Instructions to candidates
- This paper consists of two Sections; A and B.
- Answer all the questions in Section A.
- Answer question 6 and any other two questions from Section B.
SECTION A
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION
-
- Define the term Geography (2mks)
- What is the relationship between Geography and Biology (2mks)
-
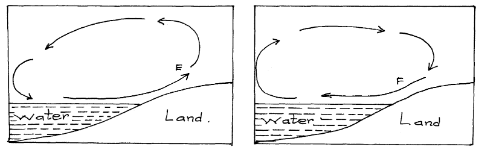
- Use the diagram below to answer the following questions
- Name the air currents marked E. (1mk)
- Why does the air current marked F flow at night. (3mks)
- Give reason why air cools as it rises. (2mks)
- Use the diagram below to answer the following questions
-
- Define folding. (2mks)
- List four types of folds. (4mks)
- The diagram below illustrates a mass wasting process. Use it to answer question (a) and (b)
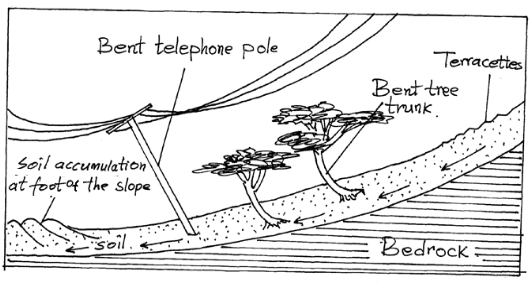
- Identify the process. (1mk)
- Explain how the process occurs . (3mks)
-
- What is a river profile? (2mks)
- Name the three stages of a river profile. (3mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of Nyeri 1: 50 000 (sheet 120/4) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Identify the sheet number of the map provided (1mk)
- Convert the scale of map into a statement scale. (2mks)
- What is the bearing of the trigonometrical station 1906 in grid square 6860 from the trigonometrical station 1865 in grid square 6957. (2mks)
-
- Identify three physical features found in grid square 6259. (2mks)
- Give the latitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
- Identify two districts in the area covered by the map. (2mks)
-
- Using a scale of 1 cm represents 20m, draw a cross section from Easting 68 to Easting 74 along Northing 64 . (4mks)
On it mark and name- A hill top (1mk)
- A stream/river (1mk)
- All weather road loose surface (1mk)
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross-section. (2mks)
- Using a scale of 1 cm represents 20m, draw a cross section from Easting 68 to Easting 74 along Northing 64 . (4mks)
- Citing evidence from the map, identify two social services offered in Mweiga Township. (4mks)
-
-
-
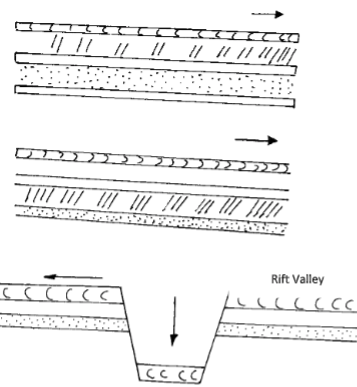
- What is faulting? (2mks)
- Name four types of faults (4mks)
- With the aid of well-labelled diagrams, describe how a Rift Valley is formed by Tensional force (8mks)
- Apart from the Rift Valley, name other three relief features that may form as a result of faulting. (3mks)
- Explain four ways in which features resulting from faulting are Economic significance. (8mks)
-
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate. (2mks)
- Explain two ways in which human activities influence rainfall of a given place.(4mks)
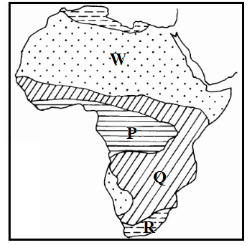
- The map below shows some climatic regions of the world. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the climatic types marked P, Q and R. (3mks)
- Describe the characteristics of the climatic type labeled W. (5mks)
-
- Name three greenhouse gases likely to be found in the atmosphere. (3mks)
- Give three ways of combating global warming. (3mks)
- Members of your class plan to conduct a field study on weather in a local weather station
- State three factors they may identify for the citing of the weather station. (3mks)
- State two advantages of studying weather through a field study. (2mks)
-
-
- Define the term hydrological cycle. (2mks)
- Explain the following processes of the hydrological cycle;
- Evaporation (2mks)
- Surface run off (2mks)
- Citing an example in each case, name three sources of rivers in Kenya. (3mks)
- State four factors that influence river erosion. (4mks)
- The diagrams below show formation of a feature of river deposition. Use them to answer the questions that follow.
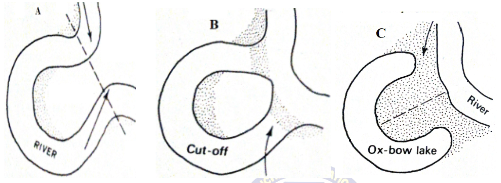
- Describe the processes in the diagrams labeled:
- A (1mk)
- B (2mks)
- C (2mks)
- Name two examples of ox-bow lakes in Kenya. (2mks)
- Describe the processes in the diagrams labeled:
-
- Members of your class plan to conduct a field study on the lower course of River Nzoia.
- Give two equipment they are likely to carry for the study. (2mks)
- State three characteristics of the river they are likely to observe during the study (3mks)
-
- The diagram below represents underground features in a limestone area. Use it to answer question.
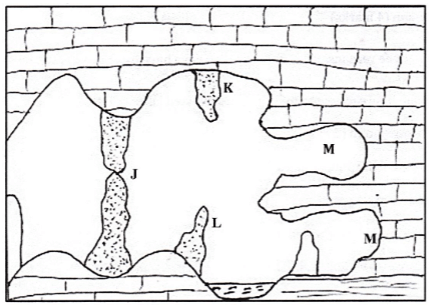
-
- Name the features marked K,L and M. (3mks)
- Describe how the feature marked J is formed. (6mks)
-
- What is a water table (2mks)
- Explain three conditions necessary for the development of karst scenery. (6mks)
- You are supposed to carry a field study of an area eroded by water.
- Give three ways you would prepare before conducting the field study. (3mks)
- Name two erosional features you are likely to identify during the field stud (2mks)
- State three significance of the resultant features in limestone areas. (3mks)\
-
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- Define the term Geography (2mks)
- Is the descriptive study of the distribution and inter-relationship of natural and human phenomena on the earth’s surface.
- What is the relationship between Geography and Biology (2mks)
- Biology applies geographical information to explain factors determining the distribution of organisms
- Define the term Geography (2mks)
-
- Use the diagram below to answer the following questions
- Name the air currents marked E (1mk)
- Sea breeze
- Why is the air current marked F flow at night (3mks)
- At night, land loses heat faster than sea. Air upon the land becomes cooler and heavier than that upon the sea. The relatively warmer air upon the sea is lighter and therefore it rises while the cooler heavier air on the land flows towards the sea to replace the rising air.
- Name the air currents marked E (1mk)
- Give reason why air cools as it rises (2mks)
- As air rises it expands thus spreading out its molecules over a wider area and hence becoming cooler
- Use the diagram below to answer the following questions
-
- Define folding (2mks)
- Its bedding of rocks in the crust due to tectonic forces during earth movement
- List four types of folds (4mks)
- Simple / Symmetrical fold
- Asymmetrical / monoclinal fold
- Overfold
- Isoclinal
- Recumbent
- Nappe
- Anticlinorium andSynclinorium complex
- Define folding (2mks)
- The diagram below illustrate a mass wasting process. Use it to answer question (a) and (b)
- Identify the process (1mk)
- Soil Creep
- Explain how the process occurs. (3mks)
- Occurs on gentle slopes . soil along the slope undergoes strain which leads to breaking over a period of time the soil moves slowly downslope. It accumulates behind the poles and trees leading to bending at the base.
- Identify the process (1mk)
-
- What is a river profile (2mks)
- It’s is the entire length of the river’s course from its source to its mouth
- Name the three stages of a river profile (3mks)
- Youthful / upper stage
- Mature/Middle stage
- Old /Lower stage
- What is a river profile (2mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of Nyeri 1: 50 000 (sheet 120/4) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Identify the sheet number of the map provided (1mk)
- 120/4
- Convert the scale of map into a statement scale. (2mks)
1 : 50000 = 0.5
100000
Therefore 1 cm rep 0.5km or 1 cm rep ½km - What is the bearing of the trigonometrical station 1906 in grid square 6860 from the trigonometrical station 1865 in grid square 6957. (2 marks)
338° ±1 or N22°W
- Identify the sheet number of the map provided (1mk)
-
- Identify two physical features found in grid square 6259. (2mks)
- Stream/river
- River/valley
- Scrub vegetation
- Woodland vegetation
- Give the latitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2mks)
18.3cm = 5l
5.7cm = ?
5 × 5.7 = 1.5l
18.3
1 min = 60sec
0.5 = 30sec
∴ 5.7cm = 1l30ll
0020l00ll
1l30ll
0l18l30ll
Latitudinal extent = 0l18l30ll s = 0031ls - Identify two districts in the area covered by the map. (2mks)
- Nyeri district
- Laikipia district
- Identify two physical features found in grid square 6259. (2mks)
-
- Using a scale of 1 cm represents 20m, draw a cross section from Easting 68 to Easting 74 along Northing 64. (4mks)
On it mark and name- A hill top (1mk)
- A stream/river (1mk)
- All weather road loose surface (1mk)
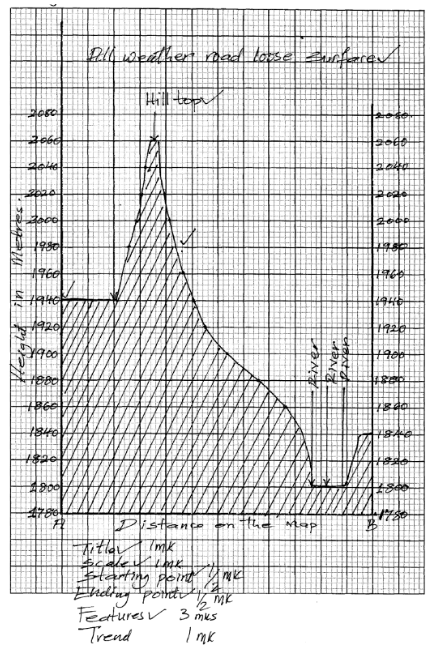
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross-section. (2mks)
V.E = V.S
H.S
= 1 ÷ 1
20m 50000cm
= 1 × 50000
2000 1
= 25 times
- Using a scale of 1 cm represents 20m, draw a cross section from Easting 68 to Easting 74 along Northing 64. (4mks)
- Citing evidence from the map identify two social services offered in Mweiga township.
- Recreation services as evidenced by presence of youth club
- Education as evidenced by presence of school
- Medical/ Health as evidenced by presence of dispensary
- Administration as evidence by the chief’s office
- Security as evidenced by presence of police station.
-
-
-
- What is faulting
- A process through which britle crustal rock fracture (break) due to tectonic forces (tensional / compression) (2mks)
- Types of faults
- Normal fault
- Reverse fault
- Tears fault
- Shear /slip fault
- Thrust fault (4mks)
- What is faulting
- How a rift valley is formed by tension forces.
- The layer of crustal rode is subjected to tensional forces line of weakness occurs this leads to the development of the adjacent normal faults. The central block eventually sinks or subside as the central bloke are pulled apart
- The layer of crustal rode is subjected to tensional forces line of weakness occurs this leads to the development of the adjacent normal faults. The central block eventually sinks or subside as the central bloke are pulled apart
- Other relief features formed as a result of faulting.
- Fault scarp / escarpment
- Fault steps
- Fault blocks
- Tilt blocks (3mks)
- Ways in which feature resulting non faulting are of economic significance
- Faults may expose mineral on the surface for easy extraction.
- Features resulting from faulting eg rift valleys, hotsprings, etc attract tourist.
- Vertical faulting across a river may cause a water fall which may be used to generate H.E.P
- Rift valley lakes are used for fishing and mining e.g soda ash
- Fault Mountains are catchments areas and sources of rivers which are used for irrigation and domestic use.
- Fault scarp slopes may expose underground water result ground water result in the formation of clean water encouraging settlements.
-
-
- Differentiate between weather and climate.
- Weather is the atmospheric conditions of a particular place within a short period of time while climate is the average weather condition of a given place within a long period of time. 2mks
- Explain two ways in which human activities influence rainfall of a given place.
- Creation of multipurpose dams may lead to more evaporation in a region leading to more/increased rainfall
- Afforestation/reforestation/agroforestry programs may increase more moisture in the atmosphere through increased evapotranspiration hence more rainfall
- Deforestation may reduce moisture in the atmosphere leading to reduced rainfall
- Seeding of clouds i.e. practice of putting more nuclei into clouds. in order that more water droplets will condense on to the nuclei and form sufficiently heavy droplets to fall as rain
- The map below shows some climatic regions of the world. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the climatic types marked P, Q and R
- P – Equatorial
- Q – Tropical Continental/Savanna/Sudan
- R – Warm Temperate Continental/Steppe 3mks
- Describe the characteristics of the climatic type labeled W.
- W – Tropical Desert Climate
- High mean monthly temperature/about 30° C.
- Relatively low temperatures during the night/about 10° C.
- Large diurnal temperature range/ 20° C.
- Low rainfall /less than 250 mm annually.
- Rainfall is erratic and unreliable.
- Low humidity.
- Strong winds which are dry and warm are frequent.
- Intense solar insolation and terrestrial radiation due the cloudless skies.
- Low pressure in summer and high pressure in winter.
- Occasional flash floods caused by sporadic rains.
- High evaporation rates. 5mks
- Name the climatic types marked P, Q and R
-
- Name three greenhouse gases likely to be found in the atmosphere.
- Methane
- Carbon (IV) oxide
- Nitrous oxide
- Chlorofluorocarbons 3×1mk=3mks
- Give three ways of combating global warming.
- Legislation against air pollution
- Afforestation
- Reforestation
- Use of green energy/alternative energy sources other than wood fuel
- Use of natural fertilizers e.g. cow dung rather than artificial fertilizer 3mks
- Name three greenhouse gases likely to be found in the atmosphere.
- Members of your class plan to conduct a field study on weather in a local weather station
- State three factors they may identify for the citing of the weather station.
- Open place free from obstructions
- Area with free flowing air
- Fairly level/gently sloping to avoid flooding
- Larger area near and beyond the weather station 3mks
- State two advantages of studying weather through a field study.
- Learners able to draw local examples from their own learning experiences
- It breaks classroom boredom of learning about weather, making the study interesting and real
- It enables learners to practice skills of data collection, recording, interpretation and analysis earlier learnt in class 2mks
- State three factors they may identify for the citing of the weather station.
- Differentiate between weather and climate.
-
-
- Define the term hydrological cycle.
- Hydrological cycle is the endless or continuous circulation of water between water bodies (lakes, seas, rivers, swamps and oceans), atmosphere and land. 2mks
- Explain the following processes of the hydrological cycle;
- Evaporation
- The process by which moisture is directly lost into the atmosphere from various water surfaces and soildue to air movement and heat from the sun 2mks
- Surface run off
- This is the excess water that flows away over the earth’s surface when the ground is unable to absorb all the rain. 2mks
- Evaporation
- Define the term hydrological cycle.
- Citing an example in each case, name three sources of rivers in Kenya.
- Mt. Elgon –R. Nzoia
- Mt. Kenya – R. Tana, R. Ewaso Ngiro
- Nandi Escarpment – R. Yala
- Mau Escarpment – R. Sondu, R. Njoro
- Kiabonyoru Highlands – River Kuja 3×1mk=3mks
- State three factors that influence river erosion.
- River beds with less resistant rocks are easily eroded especially if the rocks are well jointed or soluble in water.
- Steep slopes experience higher velocity of river water due to greater influence of gravitational force. The rivers flow very fast and exhibit higher rates of erosion
- Large and resistant objects e.g. boulders and rock pebbles cause more erosion compared to smaller and finer objects
- When a river carries more/a lot of load undertake more erosion of the river channel the larger the volume of river water, the greater the force of moving water and hence the greater the erosion. 3mks
- The diagrams below show formation of a feature of river deposition. Use them to answer the questions that follow.
- Describe the processes in the diagrams labeled:
- A
- Neck of land separates two concave banks where erosion is more active. 1mk
- B
- Continued erosion on outer bank and deposition on the inner bank makes the neck to be cut through Deposition seals up the ends of the cut off meander. 2mks
- C
- Continued deposition seals the cut off meander to form an ox-bow lake. 2mks
- A
- Name two examples of ox-bow lakes in Kenya.
- Kanyaboli
- Shalu
- Shakababo
- Bilisa
- Gambi 3mks
- Describe the processes in the diagrams labeled:
- Members of your class plan to conduct a field study on the lower course of River Nzoia.
- Give two equipment they are likely to carry for the study.
- Camera
- Route map
- Writing materials
- Questionnaires 3mks
- State three characteristics of the river they are likely to observe during the study.
- The river flows slowly/sluggishly
- The river gradient is gentle
- The river channel is wide/wider
- Deposition is the most dominant river process
- The river is shallow
- Flooding is common in this course
- Give two equipment they are likely to carry for the study.
-
- The diagram below represents underground features in a limestone area. Use it to answer question.
-
- Name the features marked K,L and M. (3marks)
- K – Stalactite
- L – Stalagmite
- M – Cave
- Describe how the feature marked J is formed. (6 marks)
- Solution of calcium carbonate trickles down slowly through the roof of a cave or cavern
- Solution droplets hang on the roof of the cave.
- Water evaporates and calcium carbonate is precipitated.
- The precipitated calcium carbonate gradually builds downwards over a period of time as the solution continues to drip from the roof. This forms a stalactite.
- The solution splashes on the floor and water evaporates.
- The calcium carbonate in it precipitates and gradually builds upwards to form a stalagmite.
- Over time, the stalactite and stalagmite join to form a pillar/column.
- Name the features marked K,L and M. (3marks)
-
- What is a water table (2mks)
- Water table – is the level of groundwater below which all available space is saturated with water
- Explain three conditions necessary for the development of karst scenery. (6mks)
- An area should have thick limestone, dolomite or chalk.
- Low water table to allow formation of conspicuous features if close to the surface, limestone rocks would dissolve.
- The rocks should be well jointed – passage of water.
- Moderate to abundant rainfall/the climate should be hot and humid – to allow chemical weathering by solution.
- What is a water table (2mks)
- You are supposed to carry a field study of an area eroded by water.
- Give three ways you would prepare before conducting the field study. (3mks)
- Seek permission from relevant authorities.
- Read material concerning topic of study.
- Conduct reconnaissance – pre-visit.
- Choose method of date collection.
- Prepare questionnaire.
- Assemble necessary tools
- Prepare working schedule
- Divide the students into groups.
- Name two erosional features you are likely to identify during the field study. (2mks)
- Exposed rocks
- Ridges or clints
- Gullies, or wadis or grikes or dry river beds or gorges.
- Earth pillars, Bates, Mesas, Swallow hole, dolines, Poljes, Uralas.
- State three significance of the resultant features in limestone areas. (3mks)
- Attract tourists – underground features
- Provision of building materials – the limestone blocks.
- Limestone landscape discourage settlement because of its rugged nature and scarcity of surface water
- Give three ways you would prepare before conducting the field study. (3mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Sunrise Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students