INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Answer ALL the questions in section A by filling in the spaces provided.
- In section B, answer question 6 (compulsory question) and any other one question from the remaining two questions. (i.e. 7 or 8)
- Candidates may be penalized for false information and even wrong spellings of technical terms.
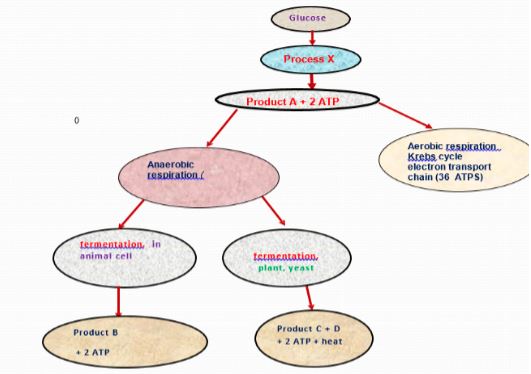
- The flow chart below shows a process in a plant and animal cell.
- Why is this process necessary in living organisms (3 marks)
-
- Name the process labelled X (2 marks)
- Name the part of the cell where process X occurs (1 marks)
- Name products A, B (2marks)
-
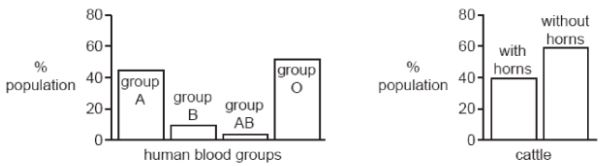
- The bar charts show the percentages of a human population with each type of blood group and the percentages of a cattle population with and without horns.
Which type of variation is shown in each population? (1mark)
Human:
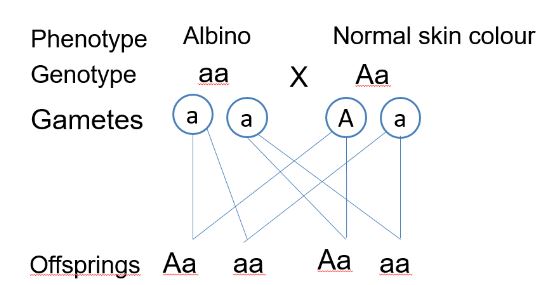
Cattle: - Albinism (lack of skin pigmentation) in humans is caused by two recessive alleles. A phenotypically normal (non-albino) couple have three children; the first two are non-albino, the third is an albino. In your answer, use “A” for the dominant allele and “a” for the recessive allele.
- What are the genotypes of the parents? (1mark)
- Is there a possibility that their next child will be an albino? Explain your answer (2 marks)
- The albino child eventually marries a non-albino whose father was an albino. What is the probability that their first child will be an albino? Show all working. (4marks)
- The bar charts show the percentages of a human population with each type of blood group and the percentages of a cattle population with and without horns.
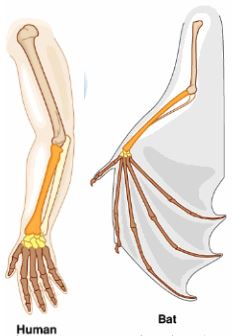
- The diagram below shows structures of the bat wing and human arm.
These structures are thought to have same ancestral origin.- State one structural similarity and one adaptational difference between the two.
- Structural similarity. (1 mark)
- Adaptation difference. (2 marks)
- Give two other examples of structures in nature that show the type of evolution as in (a) above. (2 marks)
- Distinguish between the terms ‘chemical evolution’ and ‘organic evolution’. (2 marks)
- What is the study of fossils called? (1 mark
- State one structural similarity and one adaptational difference between the two.
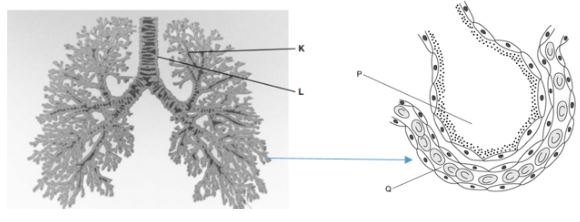
- The diagram below shows structures of gaseous exchange system in man
- Name the structure labeled K (1 mark)
- Structure labelled L is lined with two cells name these two cells (2 marks)
- Explain the function of these two cells identified in 4 (b) above in the structure labelled L (2 marks)
- Explain how oxygen moves fro P to Q ( 2 marks)
- Tobacco smoke affects gaseous exchange system name the component of the tobacco that affects this gaseous exchange system (1mark)
-
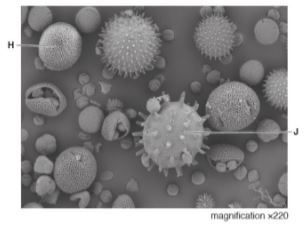
- The diagram below shows a scanning electron micrograph of some pollen grains from insect pollinated flowers and wind pollinated flowers
With reasons identify the pollen grains that are from- Insect pollinated flower (1mark)
Reasons (2marks) - Wind pollinated flower (1 mark)
Reason (1mark)
- Insect pollinated flower (1mark)
- Write the formula that would be used to calculate the actual diameter of pollen grain H (1mark)
- After pollination pollen grains germinate into pollen tubes. State two functions of pollen tube (2maks)
- The diagram below shows a scanning electron micrograph of some pollen grains from insect pollinated flowers and wind pollinated flowers
Section B
Answer two questions in this section questions 6 is compulsory and chose either question 7 or 8
- The table below shows the fresh weight and dry weight of maize plants at different stages of growth.
Time in weeks 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Fresh weight (g) 20 120 300 700 1000 1220 1500 1400 1100 Dry weight (g) 20 60 200 500 680 800 880 1000 100 - On the same axes, plot graphs of fresh and dry weights against time. (8mks)
- Account for the shape of the curve of fresh weight between:
- 2—10 weeks. (2mks)
- 12—16 weeks. (2mks)
- Suggest why dry weight remains constant after week 14. (2mks)
- Describe how the dry weight of the maize could have been determined at various times. (3mks)
- State two advantages and one disadvantage of fresh weight as a measure of growth. (3mks)
- Describe how the leaves of mesophyte are suited to their function (20marks)
- Describe the nitrogen Cycle (20 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
- The flow chart below shows a process in a plant and animal cell
- Why is this process necessary in living organisms (3 marks)
- Respiration leads to production of energy which is essential for the following body activities
- Muscular contraction to bring about movement
- Conduction of nerve impulses
- Secretion of enzymes, hormones, mucus etc.
- Growth and repair of worn out tissues
- Functioning of the body organs e.g. Kidneys, heart, brain
-
- Name the process labelled X (2 marks)
- Glycolysis
- Name the part of the cell where process X occurs (1 marks)
- Cytoplasm
- Name the process labelled X (2 marks)
- Name products A, B (2marks)
- A - Pyruvic acid
- B - Lactic acid
- Why is this process necessary in living organisms (3 marks)
-
- The bar charts show the percentages of a human population with each type of blood group and the percentages of a cattle population with and without horns.
Which type of variation is shown in each population? (1mark)
Human: Discontinuous variation
Cattle: Discontinuous variation ( both to be correct to score 1 Mark) - Albinism (lack of skin pigmentation) in humans is caused by two recessive alleles. A phenotypically normal (non-albino) couple have three children; the first two are non-albino, the third is an albino. In your answer, use “A” for the dominant allele and “a” for the recessive allele.
- What are the genotypes of the parents? (1mark)
- Aa
- Is there a possibility that their next child will be an albino? Explain your answer (2 marks)
- Yes; the chance of them getting an albino child is 0.25 25%
- The albino child eventually marries a non-albino whose father was an albino. What is the probability that their first child will be an albino? Show all working. (4marks)
The chance of getting an alnino child is a half / 50%/0.5
- What are the genotypes of the parents? (1mark)
- The bar charts show the percentages of a human population with each type of blood group and the percentages of a cattle population with and without horns.
-
These structures are thought to have same ancestral origin.- State one structural similarity and one adaptational difference between the two.
- Structural similarity. (1 mark)
- Both are pentadactyl limb / the end in 5 digits
- Adaptation difference. (2 marks)
- One is adapted for gasping things and the other one is adapted for flying
- Structural similarity. (1 mark)
- Give two other examples of structures in nature that show the type of evolution as in (a) above. (2 marks)
- Beaks of birds
- Feet of birds
- Distinguish between the terms ‘chemical evolution’ and ‘organic evolution’. (2 marks)
- Chemical evolution is view of origin of life that supposes that life began through catalytic effect of lightening or other catalysit that brought elements togeteher to form simple molecules that formed compounds and latter complex self replicating molecules; organic evolution a process where present life forms gradually arose from simple life forms over a long period of time.
- What is the study of fossils called? (1 mark
- Paleontology
- State one structural similarity and one adaptational difference between the two.
- The diagram below shows structures of gaseous exchange system in man
- Name the structure labeled K (1 mark)
- Bronchiole
- Structure labelled L is lined with two cells name these two cells (2 marks)
- Goblet cells
- Ciliated cells
- Explain the function of these two cells identified in 4 (b) above in the structure labelled L (2 marks)
- Goblet cells secretes mucus that trap dust and other solid particles in the inhaled air;
- Ciliated cells waft the trapped particles and dust into the nasal cavity
- Explain how oxygen moves fro P to Q ( 2 marks)
- There is more oxygen in structure labelled P than in Q it moves by diffissuin into Q
- Tobacco smoke affects gaseous exchange system name the component of the tobacco that affects this gaseous exchange system (1mark)
- nicotine , tar
- Name the structure labeled K (1 mark)
-
- The diagram below shows a scanning electron micrograph of some pollen grains from insect pollinated flowers and wind pollinated flowers
With reasons identify the pollen grains that are from- Insect pollinated flower (1mark)
J
Reasons (2marks)- Large with pricky hairs to stick on the body of the insect
- Wind pollinated flower (1 mark)
H
Reason (1mark)- Small and smooth to be easily carried by wind
- Insect pollinated flower (1mark)
- Write the formula that would be used to calculate the actual diameter of pollen grain H (1mark)
Drawing length of H
Actual length of H - After pollination pollen grains germinate into pollen tubes. State two functions of pollen tube (2maks)
- Offer passage through which male nuclei pass through to reach the embryo sac to enhance fertilization
- Secretes enzymes that digest tissues of the style ovary
- The diagram below shows a scanning electron micrograph of some pollen grains from insect pollinated flowers and wind pollinated flowers
Section B
Answer two questions in this section questions 6 is compulsory and chose either question 7 or 8
- The table below shows the fresh weight and dry weight of maize plants at different stages of growth.
Time in weeks 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Fresh weight (g) 20 120 300 700 1000 1220 1500 1400 1100 Dry weight (g) 20 60 200 500 680 800 880 1000 100 - On the same axes, plot graphs of fresh and dry weights against time. (8mks)
- Account for the shape of the curve of fresh weight between:
- 2—10 weeks. (2mks)
- Rapid increase in fresh weight/ very rapid growth plants absorb water and nutrients from the soil and use them for growth
- 12—16 weeks. (2mks)
- Fresh weight decreases due to loss of water drying up of the plant since the plants have matured
- 2—10 weeks. (2mks)
- Suggest why dry weight remains constant after week 14. (2mks)
- The plant has matured and cells have died hence there is no further growth
- Describe how the dry weight of the maize could have been determined at various times. (3mks)
- By uprooting the plants removing all the soil dry them in an oven at 110 degrees Celsius remove the plants in oven at intervals and reweigh them till a constant weight is obtained
- State two advantages and one disadvantage of fresh weight as a measure of growth. (3mks)
Advantage
The plant are not killed thus their growth can be monitored
Disadvantage
Fresh weight is influenced by water content hence it does not give actual biomass
- Describe how the leaves of mesophyte are suited to their function (20marks)
- The main functions of the leaves is gaseous exchange; photosynthesis and transpiration
- Has broad and flat lamina to increase surface area to trap maximum light for photosynthesis and provide a large surface area for gaseous exchange
- Have a thin lamina to reduce distance for diffusing gases and also for maximum penetration of light to reach photosynthetic tissues
- Cuticle and epidermis are transparent to allow light pass through
- The epidermis is thin to reduce the diffusion distance for the gases and easier penetration of light to photosynthetic tissues
- Have palisade cells with numerous chloroplast bellow the upper epidermis for maximum trapping of light
- Have veins which contain vascular bundles which transport water and mineral salts to the photosynthetic cells and translocate manufactured food from photosynthetic tissues
- Have stomata which allow diffusion of gases in and out the leaf
- Have guard cells which control the opening and closing of the stomata hence regulating water loss from the leaf
- Spongy mesophyll cells are irregularly arranged creating large air spaces for circulation of gasses within the leaf
- Describe the nitrogen Cycle (20 marks)
This is the cycling of nitrogen and its compounds in nature; it involves the following processes- Nitrogen fixation - atmospheric nitrogen converted into nitrates/ ammonia for plant use/absorption through biological and non-biological nitrogen fixation.
- Biological - Nitrogen fixation by symbiotic bacteria e.g. Rhizobium in the root nodules of the legumes (which convert nitrogen gas into ammonia which are then converted into ammonium compounds).
- Biological - Nitrogen fixation by non- symbiotic bacteria and free living micro- organisms found in the soil e.g. Azotobacter sp, Clostridium sp, and some algae e.g. Nostoc, blue green algae, chlorella,
- Anabaena (which fix nitrogen into ammonia which is then converted into nitrates).
- Non- biological/ Lightning - During thunderstorm the lightning energy combines atmospheric nitrogen with oxygen to form Nitrogen (IV) oxide. Nitrogen (IV) oxide later dissolves in rain water to form weak nitric acid and nitrous acid. The nitric acid combines with metal ions in the soil to form nitrates.
- Absorption by plants - plants absorb nitrate ions or ammonium ions directly from the soil and them to make amino acids/plant proteins through the process of photosynthesis (hence nitrogen is incorporated into the plant protein).
- Feeding - by animals on plant proteins and assimilate them to form animal proteins.
- Ammonification/petrification/d eath and decay- When animal and plants die they and their wastes and droppings are acted upon by saprophytic bacteria and fungi to form ammonium compounds.
- Nitrification - Ammonium compounds are converted into nitrites by nitrifying bacteria e.g. Nitrosomonas and Nitrococcus . Nitrites are then converted into nitrates by nitrifying bacteria e.g. Nitrobacter. Nitrification enriches the soil with nutrients.
- Denitrification - Nitrates in the soil are converted into nitrites, ammonia or free nitrogen gas by denitrifying bacteria e.g. Pseudomonas denitrificans and Thiobacillus denitrificans.
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Lugari Constituency Joint Mocks Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students