Instructions to candidate
- Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided
- All working MUST be clearly shown where applicable
- KNEC mathematical tables and silent non-programmable electronic calculators may be used
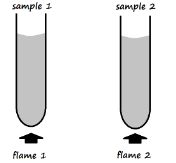
- Equal volumes of water in two separate boiling tubes were separately heated using two different Bunsen burner flames.
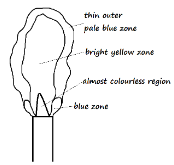
Sample 1 registered a higher temperature than sample 2.- Name and draw flame 2 (2 Marks)
Name _____________________________________________________________________ - State the condition under which flame 1 is produced by a Bunsen burner (1 Mark)
- Name and draw flame 2 (2 Marks)
- The table below shows the colours obtained when some indicators were added to various solutions
Solution Phenolphathalein Indicator Methyl Orange INdicator Indicator W Distilled water Green Ammonium hydroxide Pink Blue Hydrochloric acid Red Red Sodium hydroxide Violet - Fill in the blank spaces in the table above? (3 Marks)
- State the possible identity of Indicator W. (1 Mark)
- What is the advantage of using Indicator W? (1 Mark)
- State the laboratory rules that should be applied to prevent the following accidents:
- Mistaking hydrochloric acid to be distilled water (1 Mark)
- A student got burnt after secretly lighting up a magnesium ribbon (1 Mark)
- A student got severe stomach upset after eating some bread during a Chemistry laboratory session (1 Mark)
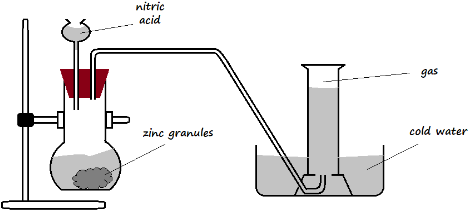
- The setup below was arranged for the collection of dry hydrogen gas in the laboratory. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify two mistakes in the set-up (2 Marks)
- Suggest remedies for the mistakes identified in a) above (2 Marks)
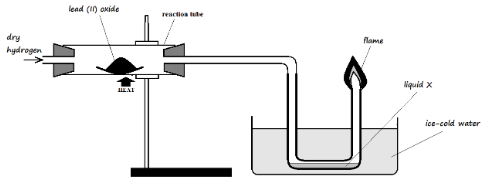
- Dry hydrogen gas was passed over heated lead (II) oxide in a combustion tube as shown in the diagram below.
- State two observations that were made in the combustion tube (2 Marks)
- Write a word equation for the reaction taking place in the combustion tube (1 Mark)
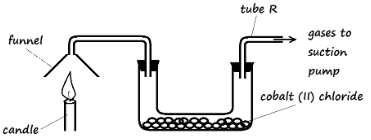
- The products of a burning candle were passed through a U-tube containing anhydrous cobalt (II) chloride as shown in the diagram below
- State the observation that was made in the U-tube (1 Mark)
- Write a word equation for the reaction taking place in the U-tube (1 Mark)
- Name the gas that came out through tube R (1 Mark)
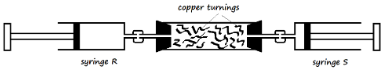
- Copper turnings were packed in a combustion tube connected to two syringes as shown in the diagram below. Syringe R contained 120cm3 of air while syringe S was empty.
The copper turnings were heated strongly as air was being passed from syringe R to syringe S slowly and repeatedly, until there was no further change in volume of air in syringe R. The final volume of air was 95.5cm3.- Why was air passed over the heated copper turnings slowly and repeatedly? (2 Marks)
- State one observation made in the combustion tube during the experiment (1 Mark)
- Determine the percentage of oxygen used during the experiment (2 Marks)
- The apparatus below was used to separate a mixture of liquid A and B
State two properties of the liquids that make it possible to separate them using this apparatus (2 Marks) - A mixture contains iron filings, sulphur, and table salt. Describe a procedure that a student can use to separate the mixture and recover all the components of the mixture. (3 Marks)
-
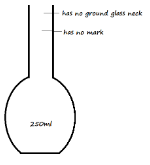
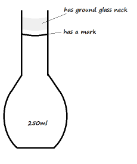
- Draw two separate diagrams to differentiate a flat-bottomed flask of 250ml and a volumetric flask of 250ml (2 Marks)
- State the main use of a volumetric flask (1 Mark)
- Flat bottomed flasks and volumetric flasks are made of glass. Explain (1 Mark)
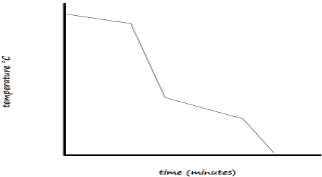
- The diagram below shows the cooling curve of a certain substance
Is this substance pure or impure? Explain (2 Marks) - Write word equations for the following reactions: (3 Marks)
- Sodium and water
- Calcium oxide and nitric acid
- Magnesium carbonate and hydrochloric acid
- Salt is normally sprinkled on roads during winter in temperate countries.
- State and explain why salt is put on roads during winter (2 Marks)
- Why is this practice of great concern to motorists (1 Marks)
- Explain how each of the following components is removed from a sample of air, before the fractional distillation of liquefied air:
- Carbon (IV) oxide (1 Mark)
- Water vapour (1 Mark)
- Solid impurities (1 Mark)
- Why is it important to remove carbon (IV) oxide from the air sample? (1 Mark)
- Name the constituent element in each of the following compounds:
- Copper (II) sulphate (1½ Marks)
- Sodium nitrate (1½ Mark)
- Potassium iodide (1 Mark)
-
- Complete the table below (3 Marks)
English Name Symbol Sodium P Lead K Au Hg - State the difference between a compound and a mixture (2 Marks)
- Complete the table below (3 Marks)
- The diagram below represents a change
- What type of change is represented above? (1 Mark)
- Give four characteristics of the change (2 Marks)
- Give any three apparatus that are used to measure accurate volumes of liquids and solutions in the laboratory (3 Marks)
- Define the following:
- Boiling point (1 Mark)
- Matter (1 Mark)
- Indicator
- Substance W is highly soluble in propanone, while substance M has low solubility in propanone. Which of the two substances will travel the shortest distance on an adsorbent material during paper chromatography? Explain (3 Marks)
- Name the following apparatus and state its use in the laboratory (2 Marks)
- When separating solid copper (II) sulphate from a copper (II) sulphate solution, the solution was first heated then transferred to a water bath. Why was it important to heat the solution over a water bath? (2 Marks)
- State two major differences between the properties of solids and those for gases (2 Marks)
- After carrying out the process of distillation, describe how one can confirm that the distillate contains no dissolved solute (2 Marks)
- Which method of separation can be used to obtain the following:
- Petrol from crude oil (1 Mark)
- Oil from sunflower seeds (1 Mark)
- Distinguish between a homogenous mixture and heterogenous mixture (2 Marks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Equal volumes of water in two separate boiling tubes were separately heated using two different Bunsen burner flames.
Sample 1 registered a higher temperature than sample 2.- Name and draw flame 2 (2 Marks)
Name - Luminous flame - State the condition under which flame 1 is produced by a Bunsen burner (1 Mark)
- It is produced when the air hole is fully open
- Name and draw flame 2 (2 Marks)
- The table below shows the colours obtained when some indicators were added to various solutions
- Fill in the blank spaces in the table above? (3 Marks)
Solution Phenolphathalein Indicator Methyl Orange INdicator Indicator W Distilled water Colourless Orange Green Ammonium hydroxide Pink Yellow Blue Hydrochloric acid Colourless Red Red Sodium hydroxide Pink Yellow Violet - State the possible identity of Indicator W. (1 Mark)
- Universal indicator
- What is the advantage of using Indicator W? (1 Mark)
- It shows the strengths of acids and bases
- Fill in the blank spaces in the table above? (3 Marks)
- State the laboratory rules that should be applied to prevent the following accidents:
- Mistaking hydrochloric acid to be distilled water (1 Mark)
- Label all chemicals correctly to avoid confusion
- A student got burnt after secretly lighting up a magnesium ribbon (1 Mark)
- Do not carry out any experiment without informing the teacher
- A student got severe stomach upset after eating some bread during a Chemistry laboratory session (1 Mark)
- Avoid tasting or eating anything in the laboratory to prevent poisoning
- Mistaking hydrochloric acid to be distilled water (1 Mark)
- The setup below was arranged for the collection of dry hydrogen gas in the laboratory. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify two mistakes in the set-up (2 Marks)
- The stem of the thistle funnel is not dipped into the solution in the flask
- The gas is collected over water (should be dry)
- Suggest remedies for the mistakes identified in a) above (2 Marks)
- Extending the stem of the thistle funnel into the solution, or using a dropping funnel
- Collecting the gas by using downward displacement of air, or using a syringe
- Identify two mistakes in the set-up (2 Marks)
- Dry hydrogen gas was passed over heated lead (II) oxide in a combustion tube as shown in the diagram below.
- State two observations that were made in the combustion tube (2 Marks)
- Orange lead (II) oxide changes to a grey substance
- Droplets of a colourless liquid are observed on the cooler parts of the tube
- Write a word equation for the reaction taking place in the combustion tube (1 Mark)
Lead (II) oxide + Hydrogen ? Lead metal + Water
- State two observations that were made in the combustion tube (2 Marks)
- The products of a burning candle were passed through a U-tube containing anhydrous cobalt (II) chloride as shown in the diagram below
- State the observation that was made in the U-tube (1 Mark)
- The blue solid turns pink
- Write a word equation for the reaction taking place in the U-tube (1 Mark)
Anhydrous cobalt (II) chloride + Water ? Hydrated Cobalt (II) chloride - Name the gas that came out through tube R (1 Mark)
- Carbon (IV) oxide
- State the observation that was made in the U-tube (1 Mark)
- Copper turnings were packed in a combustion tube connected to two syringes as shown in the diagram below. Syringe R contained 120cm3 of air while syringe S was empty.
The copper turnings were heated strongly as air was being passed from syringe R to syringe S slowly and repeatedly, until there was no further change in volume of air in syringe R. The final volume of air left was 95.5cm3.- Why was air passed over the heated copper turnings slowly and repeatedly? (2 Marks)
- It was passed slowly to give time for the copper turnings to react with oxygen, and passed repeatedly to ensure all oxygen reacts
- State one observation made in the combustion tube during the experiment (1 Mark)
- The copper turnings turn from brown to a black substance
- Determine the percentage of oxygen used during the experiment (2 Marks)
Volume of air used = Initial volume − Final volume
= 120 − 95.5
= 24.5cm3
% Air used = volume of air used × 100
initial volume of air
= 24.5 × 100
120
= 20.42%
- Why was air passed over the heated copper turnings slowly and repeatedly? (2 Marks)
- The apparatus below was used to separate a mixture of liquid A and B
State two properties of the liquids that make it possible to separate them using this apparatus (2 Marks)- The liquids have different densities
- The liquids are immiscible
- A mixture contains iron filings, sulphur, and table salt. Describe a procedure that a student can use to separate the mixture and recover all the components of the mixture. (3 Marks)
- Use a magnet to remove the iron filings from the mixture. Add water to the remaining mixture and stir to dissolve the table salt. Filter the mixture to obtain sodium chloride solution as a filtrate, and sulphur as a residue. Heat the filtrate to saturation and allow to cool to obtain crystals of sodium chloride.
-
- Draw two separate diagrams to differentiate a flat-bottomed flask of 250ml and a volumetric flask of 250ml (2 Marks)
Flat-bottomed flask Volumetric flask - State the main use of a volumetric flask (1 Mark)
- To prepare solutions of specific concentration
- Flat bottomed flasks and volumetric flasks are made of glass. Explain (1 Mark)
- Glass is transparent and makes reactions in the vessels easily visible
- Draw two separate diagrams to differentiate a flat-bottomed flask of 250ml and a volumetric flask of 250ml (2 Marks)
- The diagram below shows the cooling curve of a certain substance
Is this substance pure or impure? Explain (2 Marks)- Impure. It melts and boils over a range of temperatures//It does not have a sharp melting point and boiling point.
- Write word equations for the following reactions: (3 Marks)
- Sodium and water
Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas - Calcium oxide and nitric acid
Calcium oxide + Nitric acid → Calcium nitrate + Water - Magnesium carbonate and hydrochloric acid
Magnesium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Carbon (IV) oxide + Water
- Sodium and water
- Salt is normally sprinkled on roads during winter in temperate countries.
- State and explain why salt is normally sprinkled on roads (2 Marks)
- The salt makes the ice on the road to melt away. Salt acts as an impurity and lowers the freezing point of water.
- Why is this practice of great concern to motorists (1 Marks)
- Salt increases the rate at which motor vehicle body parts rust.
- State and explain why salt is normally sprinkled on roads (2 Marks)
- Explain how each of the following components is removed from a sample of air, before the fractional distillation of liquefied air:
- Carbon (IV) oxide (1 Mark)
- By bubbling the sample of air through concentrated sodium hydroxide solution or concentrated potassium hydroxide solution
- Water vapour (1 Mark)
- By cooling the air sample to temperatures below -25°C
- Solid impurities (1 Mark)
- Through filtration of the air sample//Through electrostatic precipitation of the air sample
- Why is it important to remove carbon (IV) oxide from the air sample? (1 Mark)
- Carbon (IV) oxide solidifies at extremely low temperatures and may block the thin pipes in the fractional distillation process system.
- Carbon (IV) oxide (1 Mark)
- Name the constituent element in each of the following compounds:
- Copper (II) sulphate (1½ Marks)
- Copper, Sulphur, and Oxygen
- Sodium nitrate (1½ Mark)
- Sodium, Nitrogen, and Oxygen
- Potassium iodide (1 Mark)
- Potassium and iodine
- Copper (II) sulphate (1½ Marks)
-
- Complete the table below (3 Marks)
English Name Symbol Sodium Na Phosphorus P Lead Pb Potassium K Gold Au Mercury Hg - State the difference between a compound and a mixture (2 Marks)
- A compound is a substance in which the elements are chemically combined and have a new property, while a mixture is composed of various elements or substances that are not chemically combined and each component retains its physical and chemical properties.
- Complete the table below (3 Marks)
- The diagram below represents a change
- What type of change is represented above? (1 Mark)
- Temporary physical change
- Give four characteristics of the change (2 Marks)
- No new substances are formed
- The change is reversible
- There is no net heat change
- There is no change in mass
- What type of change is represented above? (1 Mark)
- Give any three apparatus that are used to measure accurate volumes of liquids and solutions in the laboratory (3 Marks)
- Pipette
- Burette
- Syringe
- Volumetric flask
- Define the following:
- Boiling point (1 Mark)
- This is the constant temperature at which a liquid is converted to gas when heated.
- Matter (1 Mark)
- Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space
- Indicator
- This is a chemical substance that shows a specific colour when added to acid, and a different specific colour when added to a base.
- Boiling point (1 Mark)
- Substance W is highly soluble in propanone, while substance M has low solubility in propanone. Which of the two substances will travel the shortest distance on an adsorbent material during paper chromatography? Explain (3 Marks)
- Substance M. Its inability to dissolve makes it stick more to the adsorbent material.
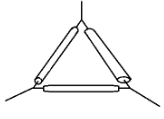
- Name the following apparatus and state its use in the laboratory (2 Marks)
- Pipe-clay triangle. For holding crucibles during heating.
- When separating solid copper (II) sulphate from a copper (II) sulphate solution, the solution was first heated then transferred to a water bath. Why was it important to heat the solution over a water bath? (2 Marks)
- To prevent spitting of the copper (II) sulphate crystals, and to prevent loss of the water of crystallization.
- State two major differences between the properties of solids and those for gases (2 Marks)
- The forces of attraction between solid particles are strong while those in gases are weak
- Solids have a definite shape and volume while gases have a definite volume but no definite shape
- Solid particles vibrate within fixed positions while liquid particles can change positions.
- After carrying out the process of distillation, describe how one can confirm that the distillate contains no dissolved solute (2 Marks)
- Put a sample of the distillate on a clean watch glass and heat gently to evaporation. If the watch glass remains clean, it indicates that the distillate no longer contains dissolved solute.
- Which method of separation can be used to obtain the following:
- Petrol from crude oil (1 Mark)
- Fractional distillation
- Oil from sunflower seeds (1 Mark)
- Solvent extraction
- Distinguish between a homogenous mixture and heterogenous mixture (2 Marks)
- A homogenous mixture is one in which the components cannot be distinguished, while a heterogenous mixture is one in which the components can be clearly distinguished.
- Petrol from crude oil (1 Mark)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions and Answers - Form 1 End Term 3 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students