- This paper consists of 3 sections; Section A, B and C respectively.
SECTION A (30 MARKS
Answer all questions in this section.
- State four characteristics of exotic dairy breeds. (2mks)
- Differentiate between the following terms; (2mks)
- Steer and a bullock.
- Boar and Sow.
- Name two tools used for dehorning. (1mk)
- Name two hormones that control milk let- down. (1mk)
- State four signs of farrowing in pigs. (2mks)
- Outline four management practices carried out while rearing a heifer. (2mks)
- State two effects caused by Keds in sheep. (1mk)
- Outline four characteristics of an African wild bee. (2mks)
- Name the breeding terms used to describe parturition in the following farm animals; (2mks)
- Sheep. ………………………………………………………………………………………
- Cattle. ……………………………………………………………………………………
- Rabbit. ……………………………………………………………………………………
- Goat. ……………………………………………………………………………………
- Name four routes through which the vaccines can be administered. (2mks)
- State two abnormalities observed during egg candling. (1mk)
- State four advantages of natural incubation. (2mks)
- Outline four disease causing micro-organism. (2mks)
- State two factors that determine amount of water required by a dairy cow. (1mk)
- Name two dual purpose sheep breeds. (1mk)
- Name four parts found in a piggery unit. (2mks)
- State four advantages of embryo transplant. (2mks)
- Name four disorders caused by mineral imbalances in cattle. (2mks)
- Outline two physiological body functions that indicate illness in livestock. (1mk)
SECTION B: (20 MARKS)
-
- A farmer was advised to prepare 180kg of calf ration containing 20% DCP. Using Pearson’s square method, calculate the amount of maize containing 10% DCP and sunflower containing 40% DCP the farmer needs to use. Show your working.
(4 mks) - State two factors considered when formulating a livestock ration. (2 mks)
- A farmer was advised to prepare 180kg of calf ration containing 20% DCP. Using Pearson’s square method, calculate the amount of maize containing 10% DCP and sunflower containing 40% DCP the farmer needs to use. Show your working.
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name the type of identification illustrated above. (1 mk)
- Give the identification number of the pig illustrated above. (1 mk)
- Using a diagram, illustrate how animal number 83 can be identified using the above method. (2 mks)
- What is the use of metal rails in a farrowing pen? (1 mk)
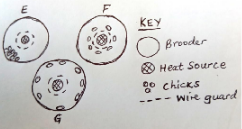
- The diagrams below show the behaviour of chicks in a brooder in response to heat.
- Explain the behaviour of chicks in brooder;
- E – (1 mk)
- F – (1 mk)
- G – (1 mk)
- Explain why the brooder is rounded. (1 mk)
- Explain the behaviour of chicks in brooder;
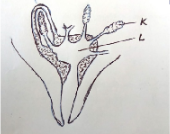
- The diagram below shows the structure of the udder of a cow. Study it then answer the questions that follow.
- Identify parts labeled K and L. (2 mks)
- Name two hormones that control milk let-down in a dairy cow. (2 mks)
- Name one disease that attack part labeled L. (1 mk)
SECTION C: (40 MARKS
Answer ONLY TWO questions from this section.
-
- Describe the physical characteristics of a good dairy cow for breeding. (10 mks)
-
- State five functions of water in the body of livestock. (5 mks)
- Explain the advantages of a four-stroke cycle engine. (5 mks)
-
- Explain five factors that affect milk composition in dairy cattle. (5 mks)
- Describe five factors that may lead to failure of a cow to conceive after service. (5mks)
- Explain the factors that a farmer should consider when selecting materials to construct a zero-grazing unit. (10 mks
-
- Describe milk fever under the following sub-headings:
- Animal affected. (1 mk)
- Cause of disease. (1 mk)
- Symptoms. (5 mks)
- Control measures. (3 mks)
- Outline the advantages of artificial insemination in cattle. (10 mks)
- Describe milk fever under the following sub-headings:
MARKING SCHEME
- Physical characteristics of exotic breeds.
- Straight top line.
- Wedge/triangular shape.
- Absence of hump.
- Prominent milk veins.
- Well set hindquarters and large teats.
-
-
- Steer- young castrated male cattle.
- Bullock- mature castrated male cattle.
-
- Boars are male pigs that are used for breeding.
- Sows are female pigs that have given birth to a litter of piglets
-
- Dehorning tools.
- Dehorning iron/disbudding iron.
- Dehorning wire or saw.
- Dehorning collodion.
- Caustic potash stick.
- Rubber ring and elastrator.
- Has antibodies that help resist early diseases infections.
-
- Oxytocin.
- Adrenalin.
- Signs of farrowing.
- Restlessness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Enlarge of the udder and teats.
- Sow collects bedding and build a nest.
- Enlargement of vulva.
- Management practices of a heifer.
- Diseases and parasite control.
- Vaccination.
- Feeding.
- Deworming.
- Identification.
- Dehorning.
- Effects of keds.
- Cause irritation.
- Damage of wool.
- Retarded growth.
- Anaemic conditions.
- Characteristics of African wild bee.
- Adapted to local weather conditions.
- Highflying power hence fly for longer distances.
- Active in search of food and water.
- Vicious if manhandled.
- Resistant to diseases like Acarive and American foul brood diseases.
-
- Cattle- calving.
- Rabbits-kindling.
- Sheep-lambing.
- Goats- kidding.
- Routes for vaccination.
- Nose.
- Mouth.
- Cloaca.
- Skin.
- Candling abnormalities.
- Double yolk.
- Broken egg shell.
- Hair cracks.
- Blood/meat spots.
- Advantages of natural incubation.
- Low marginal cost.
- Requires less skills.
- Suitable for small scale farmers.
- Less laborious since it does not involve egg turning.
- Diseases causing micro-organisms.
- Bacteria.
- Virus.
- Protozoan.
- Fungi.
- Factors that determine amount of water taken by a dairy cow.
- Animal requires more water during hot season due to sweating.
- Type of feed eaten by the animal.
- Level of production
- Weight of the animal or the body size.
- Dual purpose breeds in sheep.
- Corriedale.
- Hampshire Down.
- Romney marsh.
- Parts of a piggery.
- Feed store.
- Record room.
- Water trough/drinking nipples.
- Running yard.
- Pig pens: gilt, boar, in pig, weaner, fattener pig pen.
-
- Increase in the number of offspring per female.
- Easier and more rapid exchange of genetic material between countries.
- Less transport of live animals, thereby reducing risks of disease transmission.
- Storage and expansion of rare genetic stock.
-
- Milk fever.
- Anaemia.
- Paraketosis.
- Oestomalacia.
- Grass tetany/stagger/hypomagnecia.
- Physiological body functions that indicate illness.
- Abnormal appetite.
- High /low body temperature.
- Abnormal defecation.
- High/low respiratory.
- Abnormal colour of the urine/frequent urination.
SECTION B
-
- Maize = 20/30 x 180 = 120kg
Sunflower = 10/30 x 180 = 60kg -
- Age of the animal
- Cost of feedstuff
- Type of animal whether ruminant or non-ruminant
- Nutrient requirement of the animal
- Availability of feedstuff
- Maize = 20/30 x 180 = 120kg
-
- Ear notching
- 5 + 3 + 2 + 50 + 30 + 20 = 110 (must show the working) (Any other combination unacceptable)
- Prevents sow from crushing the piglets
-
-
- E – There is draught from the side directly opposite where the chicks have crowded.
- F – Its very cold in the brooder chicks crowd around heat source
- G – Too much heat making chicks move far away from heat source
- To avoid overcrowding at one point which may lead to suffocation.
-
-
- K – alveoli L – gland cistern
- Oxytocin, Adrenalin
SECTION C: (40 MARKS)
-
-
- Wedge/Triangular shaped.
- Big stomach to store more food
- Large well-developed udder and teats
- Well set hind quarters to allow room for big udder
- Long thin neck and small head
- Lean body with little flash
- Large milk veins and milk wells
- Straight top line
- Long thin legs
- Prominent pin bones
-
-
- Regulates body temp
- Transportation of nutrients
- Component of body cells and fluids
- Make cells turgid
- Used in biochemical reactions
- Helps in excretion of waste products
- Forms part of animal products.
-
- Produce high power
- Have efficient fuel and oil utilization
- Performs wide range of farm operations
- Engines are efficiently cooled with water
- Exhaust gases are effectively expelled
-
-
-
-
- Age of the animal: old animals produce milk with low butter fat content
- Stage of lactation: butter fat content is high in the middle phase of lactation
- Completeness of milking: Last drawn milk from udder has higher butter fat content.
- Season of the year: butter fat content increases during cold season.
- Type of food eaten: food rich in roughages are richer in butter fat content.
- Animals health: mastitis reduces butter fat content leading to watery milk
- Breed – Jersey produce milk with more butter fat content
- Physiological condition: Last stage of pregnancy has milk with lower butter content
- Nutrition: Mexican marigold and silage taints milk if fed before milking.
-
- Wrong timing of service
- Low quality/expired semen
- Poor skilled veterinary officer
- Infertile cow
- Blocked fallopian tubes/oviduct
- Hormonal imbalance
- Disease infection e.g., brucellosis
-
- Cost of the material
- Durability
- Workability
- Toxicity of materials to workers/animal
- Farmers taste and preferences
- Type of zero-grazing unit
- Availability of skilled labour
- Capital available
- Suitability
- Environmental conditions
-
-
-
- Cows/Nannies/sows that have recently given birth
- Low calcium levels in blood leading to increase in magnesium and sugar levels.
-
- Muscular twitching causing animals to tremble
- Staggering as the animal moves
- Animal lies down on its side and whole body stiffens/neck twisted
- Body functions e.g., urination stops
- Stomach contents drawn to the mouth
- Complete loss of appetite/anorexia
- Dullness
- Animal falls down and becomes unconscious
- Control
- Partial milking for first 10 days
- Intravenous injection with calcium salts
- Feed the animal with diet rich in calcium and phosphorus
- Giving high doses of vitamin D
- AI
- Semen of a bull can be used even after its death
- Heavy bulls can produce semen to serve
- Controls breeding diseases
- Prevents inbreeding
- Eliminates dangerous bulls in the farm
- Useful as a research tool
- Easier and cheaper to transport semen that a bull
- Quicker method to obtain a proven sire
- Semen from one superior bull can serve many cows
- Saves costs of rearing a bull
- Controls breeding
-
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sunrise Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students