- This paper consists of two sections, A and B.
- Answer all questions in section A.
- Answer question 6 and any other two questions in section B.
- All answers must be written in English
-
- Why is Geography a unique subject? (2 marks)
- Give three branches of human Geography (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between a forest and forestry. (2 marks)
- State three factors that have hindered exploitation of equatorial rainforest in Africa. (3 marks)
-
- Define mining (2 marks)
- Name three exotic breed of dairy cattle reared in Kenya (3 marks)
-
- Name two major imports from Europe to Kenya. (2 marks)
- State three problems facing developing countries in international trade. (3 marks)
-
- State two factors which have led to the growth of Mombasa as a major sea port (2 mks)
- Name a town in Kenya where each of the following industries is located. (3 marks)
- Oil refinery -
- Paper manufacturing -
- Motor vehicle assembly -
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
-
- The table below shows the area under the horticultural crops in Kenya between 2000 and 2002. Use it to answer the questions below:
crop 2000 2001 2002 cabbages 320 340 380 tomatoes 360 360 330 onions 340 320 360 oranges 380 380 400 - Name the crop that has the highest production within the period(1mk)
- Explain THREE reasons why horticultural farming is increasingly becoming important to Kenyan farmers. (6mks)
- Using 1cm to represent 10000 tonnes, draw a compound bar graph to present the data above. (6mks)
- Give FOUR features of horticultural farming. (4mks)
-
- Describe any THREE physical factors favoring maize caltivation in Kenya. (6mks)
- A part from Trans-Nzoia county, name any other two counties where maize is grown on large scale, in Kenya (2mks)
- The table below shows the area under the horticultural crops in Kenya between 2000 and 2002. Use it to answer the questions below:
-
-
- Define the term population density. (2 marks)
- Identify any three reasons for carrying out population census in Kenya recently. (3 marks)
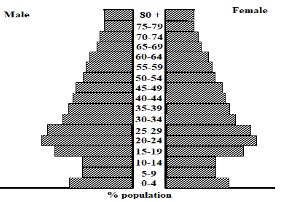
- The pyramid shown below shows population structure for a country. Use it to answer question (a).
- Identify any two countries that have population structures similar to one shown. (2 marks)
- Identify any four characteristics associated with the population of the country. (4 marks)
- Explain three problems that are likely to face a country experiencing a high population growth rate. (6 marks)
- Describe four ways in which the population of Kenya differs from that of Sweden. (8 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation (2 marks)
- Identify three methods of land reclamation in Kenya (3 marks)
-
- State four physical factors that influenced the location of Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme (4marks)
- Explain four problems facing Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme (8 marks)
-
- Name two major land reclamation projects that were undertaken in Netherlands (2 mark)
- Give three differences between land reclamation in Kenya and the Netherlands. (6 marks)
-
-
-
- What is flooding (2mks)
- Name THREE rivers that cause large scale flooding, (3mks)
- State FOUR ways in which people are affected by floods. (4mks)
-
- What is pollution ? (2mks)
- Explain three ways in which farming activities contribute to water pollution. (6mks)
-
- Explain THREE measures taken by the government to manage and conserve the environment. (6mks)
- Name two Non –Governmental organization (NGOs)concern with environmental conservation. (2mks)
-
-
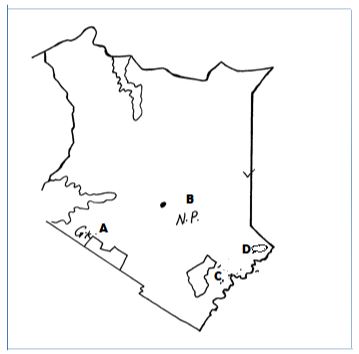
- Using the map below, name the following National parks and game reserves.
A,B,C and D . (4mks)
-
- List four problems facing wildlife conservation in Kenya. 4mks
- Give three reasons why there has been an increase in the tourist visiting Kenya (2003-2006) (3mks)
- State two characteristics of eco-tourism (2mks)
- Explain the measures the Kenya government is undertaking to improve domestic tourism (6mks)
- Explain three physical factors favouring tourism in Switzerland (6mks)
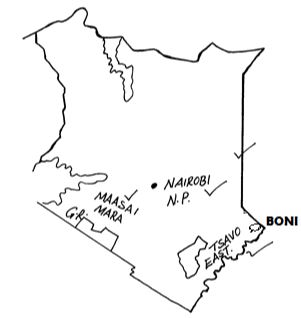
- Using the map below, name the following National parks and game reserves.
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
- Uniqueness of geography as a subject
- It relates with other disciplines in relation to human and physical phenomena (2mks)
- Branches of human geography
- Medical, economic, agricultural, historical geography etc. avoid examples such as agriculture, mining , forestry, fishing, trade and land reclamation ( any 2 x 1 = 2mks)
- Uniqueness of geography as a subject
-
- Differentiate the difference between a forest and forestry. (2 marks)
- A forest is a continuous growth of trees and under growth covering extensive land while forestry is the science of developing and managing forests including cultivating them.
- Hinderance in exploitation of equatorial
- Differentiate the difference between a forest and forestry. (2 marks)
-
- Define mining (2 marks
- Extraction of valuable minerals from the earths crust
- Name three exotic breed of dairy cattle reared in kenya (3 marks)
- Guerney
- Alderney
- Swiss brown/ brown swiss
- Fleck-vieh/simmental
- Jersey
- Aryshire
- Fresian/holstein (Any 3x1=3mks)
- Define mining (2 marks
-
- Name two major imports from Europe to Kenya. (2 marks)
- Machinery,
- Textiles,
- Fertilizers,
- Automobiles,
- Capital equipment,
- Pharmaceutical production,
- Steel,
- Electronics.
- State three problems facing developing countries in international trade. (3 marks)
- Political instability/civil wars in some of the countries within the region discourage/ hinder trade e.g. in southern Sudan.
- The similarity of the goods produced results into competition and therefore inadequate market for the goods.
- Political instability/civil wars in some of the countries discourage foreign investors from investing in some of the countries.
- Inadequate capital to establish industries/add value to agricultural produce as well as low standards of living / incomes discourages trade.
- Many of the countries still maintain historical ties with their former colonial masters / trade links.
- Inadequate/ poor means of transport and communication hinder trade as the cost of transport and communication is high.
- Corruption in many African countries discourages trade as the cost of doing business becomes high.
- Name two major imports from Europe to Kenya. (2 marks)
-
- FOUR factors leading to growth to Mombasa (4marks)
- It has a deep harbor
- It has a well sheltered harbor
- It has a large/rich hinterland
- Its located at a strategic point on the East African coast
- Its well linked ko the interior by railway, road an air transport
- Early settlement le to the growth and expansion of the town.
- Early trade in the region led to its growth.
- Name a town in Kenya where each of the following industries is located. (3 marks)
- Oil refinery - Mombasa.
- Paper manufacturing - Webuye.
- Motor vehicle assembly - Nairobi / Mombasa/ Thika.
- FOUR factors leading to growth to Mombasa (4marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
-
-
- Oranges (1mk)
-
- High income
- Requires a small piece of land.
- Less labour as compared to others.
- Availability of market in urban centres.
- Improved transport and communication. Well explained (3x2=6mks)
- Compound bar graph
- title 1mk
- origin 1mk
- variable 3mks
- trend 1mk
-
- Availability of advanced technology.
- Developed infrastructure e.g. roads, ports etc.
- Availability of advanced labour.
- Readily available market
- Well drained and fertile soil.
- Good management
- Availability of capital. (1x4=4mks)
-
-
- Temperatures ranging from 18°C to 27°C/moderate temperatures
- 20 weeks free of frost to allow maturity and harvesting
- Moderate rainfall / 600-1100mm for optimum growth
- Well drained/red volcanic/loamy soils
- Undulating topography to allow use of machinery. (well explained 3x2=6mks)
-
- Narok
- Nakuru
- Uasin Gishu
- Laikipia
- Bungoma
- Vihiga
-
-
-
-
- Define the term population density. (2 marks)
- This is the number of people found within a given area (sq.km)
- Identify any three reasons for carrying out population census (3 marks)
- To serve as a basis for planning and policy making.
- To help in planning for education / training facilities
- To plan for future social amenities provision.
- To reveal the population growth rate.
- To reveal the dependency ratio.
- To reveal the occupational level hence plan for job creation. (3x1=3mks).
- Define the term population density. (2 marks)
- The pyramid shown below shows population structure for a country. Use it to answer question (a).
-
- Identify any two countries that have population structures similar to one shown. (2 marks)
- Sweden
- Canada
- New Zealand
- Japan (any 2x1=2 marks)
- Identify any two countries that have population structures similar to one shown. (2 marks)
- Identify any four characteristics associated with the population of the country.(4 mks)
- The number of male and female population is almost equal at all levels
- From 0- 14 years, the population is low
- From 14 -44 the population is high
- The ageing population is low
- The population has high life expectancy
- The dependency ration is low
- The population has a low birthrate
- The population has a low death rates (any 4x1 =4mks)
- Explain three problems that are likely to face a country experiencing a high population growth rate. (6 marks)
- There is likely to be high unemployment rate/ rate of creation of job opportunities would increase at a lower rate than increasing number of job seekers/ low standard living.
- There may be limited government resources to provide adequate social amenities/inadequate social facilities
- It may lead to a high dependency ratio which will slow down the economic growth
- Strain on natural resources/ scarcity of land which would lead to landlessness and land fragmentation
- There would be inadequate food production/ food shortages
- Describe four ways in which the population of Kenya differs from that of Sweden. (6 marks)
- The population of Kenya has a large number of young people below 20 years of age while Sweden has an ageing population.
- Kenyans population has a lower life expectancy while Sweden has a lower life expectancy.
- Population birth rate in Kenya is high while it is low in Sweden
- The fertility rate in Kenya is high while in Sweden it is low
- The population growth rate is high in Kenya and low/negative in Sweden.
- A high percentage of the population in Kenya live in rural areas while in Sweden most people live urban areas (the difference must be complete) (any 3 x2 =6mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation (2 marks)
- Land reclamation is the process of converting less productive land into a more productive state for agricultural or settlement purposes while land rehabilitation is the process of restoring degraded/impoverished/damaged land back to its former useful state.
- Identify three methods of land reclamation in Kenya (3 marks)
- Irrigation
- Draining of swamps
- Afforestation
- Control of tse tse flie
- Differentiate between land reclamation and land rehabilitation (2 marks)
-
- State four physical factors that influenced the location of Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme (4marks)
- Gently sloping land which permits flow of water by gravity hence reducing the costs of pumping water to the fields
- Presence of clay soil/ black cotton soils which retain water for longer use by crops
- Presence of river/ reservoirs/ lake which provide regular water supply/ permanent/ constant making it possible to irrigate land throughout the year
- High temperatures throughout the year which allows multiple cropping continuous farming activities throughout the year
- Availability of large tracts of land makes the project viable
- Sparsely populated land reduces cost of resettlement / Provides land for large scale farming
- Explain four problems facing Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme (8 marks)
- Siltation of canals/ pipes/ reservoirs making the cost of operations high
- High rate of evaporation
- Salinization of the soil leading to deterioration of soils hence lowering the yields
- Presence of pests e.g. the quelea quelea birds which destroy grains hence lowering yields to farmers
- Clogging up of canals by water weeds which reduces the volume of water in canals
- Stagnant water leading to waterborne diseases e.g. bilharzias/malaria which affect productivity of the farmers
- Fluctuating regimes of rivers/ water for irrigation which lead to water shortages during the dry season hence reducing yields
- Poor marketing strategies leading to low prices for rice hence low income from the crop
- Land tenure problems due to absence of land titles which has limited the development in the plots allocated
- Mismanagement of mills/National irrigations Board leading to the delayed payments hence demoralizing the farmers
- Expensive farm inputs/ inadequate capital hence limited profits/limited expansion
- State four physical factors that influenced the location of Mwea Tebere irrigation scheme (4marks)
-
- Name two major land reclamation projects that were undertaken in Netherlands (2 marks)
- Zuyder zee project
- Delta plan
- Give three differences between land reclamation in Kenya and the Netherlands.(6mrks)
- In Kenya, the area that is reclaimed is relatively small while the areas reclaimed in the Netherlands are large.
- In Kenya, land is mainly reclaimed from swamps and marginal areas while in Netherlands reclamation is from sea.
- In Kenya the methods used for draining water form marshy areas is digging of canals/ditches while in the Netherlands the methods are advance/use of wind pumps to drain sea water from the polders.)
- In Kenya irrigation is used as reclaiming dry areas while irrigation in the Netherlands is used to lower the salinity of the soil in the claimed lands.
- In Kenya the methods of land reclamation are simple like digging canals/ditches to drain water from lad while in the Netherlands the method used are highly advanced like reclaiming land from the sea/creation of polders.
- Furrow/ridges protect the reclaimed land from invasion by the sea. (Any 3 x 2 = 6marks)
- Name two major land reclamation projects that were undertaken in Netherlands (2 marks)
-
-
-
- Flooding refers to the periodic rise in the level of water in river, lakes or oceans which causes overflow is normally dry lands. 1x2=2mks
- River causing floods in Kenya any 3x1=3mks
- R. Tana
- R. Nyando
- R. Kuja
- R. Nzoia
- How people are affected by flood 4x1=4mks
- Causes displacement of people / settlement.
- Causes destruction of property/ deaths
- Leads to outbreak of water borne diseases.
- Disrupts farming activities thereby leading to food shortages or famine.
- Causes destruction of transport and communication facilities making areas inaccessible.
-
- Pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances into the environment/ contamination of the environment with materials that interfere with human health or quality of life.
- How farming activities contribute to pollution. 4x2=8mks
- Agro chemicals used such as DDT used in agriculture are caused by running water into rivers and lakes causing water pollution.
- Remains of fertilizers such as nitrates and phosphates are also carried by running water into rivers.
- Poor farming methods such as ploughing along contours and along river banks lead to soil erosion. The soil is deposited in water causing pollution.
- When animals from farms are slaughtered the slaughter houses discharge blood and the wastes into rivers causing water pollution
-
- Measures taken to manage and conserve the environment. 4x2=8mks
- Afforestation and re- Afforestation programmes mainly in arid and semi arid lands.
- Encouraging agro forestry
- Protection of natural resources by limiting the use of pesticides and other toxic chemicals. This is also done through creation of national parks and game reserves.
- Public awareness campaigns having been carried out through the provincial administration, schools and other bodies.
- Enactment of laws which govern management and conservation of the environment.
- NGOs concerned with environment
- Green belt movement
- ICRAF
- CARE Kenya
- SIDA
- Measures taken to manage and conserve the environment. 4x2=8mks
-
-
- Outline 1mk
- A - Maasai Mara 1mk
- B - Nairobi N.P 1mk
- C -Tsavo East 1mk
- D - Boni 1mk
-
-
- Poaching
- Wildlife-human conflict
- Pollution of the environment e.g. sewage disposal from the lodges
- Population increase which put pressure on land
- Off road driving by tourist vehicles
- Drought
- Bush fires
- Overgrazing
- Inadequate capital
- Pest and disease control 4x1=(4mks)
-
- Improved security in the parks/air ports/ introduction of tourists police
- Tourist promotion in foreign countries by the Kenya Tourist Board (KTB)
- Political stability in the country
- Encouragement of domestic tourism by various tourist agencies
- The government has set up mechanisms to combat terrorism 3x1=(3ks)
-
-
- Characteristics of eco-tourism 2x1=(2mks)
- Tourists walks through footpaths instead of driving to the tourists attraction sites
- Telescope viewing of animals from a distance to avoid disturbing them
- Building camping sites instead of big tourists hotels to avoid putting pressure on resources which animals depend on
- Allow only particular types of vehicles to be used in some national parks and game reserves especially those that does not produce a lot of noise
-
- Tourist attraction promotions by the government through various agencies
- Favourable accommodation rates being offered in hotels and lodges during the off peak tourist season
- The gate fees to the parks and game reserves are lower for the local people
- Provision of free entry to the parks during some special days in an year.
- Provision of free transport to paying Kenyan citizens to the parks e.g. in Lake Nakuru National park 2x3=(6mks)
- Characteristics of eco-tourism 2x1=(2mks)
-
- Magnificent mountain scenery-Alps mountains with its peaks, hanging valleys, water falls and ice capped peaks.
- Glaciated lakes-There are numerous lakes on the Swiss plateau e.g. Lugano, Maggiore, Zurichsee. These lakes are used for sport-fishing, boating, swimming
- Climate-Switzerland has a double climate i.e. summer and winter summer attractions include, swimming, viewing ice-capped pearks, sunbathing. In winter there are winter sports such as skiing and ice-skating.
- Rivers-Switzerland has numerous rivers which are used in HEP production use in transport and hotels
- Suitable location-Switzerland is centrally situated in Europe. This makes the country relatively close to the industrialised countries which are the major source of its tourists.
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Lugari Constituency Joint Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students