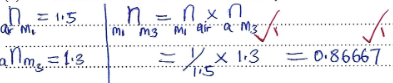Instructions to Candidates;
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical tables and electronic calculator may be used.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
Section A; 25 Marks
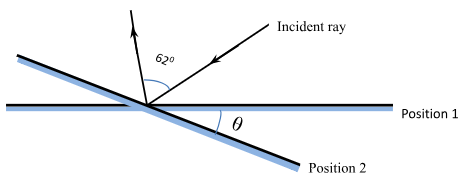
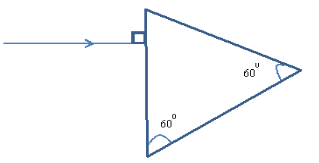
- The diagram below shows a ray of light initially incident at an angle of 25° to the horizontal mirror at position one. While the ray is maintained in the same position, the mirror is then turned clockwise through an angle θ to position 2, where the angle between the incident and the reflected ray becomes 62°. Using the diagram, determine:
- The angle through which the reflected ray is rotated through. (2marks)
- Find the angle of rotation of the mirror θ (1mark)
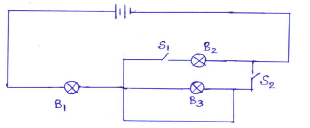
- The diagram below shows a simple circuit.
- State the observation made on B1, B2 and B3 when both switches S1 and S2 are closed (1 mark)
- Give reason for the above observation (1 mark)
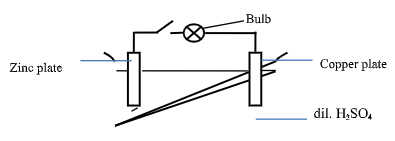
- The figure below shows a simple cell made of copper and zinc electrodes dipped in dilute sulphuric acid.
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction at
- The Zinc plate (1 mark)
- The Copper plate (1 mark)
- State the colour of the positive plate of a lead acid accumulator when it is fully charged (1 mark)
- Write the ionic equation for the reaction at
-
- A charged glass rod is brought close but not touching the cap of a lightly charged electroscope. It is observed that the leaf initially falls then rises again.
- State the type of charge in the electroscope (1mark)
- Give the explanation for the observation made (2 marks)
- State two uses of an electroscope (2 marks)
- A charged glass rod is brought close but not touching the cap of a lightly charged electroscope. It is observed that the leaf initially falls then rises again.
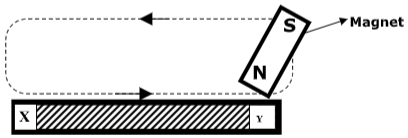
- The figure below shows one method of making a magnet.
- Name the method of magnetization shown above (1 mark)
- Identify the resulting magnetic pole formed at X; (1 mark)
-
- Using Domain theory, explain how the above process is achieved (3 marks)
- Give the reason why the strength of a magnet is greatest at the poles (1 mark)
- A student stands between two high walls at a distance 1600m from the nearest wall. Each time the student claps the hands, two echoes are heard; the first after 10s while the second follows 5 seconds later. Calculate the distance between the two high walls. (3 marks)
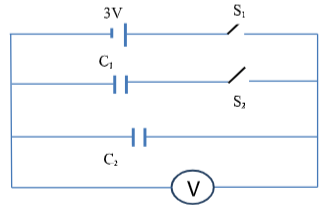
- The capacitors in the circuit below are identical and initially uncharged.
When switch S1 is closed and switch S2 left open, the voltmeter shows a reading. Explain the observation made (3marks)
Section B (55 Marks)
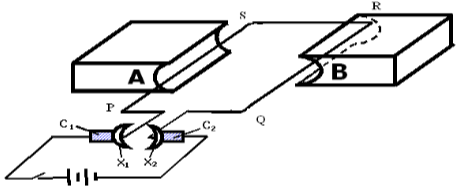
- The diagram below shows a coil PQRS lying between two unlike magnetic poles A and B of an electric motor.
- Identify the parts labeled; (2marks)
- X1X2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………..
- C1C2………………………………………………………………………………………………
- State the role of parts A and B. (1mark)
- Given that the coil rotates in the direction shown, state the polarity of; (1mark)
- A ……………………………………………………………………………………………..
- B ……………………………………………………………………………………………..
- State the observation made when the terminals of the batteries were reversed (1mark)
- State two ways in which the speed of rotation of the coil PQRS can be increased. (2marks)
- Identify the parts labeled; (2marks)
-
- Define the Principal focus of a convex mirror (1 mark)
- The Figure below (drawn to scale) shows an image; I formed by an object placed in front of a convex mirror.
- On the diagram draw appropriate rays and locate the position of the object. (3marks)
- From your drawing determine the magnification produced (2marks)
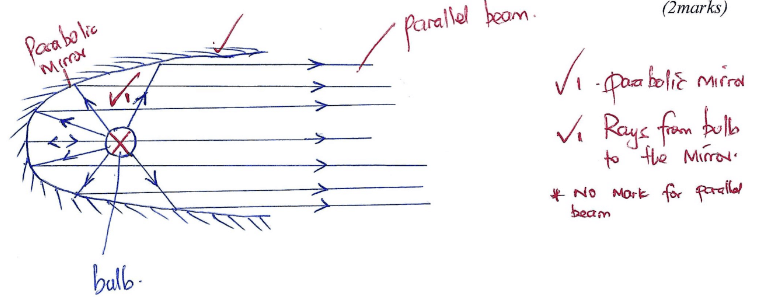
- Using a well labeled diagram, show how a parabolic mirror produces a parallel beam (2marks)
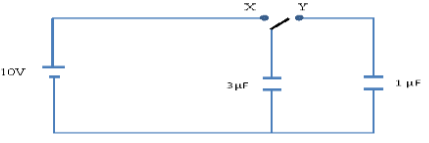
- In the circuit shown below a 3µF capacitor is charged from a 10V battery by connecting the switch to terminal X.
- The switch is then connected to terminal Y to charge the 1µF capacitor from the 3µF capacitor. Calculate:
- The energy stored initially in the 3µF capacitor (2 marks)
- The final potential difference across the parallel arrangement (2 marks)
- The total energy stored in the parallel arrangement. (2 marks)
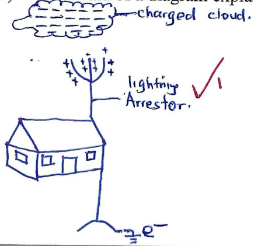
- With the aid of a diagram explain how a lightning arrestor works. (3 marks)
- The switch is then connected to terminal Y to charge the 1µF capacitor from the 3µF capacitor. Calculate:
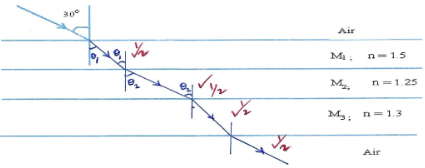
- The diagram below shows a ray of light from air through a series of media.
Sketch the path of the refracted ray from air through all the media till it emerges in air. (2 marks)- Determine the angle of incidence at the M2 – M3 interface (3 marks)
- Determine the refractive index of M3 with respect to M1 (2 marks)
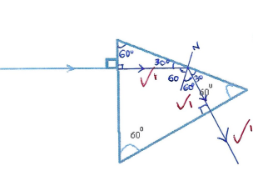
- The diagram below shows a ray of light meeting the surface of a glass prism of refractive index 3/2 at 90°. Complete the path of light through the prism till it emerges (show all your working) (3 marks)
-
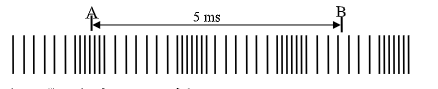
- The figure below shows a longitudinal wave that takes 5 ms to move from point A to B and at a speed of 320 m/s.
Calculate;- The frequency of the wave (2 marks)
- The wavelength of the wave (2 marks)
- Define the term interference as used in waves (1 mark)
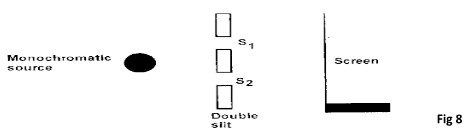
- In an experiment to observe interference patterns of light waves, a double slit is placed close to the source as shown below.
- State the function of the double slit, S1 and S2 (1mark)
- State and explain what is observed on the screen. (2 marks)
- State the observation on the screen when the slit separation S1–S2 is reduced. (1mark)
- Explain the mirage; the phenomenon which is experienced in cold polar regions during winter. (2 marks)
- The figure below shows a longitudinal wave that takes 5 ms to move from point A to B and at a speed of 320 m/s.
-
- Distinguish between electromotive force and potential difference (2 marks)
- Explain the function of a fuse as used in electrical appliances (2 marks)
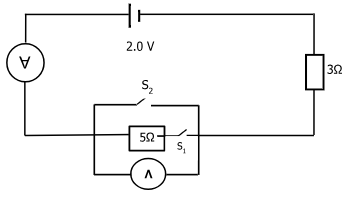
- The diagram below shows a circuit with some electrical appliances connected as shown.
- Switch S1 is closed while S2 is open. Determine the;
- The ammeter reading (2 marks)
- The voltmeter reading (2 marks)
- Determine the voltmeter reading when both S1 and S2 are closed. Give a reason for your answer. (2 marks)
- Switch S1 is closed while S2 is open. Determine the;
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Initially angle between ∠i and r = 50°
- After rotation to 62°, 62−50°= 12°
- Reflected ray rotated through 12°
- Mirror rotation = θ/2 = 12/2 = 6° (working must be shown)
-
-
- Only bulb B1 lights,
- Bulbs B2 and B3 are short circuted.
-
-
- Zn(s) → Zn2+(aq) + 2e
- 2H+(aq) + 2e → H2(g)
- Brown
-
-
-
- negative charge
- Initially negative charge is attracted and neutralised. Later on, electrons are atttracted from plate and leaf leaving them with positive charge hence leaf rises.
-
- Test for presence of charge
- Test for sign of change
- Test for amount of charge
- Test for insulation properties of materials
-
-
- Single stroking
- North pole
-
-
- Before magnetization, domains face different directions.
- During magnetization, domain start getting aligned to one direction
- Magnetic saturation, all domains fully aligned in one direction
- Magnetic field lines at the poles are closer/ nearer and more at the poles than at the sides.
-
- Speed of sound = 2d/t = 2 × 1600 = 320m/s
10
Distance 2x = speed × time
= 320 × 15
2x = 4800m ⇒ x = 2400m
Total distance = 1000 + 2400
= 3400m -
- When switch is closed, electrons move from negative terminal to one of the plates of capacitor.
- At the same rate, negative charge move from the opposite plate of capacitor to the positive terminal of the cell.
- At the end equal negative and positive charge accumulate on the plates and the final voltage is equal to that of cell,no more charge moves at this maximum p.d.
-
-
- M - Commutator
- N - Carbon brush
- Provide the radial magnetic field/ magnetic field/ flux.
-
- A - North
- B - South
- Coil rotates in the opposite direction/ anticlockwise/ reverse direction
-
- Increasing the stremgth of magentic field.
- Increasing the amount of current
- Increasing the number of turns.
-
-
- Point along the principal axis where paraxial rays parallel and close to the principal axis appear to diverge from after reflection.
-
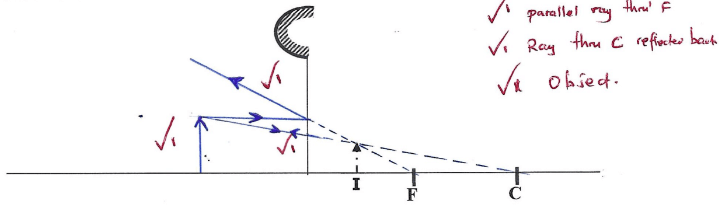
- v = 6mm ± 1
u = 2.5mm ± 1
6/25 = 0.24
m = v/u = 6.25
= 0.24
or
ho = 1.8mm ± 1
hi = 7mm
m = hi/ho = 7.0/1.3 = 0.538
-
-
-
- E = ½CV2
= ½ × (3×10−6) × 102 = 1.5 × 10−4J - Q = CV
= 10 × 3 × 10−6
= 3.0 × 10−5c
QT = Q1 + Q2
3.0 × 10−5 = C1V1 = C2V2
3.0 × 10−5 = V (3+1) × 10−6
V = 7,5v - E = ½C1V12 + ½,C2V22
= ½ × 7.52 (3+1) × 10−6
E = 1.125 × 10−4J
- E = ½CV2
-
- Opposite charge induced on spikes of arrestor.
- Negative charge on cloud attracted to spikes hence reducing charge build up on cloud. (excess electrons ar earthed)
- Incase of lightning discharge, arrestor provides conducting path to the earth hence minimal/ no destructions
-
-
-
-
-
n = 1/sin C
Sin C = 1/1.5 = 0.6667
Sin−1 0.6667 = 41.81°
60° > 41.81° hence total internal reflection
-
-
-
- 2½ wave = 5ms
∴ 1 wave = T = 5/2.5
T = 2ms
f = 1/T
= 1
2×10−3
= 500Hz
OR
= 2.5
5×10−3
= 500Hz - λ = v/f = 320/500 = 0.64m
- 2½ wave = 5ms
- Superposition/ merging up of waves moving in same medium.
-
- Provide coherent sources
- To cause difraction/ spreading of wave from the monochromatic source
-
- Alternating bright and dark bands/fringes
- Bright fringes/ spots - constructive interference
- Dark fringes/spots - destructive interference
- Fringes separation increases

- Colder air has high refractive index than warmer air.
- This causes total internal reflection in the optically dense nedium/ continuous refraction
- Therefore the inverted image appear to be above the observe as shown.
-
-
e.m.f P.d Voltage across the terminals of cell/ battery in an open circuit Voltage acrosss the cell/ battery in a mclosed circuit - Since its a short wire of low melting point, It melts and breaks when excess current flows through it. To protect/ safeguard electrical mappliances against damage from excess current.
- Total resistance = R1 + R2
= 3 + 5
RT = 8Ω
I = V/R
= 2/8 = 0.25A - V = IR
= 0.25 × 5
= 1.25V
- Total resistance = R1 + R2
- Voltmeter reading = 0
S1 short circuits the voltmeter/ voltmeter has very high resistance
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mokasa 1 Joint Pre Mocks Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students