- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer all the questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C.
- Candidates should answer all the questions in English.
SECTION A (30 Marks)
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
- Name a breed of livestock described below.
- A beef cattle breed, deep red in colour, the face and part of the legs below knees and hocks are white. (11/2mk)
- A pig breed which is white in colour, with a straight snout and long ears dropping over the face. (11/2mk)
- Name two cattle diseases caused by viruses. (1mk)
- State four pre-disposing causes of calf pneumonia diseases. (2mks)
- Give three effects of external parasites that are harmful to livestock. (11/2mk)
- State two reasons for housing calves singly in cattle management. (1mk)
-
- Name two methods of extracting honey from honey combs. (1mk)
- Outline four factors that affect the quality of honey. (2mks)
- Give four reasons why farm tools and equipment should be maintained (2mks)
-
- What is caponisation as used in poultry (1/2mk)
- Give a reason for using water paints to paint the walls of calf pen. (1/2mk)
- State four factors considered when siting a fish pond. (2mks)
- Give four functions of vitamins in livestock nutrition. (2mks)
- Name four various parts of pig pens. (2mks)
- State two factors that affect respiratory rate in livestock. (1mk)
- State four signs of heat in rabbits. (2mks)
- Give three reasons for castrating a breeding boar. (11/2mks)
- State four qualities of eggs suitable for incubation. (2mks)
- Outline four disadvantages of inbreeding in livestock production. (2mks)
- State four conditions that would encourage egg eating in poultry. (2mks)
- State two conditions that may inhibit milk let-down during milking. (1mk)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
- Below is diagram of a cow suffering from a deficiency disease? Study it and answer the question that follows.
- Identify the diseases of the above animal is suffering from. (1mk)
- What stage of the state of the body condition encourages the disease above? (1mk)
- List two symptoms of the above disease. (1mk)
- Give one control measure of the identified disease. (2mks)
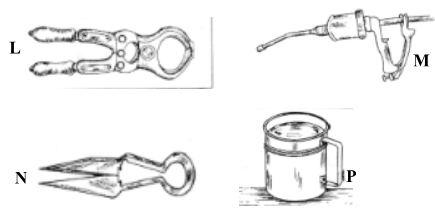
- Study the diagram of the tools labelled L,M,N and P and answer the following questions.
Name the tools labelled L,M,N and P and give their uses. (4mk)
-
- Name two major physical differences between Bactrian and dromedary breed of camel. (2mks)
- Name four dairy breeds of dairy goats. (2mks)
- Name one characteristic of goats that make them perform better in the dry parts of the Country. (2mks)
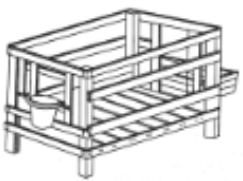
- Study the diagram of a calf pen illustrated below.
- Name the type of floor shown in the diagram. (1mk)
- What is the purpose of the floor begin raised. (1mk)
- Name two factors considered when siting a calf pen. (1mk)
- Give one function of good ventilation in the animal house. (1mk)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section.
-
- Describe new cattle diseases under the following sub-headings
- Causal organism. (1mk)
- Symptoms of attack. (6mks)
- Control measures (3mks)
- State five signs of parturition in a cow. (5mks)
- Describe the uses of five equipment required for hand milking. (5mks)
- Describe new cattle diseases under the following sub-headings
-
- Explain seven ways in which ticks can be controlled on a livestock farm. (7mks)
- State four disadvantages of using live fences on a farm. (4mrks)
- Describe nine advantages of the battery cage system of rearing layers. (9mks)
-
- Give five reasons for keeping livestock health. (5mks)
- Describe the process of digestion in the small intestines of a non-ruminant animals. (5mks)
- Describe six diseases control routine management practices in calf rearing. (6mks)
- Describe the procedure of stocking a bee hive. (4mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 Marks)
- Name a breed of livestock described below.
- A beef cattle breed, deep red in colour, the face and part of the legs below knees and hocks are white. (1½mk)
- Hereford
- A pig breed which is white in colour, with a straight snout and long ears dropping over the face. (1½mk)
- Landrace
- A beef cattle breed, deep red in colour, the face and part of the legs below knees and hocks are white. (1½mk)
- Name two cattle diseases caused by viruses. (1mk)
- Foot and mouth diseases
- Rabies
- Rinderpest
- State four pre-disposing causes of calf pneumonia diseases. (2mks)
- Overcrowding of calves in the pen
- Dampness in the pen
- Poor ventilation
- Age / Younger calves are more prone to pneumonia than older calves
- Effects of diarrhoea and other illness.
- Chilliness/ Coldness in the pen
- Give three effects of external parasites that are harmful to livestock. (1½mk)
- Introduce toxins that are harmful to the animal
- Cause anaemia / transit diseases
- Cause wounds that allow secondary infection.
- Cause irritation which leads to scratching / destroy of wool.
- State two reasons for housing calves singly in cattle management. (1mk)
- To control licking and sucking each other’s this leads to hair balls.
- Control diseases
- Controls spread of parasites
-
- Name two methods of extracting honey from honey combs. (1mk)
- Squeeze method
- Heat method
- Centrifugal method
- Outline four factors that affect the quality of honey. (2mks)
- Method of processing honey
- Method of harvesting
- Maturity stage of honey at the time of harvesting
- Type of plants from which the nectar was obtained
- Name two methods of extracting honey from honey combs. (1mk)
- Give four reasons why farm tools and equipment should be maintained (2mks)
- To avoid injury to the user
- To reduce repair / replacement cost
- To increase their durability / life span
- To make them more efficient.
-
- What is caponisation as used in poultry (½mk)
- is a process used in poultry farming, specifically with chickens, to create capons.
- Give a reason for using water paints to paint the walls of calf pen. (½mk)
- To avoid the calf setting poisoned when it leaks the paints / wall
- Easy to clean / wash
- What is caponisation as used in poultry (½mk)
- State four factors considered when siting a fish pond. (2mks)
- Reliable water source
- Slope topography of the land
- Type of soil, clay soil is preferred
- Security of the area, should be secure from predators and thieves
- Should be accessible
- Market / demand for the fish.
- Give four functions of vitamins in livestock nutrition. (2mks)
- Protection against infection
- Promote growth
- Bone formation
- Muscular activity
- Organic catalysts
- Name four various parts of pig pens. (2mks)
- Farrowing pens
- Gilts pen
- In – pen
- Weaners / fattening pen
- Boar pen`s
- Running yard
- Water troughs / Drinking nipples
- State two factors that affect respiratory rate in livestock. (1mk)
- The body size of the animal
- The amount of exercise done by the animal
- The degree of excitement
- The ambient / environmental temperature
- State four signs of heat in rabbits. (2mks)
- Restlessness
- Frequent urination
- Swollen vulva
- The doe throws itself on its sides
- She rubs herself against the wall or any other solid object.
- The doe tries to contact other rabbits in the next hutch by peeping through the cage walls.
- Give three reasons for castrating a breeding boar. (11/2mks)
- To make it docile
- To prevent in breeding
- To continue breeding
- To control in breeding diseases
- To fasten it
- Due to old age
- State four qualities of eggs suitable for incubation. (2mks)
- Should be fertilized
- Should be medium sized
- Should be oval in shape
- Should not be cracked
- Should be clean
- Should be free from abnormalities / blood spots / meat spots/ double york
- Should be 5 -10 days old
- Should have smooth shell.
- Outline four disadvantages of inbreeding in livestock production. (2mks)
- In breeding can cause loss of hybrid
- May lead to decline in fertility leading to species extinction
- Bring about reduction in performance.
- Leads to high rate of pre – natal mortality
- State four conditions that would encourage egg eating in poultry. (2mks)
- Calcium deficiency in the birds body
- Bright light in the layering nests
- Birds laying on the floor
- Presence of broken soft shelled eggs
- Prolonged stay of eggs in the layering boxes
- Idleness of birds
- Inadequate feeding.
- State two conditions that may inhibit milk let-down during milking. (1mk)
- Changing of milk routine
- Strange surrounding / strangers / sudden noise / storm
- Poor milking tehnigues / pain
- Sickness.
SECTION B (20 marks)
-
- Milk fever.
- High milk production.
-
- Muscular twitching causing the animal to tremble.
- Animal lies on the sternum with neck twisted on one side.
-
- Feed the diet rich in calcium during pregnancy.
- Give intramuscular injection of calcium boroglucolate 2-3 days after calving.
-
Identity Use L Burdizo Carrying out bloodless castration M Drenching gun Shooting liquid medicine to the mouth of livestock. N Shears Shearing sheep P Strip cup Testing mastitis in lactating cows. -
-
- Bactrian has two humps while dromedary has one hump.
- Bactrian has more fur while dromedary has less fur.
-
- Saanen
- Toggenberg.
- Anglo Nubian
- German alpine.
-
- Requires little feed.
- They are both grazers and browsers.
- They withstand high temperatures.
-
-
- Slatted floor.
- To keep the floor free of dampness because urine and dung drains off easly.
-
- Type of soil.
- Topography of an area.
- Nearness to the milking shed
- Direction of the prevailing wind.
-
- Allows free circulation of air.
- Prevents dampness.
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
-
- Describe new castle disease under the following sub headings.
- Causal organism. (1mk)
- Virus
- Paramyxo virus
- Symptoms of attack. (6mks)
- Sudden death in acute forms
- Breathing difficulties.
- Beaks remain wide open
- Watery greenish diarrhoea.
- Nasal discharges
- Coughing and sneezing
- Staggering due to infection of the nervous system.
- Drooping wings and bending of neck.
- Eggs laid have soft shells.
- Control measures. (3mks)
- Vaccination
- Mass slaughter.
- Practicing farm hygiene
- Quarantine.
- Causal organism. (1mk)
- State five signs of parturition in a cow. (5mks)
- Restlessness
- Enlarged or swollen vulva
- Clear mucus discharge from the vulva.
- Slackening of the pelvic muscles or the relaxing of the hip muscles.
- Full and distended udder.
- Thick milky fluid from the teats.
- A water bag appears and bursts, just before calving.
- Describe the uses of five equipment required for hand milking. (5mks)
- Udder clothes/towels-Used to wash and dry the udder.
- Filtering pads-Used for straining milk.
- Milking jelly-Smeared on the teats after milking to prevent from cracking.
- Warm water-Necessary for washing the udder before milking to remove dirt and stimulate milk let- down.
- Milking pails/buckets-Used to hold milk during milking.
- Milking stool-Used to sit on during milking.
- Strip cup-Necessary for detecting mastitis.
- Milk cans/churns-Used to hold milk during storage and transportation.
- Chain/rope-Used to restrain the animal.
- Concentrates/feeds-Used to stimulate milk let-down.
- Weighing scale-Used to determine the amount of milk.
- Milking machine-Milking animals.
- Describe new castle disease under the following sub headings.
-
- Explain six non-chemical methods of controlling ticks in cattle. (6mks)
- Using natural enemies eg ants, birds eg egrets which predate on the ticks.
- Self-licking by the animal may also dislodge the ticks from the body.
- Burning the infested pastures destroys a large number of eggs, larvae, nymphs and adults.
- Interfering with or altering the tick’s environment in the following ways:
- Ploughing pasture land to expose the eggs to suns heat for desiccation or by burying them deeply.
- Top dressing pastures using lime or dressing using an acaricide.
- Double fencing off the pasture land and farm combined with regular use of acaricides.
- Starving the ticks to death by keeping the animals away from infested pastures through rotational grazing.
- Hand picking the ticks from livestock and killing them (deticking)
- State the disadvantages of using live fences on a farm. (6mks)
- They take many years to grow and make an effective fence.
- They cannot be used for paddocking because they occupy a wide space.
- The edges can be hiding places for rodents and thieves.
- Thorny species can cause injury to human and livestock.
- They require regular trimming and infilling of gaps which is both laborious and expensive.
- Their growth may be irregular thus allowing gaps for thieves and animals to pass through.
- Describe eight advantages of the battery cage system of rearing layers. (8mks)
- Higher egg production due to less energy wastage by birds.
- Accurate egg production records can be kept.
- Cannibalism and egg eating are minimized
- Eggs are clean because hens do not step on them.
- The system can easily be mechanized.
- Birds do not contaminate food and water.
- Handling is easy as hens are restricted to a small place.
- Broodiness is discouraged as birds do not reach the eggs.
- A large number of birds’ can be kept in a small space hence higher stocking rate.
- Sick birds can easily be detected and isolated for treatment.
- Wire floors prevent re-infestation of parasitic worms and coccidia.
- There is no bullying during feeding.
- There is low labour requirement.
- Explain six non-chemical methods of controlling ticks in cattle. (6mks)
-
- State five reasons for keeping livestock healthy. (5mks)
- Healthy animals grow well and fast enough to reach maturity quickly.
- Healthy animals live longer and therefore have longer productive lives than sickly animals.
- Healthy animals give maximum production or performance ie they maintain high productivity.
- Healthy animals produce good quality products and consequently command a high market value.
- Healthy animals are safe to other animals and human beings as there is little risk of transmitting zoonotic diseases eg brucellosis.
- It is economical to keep healthy animals since veterinary expenses on them are low.This leads to profit maximization.
- Describe the process of digestion in the small intestines of a non- ruminant animals.(5mks)
- In the duodenum, food is mixed with bile and pancreatic juice(pancreatic amylase, lipase and trypsin)
- Bile emulsifies fat to increase the surface area for enzyme action/ it has salt that neutralizes acids.
In the duodenum: - Pancreatic amylase-Converts starch to maltose
- Lipase-Converts fats to fatty acids and glycerol.
- Trypsin-Converts proteins to peptones and peptides
In the rest of the small intestines: - Erepsin (peptidase)-Converts peptones and peptides to amino acids.
- Maltase-Converts maltose to glucose.
- Sucrase (invertase)-Converts sucrose to glucose
- Lactase-Converts lactose to glucose.
- Digested food materials are absorbed in the ileum.
- Undigested and indigestible food materials then move to the large intestines for further digestion.
- Describe the pest and disease control routine management practices in calf rearing. (6mks)
- Vaccination-Stimulates the production of antibodies against diseases.
- Deworming-This is the control of internal parasites in animals especially sheep eg roundworms, tapeworms, liverflukes etc using antihelminthics.
- Hoof trimming-This is the practice of cutting back the overgrown hooves in animals especially sheep to control foot rot disease.
- Docking/tailing in sheep-This is the practice of cutting short the sheep’s tail or removal of part of it to prevent blowfly infestation.
- Dipping and spraying -These are routine practices done to control external parasites eg ticks, lice, mites and fleas which suck blood and transmit diseases. Hand dress hidden areas.
- Dusting-This is either rubbed into the animals’ skin or applied to the house where the animal is usually confined to control parasites.
- Describe the procedure of harvesting fish. (4mks)
- The inflow of water from the river is stopped by closing the channel.
- The normal cropping is done to remove all the large fish by use of a seine net.
- The outlet is then opened to allow the water to flow out.
- A scoop net is used to catch the fingerlings and kept in a holding pond.
- Water is completely drained for the pond to dry up.
- State five reasons for keeping livestock healthy. (5mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mokasa 1 Joint Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students