Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
-
- Distinguish between flood irrigation and basin irrigation (1mk)
- Give two maintenance practices required in flood irrigation system. (1mk)
- State the fate of water added to soil in crop field. (2mks)
-
- Name two crops which after harvesting are processed using a flail. (1mk)
- What name is give to the practice in 3a above. (1/2mk)
- State two conditions under which opportunity cost can be zero. (2mks)
- Shown below is part of a record found in Nyali farm
Item Quantity Date Acquired Original unit cost (ksh) Watering trough
Hand hoes
Wheel barrow
Machetes
Buildings
Milking shed
Cattle
Sheep2
4
1
6
2
1
11
1403.03.2006
31.05.2005
04.01.2005
11.07.2004
Diverse dates
02.02.2004
Diverse dates
Diverse dates3600
250
2310
169
284000
32600
66000
2100-
- Identify the type of record shown above. (1mk)
- Give reason for your answer to a (i) above. (1mk)
- What other column should be added to this record, to make it complete. (1mk)
-
- Give two disadvantages associated with burning as a land clearing method. (1mk)
-
- Name three components of rooting mixture used in polythene sleeves in raising tree seedlings. (3mks)
- State two benefits of using polythene sleeves, in raising tree seedlings. (2mks)
-
- Define tissue culture. (1mk)
- Give three advantages of tissue culture
- Shown below is the average yield and total digestible nutrients (TDN) per hectare of hay cut in June July, August and September
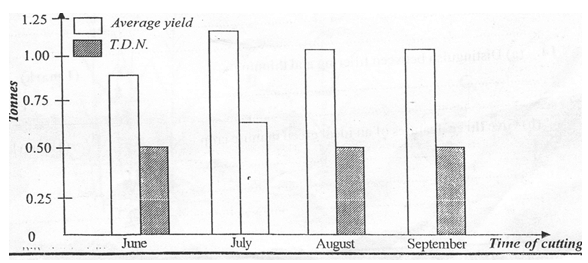
- From the graph identify the relationship between average yield and total digestible nutrients of hay. (1mk)
- From the graph, identify the most appropriate month of harvesting hay. (1mk)
- Outline how the age of an animal influences the quality of farm yard manure production form it. (1mk)
- List four soil requirements for tomatoes. (2mks)
- Under what circumstance are beans referred to as vegetables. (1mk)
-
- State two conditions that may lead to land fragmentation. (1mk)
- Give two benefits of land fragmentation. (1mk)
-
- Distinguish between tillering and thinning. (1mk)
- Give three features of an ideal green manure crop. (11/2 mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
- Given below is an illustration of water levels of undrained and tile – drainage land in the sowing and maturation stage of cereal crop
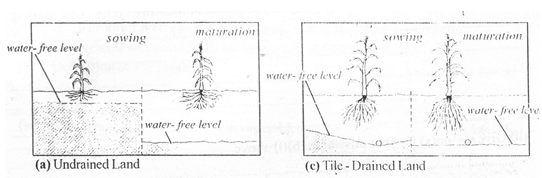
- What benefit of land drainage is shown in the illustration above? (1mk)
- What three advantages may be associated with tile-drainage? (11/2mks)
- State two maintenance requirements of tile-drainage system. (1mk)
- The diagrams labeled A,B and C below illustrate some weeds. Study the diagrams carefully and then answer the questions that follow.
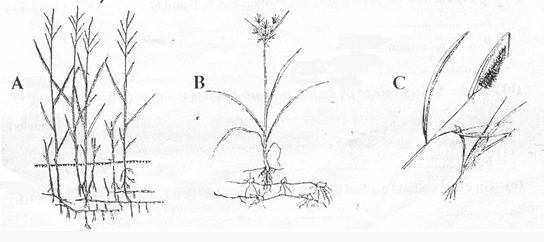
- Identify each of the weeds illustrated in diagram A,B and C. (3MKS)
A
B
C -
- Classify the weeds into two groups, on the basis of their life cycles. (21/2marks)
- Give reasons for you answer in (bi) above. (3mks)
- State two negative effects of weed C, on livestock. (1mk)
- Identify each of the weeds illustrated in diagram A,B and C. (3MKS)
- The diagram labeled E, F and G below illustrate some pest found in vegetables study the diagrams carefully and then answer the questions that follow
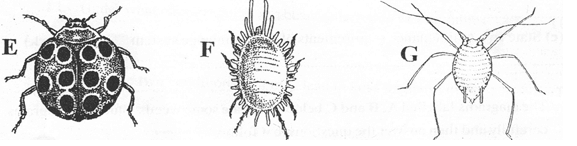
- Identify each of the pest illustrate in diagram E,F, and G. (3MKS)
- State the damage caused by each of the pest labeled E and F, on the host plants. (mksa_
- Give one cultural control measure for the pest labeled E (1mk)
- Other than vegetables name two crop plants that may be infested with the pest labeled G
SECTION C (40MKS)
Answer an two question in this section the space provided
- Discuss vegetable crops under the following sub- headings
- Definition of vegetable. (1mk)
- Management of perishability vegetables. (4mks)
- Importance of vegetables. (6mks
- Common stem vegetables. (4mks)
- Staking in tomatoes. (5mks)
- Discuss budding a applied in crop production under the following sub-headings
- Timing (5mks)
- Advantages over grafting. (4mks)
- Materials used. (6mks)
- Briefly describe whip grafting. (5mks)
- Discuss wind erosion under the following sub- headings
- Destructive effects of wind erosion on crop plants. (5mks)
- Factors affecting susceptibility of soil to wind erosion. (15mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Flood – water allowed to freely cover the whole field to a depth of a few cm; basin. - the field enclosed by embankments;
ark x 2 = 1 mark) - Keep outlets open, to allow excess water to flow away; remove any barriers in the field (rocks, trees);
('/, mark x 2 = 1 mark)
- Flood – water allowed to freely cover the whole field to a depth of a few cm; basin. - the field enclosed by embankments;
- Used up by plants; eroded, drained away; evaporate into the atmosphere; used up by soil organisms;
(1 mark x 2 = 2*marks) -
- Maize; Sorghum; rice; wheat; millet; rye; oats; barley; sesame;
('/, mark x 2 = 1 mark) - Threshing;
('/, mark)
- Maize; Sorghum; rice; wheat; millet; rye; oats; barley; sesame;
- Where there are no alternatives; where the alternatives vield the same utility/benefit;
(1 mark x 2 = 2 marks) -
-
- Inventory;
(1 mark) - Record of assets ; and their respective (monetary) value; (1, mark x 2 = 1 mark)
- Inventory;
- Total cost/value
(1 mark)
-
- Destroy organic matter; kill (useful) soil organisms; burn (usesul) vegetation; expose the land to agents of erosion; may destroy farm property; evaporation of soil moisture;
(any 2 1/2 mark x 2 = 1 mark) -
- Manure; sub-soil; phosphatic fertilizer; rooting hormone; (1 mark x 3 = 3 marks)
- Easy to transport; minimum disturbance to plant roots at transplanting
(1 mark x 2 = 2 marks)
-
- raising plants from a mass of cells;
(1 mark) - Fast; obviates the need for a male and female; the offspring are disease- frec; large numbers of offspring produced;
(1/2 mark x 3 = 1 /2 marks)
- raising plants from a mass of cells;
-
- The higher the total yield, the higher the TDN;
(1 mark) -
- July;
(1 mark) - Flowering stage, plants with highest nutrient content;
(1/2mark)
- July;
- The higher the total yield, the higher the TDN;
- Older animals have well-developed digestive systems; utilize most of the nutrients in the feed, producing poorer quality manure;
(12 mark x 2 = 1 mark) - Deep; fertile; well drained; high organic matter content; (1, mark x 4 = 2 marks) 12.
- When harvested and eaten fresh;
(1 mark) -
- Need to sell off portions of the land; inheritance of heirs; holding land for speculative purposes;
('/, mark x 2 = 1 mark) - The landless can acquire land; utilize idle land;
ks x 2 = 1 mark)
- Need to sell off portions of the land; inheritance of heirs; holding land for speculative purposes;
-
- Tillering-production of many stems by a plant; thinning-removing excess plants from a crop field;
('/, mark x 2 = 1 mark) - High leaf : stem ratio; fast growing; leguminous; hardy; ('/, mark x 3 = 1', marks)
- Tillering-production of many stems by a plant; thinning-removing excess plants from a crop field;
-
- Improved aeration/large mass of soil from which the plant can draw nutrients; *
(1 mark) - Large amounts of water drained away in a short time; once set, effective for long;
land useful for farming is not consumed by the tiles; (!!, mark x 3 = 1 %, marks) - Repair broken tiles; remove sediment at outlets; (22 marks x 2 = 1 mark)
- Improved aeration/large mass of soil from which the plant can draw nutrients; *
-
- A couch grass; B Nutgrass; C Setaria grass;
(1 mark x 3 = 3 marks) -
- A perennial; B; perennial; C; Annual; (1/2 mark x 5 = 2 %2 marks)
- Perennial – complete life cycle in more than two years; annual- complete life cycle in one year;
(1 mark x 3 = 3 marks)
- Injure eyes; damage hides and skins; irritate skin; ("/, mark x 2 = 1 mark)
- A couch grass; B Nutgrass; C Setaria grass;
-
- E beetle; F Mealy bug; G aphid;
(1 mark x 3 = 3 marks) - E feed on leaves, reducing photosynthetic area; F puncture stem, feed on sap;
(1 mark x 2 = 2 marks) - Early planting; crop rotation; field hygiene; pruning; weed control; .(1 mark)
- Maize; rice; banana; citrus;
('/, mark x 2 = 1 mark)
total = 20 marks
- E beetle; F Mealy bug; G aphid;
-
- Plant (part) harvested, eaten fresh;
(1 mark) - Rapid means of transport to the market; sell from the farm (rather than at the market)
; sell to the market closest; identify customers with regular needs -- schools, hospitals, hotels;
(1 mark x 4 = 4 marks) - Spice food; source of vitamin A, B,, C, Calcium, Iron, Phosphorus; quick source of income; waste is used as feed for livestock;
(1 mark x 6 = 6 marks) - Leek; Asparagus; onion, mushroom; coriander; sweet potato; (1 mark x 4= 4 marks)
- Stakes used to support; tall varieties; by tying the plants onto the stakes at 20 cm
intervals; produce clean fruits; facilitate weeding, spraying, harvesting; control disease; prevent pest infestation;
(1 mark x 5 = 5 marks)
- Plant (part) harvested, eaten fresh;
-
-
- At the peak of the growth period; when moisture content high, plants easily
recover from wounds caused; buds actively growing; rate of cell division and elongation highest;
(1 mark x 5 marks) - Fast; smaller wounds caused; success rate is high; lesser risk of disease, pest infestation;
(1 mark x 4 = 4 marks) - Budding knife; to cut the plants; raffia / polythene / clay; to bind the scion and root stock; disease, pest-control chemicals; for disease, pest control;
(1 mark x 6 marks)
- At the peak of the growth period; when moisture content high, plants easily
- Scion and rootstock same size; make slanting cut; so that the two lit; tie; to maintain cambial contact; once set, remove the material used for tying;
(1 mark x 5 = 5 marks)
[Total = 20 marks
-
-
- Loss of top soil – the most fertile part of soil; depriving plants of nutrients; expose
plant roots; lodging; deposit sediment on plant leaves; (1 mark x 5= 5 marks) - Moisture content of soil; dry soils easily blow; wind velocity, turbulence; strong
winds have more effect; type of soil; fine soils blow faster, vegetation cover; reduces effect of wind; width of field; wide fields allow winds to gather speed; cause more destruction, roughness of soil surface; smooth fields aggravate effect of wind; cementing agents in the soil; hold soil particles, reducing effect of wind;
(1 mark x 15 = 15 marks)
[Total = 20 marks]
- Loss of top soil – the most fertile part of soil; depriving plants of nutrients; expose
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions- Mwakican Joint Pre Mock Examination 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

