INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of two sections. Section A and section B.
- Answer ALL questions in section A in the spaces provided. In section B answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
Section A (40 marks)
Answer all the questions
- The equation below represents a metabolic process that occurs in a certain organ in the mammalian body.
Ammonia + carbon (IV) oxideenzyme organic compound Q + water
- Name the process represented in the equation above. (1 mk)
- Name the organ in which the process occurs. (1mk)
- Why is the process important to mammals (1mk)
- Identify the organic compound Q. (1mk)
- Explain the source of ammonia in the organ named in (b) above. (2mks)
- What happens to organic compound Q.? (2mks)
- An athlete training to take part in an international competition moved to a high altitude area where he was to train for twelve (12) days before the competition. He took his pulse rate per minute daily and tabulated them as shown below
Day 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Pulse per minute 72 78 89 92 92 90 86 80 77 74 72 72 - Other than pulse rate, name one other process which was affected by change in altitude. (1mrk)
- Account for the change in pulse rate from.
- Day 1 to day 7 (1mrk)
- Day 8 to day 12 (1mrk)
- Explain the advantage this athlete has over the one who trains in a lower altitude area. (2mks)
- The equation below represents a reaction which takes place during rapid muscular movements in humans.
Glucoselactic acid + 150kj
- State two effects of this reaction to an individual (2mks)
- How is lactic acid finally eliminated from the muscle tissue after the muscle return to normal movement (1 mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follows
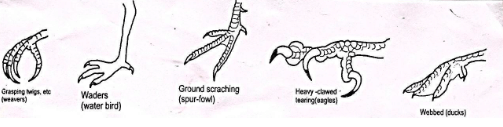
- What type of evolution is illustrated by the limbs (1mk)
- What does the origin of the limbs suggest about the ancestry of these animals (1mk)
-
- What are vestigial structures? (1mk)
- State an example of vestigial structure in humans (1mk)
-
- What is natural selection? (2mks)
- Give one example of nature selection in action (1mk)
- Explain comparative serology as evidence of evolution. (1mk)
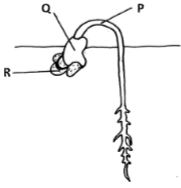
- The diagram below represents a stage of growth in a seed during germination.
-
- Name the type of germination illustrated above (1mk)
- Give a reason for your answer in (i) above (1mk)
- Name the part labellled R in the above diagram. (1mk)
- Give two functions of the part labeled Q (2mks)
- Explain how the part labeled P straightens. (3mks)
-
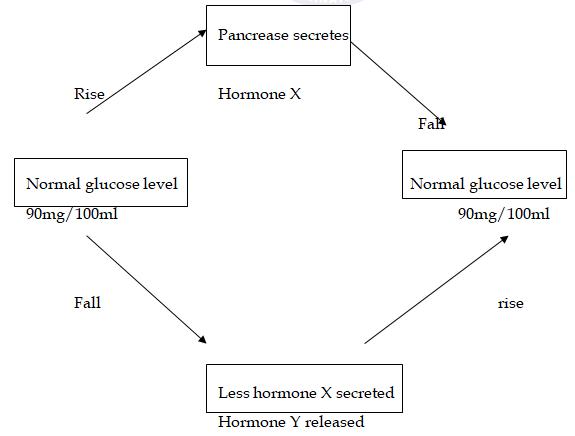
- The diagram below shows how blood glucose in mammalian body is regulated.
- Name the hormone X and Y (2mks)
- State two ways by which hormone X lowers glucose level in the blood when it rises above 90mg/100ml (2mks)
- Name the organ that produces hormone Y (1mk)
- Suppose there is deficiency of hormone X, state the disease the person would suffer from (1mk)
- Explain how the disease mentioned in (d) above can be controlled. (2mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 compulsory and either question 7 or 8 in the space provided
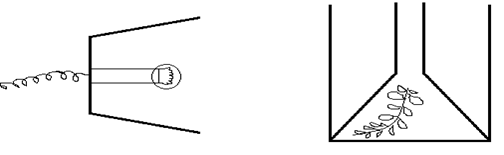
- The diagram below shows an experiment that was carried out to measure rate of photosynthesis in a water plant when exposed to different light intensities.
The shoot was exposed to different light intensities and the rate of photosynthesis estimated by counting the number of bubbles of the gas leaving the shoot per minute. The results are tabulated below.
Number of bubble per minute 7 14 20 24 26 27 27 27 Light intensity (arbitrary units) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 - Draw the graph of the number of bubbles produced per minute against light intensity. (6 marks)
- At what light intensity did the shoot produce
- 18 bubbles per minute (1mk)
- 25 bubbles per minute (1mk)
- Give two better ways of measuring the rate of photosynthesis other than counting bubbles produced per minute. (2mks)
- What is role of light intensity in photosynthesis (2mks)
- Account for the expected results if the experiment was done at the following temperatures.
- 4°C (2mks)
- 34°C ( 2mks)
- 60°C ( 2mks)
- Apart from light intensity and temperature, name other two factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis. (2mks)
-
- How are lungs adapted to their function? (10mks)
- Describe the mechanism of opening and closing of the stomata using the photosynthesis theory.
-
- Describe the various mechanism of fruit and seed dispersal. (12mks)
- Describe the various events that occur in a flower after fertilization. (8mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Detoxification;
- Liver;
- Prevents ammonia from accumulating to toxic levels;
- Urea;
- Excess amino acids are broken down/deaminated to form amino group; which is combined with hydrogen atom to form ammonia;
- It is transported to the kidney; where it is excreted;
-
- Increase in breathing rate;
-
- Lower concentration of oxygen in high attitude area; raises the demand of oxygen by body cells;
- Number of red blood cells has increased hence enough oxygen is reaching all body Cells adequately;
- Has a higher capacity of transporting oxygen to body cells; due to higher number of redblood cells in the body;
-
-
- Muscle crumps;
- Muscle fatigue
- It is completely oxidized by oxygen into water, Carbon (IV) oxide and energy/is converted into glycogen for storage; (2mks)
-
-
- Divergent evolution 1mk
- Ancestry origin of the limb suggest there were habitants of aquatic environment. 1mk
-
- Vestigial structures
- Highly reduced structure due to disuse 1mk
- Appendix ,coccyx ,nictating membrane eye ,muscles that moves the ear. 1mk
- Vestigial structures
-
- Natural selection
- Situation whereby the nature Favours organisms suited for survival and eliminate those that are less adapted. 2mks
- an example of nature selection in action 1mk
- Resistance to antibiotics and pesticides
- Industrial mechanism
- Natural selection
- More precipitation is observed when serum of closely related organism are mixed and vice versa. 1mk
-
-
- Epigeal germination .
- Reasons: Hypocotyl grows / elongates fast ; pulling / raising the cotyledons above the ground / soil level.
- Seed coat / Testa
-
- protect the embryo /plume and radical/ plume
- food storage / starch /lipids/ vitamin/ mineral salt / enzymes / hormones.
- photosynthesis /manufacture food / provide food
- site of food hydrolysis
- On exposure to light / exposure of the cured part to light; stimulates migration of auxines to the lower side / underside / dark side ;High auxine concentration to the lower side / under side/ dark side ,stimulates faster growth / elongation than on the upper side ; faster elongation of the lower side straighten the seedlings;
-
-
-
- X – Insulin;
- Y – Glucagon;
-
- Stimulates conversion of glucose to glycogen/fats;
- Oxidation of glucose to release energy;
- Pancreas;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Regular insulin injection; with controlled diet and exercise;
-
-
-
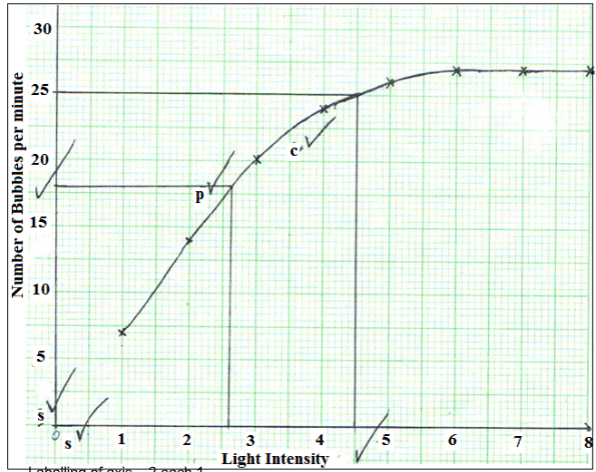
Labelling of axis – 2 each 1
Plotting – 1
Curve – 1
Scale – 2 each 1
Scale – Should have origin necessarily zero -
- 2.6 ± 0.1
- 4.5 ± 0.1
-
- Volume of CO 2 consumed/volume of O 2 liberated;
- Change in dry mass
-
- Photolysis of water
- ATP synthesis
-
- 4°C – Rate of photosynthesis is very low; because enzymes are inactive;
- 34°C – Rapid rate of photosynthesis; because of the optimum temperature for enzyme reaction.
- 60°C – very low /no photosynthesis; because high temperatures denature enzymes;
-
- Carbon (IV) oxide concentration;
- Water availability;
-
-
-
- Has numerous alveoli; that provide large surface area for efficient gaseous exchange;
- Epithelial lining between alveoli wall and blood capillaries is thin; to provide a shorter diffusion distance for easy gaseous exchange;
- It is highly supplied with blood capillaries; that transport oxygen and carbon (IV) oxide to and from the body tissues respectively;
- Lungs are covered with pleural membrane; which is gas tight thus changes in pressure ,within the lungs can occur without external interference;
- Lungs is spongy & has numerous alveoli; that accumulate large volume of gases.
-
- Opening
- In the guard cells there are chloroplasts; which carry out photosynthesis in the presence of light;
- During the day glucose is produced in the guard cells; this increases osmotic pressure; compared to the neighbouring epidermal; water is drawn from the epidermal cell cells into the guard cells by osmosis; their turgidity increases;
- The inner walls of guards cells are thicker than the other wall; so outer walls stretch more than the inner walls causing guard cells to bulge outwards; causing stomata to open;
- Closing
- During the night there is no light; no photosynthesis takes place in the guard cells; Glucose in the guard cells is converted into starch. This lowers the osmotic pressure of the guard cells than the neighbouring cells;
- Water is then drawn from the guard cells by osmosis into the epidermal cells making them to be flaccid
- Thinner outer wall shrink and the curvature of the thicker inner wall reduces; the stomata close;
- Opening
-
-
-
- Water dispersal
- Such seeds and fruits enclose air in them to lower their density for buoyancy;
- They have fibrous/spongy to lower the density for buoyancy;
- Have impermeable seed coat or epicarp to prevent water from entering during floatation so as to avoid rotting;
- The seeds can remain viable while in water and only germinate while on a suitable medium;
- Wind dispersal
- They are light; and small; to be easily carried by wind currents due to lower density;
- Have developed extension which create a larger surface area; so as to be kept afloat in wind currents e.g. Parachute like structures, Wing like surface;
- Animal dispersal
- Brightly coloured to attract animals
- Fleshy to attract animals;
- Some have hook like structures to attach on animals furSelf-dispersal
- They have weak lines on the fruit wall along which they burst open to release seeds, which get scattered. This occurs when temperature changes suddenly.
- Water dispersal
-
- Inner and outer integuments develops into the seed testa.
- The ovary wall forms fruit wall
- The ovule develops into seed (s)
- The corolla dries and withers away.
- The calyx may persist or dries and wither away
- Stigma and style shrivels, dries and wither away.
- The androecium (male part) shrivels dries and withers away.
- Triploid nuclei develop into primary endosperm of the seed.
- The zygote formed develops into embryo.
-
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sunrise Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students