SECTION A (30MKS)
Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
- State four factors influencing the choice of the farming methods a farmer may use. (2mks)
- State four advantages of drip irrigation. (2mks)
- Outline four farming practices that destroy soil structure. (2mks)
- State four reasons why a farmer may fail to get profit from a farming enterprise. (2mks)
- Give four advantages of preparing land early for planting sorghum. (2mks)
- Differentiate between hybrid and composite as used in crop production. (2mks)
- What is meant by term domestication as used in Agricultural production? (1mk)
- Highlight two ways of hardening off tomato seedlings before transplanting. (1mk)
- Give a reason as to why a farmer is supposed to observe the following precautions in the farm. (2mks)
- Always store farm yard manure under a shade.
- Wear gloves while applying nitrogenous fertilizers.
- Give two reasons for conserving forage. (1mk)
- Outline four ways in which grass help to conserve soil. (2mks)
- Give two signs of blight in a field of tomatoes. (1mk)
- State two factors that adapt weeds excellently to their environment. (1mk)
- Give two reasons for inoculating legume seeds before planting. (1mk)
- Give two reasons why most of Kenyan farmers practice small scale farming. (1mk)
- Define the law of profit maximization. (1mk)
- Distinguish between stocking rate and carrying capacity as used in forage production. (2mks)
- Outline four ways a farmer can use to improve labour productivity in the farm. (2mks)
- State 4 ways of modifying soil pH. (2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
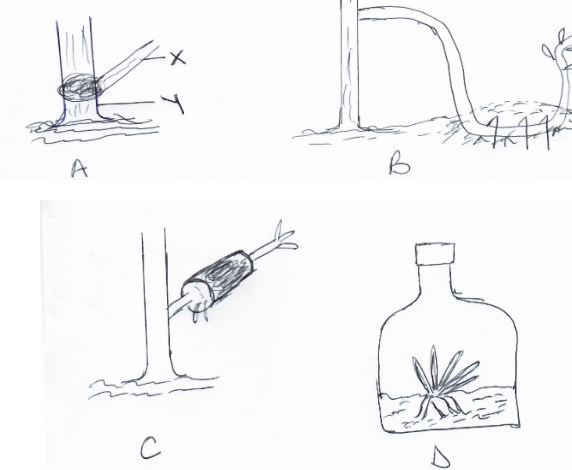
Answer all questions in the spaces provided. - The diagram below illustrates different methods used in crop propagation. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the methods of crop propagation illustrated by A, B and D. (3mks)
A:
B:
D: - Identify the parts labelled X and Y in diagram A. (2mks)
X: …………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Y: ……………………………………………………………………………………………………. - Under what conditions is method C used by farmers. (1mk)
- Give two advantages of using the method illustrated in diagram D after bananas are planted in the main field. (2mks)
- Identify the methods of crop propagation illustrated by A, B and D. (3mks)
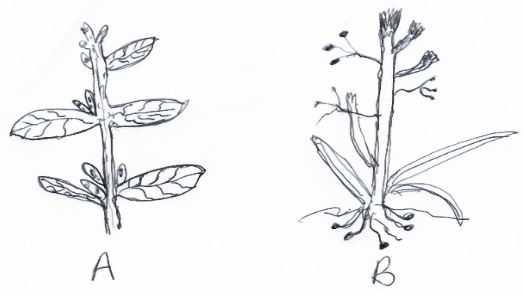
- The diagram below illustrates some common weed. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the weeds labelled A and B. (2mks)
A:
B: - State one factor that makes weed B difficult to control in a pasture field. (1mk)
- State one economic importance of each of the weeds labelled A and B. (2mks)
A:
B:
- Identify the weeds labelled A and B. (2mks)
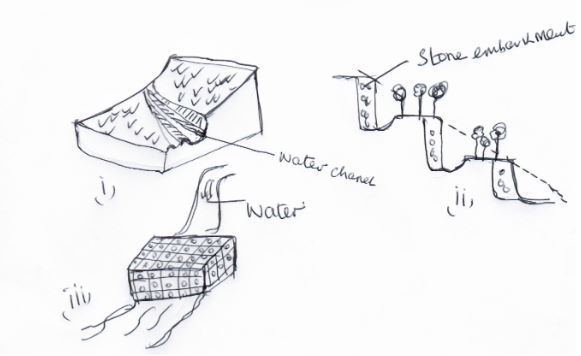
- The diagrams below illustrate different methods used in soil and water conservation. Study the methods and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the methods illustrated by (i) (ii) and (iii). (3mks)
- State two methods by which the structure in (iii) controls soil erosion. (2mks)
- Name two materials used to make the structure in (iii) above. (2mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
Answer any two questions from this section.
- Describe production of Napier grass under the following sub-headings.
- Land preparation (2mks)
- Planting and planting materials (2mks)
- Fertilizer application (2mks)
- Defoliation (2mks)
- Weed control (2mks)
- Explain six factors that can influence a well-designed crop rotation programme. (6mks)
- Give four signs that would enable you to identify compost manure that is ready for use. (4mks)
- Describe production of Napier grass under the following sub-headings.
- Describe procedure of preparing silage. (5mks)
- Outline five precautions taken in harvesting tea. (5marks)
- Describe the management practices carries out in a cabbage nursery. (10mks)
-
- Describe process of water treatment in a water treatment plant. (10mks)
- Briefly explain four factors influencing mass wasting. (4marks)
- Explain six cultural methods of controlling crop diseases. (6mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30MKS)
-
- Land size
- Socio-cultural factors
- Tastes and preferences
- Climatic conditions
- Technical skills of the farmer
- Market availability 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Minimizes labour
- Can be practiced on both slopy and flat areas
- No soil erosion
- Controls fungal diseases
- Economical use of water 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Use of heavy machinery on wet soil
- Working the soil when too wet or too dry
- Over cultivation/pulverization of the soil
- Monoculture 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Failure to reduce cost of production
- Not using improved production technics
- Failing to look for proper market
- Wrong enterprise chosen 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Allows adequate time for organic matter to decompose
- Allows adequate time for weeds to be dehydrated
- Allows for early planting so that crops establish early before the weeds grow
- Allows for soil borne pathogens and pests to die
- Minimizes labour competition. 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Hybrid – a crop developed by crossing different crop varieties under controlled pollination
- Composite – a crop developed under uncontrolled pollination. 2x1= (2mks)
- Domestication – process where both crops/plants and animals/ livestock depend on human beings for existence. 1x1 = (1mk)
-
- Gradual removal of shade
- Gradual reduction in amount of water applied
- Gradual reduction in frequency of water applied 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
-
- Volatilization of nitrates to Ammonia gas
- Leaching
- Washed away 1x1 = (1mk)
- Corrosive 1x1 = (1mk)
-
-
- Distribute forage throughout the year
- Provide feed for dry season
- Better full utilization of land
- Source of income e.g. selling baled hay 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Grass holds soil particles together
- Grass cover reduces run-off speed
- Grass reduces the impact of rain drops hence reducing splash erosion. 3 x ½ = (1 ½ mks)
-
- Dry brown lesions on stems, leaves and fruits
- Affected parts appear rotten
- Fruits fall off prematurely 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Produce large quantities of seeds
- Seeds remain viable in soil for long
- Weeds have effective means of dispersal
- Weeds have ability to propagate both by seeds and vegetatively
- Weeds have elaborate root system
- Some weeds have underground structures that are difficult to control
- Some are able to survive with limited nutrients 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Introduce nitrogen fixing bacteria to fix Nitrogen.
- Promote Nitrogen fixation before planting 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- Small pieces of land/land scarcity
- Lack of enough capital
- Lack of enough labour
- Lack of enough technology 2 x ½ = (1mk)
-
- States that profit is maximum where total cost of production is minimum and Net revenue is maximum
- Where margin revenue and marginal cost are the same 1 x1 = (1mk)
-
- Stocking rate – Number of animals/ livestock maintained per unit area of land
- Carrying capacity – Ability of forage stand to maintain a particular number of livestock units per unit area. 2x1 = (2mks)
-
- Training
- Mechanization
- Improve terms and conditions
- Labour supervision 4 x ½ = (2mks)
-
- Application of lime
- Application of basic fertilizer
- Application of acidic fertilizer
- Application of Sulphur 4 x ½ = (2mks)
SECTION B (20MKS)
-
- A- side grafting
B- layering (Trench)
C – Marcotting
D – tissue culture 3 x 1= (3mks) -
- X- Scion
- Y- Root stock 2 x 1 = (2mks)
- Hard wood where stem cannot bend easily to reach the ground. 1x1 = (1mk)
-
- Early maturing
- Big bunch
- High annual yield
- Control viral diseases 2 x 1 = (2mks)
- A- side grafting
-
-
- - Stinging Netle (Urtica masaica)
- - Nut grass (cyperus rotundus) 2x1 = (2mks)
- Has underground bulbs 1x1 = (1mk)
-
- A - Raises cost of production/difficult to control
- B - Lowers quality of pasture 2x1 = (2mks)
-
-
-
- Cut off drain
- Bench terraces
- Gabion/porous dam 3x1 = (3mks)
-
- Reduce erosive force of run-off.
- Trap soil flow through stones 2x1 = (2mks)
-
- Wire mesh
- Stones /gravel 2x1 = (2mks)
SECTION C (40MKS)
-
-
- Land preparation
- Done during dry season
- Clearing vegetation
- Remove stumps
- Remove perennial weeds
- Carry cultivation to harrow to moderate tilth
- Ridging making furrows of 90-100cm apart
- Make hole on top of ridges 50cm apart
- Fill holes with phosphatic fertilizer and organic manure 2x1 = (2mks) - Planting and planting materials
- Select desirable variety as per ecological zone
- Place stem cutting i.e 2-3 nodes/splits in the holes made in the ridges at onset of long rain in slanting angle of 45⁰
- Add phosphatic fertilizer mixed with organic manure
- Cover with soil and firm at base to avoid erosion/exposure of material 2x1= (2mks) - Fertilizer application
- Top dress with nitrogenous fertilizer at base of stump 6-8wks after planting/weeding
- Top-dress at onset of rains
- Top dress after harvesting for high yield and regeneration 2x1 = (2mks) - Defoliation
- When 3-5 months/1.5m high
- Use sharp panga to avoid damaging stump and suppress regrowth
- Cut 2.5-5cm above ground
- When leaves proportion is greater than stems 2x1= (2mks) - Weed control
- Uproot with hands
- Slashing/cutting at base of woody weed with panga
- Digging with jembe during dry and rainy season
- Mulching at base of stump to suppress weed
- No herbicide use to avoid poisoning livestock. 2x1= (2mks)
- Land preparation
-
- Crop root depth
- Crop nutrient requirement
- Weed control
- Pests and diseases control
- Soil fertility
- Soil structure 6x1= (6mks)
-
- Volume of heap/material in the heap goes down
- Materials break easily to small pieces when pressed between finger
- Growth of fungi/moulds in manure
- Temperature of the material goes down 4x1 = (4mks)
-
- Silage making procedure
- Prepare silo before harvesting depending on amount to be ensiled
- Cut crop and wilt for 6-12hrs
- Chop
- Put in silo at 10-12cm and compact
- Fill silo rapidly (less than 2 day)
- Check temperature (maintain at 32⁰C)
- Cover with polythene sheet or dry grass to protect from air and water
- Dig a trench around silo 5x1= (5mks)
- Precautions taken in harvesting tea;
- Plucked tea should be put in woven baskets and not polythene to allow free air movement.
- Pluck two leaves and a bud only because 3-4 leaves colder leaves) lower the quality due to low level of caffeine
- Leaves should not be compressed in the baskets as this can cause them to heat up and turn brown.
- Plucked tea should be kept cool and shaded while plucking continues and awaiting transportation to the factory.
- Plucked tea should be taken to the factory the same day it is harvested. (1 x5 = 5marks)
- Management practices in a cabbage nursery
- Regular watering/morning and evening
- Weed control by uprooting
- Pricking out – remove weak seedlings and transfer to seedling bed
- Mulching – apply a light mulch after sowing and remove when seedling shot to emerge
- Shading – apply shade above the nursery
- Pest control – spray suitable pesticide
- Disease control – spray suitable fungicides
- Hardening off – gradual removal of shade and reduce rate of watering 5 x 2= (10mks)
- Silage making procedure
-
-
- Filtration at intake - use sieve to remove large particles
- Softening – Add soda ash to soften water
- Add allum to allow coagulation and settling of particles
- Filtration – water passes through different sizes of particles in a filtration tank
- Chlorination – Chlorine added in chlorination tank
- Storage – water stored in large well protected ranks
- Distribution – By piping or pumping to consumers Any 5x2= (10mks)
- Briefly explain four factors influencing mass wasting. (4marks)
- The slope of the land-Steep slopes leads to faster movement of materials.
- The nature of material-Mass wasting occurs easily where massive rocks overlie sedimentary rocks which have clay material underneath and also if the material contains a lot of water.
- Climate-Heavy rainy periods encourage wasting
- Vegetation cover- It is easy and faster in bare ground than where it is covered with vegetation.
- Human activities-E.g deforestation, building, quarring etc interferes with the stability of surface layers.
- Forces within the earth’s crust e.g earth tremors and some volcanic eruptions.
-
- Using healthy planting material
- Using disease resistant varieties
- Proper drying of cereals and pulses
- Heat treatment
- Proper spacing
- Proper spacing
- Proper seedbed preparation
- Held hygiene 6x1 = (6mks)
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Form 3 End Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students