INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL the questions in this question paper.
SECTION A (30 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- Give two disadvantages of intensive system of farming. (1mk)
- List four methods of farming. (2mks)
- Give the meaning of the following terms:
- nitrogen fixation into the soil; (1mk)
- phosphorus fixation in loss of soil fertility. (1mk)
- List four ways through which soil PH influences crop production.(2mks
- Outline four factors that affect the effectiveness of a pesticide.(2mks)
- State two reasons for land fragmentation in Kenya. (1mk)
- Give four advantages of individual owner operator tenure system as practiced in Kenya. (2mks)
- State four features that should be considered when choosing water pipes for use on the farm. (2mks)
- Give four reasons for treating water for use on the farm. (2mks)
- State four factors that determine the stage at which a crop is harvested. (2 marks)
- State two activities carried out during hardening off tomato seedlings. (1mk)
- Give two reasons for carrying out each of the following operations in land preparation:
- rolling; (1mk)
- leveling. (1mk)
- Give four benefits of practicing organic farming.(2mks)
-
- Name three vegetative parts that can be used to propagate pinapples. (1½ marks)
- State three disadvantages of vegetatively propagating pinapples. (1½mks
- Name two classes of weeds on the basis of each of the following:
- growth cycle; (1mk)
- plant morphology. (1mk)
SECTION B (20 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- Below is a diagram of a weed. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the weed illustrated above. (1/2mk)
- Why is the weed illustrated above difficult to control? (1mk)
- State four ways in which the weed can be controlled in a field of maize. (2mks)
- The diagram below shows a pest and the damaged crop. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the crop pest illustrated above. (1 mark)
- Explain two ways of controlling the pests. (2 marks)
-
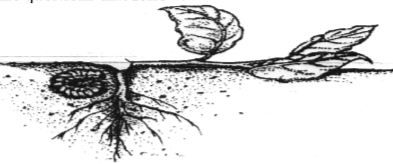
- The diagram below illustrates a nursery practice.
- Identify the practice. (1 mark)
- Describe the procedure followed in carrying out the practice illustrated.(2 marks)
- State two advantages of the practice illustrated above in crop production. (2 marks)
- State two ways in which pruning assists in controlling crop diseases. (1mk)
- The diagram below illustrates a nursery practice.
- The diagrams below illustrate field management practices. Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
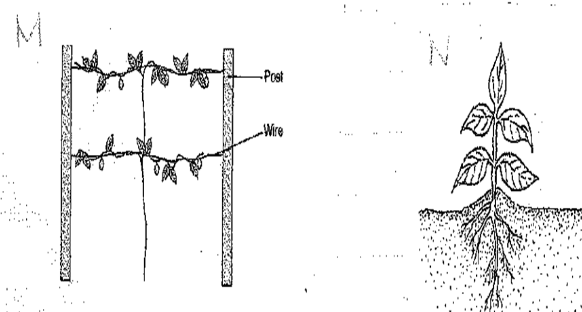
- Identify the field practices.
- M……………………………………………………………………………(1mk)
- N……………………………………………………………………………(1mk)
- Name a crop that can be managed using management (M) above.(1mk)
- Give one reason for carrying out each of the management practices above.(2mks)
- M……………………………………………………………………………………………
- N……………………………………………………………………………………………
- Identify the field practices.
- A famer is advised to apply 60kg N, 20kg P2O5 and 30kg K2O per hectare. Calculate the quantity of urea (46%N), single super phosphate (20%P2O5) and muriate of potash (50% K2O) the farmer should apply on his 10 hectares land. (5 mks)
SECTION C (40 marks)
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided after question 25.
-
- Explain eight factors that can encourage soil erosion. (8 mks)
- Describe the seven management practices that should be carried out on a vegetable nursery after sowing seeds until the seedlings are ready for transplanting. (7 mks)
- State five soil factors that should be considered when selecting a crop to grow in an area. (5mks)
-
- Outline five ways in which high temperature affects agricultural production in Kenya. (5mks)
- Describe five ways in which the following affects agriculture (7mks)
- poor economic growth
- poor health
- Explain eight types of micro-catchments used in water conservation (8mks)
-
- Explain six physical methods that can be used to control crop pests on the farm. (6mks)
- Describe SEVEN field management practices carried out in the production of tomatoes (7mks)
- Explain seven factors that influence seed rates in crop production. (7mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Requires high capital investment per unit area.
- High labour per unit area/High skiled labour.
-
- Agroforestry
- Shifting cultivation
- Organic farming
- Monadic pastoralism
- Mixed farming
-
- Nitrogen gas is converted into forms which can be absorbed by the plants.
- Phosphorus combines with other elements and becomes unavailable for plant use.
-
- Determines the type of fertilizer to apply
- Determines the availability of particular mineral elements in the soil.
- Determines the activity of micro-organisms in the soil.
- Determines the crop to grow in an area.
-
- Weather conditions
- Concentration of the pesticide
- persistence of the pesticide
- Mode of action
- Formulation of the pesticide
-
- Shifting cultivation
- Settlement and resettlement
- Traditional systems/inheritance of land among heirs.
- Population pressure on a limited area hence purchase of land
- Accumulation of land holdings
-
- Minimizes land disputes as the farmer posseses a title deed.
- It is easy to plan and make decisions.
- The owner has incentives to make long term investments.
- The title deed can be used as a security to obtain loans.
- It gives the farmer incentives to improve the land.
- The owner can sell or give away part of the land at will.
-
- The pipes should be durable.
- The cost of the pipe
- The diameter/size
- Strength/Ability to withstand pressure
- Workability/skills available
- Colour
-
- To remove chemical impurities
- To remove bad smell
- To kill disease causing micro-organisms
- To remove sedimants of solid particles.
-
- The intended use of the crop.
- Weather conditions
- Market demand
- Concentration of the required chemicals.
- Prevailing market prices and profit margins.
-
- Removal of shade.
- Reducing watering frequency
-
- rolling
- Increases seed-soil contact.
- prevents soil erosion.
- Prevents small seeds from being carried away by wind.
- levelling
- Encouraes uniform depth of planting
- Facilitates uniform germination
- Prevents depression which collect too much water which may cause rotting of seeds.
- rolling
-
- The method is environmentally friendly.
- Encourages production of chemical free products.
- The method is generally cheap.
- It improves soil structure and water infiltration
-
- Suckers
- Crows
- Slips
-
- May not result into new crop varieties.
- Keeping the materials free of diseases is difficult.
- Materials cannot be stored for a long time unlike seeds.
- Materials are bulky ∴ difficult to transport.
-
-
- Growth cycle
- Annuals
- Perennials
- Biennials
- Plant morphology
- Broad leafed
- Narrow leafed
- Growth cycle
-
- Couch grass
- It has underground rhizomes
-
- Use of selective herbicides
- Proper tillage especially in dry season.
-
- Cutworm
-
- Use of appropriate pesticides
- Early planting of the crop to establish and outgrow the pest.
- Field hygiene to prevent transmission from previous crop residues.
- Physical killng and destruction of the pest.
-
-
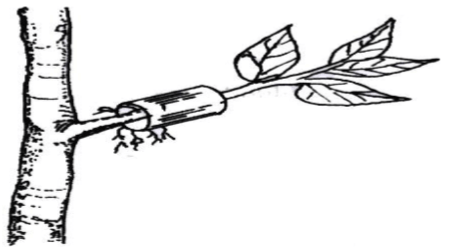
- Aerial layering.
-
- Select a healthy woody branch;
- Remove the bark and cambial layer from a section of the branch/ring back the branch;
- Heap moist rooting medium around the section;
- Wrap the rooting medium with a polythene sheet;
-
- Gives a large planting material;
- Obtain planting materials from branches that cannot easily bend bend/woody stems/ branches high up the stem.
-
-
-
- M - Trelishing
- N - Earthing up
- Passion fruit/ some bean varieties
-
- M - Provides support to crops with vines
- N
- Improves tuber formation (e.g) in irish potatoes.
- Provides support hence preventing ledging e.g in maize
- Improves drainage around the crop.
-
-
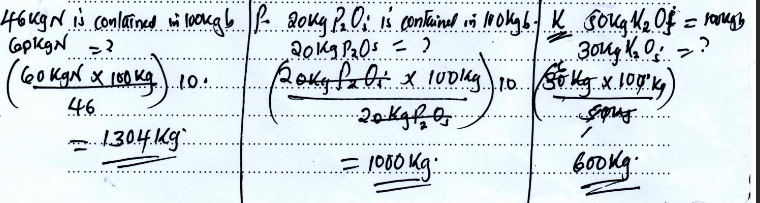
-
- Factors tha encourage soil erosion
- Lack of ground cover exposes soil to agents of soil erosion.
- Steep slopes increases the speed of surface run-off hence erosion power of water.
- Light /sandy soils are easily carried away by agents of soil erosion.
- Shallow soils are easily saturated with water and carried away.
- Overcultivation pulverises the soil making it easy to detach and be carried away.
- Overstocking leads to overgrazing which destroys ground cover exposing it to agents of erosion.
- High amount of rainfall increase saturation of soil with water thus increasing soil erosion.
- Cultivation of the river banks destroys river line vegeation exposing it to soil erosion.
- ploughing up and down the slopes creates water channels which encourage soil eorion.
- Burning of vegetation leaves land bare exposing it to erosion agents,
- Cultivating soil when too dry/ too wet destroys soil structure making soil easily eroded.
- High rainfall intensity increases impact of raindrop thus encouraging raindrop erosion.
- Nursery bed management practises.
- Mulching to conserve moisture.
- Erection of shade to minimize evaporation.
- Weed control to reduce competition with seedlings.
- Pests and disease control to ensure healthy seedlings.
- Pricking out to minimize competition.
- Watering to ensure adequate moisture aupply.
- Hardening off to prpepare seedlings adapt ecological conditions.
- Soil factors considered when selecting a crop to grow.
- Soil pH
- Soil drainage/ water retention
- Soil fertility
- Soil type & texture.
- Soil structure.
- Factors tha encourage soil erosion
-
- Effects of high temperatures in Kenya.
- Increases evaporation leading to wilting of crops
- Increases growth rate / hastens maturity of crops.
- Improves quality of crops e.g ppineapples and oranges.
- increases incidences of some crop pests and diseasese.g
- Leaf rust in coffee.
- Aphids in vegetables
-
- Poor economic growth
- leads to collapse of co-operative movemnts and factories.
- Low pricing of agricultural products resulting to low income for farmers.
- Poor infrastucture hence poor marketing of agricultural produce.
- the low use of techology in agriculture hence reduced output.
- Poorhealth
- Shortage of labour
- Lack of motivation to invest in agriculture.
- Less time is spent in farming - as people carter for the sick/
- Low standards of living.
- Lack of market for agricultural produce.
- Poor economic growth
- Micro-catchments.
- Planting pits
- Contour bunds/ furrows for crops.
- Semi-circular bunds
- Negarims/ cathcment basin
- Water spreading bunds
- Rous dams
- Trapezoidal bunds
- Effects of high temperatures in Kenya.
-
- Physical methods of controlling crop pests.
- Physical destruction of the pest.
- Flooding
- Proper drying procedure
- Use of electromagnetic radiation.
- Use of lethal temperature
- Use of scarecrows
- use of physical barriers
- Air suffocation
- Use of explosives
- Management practises done on tomatoes.
- Gapping
- Top dressing
- weeding
- staking
- prunning
- Pest control
- Control of diseases.
- Factors that influence seed rates
- Seed purity
- Germination percentage.
- Spacing
- Nuber of seeds per hole.
- Purpose of the crop.
- Physical methods of controlling crop pests.
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Sukellemo Joint Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students