- This paper contains three sections A, B and C
- Answer ALL the questions in section A and B
- Answer any Two questions from section C
-
- Name two field practices that are carried out to obtain optimum plant population in a crop field(1mk)
- Explain how each of the practices named in (a) above achieves optimum plant population. (1mk)
- State four factors that may influence labour productivity in a farm. (2mks)
- State four functions of a farm manager. (2mks)
- List four post-harvest practices that are carried out in maize production. (2mks)
-
- What is rainfall intensity? (1mk)
- State two effects of high rainfall intensity to farming. (1mk)
- State four ways in which a farmer can improve the structure of a waterlogged clay soil. (2mks)
- Apart from training and extension services, state four other agricultural support services the Kenyan government provides to a maize farmer . (2mks)
- State four factors which may affect the quality of silage. (2mks)
- Give four advantages of mixed farming. (2mks)
- Differentiate between the following terms as used in agricultural economics
- Fixed assets and current assets (1mk)
- Delivery note and purchase order. (1mk)
- Give two advantages of under sowing in pasture production (1mk)
- Name four settlement schemes that the Kenyan government started as a result of the success of the million acre scheme. (2mks)
- State any two tertiary operations carried out on the farm (1mk)
- State two ways of controlling bean anthracnose disease. ( 1mk)
- List four factors that determine the depth of planting (2mks)
- Give four causes of land fragmentation. (2mks)
- State four disadvantages of mulching in crop production. (2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
Answer all the questions in this section.
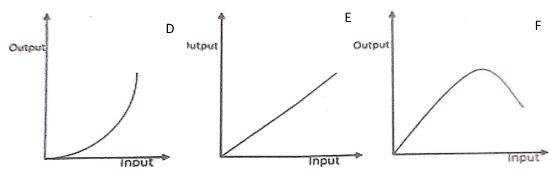
- The following illustration show different production curves in agricultural economics. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the production curves labelled D and E (2marks)
D
E - What does the law derived from the production function labelled F state? (1mark)
-
- Which one of the three production curves is rare in agriculture? (1mark)
- Give a reason for your answer in (c) (i) above. (1mark)
- Identify the production curves labelled D and E (2marks)
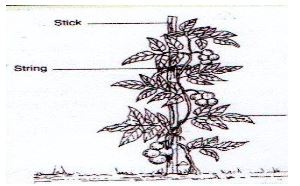
- The diagram below shows a practice carried out in tomatoes. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the practice (1mk)
- Give two reason for carrying out the practice in (a) above (2mks)
- Name two other crops that require the practice.(2mks)
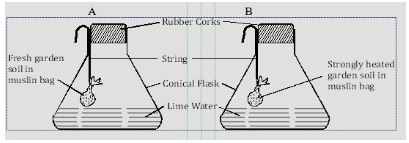
- A form one student set up experiment as shown below to study an aspect of soil. The set up was left for six hours. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- What was the aim of the experiment? (1 mark)
- State two observation that was made in each of the flask C and D. (2 marks)
- Why was the soil in flask D strongly heated? (1 mark)
- Outline one way in which soil living organisms affect Agricultural production. (1 mark)
- A farmer is advised to apply 150kg of P O 2 5 per hectare. The fertilizer available is NPK 20% P O 2 5 . Calculate the amount of NPK required for 2hectares. (5mks) show your working.
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided after question.
-
- Describe the establishment of a grass pasture from the time land is ploughed using a mouldboard plough to the time the pasture is ready for grazing. (10mks)
- State six benefits of intercropping in crop production (6mks)
- State the importance of the following stages during chemical water treatment.
- Filtration at water intake (1mk)
- Softening (2mks)
- Chlorination (1mk)
-
- Explain five disadvantages of land fragmentation. (5mks)
- State seven roles of a farm manager.(7mks)
- Explain four ways a farmer can adjust to uncertainties and risks.(8mks
-
- Describe the production of dry beans under the following subheadings
- Seedbed preparation (3marks)
- Planting (5marks)
- Field practices (4marks)
- Explain eight cultural control measures of diseases of in crop production (8marks
- Describe the production of dry beans under the following subheadings
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30 marks)
-
-
- Thinning
- Gapping 2x½=1mk
-
- Thinning - removes excess seedlings from the field
- Gapping - replaces lost/seeds that did not germinate 2x½=1mk
-
-
- Skills/level of training
- Level of mechanization/ efficiency of the machines
- Degree of motivation
- Level of supervision
- Level of remuneration 4x½ = 2mks
-
- Gathering information-
- implementing decision.
- Make short term planning
- keeping up to date records
- bearing risk
- detecting weakness 4x½=2mks
-
- Threshing/shelling
- Drying
- Cleaning
- Dusting 4x½=2mks
-
- Amount of rain that falls within a given period of time usually per hour 1x1=1mk
-
- It damages crops e.g. leaf fall, fruit fall
- It results in high water runoff thus increasing chances of soil erosion.
- Results in destruction of farm structures e.g. soil conservation projects 3x½=1½mks
-
- Apply organic manures
- Apply lime
- Drain excess water
- Plant trees e.g. eucalyptus spp
- Plant grass leys 4x½=2mks
-
- Banking
- Credit
- Artificial insemination
- Agricultural research
- Marketing
- Veterinary services
- Farm input supplies 4x½=2mks
-
- Type of silo
- Degree of compaction
- Forage species used
- Type of additives
- Stage of harvesting/leaf stem ration 4x½=2mks
-
- Mutual benefit between crops and livestock
- Income is spread over a long period
- The farmer is insured against total loss
- Animals can be used to work in the farm
- Enables distribution of labour throughout the year 4 x ½ =2mks
-
-
- Fixed assets consists of property of a durable nature used in the farm for long
- Current assets- are those properties likely to be held for a short period of time usually less than a year. Mark as whole 1mk
- Delivery note- document that accompanies goods on delivery.
- Purchase order- a request to a trading business firm to supply specified goods Mark as whole 1mrk
-
-
- Control soil erosion due to ground cover.
- Reduces cost of production.
- Saves time per pasture establishment
- Efficient land use. 2x½=1mk
-
- Haraka schemes
- Shirika schemes
- Lari settlement schemes
- Squatter’s settlement scheme 4x½=2mks
-
- Ridging
- Rolling
- Levelling (2 x ½ = (1 mrk
-
- Growing resistant varieties
- Seed dressing
- Field hygiene/ burning infected crop residues
- Spraying
- Use of clean seeds 4x½=2mks
-
- Size of seed
- Moisture content of the soil
- Type of soil
- Type of germination 4x½=2mks
-
- Shifting cultivation
- Traditional systems e.g. land inheritance by family members
- Accumulation of land holdings
- Land may be used to settle debts
-
- Trap light showers of rainfall (2mks)
- Provide breeding ground for pest
- Bulky in transportation
- They are fire risk
-
- Identify the production function curves labeled A, B and C
- A – Increasing returns production (1mk)
- B – Constant returns production. (1mk)
- C – Decreasing returns production (1mk)
Reject if the word returns is missing.
- If successive units of one variable input are added to fixed quantities of other inputs, a point is reached when additional/extra/marginal product per additional unit of input declines. 1 x 1 = 1mk
- Which one of the three production functions curves is rare in Agriculture (1mk)
- B 1 x 1 = 1mk
- The resources are under- utilized. 1mk
- Identify the production function curves labeled A, B and C
-
- staking 1x1=1
-
- pumpkin
- climbing bean varieties 2x1=2
- passion fruits.
-
- production of clean fruits 2x1=2
- facilitate easy harvesting
- prevents spread of diseases
- easy spraying.
-
- Aim of the experiment
- To investigate the presence of living organisms in the soil. (1× 1 = 1 mark)
-
- C - White precipitate formed / lime water turns milky
- D - Lime water remains clear (2×1 = 2 marks)
- To kill any living organisms in the soil. (1 mark)
- Ways in which soil living organisms affect Agricultural production.
- They aerate the soil through burrowing.
- They help in decomposition of organic matter
- Some strains of bacteria fix nitrogen in the soil.
- Some Micro-organisms cause diseases in crops.
- Some living organisms are involved in the biological process of weathering. (Any 1× 1 = 1 marks)
- Aim of the experiment
-
- Tissue culture
-
- Enable production of pathogen free plants
- Enable production of numerous propagules
- It is a very fast method of producing propagules
- It requires less space (1*3=3 marks)
- Culture medium that contains nutrients for developing propagules/provide growth regulators. (1*1 mark)
-
-
- Clear bushes
- Plough the seed bed
- Harrow to fine tilth
- Remove perennial weeds
- Prepare land early in dry season
- Roll to firm the seedbed
- Select suitable grass variety for the area
- Use phosphatic fertilizers for planting
- 200-300kg the S.S.P is used
- Drill / broadcast seeds events
- Use recommended rate of 1.53.01ha of P.G.S
- Drag gunny bag to cover the seed.
- Control weeds using appropriate method.
- Apply nitrogen fertilizer 6 weeks after germination
- Practice light grazing at initial stages.
- Do not graze when pasture are too young 10 x 1 = 10mks
-
- Control pests and disease
- When legumes are included nitrogen is added in the soil
- Cover crops supprels growth of weeds
- Cover crop helps in soil and water conservation.
- High output per unit area
- Saves on labour costs /maximize use of labour.
- Maximize use of land 6 x 1 = 6mks
-
- To remove physical inpurities 1 x 1 = 1mk
- Soda ash soften water
Allum coagulate particles 2 x 1 = 2mks - To kill pathogens 1 x 1 = 1mk
-
-
- disadvantages of land fragmentation
- Time is wasted moving from one place to another
- Difficult to control pests and diseases
- Difficult to supervise
- Difficult to control parasites and diseases
- Difficult to carry out soil and water conservation.
- Difficult to get extension services.
- Difficult to make sound decisions 5x1=5
- Roles of farm manager
- Short term planning
- Long term planning
- Gathering information
- Detecting weaknesses
- Implementing decisions
- Keeping farm records
- Comparing standards of enterprises. 7x1=7
-
- diversification-having several enterprises to minimize the risk
- Selection of more certain enterprises/ more reliable
- Contracting-enter into a contract with the suppliers , buyers
- Insurance-insure the enterprise incase of loss you are compensated
- Input rationing- minimize thecosts on in puts
- Adopting modern methods of farming
- Being flexible in the production methods
- disadvantages of land fragmentation
-
- Describe the production of common beans under the following subheadings
- Seedbed preparation (3marks)
- Clear the land
- Plough/carry out primary cultivation before the onset of the rains
- Harrow the land to a moderate tilth / medium tilth
- Prepare the land early
- Eradicate all perennial weeds
- Planting (5marks)
- Plant at the onset of rains
- Observe timely planting to ensure that harvesting coincides with the dry weather
- Plant 2 – 3 seeds per hole
- Plant on shallow farrows or through dibbling
- Observe a spacing of 30-45cm by 15cm
- Apply D.A.P. fertilizer on planting furrows at the rate of 200kg/ha
- Observe a planting depth of 4cm
- Field practices (4marks)
- Weeding – controls weeds through cultivation
Observe shallow weeding / hand weeding - Weeding should not be done at flowering stage to avoid knocking down the flowers
- Irrigation – this is done to supplement rainfall
- Pests and diseases control – control pests like American boll-worm by using appropriate insecticides
- Disease control – control diseases like anthracnose by spraying with appropriate fungicides or planting resistant varieties
- Weeding – controls weeds through cultivation
- Seedbed preparation (3marks)
- Explain eight cultural control measures of diseases of in crop production (8marks)
- proper pruning – eg open pruning in coffee to control coffee berry disease (CBD)
- use of disease-free planting materials eg certified seeds
- proper spacing – helps to control some diseases such as rosette disease in groundnuts
- use of disease-resistant varieties eg Ruiru 11 coffee variety
- crop rotation – helps to break the disease cycle
- heat treatment to control ratoon stunting
- field hygiene eg rogueing and burning of plant remains
- proper seed bed – preparation to expose soil-borne pathogens to the sun which will kill them as well as to their predators
- proper drying of cereals to prevent growth of the fungus that produces aflatoxins
- timely planting
- Describe the production of common beans under the following subheadings
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Lugari Constituency Joint Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students