- This paper consists of 3 sections; Section A, B and C respectively.
SECTION A (30MKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- State two reasons why farmers should be encouraged to practice organic farming. (1mk)
- State two ways in which crop rotation controls weeds. (1mk)
- Name two methods of sowing pasture crops. (1mk)
- State four qualities considered when selecting seeds for planting. (2mks)
- State four advantages of crop rotation. (2mks)
- State three physical agents of weathering in soil formation. (1½)
- Give four reasons for land fragmentation. (2mks)
- State two mechanical methods used in separating soil in soil analysis. (1mk)
- State three ways in which inorganic fertilizers are classified. (1½)
- State three effects of raindrops on bare soil. (1½)
- Give three reasons why layering would be preferred to the use of cutting as a method of raising planting materials. (1½)
- State the forms in which nitrogen is absorbed by plants. (1mk)
- Outline four factors which effects herbicidal selectivity. (2mks)
- State four natural factors that may influence soil erosion. (2mks)
- Name four disadvantages of zero grazing. (2mks)
- Outline four factors which encourage soil erosion. (2mks)
- Give three properties of foliar fertilizer which makes it possible to be used as a foliar feed. (1½)
- Give three reasons why Banana should be pruned. (1½)
- State four factors considered when classifying crop pests. (2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
- Students in an agriculture class set out to investigate the constituents of soil sample from school. They carried out a series of tests on various portions of the sample. They then prepared a table as shown below:
Description Quantity Mass of an empty evaporating disk Fresh soil on evaporating diskMass of dried soil at 105°C on evaporating diskVol. of water in the tinVol. of water and soil after stirringMass of empty silica diskMass of silica disk and soil after ignitionMass of silica disk and dried soil before ignitionVolume of water and soil before stirring10g 35g28g250cm3410cm315g45g65g500cm3- Calculate the percentage of soil water in the sample. (1mk)
- Why was soil heated at 105°C? (1mk)
- Calculate the percentage of soil air in the sample? (1mk)
- Calculate the percentage of soil organic matter in the sample. (1mk)
- Name one other soil constituent not tested above. (1mk)
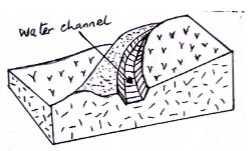
- The diagram below shows a construction on farm. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the above structure. (1mk)
- State four areas where water in the channel is directed to: (4mks)
- The diagram below shows a field practice in crop production.

- Identify the practice. (1mk) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- State two advantages of the practice named in (a) above to Irish potatoes. (2mks)
- Name two other crops that require the above practice. (2mks)
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions.
- Identify the sorghum variety shown above. (1mk)
- State two bird pests that commonly attack the crop. (2mks)
- Name two other varieties commonly grown by farmers. (2mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
-
- Outline the procedure for soil sampling. (8mks)
- Give five reasons for ridging sweet potatoes. (5mks)
- Outline seven properties of nitrogenous fertilizers. (7mks)
-
- Discuss five benefits of weeds to the farmer. (10mks)
- Discuss five importance of draining a waterlogged area. (10mks)
-
- Discuss five factors influencing crop rotation. (10mks)
- Discuss five government policies that regulate production, marketing and distribution of agricultural products. (10mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
- Reasons for organic farming.
- Helps to balance features of fertile soil i.e., organic matter and soil micro-organisms.
- It is affordable and cost effective.
- It uses local materials
- Lessens skills in preparation e.g. green manure.
- Ways in which crop rotation controls weeds.
- Cover crop smoothens weeds if alternated with other crops.
- Crops associated with specific weed as are alternated with crops of different families to remove appropriate host and break life cycle of weeds.
- Methods of sowing pasture.
- Undersowing.
- Oversowing.
- Direct sowing.
- Qualities considered when selecting seed for planting.
- High germination percentage.
- Be healthy/ free from diseases and pests.
- Have high vigour.
- Have no physical damage.
- Suitable to ecological conditions.
- Advantages of crop rotation.
- Control soil/prevent soil erosion.
- Ensure maximum utilization of soil nutrients.
- Help in weed control.
- Improve soil structure.
- Improve soil fertility.
- Offer security incase of crop failure.
- Physical agents of weathering.
- Running water.
- Moving ice.
- Temperature.
- Wind.
- Reason for land fragmentation.
- Buying or selling/ paying debts/ compensation.
- Inheritance.
- Settlement and resettlement.
- Gift or donation.
- Shifting cultivation.
- Method used in separating soil during soil analysis.
- Mixing soil with water then shaking/stirring and allowing particles to settle/sedimentation.
- By use of series of sieves with different meshed size.
- Classification of inorganic fertilizers.
- According to the nutrients they contain.
- According to soil reaction/ effect of soil Ph.
- Time of application.
-
- Splash erosion/causes soil erosion.
- Exposes seeds.
- Causes hardpans/soil capping/destroy soil structure.
-
- When cutting cannot root if detached from mother plant.
- Where large planting materials are pre-faced/rooting system.
- Faster production of planting materials/quick growth.
- Higher chances of survival.
- Has well established rooting system.
-
- Nitrate form/ nitrate ions.
- Ammonium form/ ammonium ions.
-
- Age of the weeds
- Plant morphology
- Plant physiology
- Metabolic factors
- Chemical concentration
- Stage of crop growth
- Rooting system
-
- Amount of rainfall/rainfall intensity
- Slope/topography
- Type of soil
- Size of intershade/catchment
- Length of slope
- Wind velocity/ strength of wind.
-
- High initial capital.
- High management.
- High labour.
- Diseases can easily spread.
-
- Lack of ground cover.
- Steep slopes.
- Shallow soils.
- High rainfall intensity.
- Overstocking.
- Poor method of cultivation.
- Deforestation.
-
- Should not have any scorching effects on the plants.
- Be easily absorbed by the leaves.
- Used in spray form/ soluble in water.
-
- To control banana weevils.
- To spread the production.
- To produce large bunches.
-
- Where pests are found.
- Feeding habit/type of damage.
- Scientific/biological classification.
- Crop attacked.
- Stage of development of past at which it causes damage.
- Stage of growth at which crop is attacked.
- Part of crop attacked.
SECTION B
-
- 7/35 × 100 = 20%
- To evaporate/expel the moisture.
- 90/250 × 100 = 36%
- 20/50 × 100 = 40%
-
- Soil living organisms.
- Soil mineral matter/inorganic.
-
- Cut-off drain/Diversion ditch.
-
- Natural water ways e.g river.
- Non-erodable stony/rock ground.
- Grassland with grass cover.
- Artificial waterway.
-
- Earthing up.
-
- Improves tuber formation.
- Promotes production of seeds.
- Improves drainage.
- Provides support.
-
- Cassava.
- Groundnuts.
- Sweet potatoes.
-
- Compact panicle.
-
- Sudan Dioch.
- Weavers.
- Starlings.
- Open panicle.
- Goose necked.
SECTION C(40MKS)
-
- Procedure of soil sampling. (8mks)
- Clear the vegetation from a sampling spot.
- Make a vertical cut 15-25 cm for crop land and 5 cm for pasture land.
- Take a slice from vertical cut using a spade/ soil auger.
- Put the soil in a clean suitable container.
- Repeat the above steps in 15-20 spots.
- Soil from all the spots is mixed, dried and crushed.
- A sub-sample from the mixture is taken.
- Its clearly labelled and taken to the laboratory for testing.
- Reasons for ridging. (5mks)
- Allows tuber expansion.
- Allows easy harvesting.
- Prevents greening of tubers.
- Conserves moisture.
- Controls drainage.
- Prevents pest attack.
- Properties of nitrogenous fertilizers. (7mks)
- Highly soluble in water.
- Easily leached to lower horizons.
- Have short residual effect.
- Have scorching effect/ burning effect.
- Are highly corrosive.
- Are highly volatile hence applied on moist soils.
- Are hygroscopic hence absorbs moisture from atmosphere.
- Procedure of soil sampling. (8mks)
-
- Benefits of weeds. (10mks)
- Some weeds are edible to man and livestock e.g., pigweed. They are used as food.
- Some weeds have medicinal value. Weeds are known to provide herbal medicine to man and livestock e.g., Sodom apple.
- Weed act as soil cover, preventing lose of moisture, soil capping and impacts of raindrops.
- Weeds add organic matter to the soil when they decompose hence enriching soil with humus/soil nutrients.
- Leguminous weeds fix nitrogen in the soil hence enriching soil with nitrates.
- Importance of drainage. (10mks)
- To increase soil volume; Soil around the root zone increases making it easy for plants to get nutrients.
- To increase microbial activities; Drainage increases aeration in soil which hence increases in number of micro-organisms.
- To reduce soil erosion; This increases water holding capacity and infiltration.
- To remove toxic substances; Salts such as those of sodium increases chances of waterlogged conditions.
- To raise soil temperatures; Improves the rate at which soil warms up.
- To increase soil aeration; When excess water I removed, plant roots get enough air for proper growth.
- Benefits of weeds. (10mks)
-
- Factors influencing crop rotation. (10mks)
- Crop root depth; Deep rooted crops should be alternated with shallow rooted.
- Soil structure; A grass ley is included in the rotation to bind soil particles.
- Crop nutrient requirements; Crops with high nutrient requirement should come first in a newly opened land.
- Soil fertility: Leguminous crops should be included to improve soil fertility.
- Pests and diseases control: Crops from the same family should not follow each other in the rotation programme.
- Weed control: Crops associated with certain weeds should be alternated with those that are not. Crops not easy to weed should be alternated with those easily weeded.
- Government policies regulating agriculture. (10mks)
- Heavy taxation of imports; It makes importation more expensive and encourage domestic buying.
- Subsidizing growing of locally produced commodities. This makes production of goods cheap and affordable.
- Quality control; Ensures production of high-quality goods.
- Conservation of natural resources; Natural resources help in sustaining agriculture e.g. water catchment areas.
- Stepping up the control of diseases, pests and parasites; They affect crops and livestock a great deal.
- Probability production of some crops e.g., cannabis sativa such crops pose a threat to human health.
- Growing some crops under the quota system; This prevents flooding of market by produce from only prominent producers.
- Factors influencing crop rotation. (10mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Sunrise Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students