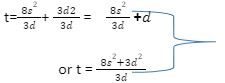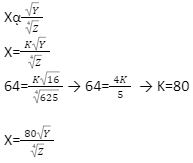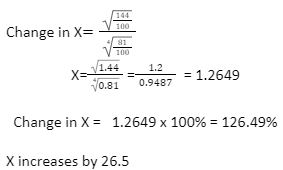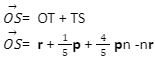SECTION I (50 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in spaces provided
- Use logarithms, correct to 4 decimal places, to evaluate (4mks)
3√83.46x0.0054
1.522 - Given that the ratio of x:y = 4:5, find to the simplest form the ratio of (7x −2y):(x + 2y) (2mks)
- Ruto bought a plot of land for Ksh.280,000. After 4 years, the value of the plot was Ksh.495,000. Determine the rate of appreciation, per annum, correct to one decimal place. (3mks)
- The height in centimeters, of 100 tree seedlings in a tree nursery are shown in the table below.
Find the quartile deviations of the heights. (3mks)Height(cm) 10-19 20-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 Number of trees 9 16 19 26 20 10 - The equation of a circle is given by 4x2 − 12x + 4y2 − 8y − 3 = 0. Determine the coordinates of the centre of the circle and the radius of the circle. (4mks)
- Simplify the expression √48 , leaving the answer in the form a√b + c where a, b and c are integers (3mks)
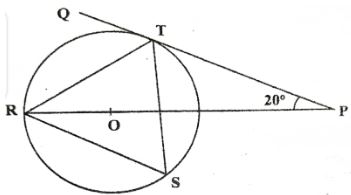
√5 + √3 - In the figure below R, T and S are points on a circle centre O. PQ is a tangent to the circle at T, POR is a straight line and <QPR = 20°.
Giving reasons find the size of <RST (2mks) -
- Expand the expression (1 + ½x)5 in ascending powers of x, leaving the coefficients as fraction in their simplest form. (2mks)
- Use the first three terms of the expansion in (a) above to estimate the value of (1.05)5 correct to 4 significant figures (2mks)
- Make t the subject of the formula in s = √3d(t − d) (3mks)
8 - A trader bought maize for Ksh 20 per kilogram and beans for Ksh 60 per kilogram. She mixed the maize and beans and sold the mixture at Ksh 48 per kilogram. If she made a 60% profit, determine the ratio of maize:beans per kilogram in the mixture. (3mks)
- The cash price of a digital television is Ksh. 27,500. A customer decided to buy it on hire purchase terms by paying a deposit of Ksh 17,250. Determine the monthly rate of compound interest charged on the balance if the customer is required to repay by six equal monthly instalments of Ksh. 2,100 each. (3mks)
- The first, the third and the seventh terms of an increasing arithmetic progression are three consecutive terms of a geometric progression. If the first term of the arithmetic progression is 10, find the common difference of the arithmetic progression. (4mks)
- The lengths of two similar pieces of wood were given as 12.5 m and 9.23 m. Calculate the absolute error in calculating the difference in length between the two bars. (3mks)
- Solve for x given that 1/3log28 + log2(2x − 4) = 5 (3mks)
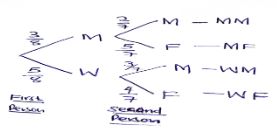
- In nomination for a committee, two people were to be selected at random from a group of 3 men and 5 women. Find the probability that a man and a woman were selected. (2mks)
- Pipe A can fill an empty tank in 3 hours while, pipe B can fill the same tank in 6 hours. When the tank is full it can be emptied by pipe C in 8 hours. Pipe A and B are opened at the same time when the tank is empty. If one hour later, pipe C is opened, find the total time taken to fill the tank. (4mks)
SECTION II (50 marks)
Answer only five questions in this section in spaces provided
- The table below shows the income tax rates for a certain year.
Monthly taxable income in Ksh Tax rate (%) in each shilling 1-11,180 10 11,181-21,714 15 21,715-32,248 20 32,249-42,782 25 Over 42,782 30 - During the year, Njuguna’s monthly income was as follows: Basic salary Ksh 40,000, House allowance Ksh 11,090 and Commuter allowance Ksh 7,000.
Calculate- Njuguna’s total monthly taxable income. (1mk)
- Total income tax charged on Njuguna’s monthly income (4mks)
- Njuguna’s net monthly tax was Ksh. 10,750.80. Determine the monthly tax relief allowed. (1mk)
- A proposal to expand the size of the first income tax band by 50% while retaining the size of the next three bands was made. The tax rates would remain as before in each band. Using the proposal, calculate:
- The tax Njuguna would pay in the first band. (2mk)
- The tax Njuguna would pay in the last tax band. (2mks)
- During the year, Njuguna’s monthly income was as follows: Basic salary Ksh 40,000, House allowance Ksh 11,090 and Commuter allowance Ksh 7,000.
-
- Given that A = (3 x x + 1 2) and B = (1 2 3 0), find the values of x for which AB is a singular matrix. (3mks)
- Otieno bought 3 exercise books and 5 pens for a total of Ksh 165. If Otieno had bought 2 exercise books and 4 pens, he would have spent Ksh 45 less. Taking letter e to represent the price of an exercise book and letter p to represent the price of a pen
- Form two equations to represent the above information. (2mks)
- Use matrix method to find the price of an exercise book and that of a pen. (3mks)
- The principal of Njabini boys decided to reward 36 students each with 2 exercise books and one pen. Calculate the total amount of money he paid. (2mks)
- Three quantities X, Y and Z are such that X varies directly as the square root of Y and inversely as the fourth root of Z. When X=64, Y=16 and Z= 625.
- Determine the equation connecting X, Y and Z. (4mks)
- Find the value of Z when Y=36 and X=160 (2mks)
- Find the percentage change in X when Y is increased by 44% and Z decreased by 19% correct to one decimal place. (4mks)
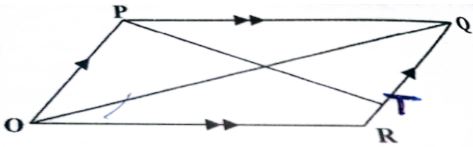
- The figure below shows a parallelogram OPQR with O as the origin, OP = p and OR= r. Point T divides RQ in the ratio 1:4. PT meets OQ at S.
- Express in terms of p and r the vectors
- OQ (1mk)
- OT (1mk)
- Vector OS can be expressed in two ways; i) OS = mOQ ii) OS = OT + nTP, where m and n are constants. Express OS in terms of
- m, p and r (1mk)
- n, p and r (1mk)
Hence find the - value of n and m (5mks)
- ratio OS:SQ (1mk)
- Express in terms of p and r the vectors
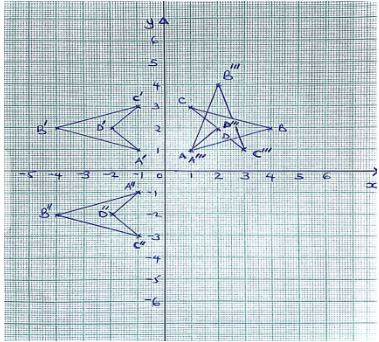
- A quadrilateral ABCD has vertices at A(1,1), B(4,2), C(1,3), D(2,2).
- Draw ABCD on the grid provided (1mk)
- Give that X = [1 0 0−1] Y= [−1 0 0 1] V = [0 −1 −1 0] . Find the coordinates of A1B1C1D1, A11B11C11D11 and A111B111C111D111 the images of ABCD under combined transformation VXY. Show all your working of coordinates below;
- Coordinates of A1B1C1D1 and draw it on the grid. (2mks)
- Coordinates of A11B11C11D11 and draw it on the grid. (2mks)
- Coordinates of A111B111C111D111 and draw it on the grid. (2mks)
- Showing your working find a single matrix that will map ABCD onto A111B111C111D111. (3mks)
-
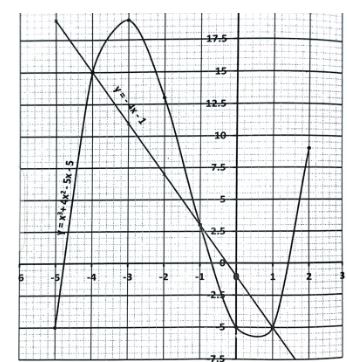
- Complete the table below for y = x3 + 4x2 − 5x −5 (2mks)
X −5 −4 −3 −2 −1 1 2 y = x3 + 4x2 − 5x −5 −5 - On the grid provided, draw the graph of y = x3 + 4x2 − 5x − 5 for −5 ≤ x ≤ 2 (3mks)
-
- Use the graph to solve the equation x3 + 4x2 − 5x − 5 = 0 (2mks)
- By drawing a suitable straight line graph, solve the equation x3 + 4x2 −x − 4 = 0 (3mks)
- Complete the table below for y = x3 + 4x2 − 5x −5 (2mks)
- A polytechnic planned to buy x lockers for a total cost of Ksh 16,200. The supplier agreed to offer a discount of Ksh 60 per locker. The polytechnic was then able to get three extra lockers for the same amount of money.
- Write an expression in terms of x, for the:
- Original price of each locker; (1mk)
- Price of each locker after the discount. (1mk)
- Form an equation in x and hence determine the number of lockers the polytechnic bought. (5mks)
- Calculate the discount offered to the polytechnic as a percentage (3mks)
- Write an expression in terms of x, for the:
-
- Using ruler and compasses only construct triangle ABC such that AB=4 cm, BC= 5cm and <ABC=120°. (3mks)
- Measure AC (1mk)
- On the same diagram draw a locus of points equidistant from point A and point C and label the locus as L1. (1mk)
- Draw on the same diagram a locus of points L2 equidistant from point C and point B and lable the locus as L2 (1mk)
- Label the point where L1 and L2 meet as O. Using O as a centre draw a locus of points L3 touching points A, B and C. Measure the length from point O to L3. (2mks)
- Draw the locus of points L4 equidistant from line AC and Line AB. Extend L4 to meet line BC and lable where they meet point D. Measure the length AD. (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
| NO | WORKING | MARKS | REMARKS | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 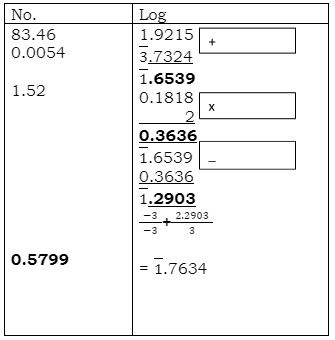 |
M1
M1
M1
A1 |
For all logs correct
For addition and subtraction
For dividing by 3
For 0.5799 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 |
7(4) − 2(5): 4 + 2(5) 18:14 |
M1
A1 |
Substituting for x and y.
For Answer |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 495,000 = 280,000(1+ R/100)4
495,000 − 280,000 (1+R/100)4 4√1.767857 = 1+ R/100 |
M1
A1 |
For 4√1.767857
For answer. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Lower quartile = 19.5 + (25 − 9)10 16 = 19.5 + 10 = 29.5 Upper quartile = 49.5 + (75-70)10 |
M1
M1
A1 |
For lower quartile
For upper quartile
For 11.25 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 4/4x2 −12/4x + 4/4y2 − 8/4y −3/4y = 0 x2− 3x + y2 − 2y = 0.75 x2− 3x +1.52 + y2 − 2y + 1 = 0.75 + 2.25 + 1 |
M1
1MK
A1 A1 |
For dividing by 4
For completing square.
For center For radius |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | √48 = √16 x 3 = 4√3
4√3(√5 − √3) |
M1
M1
A1 |
For 4√3
For multiplying b conjugate
For (2√15 − 6) |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | <RST=55° Reason; Angles in alternate segments are equal. |
B1 B1 |
For 55°
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | (a) BC for power 5 = 1, 5, 10, 10, 5, 1
1+5(½x)1+10(½x)2 +10(½x)3 + 5(½x)4 + (½x)5 1+ 5/2x + 5/2x2 + 5/4x3 + 5/16 x4 +1/32x5 (b) 1 + 5/2x + 5/2x2 are the1st 3 terms 1+ 5/2(0.1) + 5/2(0.1)2 |
M1
A1
M1
A1 |
Inserting binomial coefficients. In simplest form.
For X= 0.1
For the answer |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | s2 = 3d(t−d)8
8s2 = 3dt−3d2 |
M1
M1
A1 |
For squaring both sides
For making 3dt subject
For any of the two expressions of t. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | Cost price before profit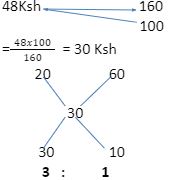 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | Amount = MI = 2100 x 6 = 12,600 Ksh
Principal = 27,500 −17250 = 10, 250 Ksh
|
M1
M1
A1
|
Substituting amt and principal in formula. Finding 6th root on both sides.
For 3.5% |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | a, a + 2d, a +6d
a +6d = a + 2d |
M1
M1
A1 |
For the three terms
For 10 +6d = 10+2d
For working out for d |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | Actual difference = 12.5 – 9.23 = 3.27
Max difference = 12.55 − 9.225 = 3.325 Absolute error = 3.325 − 3.215 = 0.055 |
M1 M1 A1 |
For max difference For minimum difference |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | Log281/3 + Log2(2x − 4) = Log232
Log22 + Log2(2x − 4)=Log232 2(2x−4) = 32 |
M1
M1
A1 |
For Log232
For the equation 2(2x − 4) = 32 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 |
P(Woman or Man) = P(MW) or P(WM) |
M1
A1 |
For working
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | Work done by A per hour = 13
Work done by B per hour = 16 Total time taken = 1 hr + 113 hrs = 213 hours |
M1
M1
M1
A1
|
Work done by A and B
Work done by all pipes.
Time by all pipes.
Total time taken |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | (i) (a) 40,000 + 11, 090 + 7,000 = 58,090 Ksh 1st band 11,180 x 10% = 1,118 Ksh 2nd band 10,534 x 15% = 1,580.10 Ksh 3rd band 10,534 x 20% = 2,106.80 Ksh 4th band 10,534 x 25% = 2,633.50 Ksh Remaining 10,534 x 30% = 4,592.40 Ksh Total tax 12,030.80 Ksh (ii) Tax relief = 12,030.80 – 10,750.80 = 1,280 Ksh (iii) (a) 11,180 x 150% = 16,770 Ksh (b) 58,090 – 48372 = 9,718 Ksh |
M1 M1 M1 M1 A1 A1 M1 M1 |
For taxable income For 1st and 2nd bands For 3rd and 4th bands For remaining amount. For total tax For tax relief |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | (a) 3 x x+1 2 1 2 3 0 =3+3x 6 x+7 2x+2 (3+3x)(2x+2)-(6x+42) = 0 6x2 + 6x − 36 = 0 Dividing by 6 we get x2 + x − 6 = 0 Solving x2 + 3x − 2x − 6 = 0 (b) (i) 3e + 5p = 165
|
M1
M1
A1
B1
M1
M1
A1 M1 A1
|
For equating product of A and B to Zero.
For solving quadratic equation. For values of x.
For equation 1
For matrix equation.
Working using inverse to get required costs.
Cost of 2 exercise books and 1 pen |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 |
(i) (ii) (iii) |
M1 M1
M1
M1
M1 A1
M1
M1
M1 A1 |
For introducing constant K For value of K For equation connecting X, Y and Z.
For making z subject and substituting values of x and y.
For substituting % change in the formula. For 1.2649 For 126.49% Accuracy to 1 d.p |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 |
(a) (i) OQ = r + p (b) (i) (ii) |
B1
B1
B1 B1
M1
M1
A1
B1
|
For equating the two values of OS.
For working out to get the scalars.
For n = 4/9 For m = 5/9 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 |
(a) (b) (i) (ii) [ 1 0 0 −1][− 1 −4 1 2 − 1 − 2 3 2] = (iii) (c) a + b = 1 c + d = 1 [a b c d] = [0 1 1 0]
|
B1
B1
B1
B1
B1
B1 B1
B1
B1
B1 |
For ABCD
For A1B1C1D1
For A11B11C11D11
For A111B111C111D111 For diagram of A1B1C1D1
For diagram of A11B11C11D11
For diagram of A111B111C111D111
For working for a,b,c,d For matrix [0 1 1 0]
For correct description of the matrix. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 |
(a)
(b) Solutions to equation x3 + 4x2 −5x −5 = 0 are on line Y = 0 (c) (i) Solution to x3 + 4x2 −x −4 = 0 (ii) y = x3 + 4x2 − 5x − 5 0 = x3 + 4x2 − x − 4 |
B2
P1
C1 S1
L1
B2
B2
|
For all the 6 correct
For plotting all points correctly. For a smooth curve. For uniform scale on both y and x axis. For line y = 4x − 1
For any two correct values of x
For any two correct values of x |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 |
(a) (i) (ii) (b) 16,200 − 16,200 = 60 Becomes X = − 3 ± 572 Or x = −30(ignore) (c) Original Price = 16,200 = Ksh 600 60 x 100 = 60 % |
B1 B1
M1
M1
M1
A1 B1
M1 M1
A1 |
For correct expression. For correct expression.
For the expression For forming quadratic equation from above expression. For the method used for working out. Either formula or any other. For x = 27
For discount = Ksh 60 For working out original price. For correct percentage discount. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 |
(i) Diagram on last page (ii) Length of AC = 7.8 ± 0.1 (iii) Locus L1 on the diagram (iv) Locus L2 on the diagram (v) Locus L3 on the diagram (vi) Length of O to L3 = 4.6 ± 0.1 (vii) Locus L4 on the diagram (viii) Length of AD = 5.0 ± 0.1 |
B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 B1 |
<ABC drawn without using protractor. For Line AC Δ ABC complete For AC = 7.8 ± 0.1 For locus L1 on the diagram For Length of O to L3 Locus L4 on the diagram AD = 5.0 ± 0.1
|
||||||||||||||||||
| total | 10 |
Download Mathematics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Lainaku 1 Joint PreMock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students