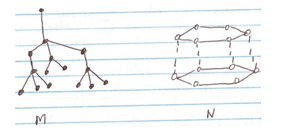END OF TERM 3
CHEMISTRY
FORM 2
- The electron arrangement of ions X3+ and Y2- are 2.8 and 2.8.8 respectively.
- Write the electron arrangement of elements X and Y.
X - (1 mk)
Y - (1 mk) - Write the formula of the compound that would be formed between element X and Y. (1 mk)
- Write the electron arrangement of elements X and Y.
- Study the equation below;
Mg(s) + ZnO(s) → MgO(s) + Zn(s)- By use of arrows, indicate oxidation and reduction reactions in the equation. (2 mks)
- Name the reducing agent in the above reaction. (1 mk)
- Distinguish between the terms deliquescent and efflorescent salts. (2 mks)
- The table below shows PH value of different solutions.
Solution A B C D Ph 14 7 2 11 - Which solution is likely to be sugar solution? (1 mk)
- Two of the solutions were found to react with both aluminium oxide and zinc oxide.
Identify the two giving reasons. (1mk)
- Identify the methods that are most appropriate to obtain. (3 mks)
- Oil from coconut
- Diesel from crude oil
- Sugar crystals from sugar solution
- An element Q has an electron arrangement of 2.8.5
- Identify the group and period to which it belongs.
- Group - (1 mk)
- Period - (1 mk)
- Is element Q a metal or a non-metal? Explain (2 marks)
- Identify the group and period to which it belongs.
- Carbon has two isotopes namely 146 C and 126 C Calculate the relative abundance of these two isotopes if the relative atomic mass of carbon is 12.4. (3mks)
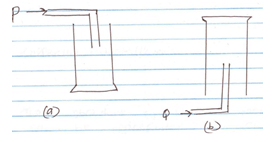
- The diagram below shows how two gases, P and Q were collected.
- Name the two methods shown above.
a - (1 mk)
b - (1 mk) - State the property of Q that enables it to be collected as shown above. (1 mk)
- Give an example of a gas that is collected using the method shown in (b) above. (1 mk)
- Name the two methods shown above.
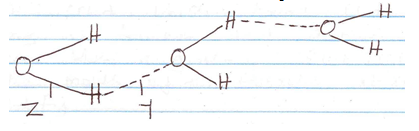
- The structure of water molecule can be represented as shown below.
Name the type of bonds represented by letters Y and Z.
Y – (1 mk)
Z - (1 mk) - Element R has a valence of 2, element Q has a valence of 1 while element B has a valence of 3. Write the chemical formulae of their sulphates, phosphates and nitrates. (4½ mks)
Element Sulphates Phosphates Nitrates R B Q - When a white solid X is heated, a yellow solid which turns white on cooling is formed and a brown gas is seen. When a glowing splint is placed at the mouth of the test-tube it relights.
- Identify;
- Solid X - (1 mk)
- The brown gas - (1 mk)
- Write an equation for the decomposition of solid X. (1 mk)
- Identify;
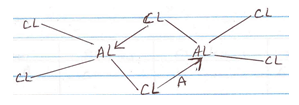
- Below is a structure of aluminium chloride.
- Identify bond A. (1 mk)
- State the observations made when aluminium chloride solution is tested with blue and red litmus paper. Explain. (2 mks)
- Which particles conduct electricity in;
- Molten lead (ii) bromide (1 mk)
- Aqueous sodium chloride (1 mk)
- Graphite (1 mk)
- The following table gives the structures of the different atoms. Study it and answer the questions that follow. (A, B, C, D and E do not represent the actual symbols of the elements).
Atom Protons Electrons Neutrons A 5 5 6 B 9 9 10 C 10 10 11 D 15 15 16 E 10 10 12 - What is the mass number of atom B? (1/2mk
- Which of the atoms has a mass number of 11? (1/2mk)
- Which of the atoms represent isotopes of the same element. (1 mk)
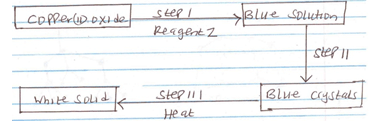
- Study the following flow chart and answer the questions that follow.
- .
- Identify reagent Z. (1 mk)
- Identify the white solid. (1 mk)
- Write a chemical equation for the formation of the blue solution. (1 mk)
- .
- State two properties that makes aluminum to be used in making of overhead electric cables.(2 mks)
- The structures below represent two allotropes of carbon. Study them and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the allotropes labeled
M - (1/2 mks)
N - (1/2 mks) - Explain in terms of structure and Bonding which of the two allotropes;
- Conducts electricity. (1 mk)
- Is used in making drilling equipment. (1 mk)
- Identify the allotropes labeled
- The table below shows properties of some substances.
Substance Melting point Boiling point Electrical Conductivity Solid Liquid A -112 -107 Poor Poor B 801 1413 Poor Good C 97.5 880 Good Good D 44 280 Poor Poor E 1700 2200 Poor Poor F -110 46.3 Poor Poor - Select a substance which;
- Has a giant ionic structure. (1 mk)
- Is a metal (1 mk)
- Has a giant atomic structure. (1 mk)
- Using dots (.) and crosses (x) illustrate bonding in ammonia molecule (NH3). (N=7, H=1) (2 mks)
- A student placed a small piece of sodium metal in a trough of water.
- State two observations made? (2 mks)
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction that took place. (1 mk)
- Select a substance which;
- The products formed by action of heat on nitrates of elements A, B and C are shown below.
Nitrate Product Formed A Metal oxide + Nitrogen(iv)Oxide + oxygen B Metal + Oxygen + Nitrogen(iv)oxide C Metal nitrite + Oxygen - .
- Arrange the metals inorder of increasing reactivity. (1 mk)
- Which element forms a soluble carbonate? (1 mk)
- Give an example of element B. (1 mk)
- Write an equation to show the effect of heat on each of the following;
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate. (1 mk)
- Copper(ii)carbonate (1 mk)
- .
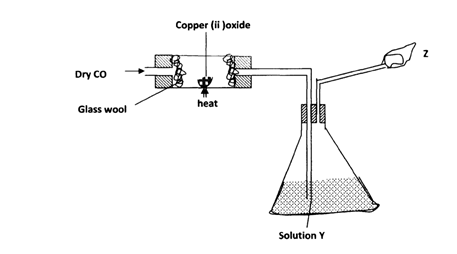
- The figure below is used to investigate the effect of carbon (ii) oxide on copper (ii) oxide.
Study it and answer the questions that follow Copper (ii) oxide.- What will be observed in the combustion tube at the end of the experiment? (l mk)
- Identify Y and give its use (2mks)
- Why is it necessary to burn the excess gas at Z (l mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction taking place at Z (l mk)
- Give two uses of carbon (II) oxide (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- X – 2.8.3 (1 mk)
Y – 2.6 (1 mk) - X2Y3 (1 mk)
- X – 2.8.3 (1 mk)
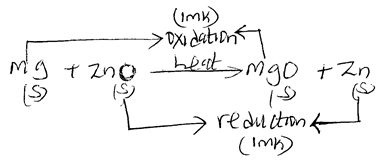
- Reducing agent – Mg (1 mk)
- Deliquescent salts absorbs water from the atmosphere and form a solution. (1 mk) while efflorescent salt loose water of crystallization to the atmosphere. (1 mk)
- B (1 mk)
- A and C (1 mk for each)
- .
- Solvent extraction (1 mk)
- Fractional distillation (1 mk)
- Crystallisation / Evaporation (1 mk)
- .
- Group – V (1 mk)
- Period – 3 (1 mk)
- A non metal (1 mk)
- .
- Let the relative abundance of isotope 126 C be X. relative abundance of isotope 146 C will be (100 – x)
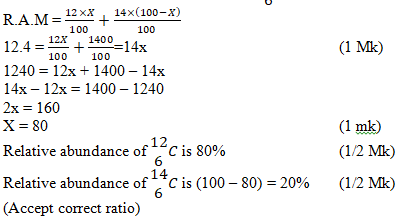
- .
- Downward delivery (upward displacement of air) (1 mk)
- Upward delivery (Downward displacement of air) (1 mk)
- It is less dense than air. (1 mk)
- Hydrogen/Ammonia (1 mk for any)
- .
- Y – Hydrogen bonding (1 mk)
Z – Covalent bonding (1 mk)
Element Sulphates Phosphates Nitrates R RSO4 R3(PO4)2 R(NO3)2 B B2(SO4)3 BPO4 B(NO3)3 Q Q2SO4 Q3PO4 QNO3 - .
- Zn(NO3)2 (1 mk)
- Nitrogen(iv)oxide or NO2 (1 MK)
- .
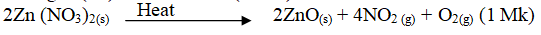
- .
- Dative bond or coordinate bond (1 mk)
- Blue litmus paper turns to red (1 mk) while red remains red since aluminium chloride dissolves in water forming an acidic solution (1 mk)
- Mobile ions (1 mk)
- Mobile ions (1 mk)
- Delocalised electrons (1 mk)
- 9 + 10 = 19 (1 mk)
- A (1 mk)
- C and E (1 mk)
- Dilute sulphuric (vi) acid or H2SO4(aq) (1 mk)
- anhydrous copper(ii)sulphate (1 mk)
- CuO(s) + H2SO4(aq) CuSO4(aq) + H2O(l)
-
- Its light (low density)
- Its not easily corroded
- It’s a good conductor of electricity
(2 mks for any two)
- .
- M – Diamond (1/2 mk)
N – Graphite (1/2 mk) - .
- N (1/2 mk) – it has delocalised electrons. (1/2 mk)
- M (1/2 mk) – it is hard since it contains giant atomic structure. (1/2 mk)
- M – Diamond (1/2 mk)
- .
- .
- B (1 mk)
- C (1 mk)
- E (1 mk)
- N – 2.5
H – 1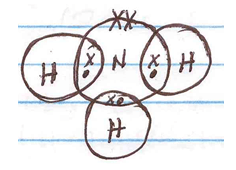
-
- .
- A hissing sound is produced.
- A ball like substance is formed.
- The ball like substance darts around the water surface.
- The solution formed turns red litmus paper to blue.
(2 mks for any two)
- 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) (1 mk)
- .
- .

- C (1 mk)
- Silver
-
- Black solid
- NaOH or KOH
- To absorb C02
- It is poisonous
- 2C0 (g) + 02(g) → 2C02(g)
- .
- Fuel
- Reducing agent’J
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Questions with Answers - Form 2 End Term 3 Exams 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students