- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all the questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C.
- Candidates should answer all the questions in English.
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
- Name four biotic factors that influence agriculture negatively. (2marks)
- State four activities that may be undertaken in organic farming. (2marks)
- Give four reasons for early preparation of a seedbed in crop production. (2marks)
- Give two reasons why crops do not do well in waterlogged soils. (1mark)
- Name four farming practices that may lead to soil erosion. (2marks)
- Give four causes of poor drainage on farmland. (2marks)
- State four advantages of a mixed grass legume pasture over a pure grass pasture. (2marks)
- Give a solution for each of the following properties of nitrogenous fertilizer when applying to crops.
- Easily leached to lower horizons. (12mark)
- Are highly volatile. (12mark)
- Are hygroscopic. (12mark)
- Give two ways in which records help farmers to obtain loans from money lending agencies. (1mark)
- State four benefits of land consolidation. (2marks)
- State four ways in which humus is beneficial to a growing crop. (2marks)
- State four disadvantages of chemical pest control. (2marks)
- Define the term ‘’integrated pest management’’ (12mark)
- State four factors considered when selecting planting material for forage crops. (2marks)
- State four disadvantages of broadcasting seeds during planting. (2marks)
- Name two sources of underground water. (1mark)
- State four factors that would determine the number of secondary cultivations to be carried out on a seedbed before planting. (2marks)
- State two characteristics of a good vegetable seedling. (1mark)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
- A member of the young farmers’ club was advised to apply a complete compound fertilizer 30-20-10 in a tomato plot measuring 10m by 5m
- Give the percentage of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) in the fertilizer. (2marks)
- Nitrogen (N) ………………………………………………………………………………..
- Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5)………………………………………………………………
- Calculate the amount of fertilizer the member would require for the plot. (3marks)
- Give the percentage of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) in the fertilizer. (2marks)
- The diagram below illustrates a field management practice in tomatoes. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the field practice. (1 mark)
- Name two materials used in the practice illustrated above. (2 marks)
- State three reasons for carrying out the practice above. (3 mars)
- Below is a photograph of a weed. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the weed above. (1mark)
- Why is the weed above difficult to control? (1mark)
- Give two ways in which the weed above can be controlled in a field of maize. (2marks)
- Classify the weed basing on its morphology. (1mark)
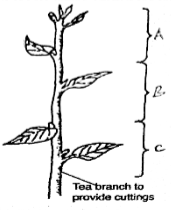
- The diagram below is of a tea cutting. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Which part of the branch is most appropriate for raising a new seedling. (1mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in (a) above. (1mark)
- Give a reason why farmers are advised to raise tea cuttings in polythene sleeves. (1 mark)
- State two factors that affect the rooting of the cutting above. (2 marks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
-
- Describe the production of tomatoes under the following sub-headings.
- Varieties (2 marks)
- Nursery establishment (4 marks)
- Transplanting (4 marks)
- Discuss the effects of wind in Agriculture. (6 marks)
- State four reasons for mulching. (4 marks)
- Describe the production of tomatoes under the following sub-headings.
-
- Describe four types of soil erosion. (9 marks)
- Outline the precautions taken when harvesting cotton. (4 marks)
- Describe seven factors considered when selecting bean seeds for planting. (7 marks)
-
- State and explain four environmental factors affecting the effectiveness of herbicides (8 marks)
- Describe five factors that determine the quality of farm yard manure. (6 marks)
- State six disadvantages of communal land tenure system. (6 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
- Name four biotic factors that influence agriculture negatively. (2marks)
- Pests
- Parasites
- Predators
- Pathogens
- State four activities that may be undertaken in organic farming. (2marks)
- Use of organic manure
- Timely planting
- Practicing crop rotation.
- Mulching
- Use of medicinal plant products to control diseases and parasites eg hot pepper solution.
- Livestock being reared by feeding them on natural feedstuffs without artificial additives.
- Physical/cultural pest, weed, parasite and disease control.
- Give four reasons for early preparation of a seedbed in crop production. (2marks)
- To kill weeds
- To incorporate manure and other organic matter into the soil.
- To destroy different stages of crop pests such as eggs larvae, pupae or adults by burying them, exposing them to the heat of the sun and predators and starving them.
- To aerate the soil.
- To encourage the penetration of roots in the soil.
- To make subsequent operations possible eg planting, fertilizer application, rolling and ridging.
- To encourage water infiltration into the soil.
- Give two reasons why crops do not do well in waterlogged soils. (1mark)
- There is poor soil aeration.
- Affects soil microbial activities.
- Name four farming practices that may lead to soil erosion. (2marks)
- Overstocking
- Deforestation
- Planting of annual crops on steep slopes
- Clean weeding
- Indiscriminate burning of vegetation before cultivation
- Ploughing up and down the slope
- Give four causes of poor drainage on farmland. (2marks)
- Too much rainfall on low lying areas.
- High amounts of clay particles in the soil.
- Presence of impermeable rock near the soil surface.
- Formation of hard pans in the soil.
- High water table.
- State four advantages of a mixed grass legume pasture over a pure grass pasture. (2marks)
- It is more palatable than pure grass.
- A farmer has security against total loss in case of pest and disease attack or bad weather.
- Yields are higher per unit area of land than in pure grass pasture.
- It is more nutritious/has a higher nutritive value than pure grass pasture.
- It makes maximum use of soil nutrients because of different nutrient requirement.
- It has better weed control effect.
- It reduces soil erosion because of good soil cover.
- It increases soil fertility because of nitrogen fixation.
- There is economy in use of fertilizers in mixed pastures.
- There is better growth in a mixture of late and early maturing species.
- Give a solution for each of the following properties of nitrogenous fertilizer when applying to crops.
- Easily leached to lower horizons. (12mark)
- They should be applied to an already established crop.
- Are highly volatile. (12mark)
- They should be applied to moist soils.
- Are hygroscopic. (12mark)
- They should be stored under dry conditions.
- Easily leached to lower horizons. (12mark)
- Give two ways in which records help farmers to obtain loans from money lending agencies. (1mark)
- They establish a farmer’s credit worthiness by indicating the cash flow of the existing enterprise and hence the financial ability of the farmer to service the loan.
- From the proposed budget, records justify the need for the loans.
- They establish whether the loan applied for is relevant to the intended purpose of farming.
- State four benefits of land consolidation. (2marks)
- Proper supervision of land
- Economic use of time and saving of transportation costs.
- Easy provision of agricultural advice by extension officers.
- Ensures sound farm planning and adoption of crop rotation programs.
- Facilitates soil conservation and land improvement.
- Promotes construction of permanent structures eg buildings and fences.
- Registered land gives the farmer legal ownership and the title deed which can be used to obtain loans.
- Weed, pest and disease control is enhanced.
- Facilitates mechanization especially because of large holdings.
- State four ways in which humus is beneficial to a growing crop. (2marks)
- It increases the water holding capacity of the soil. It also increases the infiltration rate due to its colloidal nature.
- It improves soil fertility by releasing a wide range of nutrients into the soil.
- It provides food and shelter for soil micro-organisms responsible for the decomposition of organic matter.
- It improves soil structure. Humus binds soil particles together thus improving soil structure.as a result of this drainage and aeration of soil improves.
- It buffers soil ph ie moderates soil ph by avoiding rapid chemical changes due to the addition of acidic fertilizers and liming materials.
- It reduces the toxicity of plant poisons that may have built up in the soil as a result of continuous use of pesticides and fungicides.
- Humus gives soil its dark colour which absorbs heat helping to moderate soil temperature.
- State four disadvantages of chemical pest control. (2marks)
- Expensive.
- Most are not environmental friendly since they are toxic to man and livestock
- They require care and skill when handling and applying them.
- Most are non-selective and therefore they kill useful insects such as pollinators and pest predators.
- Pests establish resistance to pesticides if they are used continuously against them. E.g. DDT.
- Define the term ‘’integrated pest management’’ (12mark)
- This is a combination of chemical physical, biological and pest control methods.
- State four factors considered when selecting planting material for forage crops. (2marks)
- Adaptable to the local ecological conditions.
- Fast growth
- High herbage yield/high leaf:stem ratio
- High germination percentage/viable
- High nutritive value
- Pure/true to type
- Certified seed
- Healthy/free from pests and diseases.
- State four disadvantages of broadcasting seeds during planting. (2marks)
- It uses more seed than row planting.
- Seeds are spread unevenly leading to crowding of plants in some places.
- Lack of uniformity in seed placement causes lack of uniformity in establishment.
- There is uneven germination due to uneven depth of seed placement.
- Mechanization is hard eg weeding.
- Name two sources of underground water. (1mark)
- Springs
- Wells
- Boreholes
- State four factors that would determine the number of secondary cultivations to be carried out on a seedbed before planting. (2marks)
- Size of planting materials.
- Slope of the land.
- The moisture content of the soil.
- Condition of the soil after primary cultivation.
- The type of weeds to be controlled
- Soil texture
- State two characteristics of a good vegetable seedling. (1mark)
- Healthy/free from diseases and pests.
- Free from physical deformities.
- High yielding.
- Correct stage of growth/height 10-15cm, 4-6 true leaves, 4-6 weeks old.
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
- A member of the young farmers’ club was advised to apply a complete compound fertilizer 30-20-10 in a tomato plot measuring 10m by 5m at the rate of 300kg per hectare.
- Give the percentage of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) in the fertilizer. (2marks)
- Nitrogen (N) - 30%
- Phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5)- 20%
- Calculate the amount of fertilizer the member would require for the plot. (3marks)
Area of land 10x5=50msq;
1ha = 10000msq
If 300kg = 10000msq;
? = 50msq
300x50
10000
=1.5kg;
- Give the percentage of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5) in the fertilizer. (2marks)
- The diagram below illustrates a field management practice in tomatoes. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the field practice. (1 mark)
- Staking.
- Name two materials used in the practice illustrated above. (2 marks)
- Stick/peg
- String
- State three reasons for carrying out the practice above. (3 marks)
- Promotes the production of clean fruits.
- Facilitates spraying and harvesting of the crop.
- Prevents infestation by soil borne pests.
- Controls incidences of disease outbreaks eg blight.
- Identify the field practice. (1 mark)
- Below is a photograph of a weed. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the weed above. (1mark)
- Couch grass (Digitaria scalarum)
- Why is the weed above difficult to control? (1mark)
- Has underground stems/rhizomes which are difficult to control.
- Give two ways in which the weed above can be controlled in a field of maize. (2marks)
- Use of herbicides.
- Good cultivation of seed bed.
- Classify the weed basing on its morphology. (1mark)
- Narrow leaved.
- Identify the weed above. (1mark)
- The diagram below is of a tea cutting. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Which part of the branch is most appropriate for raising a new seedling. (1mark)
- Part B
- Give a reason for your answer in (a) above. (1mark)
- The top part tends to rot when planted and the bottom part takes long to root.
- Give a reason why farmers are advised to raise tea cuttings in polythene sleeves. (1 mark)
- The rooting system is not disturbed during transplanting.
- Seedlings can be stored further if transplanting is delayed after the seedlings have been collected from the nursery.
- Sleeved seedlings grow very fast and take a shorter time in the nursery.
- State two factors that affect the rooting of the cutting above. (2 marks)
- Temperature
- Relative humidity
- Light intensity
- Oxygen supply
- Chemical treatment
- Leaf area.
- Which part of the branch is most appropriate for raising a new seedling. (1mark)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
-
- Describe the production of tomatoes under the following sub-headings.
- Varieties (2 marks)
- Fresh market eg Money maker, hundred fold, beef eater, hot set, Ailsa Craig, super Marmande, ponderosa and Marglobe.
- Processing varieties eg Primabel, Sn Merzano, Cal J, Seinz, Kenya beauty, Rutgers and 10x hybrid. (Accept any two varieties given)
- Nursery establishment (4 marks)
- The nursery should be sited on a gently sloping ground.
- It should be prepared to a fine tilth. Seed boxes may also be used as nursery beds.
- Drills are made across the bed 10-15cm apart using a finger or a stick.
- Seeds are dropped singly in the drills and covered lightly. More than 1cm soil cover will lower the germination %.
- Water, mulch and shade the nursery appropriately.
- Transplanting (4 marks)
- Seedlings are ready for transplanting when they are about 10cm high,4-6wks old or have 4-5 true leaves
- The nursery should be watered before lifting the seedlings.
- Healthy and vigorously growing seedlings are lifted using a garden trowel.
- Apply phosphatic fertilizers/manures in the planting holes and mix with the soil.
- One seedling is planted per hole and soil firmed around the seedling.
- Plant at the same depth as was in the nursery.
- Transplanting should be done on a cool day or late in the evening.
- Seedlings are mulched and watered regularly.
- Provide temporary shade
- Transplant at the onset of rains.
- Varieties (2 marks)
- Discuss the effects of wind in Agriculture. (6 marks)
- Increases the rate of evaporation of moisture from the soil.
- Causes lodging in cereals and damage to crops.
- Blowing away and bringing rain bearing clouds.
- Acts as an agent of seed dispersal.
- High winds leads to higher rates of evapotranspiration resulting into water stress in plants.
- Increases the spread of pests and diseases.
- Wind facilitates pollination in some plants.
- Areas with high humidity tend to be hotter but when wind blows away atmospheric water, a cooling effect occurs.
- Destroy farm structures.
- State four reasons for mulching. (4 marks)
- Prevents water evaporation thus maintaining moisture in the soil for crop use.
- Acts as an insulator thus modifies or regulates the soil temperature.
- Controls soil erosion by reducing the speed of running water intercepting the rain drops and increasing the rate of infiltration.
- Controls weeds by suppressing their growth.
- Organic materials improve soil fertility by releasing nutrients after decomposition.
- Decomposition of organic matter results into humus that improves soil structure and water holding capacity.
- Describe the production of tomatoes under the following sub-headings.
-
- Describe four types of soil erosion. (9 marks)
- Splash/rain drop erosion-Continuous falling of raindrops on loose soil surface detaches and disperses soil creating a hole which will enlarge to form a gulley.
- Sheet erosion-This the uniform removal of soil in thin layers caused by surface flow of water and wind which detaches and transports sheets of top soil over a wide area.
- Rill erosion-This is the removal of soil by water from small but well defined channels (rills) or streamlets where there is a concentration of flowing water down the slope.
- Gully erosion-This is an advanced stage of rill erosion.
- Outline the precautions taken when harvesting cotton. (4 marks)
- Picking should be done immediately the bolls open/split to prevent staining by dust.
- Picking should be done when the lint is dry to prevent fibres from sticking together.
- Hands should be clean to avoid staining of the lint.
- Do not mix cotton with foreign matter eg leaves and small twigs.
- Use separate containers for separate cotton grades to ensure quality.
- Avoid using sisal bags for collecting the bolls because their fibres may mix with the seed cotton thus creating problems during ginning.
- Describe seven factors considered when selecting bean seeds for planting. (7 marks)
- Select varieties adapted to the ecological conditions of the area.
- Select dry mature seeds.
- Select sound seeds that are free from physical damage and wrinkles/ Size and shape of the material.
- Select pure and health seeds.
- Disease resistance capability of the seeds should be good.
- Qualities of the plant such as its yield capacity should be high.
- Germination percentage of the seeds should be high.
- Use certified seeds/ obtain seeds from a reputable source.
- Describe four types of soil erosion. (9 marks)
-
- State and explain four environmental factors affecting the effectiveness of herbicides (8 marks)
- Wind-May blow away spray wash to unintended plants while decreasing chemical concentration on the intended plants.
- Rain-If rain falls immediately after herbicide application the chemical is diluted to non-toxic levels. Where only shallow rooted plants were intended to be killed, rain water may cause the herbicides to leach and reach roots of deep rooted plants thus killing them.
- Soil-Some soils are capable of absorbing and retaining more herbicides than others.
- Light-Increase in light intensity increases the rate of light absorption and photosynthesis by plants hence increasing absorption and translocation of herbicides.
- Some herbicides are decomposed by high light intensity hence become less effective.
- Temperature-Increases translocation hence absorption of more herbicides and therefore death of the plant.
- Describe five factors that determine the quality of farm yard manure. (5 marks)
- The type of animals’ used-Non ruminants eg pigs and poultry absorb less nutrients from their feed and therefore give dung which has a higher level of nutrients.
- Type of food eaten-Feedstuffs that are highly nutritious result in manure with a higher level of nutrients.
- Type of litter used-Leguminous materials used decompose faster and provide more nutrients.
- Method of storage-Preferably in a place with a leak free roof and a concrete floor to prevent loss of nutrients through leaching and vaporization.
- Age of FYM-Well rotted manure is rich in nutrients and it is easy to handle and mix with the soil.
- State seven disadvantages of communal land tenure system. (7 marks)
- No individual has the responsibility of taking care of land or developing it.
- Farmers have no incentive to manage and develop the land well nor do they risk investing in permanent development projects because the land can be taken away from them anytime.
- Overstocking and overgrazing are common due to uncontrolled number of livestock leading to low yields.
- Poor breeding programs due to random mating and uncontrolled breeding.
- Pest and disease control is very difficult due to mixing of animals.
- Leads to soil erosion and land denudation.
- It is virtually impossible for a farmer to get loans from money lending agencies.
- State and explain four environmental factors affecting the effectiveness of herbicides (8 marks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mokasa 1 Joint Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students