
- Name the process that takes place at point Q………………………………….. (1mk) (
- Name one substance present at point R but absent at point S in a healthy mammal. (1mk)
- The appearance of the substance you have mentioned in (c) above is a symptom of a certain disease caused by a hormone deficiency.Name the
- Disease………………………………………………………………………… (1mk)
- Hormone………………………………………………………………………. (1mk)
- State the structural modifications of nephrons found in the desert mammal. (2mks)
- Name the
-
- What is organic evolution? (2mks)
- State two ways in which Homo sapiens differ from homo habilis. (2mks)
- Distinguish between divergent and convergent evolution giving examples in each case. (4mks)
- The chart below shows a feeding relationship in a certain ecosystem
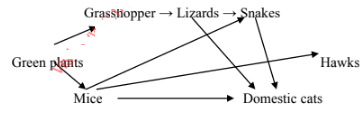
- Construct two food chains ending with a tertiary consumer in each case. (2 mks)
- Which organism has the largest variety of predators in the food web? (1 mk)
- Name two secondary consumers in food web. (2 mks)
- Suggest three ways in which the ecosystem would be affected in there was a prolonged drought. (3mks)
- The diagram below shows the position of an image formed in a defective eye.

- Name the defect: (1mk)
- Explain how the defect named in (a) above can be corrected (2mks)
- Apart from hearing, state another function of the human ear. (1mk)
- State two functional differences between the rods and cones in the human eye. (2mks)
- State the function of the following structures:
- Eustachian tube. (1mk)
- Ear ossicles. (1mk)
- Red-green colour blindness is inability to distinguish red and green colours.
It’s caused by sex- linked recessive gene.-
- In which chromosome is this gene found. (1mk)
- Which part of the eye fails to develop? (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- A colour blind man marries a homozygous normal woman. Show the genotypes of the resulting offsprings. (Use R to stand for a dominant gene.) (4mks)
- Why is it that the colourblind man cannot transmit this trait to his sons? (2mks)
-
SECTION B
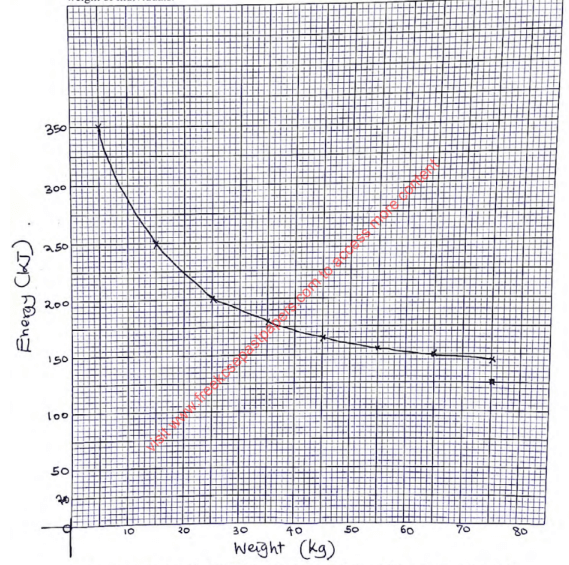
- In an experiment to determine the energy requirements per day by persons of different sizes at rest, the following results were compiled.
Weight of individual (kg) Energy requirement per day at rest (KJ) 5 350 15 250 25 200 35 180 45 165 55 155 65 150 75 145 - Using a suitable scale, draw a graph of the amount of energy required per day against the weight of individuals. (6mks)
- From the graph, determine the difference in energy requirements between persons weighing:
- 20kg and 30kg. (1mk) ……………………………………
- 40kg and 70kg. (1mk) ……………………………………
- Account for the difference in energy requirements per kilogram of body weight between individuals of 5kg and 75kg. (3mks)
-
- On the graph drawn above, draw a curve that would represent energy requirements of a reptile instead of a man. (1mk)
- Account for the difference between the two curves. (2mks)
- Other than body size, state any three factors that determine energy requirement in man. (3mks)
- Name food substrate that provides the most and least energy per unit mass:
- Most energy. (1mk) …………………
- Least energy. (1mk) …………………
- Write down a balanced chemical equation of complete oxidation of glucose molecule. (1mk)
- Discuss seed dormancy, its importance, causes and ways of breaking it. (20mks)
-
- Explain how blood sugar is regulated in the human body. (12mks)
- Explain the fate of digested protein. (8mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Efferent arteriole;
- loop of henle;
- Ultrafiltration;
- Sugars(Glucose), Amino acid, Vitamins
-
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Insulin;
-
- Long loo pf Henle to increase surface area for water reabsorption;
- Has small glomerulus to reduce water ultrafiltration;
-
-
- Emergence of complex form of life from simple forms; over a long period of time;
Homo Sapien Homo Habilis 1) Higher brain capacity 1) Lower brain capacity 2) Highly developed culture 2) Less cultural development 3) Reduced brow ridge 3) Prominent brow ridge 4) Bipedal 4) Quadripedal -
- Divergent evolution: where one basic structural form is modified to give rise to various different forms;
- Convergent Evolution; Where structures with different embryonic origin are modified to perform similar functions;
-
-
- Green plants → mice → snake → Domestic cat
- Green plants → Grasshoper → Lizard → Snake
- Green plants → Grasshoper → Lizard → Domestic cat
- Mice
-
- Lizard;
- Snake;
- Hawk;
-
- Reduced grass plant;
- Reduced mice;
- Reduced Grasshoper;
-
-
- Myopia/ short sightedness;
- Use of concave/ Divergent lense; To bring the light to focus on the retina;
- Body posture and Balance;
-
Rods Cones 1) Sensitive to low light intensity; 1) Sensitive to high light intenstity; 2) Not sensitive to colour 2) Sensitive to colour; 3) Has retinal convergence 3) Lack retinal convvergence 4) No perception of fine details 40 has perception of fine details -
- Equalizes air pressure between the inner ear and outer ear to prevent ear drum distortion
- Amplified sound vibrations.
-
-
- X chromosome;
- Retina;
-
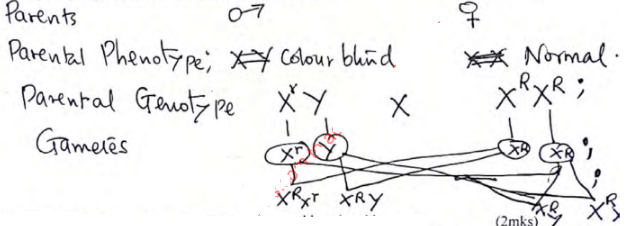
- Man has only 1 x chromosome; which is only inherited to daughters;
-
-
-
-
- 225 − 190 = 35kJ;
- 170 − 145 = 25kJ;
- Individual of 5kg has higher energy requirement than individual of 75kg; because individual of 5kg has large surface area to volume rationthan 75kg; hence require loose more heat to the environment;
-
- Basal metabolic rate;
- Age;
- Occupation/ everybday activity;
- Sex;
-
- Lipids/ fats/ oil;
- carbohydrates;
- Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon (IV) Oxide + Water + Energy
-
-
- Seed Dormancy: Temporary inhibition to germination when a seed in a resting condition; with reduced metabolic reactions; (max 2)
- Importance of Seed Dormancy;
- Enables the seed to withstand unfavourable conditions;
- Allows time for dispersal of seeds; which ensures colonisation of new habitats and reduce competition for resources,
- Allows time for seeds to mature before germinating; (max 4)
- Causes of Seed Dormancy:
- Immature embryo;
- Presence of hard seed coat (Testa);
- Presence of growth inhibitors; e.g abscic acid;
- Absence of growth promoters/ Hormones; e.g ( Gibberellins);
- Lack of oxygen;
- lack of exposure of the seed to light for a certain duartion of time/ light of right wavelength;
- lack moisture/ water.
- Lack of optimum temperature; (max 7)
- Breaking Seed Dormancy
- allow seeds enough time to break immaturity;
- Removable of impermeable tsta through scarification, pin pricking, use of fires
- Soaking in water to dilute inhibitors;
- Treatment with growth promoters;
- Drainage to increase soil ait holding capacity;
- Removal of mucilage;
- Exposure to long period of heat.
-
-
- Increase of sugar above noormal/ excess
- Hypothalamus; is stimulated to stimulate pancrease to secret insulin hormones;
- Insulin stimulate liver cells; to convert excess sugar to glycogen; or fats; for storage. inhibits conversion of ,glcogen to glucose; incraese oxidation of glucose;
- Drop of blood sugar below normal
- Hypothalamus is stimulated; Hypothalamus stimulates pancrease; to secret glucagon hormone;
- Glucagon stimulates liver cells; to convert glycogen to glucose + fats, reduce break down of glucode to glycogen
(max 12)
- Increase of sugar above noormal/ excess
- Fate of digested proteins
- Component of structures in living things ; e.g plasma membrane/ connective tissues/ Hair/ Hoves/ Nails/ muscles;
- Repair of worn out tissues;
- Act as metabolic regulators; e.g Hormones; Enzymes;
- Provision of body immunity; e,g antibodies;
- Broken down during starvation to give energy;
- Transport of Respiratory gases; e.g Haemoglobin
- Lubricant of body tubes; e,g mucus;
- Excess amino acids are deaminated;
(max 8)
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Maranda High Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students