SECTION A : (40 MARKS)
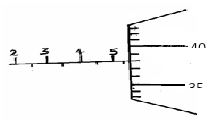
- Figure 1 shows a micrometer with a negative error of 0.02mm used to measure the diameter of a ball bearing.
Record the diameter of the ball. (2mks) - An oil drop of volume 0.4mm³ was placed on a clean water surface. It spreads to form a monolayer circular patch of area 2000mm². Use this data to calculate the thickness of a molecule of oil. (3mks)
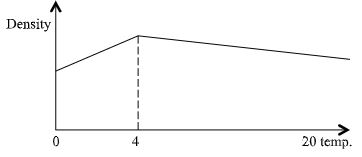
- A fixed mass of pure water was heated from 0°C to 2O°C. Sketch a graph of density of the water against temperature. (2mks)
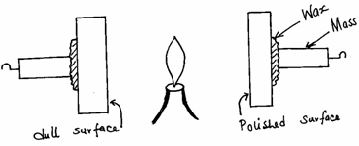
- Two 10g masses are fixed onto two similar aluminum plates, one polished and the other painted black, using wax as shown in the figure below.
- State which one will fall first (1mk)
- give a reason for the answer above. (1mk)
- The figure below shows a negatively charged leaf electroscope.
State and explain what happens to the electroscope when highly positive rod is brought near the cap of the electroscope. (2mks) - State one advantages of alkaline accumulator over the lead-acid cell. (1mks)
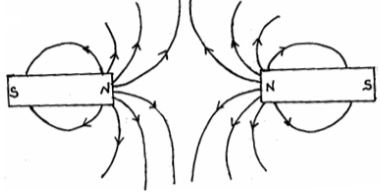
- The figure below shows two magnets whose North poles are brought close to each other.
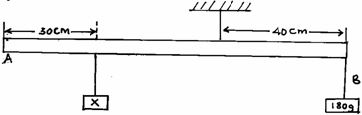
Indicate the magnetic field pattern between the two magnets. (2mks) - The diagram shows a system in equilibrium with the uniform rule supported at Q and resting horizontally.
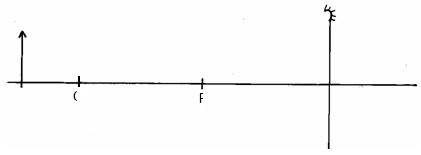
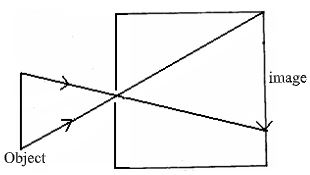
The rule is 1m long and weighs 1.8N. Calculate the weight of the block X. (3mks) - An object is placed in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure below.
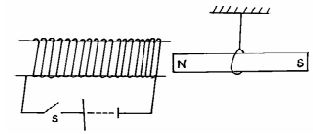
Complete the diagram to show how the image is formed. (3mks) - State and explain what will happen to the freely suspended magnet when the switch S is closed. (2mks)
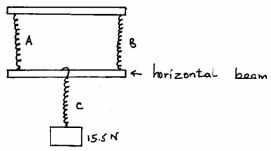
- Three identical springs A, B and C and of negligible weight are used to support a 15.5N weight as shown in the figure below.
If the weight of the horizontal beam is 0.5N, determine the extension of each spring given that the spring constant of each spring is 4N/cm (3mks) - State one of the major differences between mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. (1mk)
- A boat sent an ultrasound signal to the bottom of the sea and its echo received after 0.5 seconds. If the velocity of the sound in water is 1500m/s, calculate the depth of the sea. (3mks)
- 1800cm3 of fresh water of density 1g/cm3 is mixed with 2200cm3 of sea water of density 1.025g/cm3
Calculate the density of the mixture (4mk) - Distinguish between a basic physical quantity and a derived physical quantity giving an example of each. (3mks)
Physical quantity Derived physical quantity difference example - State any two ways by which frictional force between two surfaces can be reduced. (2mk)
- Explain why large mercury drops form oval balls on a glass slide (1mks)
SECTION B: (60 MARKS)
-
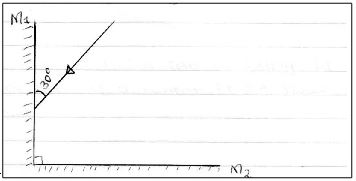
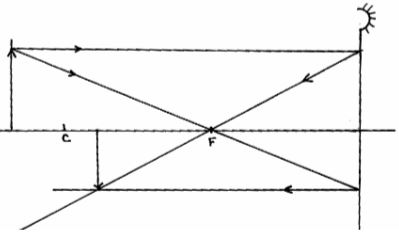
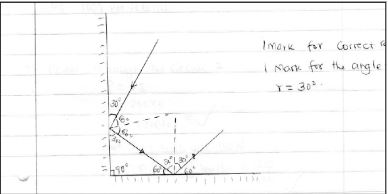
- Figure1 below shows two mirrors M1 and M2 are inclined at right angles to each other.
Trace the reflection of the ray through the two mirrors and find the angle between the incident ray and reflected ray of mirror M2 . (2mks) - Distinguish between Lunar and Solar eclipse by stating the arrangements that lead to the formation of each (4mks)
- Complete the diagram below to show how an image is formed in a pinhole camera. (3mks)
- State two characteristics of the image above. (2mks)
- State two changes that will be observed about this image if the pinhole is made wider. (2mks)
- If x = 30cm, y = 12cm and the heights of the image is 4cm, calculate the height of the object. (3mks)
- Figure1 below shows two mirrors M1 and M2 are inclined at right angles to each other.
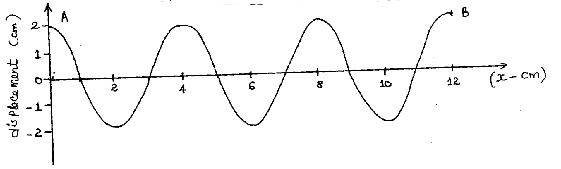
- The diagram below shows the wave profile of a transverse wave.
- Determine
- the amplitude of the wave. (1mk)
- the wavelength of the wave in metres. (2mks)
- the period of the wave if it takes 1.5 seconds to move from A to B. (3mks)
- Calculate:
- the frequency of the wave. (2mks)
- the velocity of the wave. (2mks)
- Determine
-
- What is diffusion? (1mk)
- state two factors that affect diffusion (2mks)
- A smoke cell contains a mixture of trapped air and smoke. The cell is brightly lit and viewed through a microscope. State and explain what is observed. (2mks)
- A beaker is filled completely with water. A spoonful of common salt is added slowly. The salt dissolves and the water does not overflow.
- State why the salt is added slowly. (1mk)
- Why doesn’t the water overflow? (1mk)
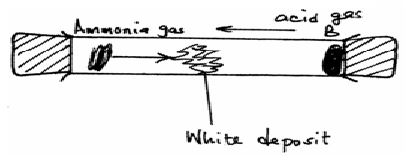
- In the figure below, ammonia gas and acid gas diffuse and react to form a white deposit on the walls near ammonia gas of a long glass tube as shown.
- What conclusion can be made from this result of this experiment? (1mk)
- why is a white deposit formed near ammonia gas? (1mk)
The experiment is performed at a lower temperature. - State what would happen to the rate of diffusion of the gases. (1mk)
- explain your answer in (iii) above (1mk)
-
- Give four differences between mass and weight. (4mks)
Mass weight - State Pascal’s Principle. (1mk)
- Name two applications of Pascal’s Principle. (2mks)
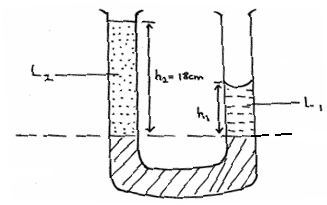
- Figure 3 shows a U-tube containing two liquids L1 and L2 of densities 1.6g/cm³ and 0.8g/cm³ respectively in equilibrium.
Given that h2 = 18cm, determine the value of h1 . (3mks)
- Give four differences between mass and weight. (4mks)
-
- Define current and state its SI unit ( 2mks)
- A charge of 120 coulombs flow through a lamp every minute. Calculate the current flowing through the lamp. ( 3mks)
- Differentiate between open and closed circuits. ( 2mks)
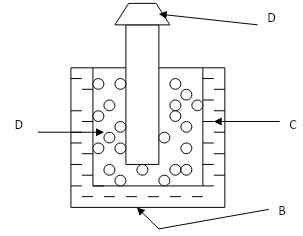
- The diagram bellow shows a dry cell. Use to answer to the question that follows.
- State the polarities of A and B. (2 mks)
- Name the chemical substances in the parts labeled C and D ( 2mks)
- Give reasons why it is necessary to leave the caps of the cells open when charging an accumulator ( 1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
- + 5.5
0.38 – 1mk (5.88)
5.88
+ 0.02
5.90mm 1mk (5.90)
= 9.112m - Ad form = V 1mk
2000d = 0.4 1mk
substitut d = 0.4
2000
= 2 x 10-4 mm
answer = 2 x 10-7m 1mk
axis
1mk label
1mk curve (4° seen)- Mass on dull tin plates falls off before mass on polished tin. 1mk
- Dull tin absorbs heat faster than polished tin (it heats up faster and wax on it melts before 1mk
-
- the leaf collapse and after sometime its divergence increases. This is due to opposite charge induced to the electroscope neutralizing negative charges. Then the electroscope becomes positively charged hence divergence increases since the rod is highly charged.
-
- It can give a larger current.
- It can be left in the discharge condition for a long time without damage.
- It requires less attention.
- It is lighter. 1, 1mks any 2 correct
pattern 1mk
Arrows 1mk- Clockwise moment = anticlockwise moment
0.3x + 1.8 x 0.1 = 1.8 x 0.4 1mk
expression
ans x = 1.8N 1mk
each ray with arrows 1,1mks
image 1mk-
- Magnet will be repelled 1
- Coil is magnetized with end near magnet acquiring North Pole 1
- For A and B
e = ¼ x 8 1mk
= 2cm each 1mk
For C
E = 1/4N x 15.5N
= 3.875cm 1mk -
- Mechanical waves require a material medium. 1mk
- Electromagnetic waves do not require a material medium.
- v=2nd/t
Depth = 1500 x 0.5 1mk
2
ans = 750m 1mk - Density of mixture = mass of mixture
Volume of mixture
Mass of fresh water = 1800 x 1 =1800g
Mass of sea water = 2200 x 1.025 = 2255g
Density of mixture = 2255 + 1800
1800 + 2200
= 1.01375g/cm 3
Basic physical quantity Derived physical quantity - quantities that cannot be obtained from any
other physical quantity e.g. length, mass, time,
electric current e.t.c- quantities that can be obtained by
multiplication or division of basic physical
quantities e.g. area, volume and density (3mks)-
-
- use of rollers
- greasing and oiling
- air cushion
- smoothening
- This is because cohesive forces between mercury molecules are stronger than adhesive force between molecules of mercury and glass (2mks)
-
SECTION B
-
-
- Lunar
- Earth in between the sun and the moon
- Earth shadow is focused on the moon
- Solar
- moon in between the Earth and the moon
- moon shadow is focused on the Earth
- occur during new moon.
- Lunar
rays 1mk both
arrows 1mk
(check that rays get to screen) 1mk image-
- Real 1mk
- Inverted 1mk
- Becomes
- Brighter Any two (2mks)
- Blurred
- Bigger
- Formular hi/ho = v/u 1mk
Substitution 4/ho = 12/30 1mk
(answer) h0 = 10cm
10mks
-
-
- 2cm 1mk
- 4cm = 0.04cm 1mk
- 3 oscli → 1.55
1 oscli →
Period = 1.55
3 2mk
= 0.55 1mk
-
- f = 1/T 1mk
= 1/0.5
= 2Hz 1mk - V = λf 1mk
= 2 x 0.04 1mk
= 0.08m/s 1mk
10mks
- f = 1/T 1mk
-
-
- It is the spreading of particles from regions of high concentration to those of low concentration. 1mk
-
- temperature difference
- density
-
- Bright specks are seen in continuous random motion. 1mk
- This is because of uneven bombardment by the invisible particles or molecules of air. 1mk
-
- To avoid splashing the water. 1mk
- Because the salt particles fitted well in the spaces between the water molecules. 1mk
-
- Ammonia gas diffuses at faster rate than hydrochloric acid gas. 1mk
- A denser gas diffuses at a slower rate than the lighter one. 1mk
- Diffusion takes longer time, because the particles are at low kinetic energy moves slowly. 1mk 9mks
Any four correct 4mksMass Weight Quantity of matter in a body Pull of gravity on a body Same everywhere Changes from place to place Measured in kilogram Measured in Newton’s Measured using a bean balance Measured using a spring balance Has magnitude only Has both magnitude and direction - Pressure applied at one part of a liquid is transmitted equally to all other parts of the enclosed liquid. 1mk
-
- Hydraulic lift 1mk
- Hydraulic brake system 1mk
- ρgh1 = ρ2gh2 1mk
1600 x 10 x h1 = 800 x 10 x 0.18 1mk
8001 x 10 x0.09 1mk
21 1600
h1 = 0.09m 1mk
= 9cm
10mks
-
- Define current and state its SI unit 2mks
- is rate flow of charge in a circuit.
- S.I unit is Amperes
- A charge of 120 coulombs flow through a lam p every minute. Calculate the current flowing through the lamp. 3mks
i = Ø = 120 = 2A
t 60 - What do you understand by open and closed circuits? 2mks
- open – no current flows
- closed – current flows
-
- State the polarities of Aand B
- A+ ve
- B– ve
- Name the chemical substances in the parts labeled C and D 2mks
- C – Ammonium chloride paste
- D – Carbon powder and manganese IV oxide.
- State the polarities of Aand B
- to allow oxygen and hydrogen (gases) produced while charging to escape hence reducing chances of battery exploding.
- Define current and state its SI unit 2mks
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Physics Questions and Answers - Form 2 End Term 2 Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students