Instructions to Candidates
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- ALL working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used.
- Use g=10N/Kg
SECTION A: 25 MARKS
-
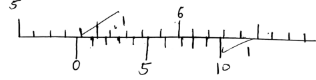
- The vernier calipers shows the reading of 5.38cm. Draw the diagram showing this. (2 marks)
- If the vernier calipers used had an error of 0.05cm, find the actual reading (1 mark)
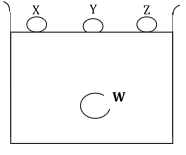
- Use the surface molecules X, Y, Z and inner molecule W shown below to explain why the surface of a liquid is under tension (3 marks)
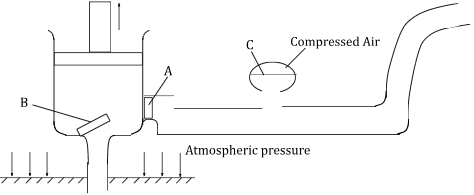
- The diagram below shows a force pump used to draw water from a well.
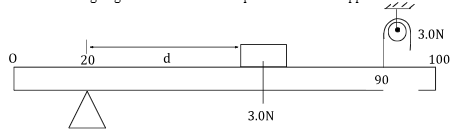
Explain how the continuous flow of water through outlet is achieved (2marks) - A uniform meter rule weighing 1.5 N is in a state of equilibrium when supported as shown below.
Calculate the distance, d (3 marks) - Oil flows through a 14cm internal diameter pipe at an average velocity of 10m/s. Find the flow rate in SI unit (3 marks)
-
- State the Newton’s second law of motion (1 mark)
- A 90kg water skier is being pulled by a speed boat. The force causes her to accelerate at 4m/s2. Calculate the accelerating force. (2 marks)
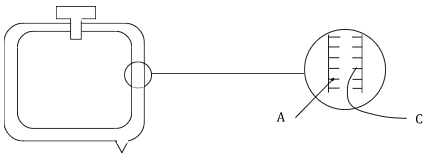
- The diagram below shows a simple diagram of a vacuum flask with an enlarged view of the part in a circle.
- What is the material of item labelled A and C? (1 mark)
- Explain why A and C is effective in reducing heat transfer. (2 marks)
-
- State Hooke’s law (1 mark)
- A mass of 200g is suspended from the lower end of a spring. If the reading when no mass is hanging on the spring is 45.5 cm and the reading after the mass is suspended is 49.5cm. Calculate the spring constant. (3 marks)
- State one assumptions made during determination of the size of oil molecule in the oil drop experiment. (1 marks)
SECTION B: 55 MARKS
-
- Define work and state its SI unit (2 marks)
- A force of 15N is applied on a body causing it to move through a distance of 2m on a surface that offers a friction of 5N Determine the useful work done (3 marks)
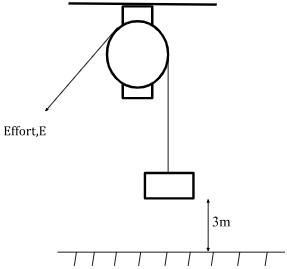
- A man uses a pulley shown in the diagram below to lift a load of 100N through a distance of 3m.
- If the friction is negligible, what is the value of effort E (2 marks)
- Determine the work done in raising the bucket through a height of 3m (2 marks)
- Determine the work done by the effort,E (2 marks)
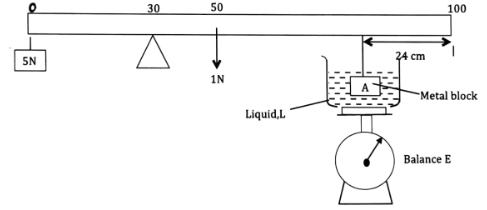
- The figure below shows a lever arrangement with a uniform meter rule of weight 1N balanced by a knife edge at the 30 cm mark. The 5N weight at 0cm mark balances metal block A of volume 2.8 x 10-3m3 which has been immersed in liquid L. The weight of the beaker is 2.0N and that of liquid is 3.0N. Balance E reads 15N.
Determine:- The apparent weight of the metal block A (2 marks)
- Upthrust on the metal block due to the liquid L (2 marks)
- The density of liquid L (2 marks)
- The weight of the metal block in air (2 marks)
- The density of the solid (2 marks)
- Why does hydrometer have a narrow stem (1 mark)
- A body is projected horizontally at an initial velocity of 120 m/s from a clift 300m tall. Calculate;
- Time of flight (2 marks)
- The range (2 marks)
- Vertical velocity at which the body strikes the ground (2 marks)
- A stone is whirled with uniform speed in a horizontal circle having a radius of 16cm. it takes the stone 12 seconds to describe an arc of length 8cm.
Calculate;- The angular displacement (2 marks)
- The angular velocity (1 mark)
- The linear velocity of the stone (2 marks)
- The periodic time (2 marks)
-
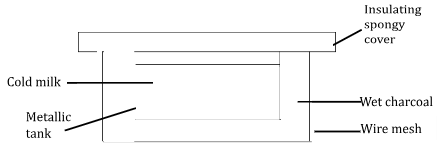
- The diagram below shows a charcoal refrigerator used to cool milk to low temperature.
Explain how the cooling takes place in this refrigerator (2 marks) - Give a reason why charcoal is suitable for cooling process (1 mark)
-
- Define the term heat capacity and state its SI unit (2 marks)
- An electric heater rated 15A, 240V is used to heat 2kg of water from 20°c to 100°c in 160 seconds. Determine the specific heat capacity of water. (2 marks)
- Explain why the value calculated in C (ii) an estimate (2 marks)
- Explain how boiling point of a substance is affected by altitude (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a charcoal refrigerator used to cool milk to low temperature.
-
- Define absolute zero. (1 mark)
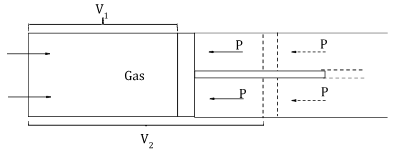
- A gas is enclosed inside a cylinder which is fitted with a frictionless piston. Initially, the gas has a volume V1 and is in equilibrium with an external pressure P. The piston is then pulled backward until the volume becomes V2 which is twice V1.
- State the change in pressure. (1 mark)
- Explain the change in pressure in (i) (2 marks)
- State the law that governs the above experiment. (1 mark)
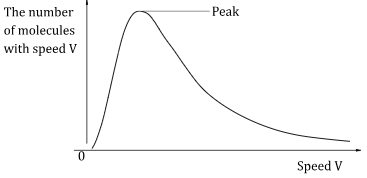
- The graph below shows the distribution of speeds of a gas at a particular temperature.
State how the peak of the graph would change if temperature is increased. (1 mark - The volume of a fixed mass of a gas reduced from 500cm3 to 300cm3 at constant pressure. The initial temperature was 90k. Determine the final temperature. (3marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Actual reading = Reading − Error
= 5.38cm − 0.05cm
= 5.33cm
-
- Molecule V is surrounded by molecules all round, net force is zero. Molecules X, Y & Z experiences a resultant inward force causing the surface of the liquid to be in tension.
- F3d3 = F1d1 + F2d2
3×70 = (3×d) + (1.5× 30)
210 = 3d + 45
3d = 165
d = 55cm - FR = VA
= 10 × (22/7 × 0.07 × 0.07)
= 0.154m3/s -
- The rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the resultant external force causing the change and it takes place in the direction of the force.
- F = ma
= 90 × 4
= 360N
-
- Silver
-
- A - Poor absorber of heat
- C - Good reflector of heat.
-
- For a helical spring or other elastic material, the extension is directly proportional to the stretching force, provided elastic limit is not exceeded.
- K = F/e
= 2N
0.04m
K = 50N/m
-
- The circular patch is one molecule thick/ only one monolayer
- There's no intermolecular distance between the molecules of oil.
-
- Product of force and distance mmoved in the direction of the force. SI unit joule(J)
- W.d = F × d
= (15 − 5)N × 2m
= 10N × 2m
= 20J -
- L = E
= 100N - W.d = P.E = mgh
= 100 × 3
= 300J - W.D = E × DE
= 100 × 3
= 300J
- L = E
-
- 5 × 0.3 = 1 × 0.2 + (T × 0.46)
1.5 = 0.2 + 0.46T
T = 2.83N - u = 15 − 3 − 2
= 10N - u = vpg
10 = 2.8 × 10−3 × pL × 10
pL = 357.14 Kg/m3 - W = T + u
= 2.83N + 10
W = 12.83N - Mass of block = 1.283kg
Volume = 2.8 × 10−3m3
density = 1.283
2.8 × 10−3
= 458.21Kgm−3 - To make it more accurate
- 5 × 0.3 = 1 × 0.2 + (T × 0.46)
-
- S = ½gt2
300 = ½ × 10 × t2
t2 = 60
t = 7.746 seconds - R = μt
= 120 × 7.746
= 929.52m - V = gt
= 10 × 7.746
= 77.46m/s
- S = ½gt2
-
- θ = s/r
= 0.08
0.16
= 0.5rad - w = θ/t
= 0.5
12
w = 0.0417 rad 5−1 - V = wr
= 0.0417 × 0.16
V = 6.67 ×10−3m/s - T = 2π
w
= 2π
0.0417
T = 150.68 seconds
- θ = s/r
-
- Water on charcoal evaporates causing cooling effect on metal tank and milk.
- It is good absorber of radiant heat causing higher evaporation rate.
-
- Heat energy required to raise the temp. of a substance by 1°C. SI - joule per kelvin
- IVt = mcΔt
15 × 240 × 160 = 2 × c × 80
C = 3600Jkg−1K−1 - The heat gained by the container and the one lost to the surrounding is not accounted for.
-
- Increase in altitude lowers the atmospheric pressure hence lowering boiling point.
- Decrease in altitude rises atmospheric pressure increasing the boiling point.
-
- The lowest temp, in Kelvin scale where the energy of the particles is zero or volume.
-
- Pressure is halved/ reduces by half
- The volume doubles. The number of collisions per unit time is halved/ rate of change nof momentum is halved.
- The pressure of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportinal to its volume at constant temperature.
- Move to the right/ shift to the right.
- V1 = V2
T1 T2
500 = 300
90 T2
T2 = 300 × 90
500
= 54K
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mokasa 1 Joint Pre Mocks Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students